DSP Math加速优化整理
Posted aron566
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了DSP Math加速优化整理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
DSP Math加速优化整理
浮点数的四舍五入
文档参考地址
浮点转整形数据四舍五入写法,注意浮点赋值给整形变量不会自动四舍五入!
float a = 3.5;
int b = a + 0.5;//b = 4
b = 3.4 + 0.5;//b = 3
浮点数的四舍五入
/*假设处理3位的小数*/
float a = 3.555;
/*先放大 取出小数位*/
int b = a *1000;//b = 3555;
/*假设保留两位小数位,四舍五入,那么需要判断第三位小数位的数值*/
b = b % 10;//b = 5
if(b < 5)
{
a = ((a * 100) /100;//a = 3.55
}
else
{
a = ((a * 100) + 1) /100;//a = 3.56
}
定点数
以下摘自硬石科技论坛,及DSP开发文档中部分内容
首先定点数就是用整数来表示浮点数。
比如Q15定点数,我们这里采用Q1.15格式,也就是1个符号位,剩下15位是数据位
作为整数,他能表示的数据范围是-32768 到 32767, 对应到浮点数能表示的范围就是 -32768 / 32768 到 32767 / 32768 ,即 -1 到 0.9999695,能表示的最小浮点数单位(即精度)是 1/ 32768 = 0.000030517578125,也就是把16位的数,最高位符号位,其他15位代表这个数,这个整数为正数,那么符号位就是0,这个数为1000(十进制),那么它Q1.15这个格式的定点数 = 1000 * (1/ 32768) = 实际值 = 0.030517578125,
如果它15位为32767(十进制),那么它Q1.15这个格式的定点数 = 32767(十进制) * (1/ 32768)(十进制) = 实际值 = 0.030517578125(十进制) = 实际值 = 0.9999695(十进制)
此时如果两个Q15格式的数据相乘,比如1 乘以 1,对应到浮点就是( 1 / 32768 ) * ( 1 / 32768 ) = 1 / (32768 * 32768) ,已经远远小于Q15所能表示的最小浮点数。
所以这两个的乘积就是0
arm_status arm_sqrt_q31(q31_t in, q31_t *pOut);
函数描述:
这个函数用于求 这个函数用于求 这个函数用于求 这个函数用于求 32 位定点数的平方根 位定点数的平方根 位定点数的平方根 位定点数的平方根 。
函数参数:
- 第1个参数是源数据地址,参数范围0x00000000 到 0x7FFFFFFF。
- 第2个参数是求平方根后的数据地址。
- 返回值,返回ARM_MATH_SUCCESS表示计算成功,返回ARM_MATH_ARGUMENT_ERROR表示计算出错。
注意事项:
这里in的输入范围是0x00000000 到 0x7FFFFFFF,转化成浮点数范围就是[0 +1)。在使用这个函数的时候有一点要特别的注意,比如我们要求1000的平方根,而获得结果是1465429,这是为什么呢,分析如下:
定点数1000 = 浮点数 1000 /(2^31) = 4.6566e-07 (用Q31表示)。输入为定点1000,转浮点过程
对4.6566e-07求平方根可得 6.8239e-04。
定点数1465429 = 浮点数 1465429/(2^31) = 6.8239e-04。对输出定点结果1465429,转浮点过程
简单的总结下上面的意思就是说,求定点数1000的平方根,实际是求浮点数4.6566e-07 (用Q31表示)的平方根
浮点转定点

定点转浮点


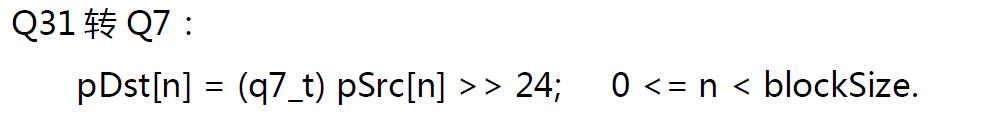
一段测试程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
/* 定点数定义 */
/**
* @brief 8-bit fractional data type in 1.7 format.
*/
typedef int8_t q7_t;
/**
* @brief 16-bit fractional data type in 1.15 format.
*/
typedef int16_t q15_t;
/**
* @brief 32-bit fractional data type in 1.31 format.
*/
typedef int32_t q31_t;
/**
* @brief 64-bit fractional data type in 1.63 format.
*/
typedef int64_t q63_t;
/**
* @brief 32-bit floating-point type definition.
*/
typedef float float32_t;
/**
* @brief 64-bit floating-point type definition.
*/
typedef double float64_t;
/**
* @brief Clips Q63 to Q31 values.
*/
static inline q31_t clip_q63_to_q31(
q63_t x)
{
return ((q31_t) (x >> 32) != ((q31_t) x >> 31)) ?
((0x7FFFFFFF ^ ((q31_t) (x >> 63)))) : (q31_t) x;
}
/*
* @brief C custom defined QADD
*/
static inline int32_t __QADD(
int32_t x,
int32_t y)
{
return ((int32_t)(clip_q63_to_q31((q63_t)x + (q31_t)y)));
}
static inline int32_t __SSAT(int32_t val, uint32_t sat)
{
if ((sat >= 1U) && (sat <= 32U))
{
const int32_t max = (int32_t)((1U << (sat - 1U)) - 1U);//有效位最大数
const int32_t min = -1 - max ;//最小数
if (val > max)
{
return max;
}
else if (val < min)
{
return min;
}
}
return val;
}
void arm_add_q31(
const q31_t * pSrcA,
const q31_t * pSrcB,
q31_t * pDst,
uint32_t blockSize)
{
uint32_t blkCnt; /* Loop counter */
/* Initialize blkCnt with number of samples */
blkCnt = blockSize;
while (blkCnt > 0U)
{
/* C = A + B */
/* Add and store result in destination buffer. */
*pDst++ = __QADD(*pSrcA++, *pSrcB++);
/* Decrement loop counter */
blkCnt--;
}
}
void arm_mult_q31(
const q31_t * pSrcA,
const q31_t * pSrcB,
q31_t * pDst,
uint32_t blockSize)
{
uint32_t blkCnt; /* Loop counter */
q31_t out; /* Temporary output variable */
/* Initialize blkCnt with number of samples */
blkCnt = blockSize;
while (blkCnt > 0U)
{
/* C = A * B */
/* Multiply inputs and store result in destination buffer. */
q63_t x = ((q63_t) *pSrcA++ * *pSrcB++);
printf("x = 0x%018lX\\r\\n", x);
out = x >> 32;
out = __SSAT(out, 31);//饱和处理
*pDst++ = out << 1U;
/* Decrement loop counter */
blkCnt--;
}
}
void arm_float_to_q31(
const float32_t * pSrc,
q31_t * pDst,
uint32_t blockSize)
{
uint32_t blkCnt; /* Loop counter */
const float32_t *pIn = pSrc; /* Source pointer */
/* Initialize blkCnt with number of samples */
blkCnt = blockSize;
while (blkCnt > 0U)
{
/* C = A * 2147483648 */
/* Convert from float to Q31 and then store the results in the destination buffer */
*pDst++ = clip_q63_to_q31((q63_t) (*pIn++ * 2147483648.0f));
/* Decrement loop counter */
blkCnt--;
}
}
void arm_q31_to_float(
const q31_t * pSrc,
float32_t * pDst,
uint32_t blockSize)
{
const q31_t *pIn = pSrc; /* Src pointer */
uint32_t blkCnt; /* loop counter */
/* Initialize blkCnt with number of samples */
blkCnt = blockSize;
while (blkCnt > 0U)
{
/* C = (float32_t) A / 2147483648 */
/* Convert from q31 to float and store result in destination buffer */
*pDst++ = ((float32_t) *pIn++ / 2147483648.0f);
/* Decrement loop counter */
blkCnt--;
}
}
static int x4 = 0;
static float x1 = 0.5;
static float x2 = 0.5;
/* 以下操作,将浮点数,转换为了定点数,再进行加减乘除加速运算 */
int main()
{
int x1_q31 = 0;
arm_float_to_q31(&x1, &x1_q31, 1);
int x2_q31 = 0;
arm_float_to_q31(&x2, &x2_q31, 1);
float x3 = x1 * x2;
printf("加法 x3 = %.2f 乘法 x3 = %.2f\\r\\n", x1 + x2, x3);
x4 = x1_q31 + x2_q31;
printf("x1_q31 = 0x%04X x2_q31 = 0x%04X\\r\\n", x1_q31, x2_q31);
printf("定点加法 x4 = 0x%08X\\r\\n", x4);
arm_add_q31(&x1_q31,&x2_q31,&x4,1);
printf("函数定点加 qx4 = 0x%08X\\r\\n", x4);
long long x7 = (long long)x1_q31 * x2_q31;
printf("定点乘 xqx7 = 0x%016X\\r\\n", x7);
arm_mult_q31(&x1_q31,&x2_q31,&x4,1);//返回64位中,高32位
printf("函数定点乘 xqx4 = 0x%08X\\r\\n", x4);
float x6 = 0.0f;
arm_q31_to_float(&x4,&x6,1);
printf("函数定点乘to float x6 = 0x%08X, %.2f\\r\\n", x6, x6);
return 0;
}
例子,算平均数
#include <string>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
const int a[] = {2,4,6,8};
/* 常规结果 */
uint64_t y = 0;
/* Q结果 */
uint64_t yq = 0;
/* Kalman循环递归结果 */
uint64_t yk = 0;
/* 除法转乘法加速 */
/* 系数0.25 定标:2^(n-1) < |max| < 2^n max按1算,n取2 */
uint32_t x = (1U<<2U)/4U; /* 转为Q2 */
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int temp = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0]); i++)
{
/* 常规循环累积 */
y += a[i];
/* Q数值 Q0*Q2=Q2 */
yq += a[i] * x;
/* 卡尔曼递归 */
yk += (a[i] - yk) / (i+1);
}
printf("常规 y = %u\\n", y/(sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0])));
printf("定点 yq = %.2f\\n", (float)((float)yq/(1U<<2U)));
printf("卡尔曼递归 yk = %u\\n", yk);
return 0;
}
0、定点数用于浮点数的转为整数的表达形式,为了保留小数部分精度,必然是放大过程,如1.2,需要放大10倍,变为12,对于这样的数,定标要求如下
1、选择合适的定标:对于32位的有符号数,数据有效位=31。如|max| = 2.75,选Q = 31 – 2 =29是最合适的。
2、最快的优化:空间换时间,即查表计算
3、最复杂的优化:根据内核取指方式不同,执行优化,通常2个指令,或者4个指令可并行操作,例如一个数组需要乘上一个系数,那么就需要写成4个或者2个一起计算,再进行下一个2个或者4个计算
复数共轭计算 CompllexConj

复数点乘 CompllexDotProduct

复数求模

复数模平方 CompllexMagSquared

复数乘法 CompllexMulltCompllex

复数乘实数 CompllexMulltReall

矩阵加法 MatAdd
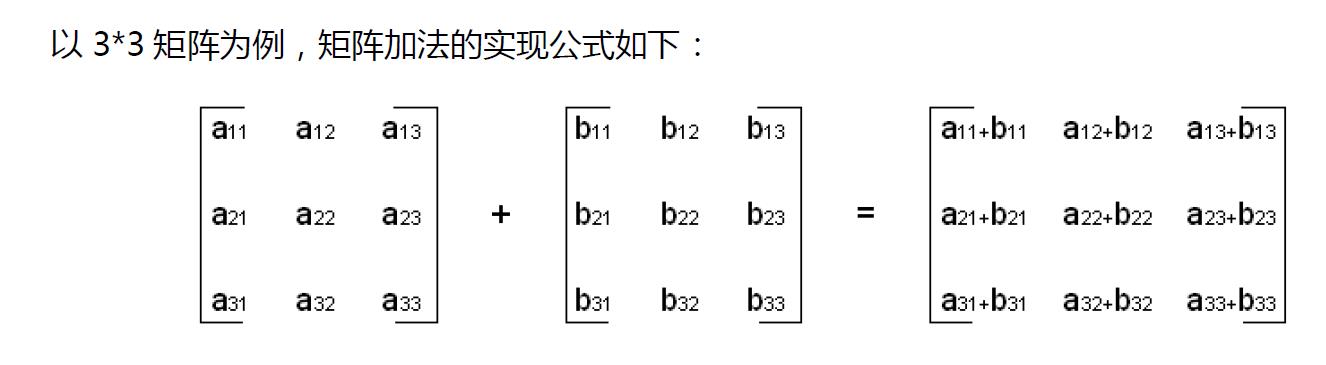
矩阵减法 MatSub
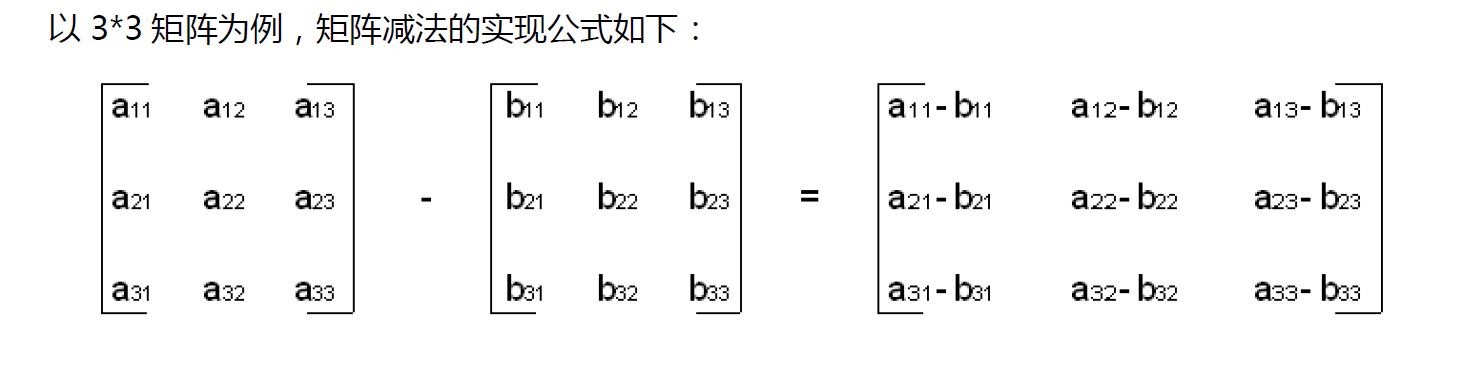
矩阵缩放 MatScalle
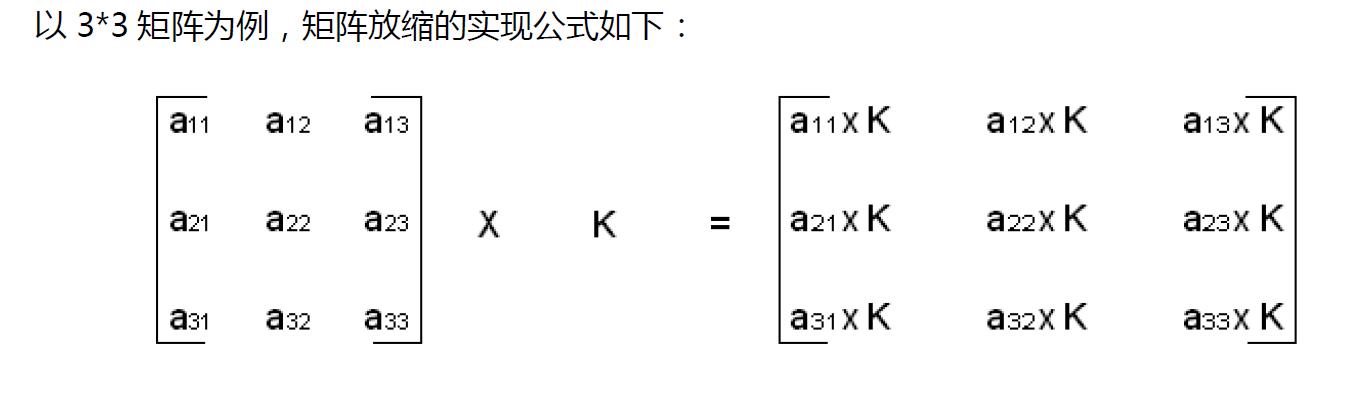
矩阵乘法 MatMullt

转置矩阵
矩阵M x N转置后是N x M。
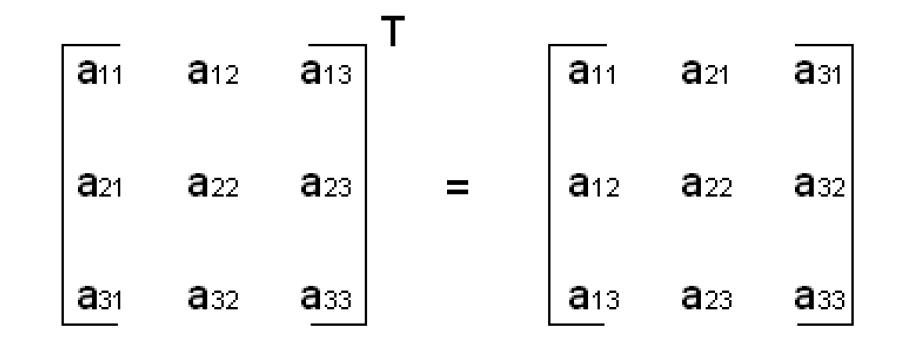
乘除法
uint32_t i = 1000;
uint32_t y = i/(2^31)
使用右移替代
y = i >> 31;
平方根魔数优化
float MagicSqrt(float x)
{
if (x < 0)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
float xhalf = 0.5f * x;
int i = *(int*)&x;
i = 0x1fbd1df5 + (i >> 1);
x = *(float*)&i;
x = 0.5f * x + xhalf / x;
//x = 0.5f * x + xhalf / x;
return x;
}
}
所以整个计算过程就是
1.i = *(int*)&x;
将输入的数转换成整数
2.i = 0x1fbd1df5 + (i >> 1);
通过魔数完成平方根的计算。
3.x = *(float*)&i;
转换回浮点数。
4.x = 0.5f * x + xhalf / x;
使用一次牛顿迭代法提高下精度,也可多迭代几次。
完成快速计算平方根x
sin cos 软件实现
用泰勒级数来求近似值。由于上面提到精度足够即可,在具体实现中我只迭代了 10 次。具体实现如下:
// sin(x) = x - (x^3 / 3!) + (x^5 / 5!) - (x^7 / 7!) + ...
template <typename T>
T f_sin(const T& x)
{
const T x2 = x * x;
T power = x;
T facter = 1;
T sign = 1;
T sum = 0;
const int loop = 22; // 10 times loop
for (int i = 3; i < loop; i += 2) {
sign *= -1;
power *= x2;
facter *= i * (i - 1);
sum += sign * power / facter;
}
return sum + x;
}
// cos(x) = 1 - (x^2 / 2!) + (x^4 / 4!) - (x^6 / 6!) + ...
template <typename T>
T f_cos(const T& x)
{
const T x2 = x * x;
T power = 1;
T facter = 1;
T sign = 1;
T sum = 0;
const int loop = 21; // 10 times loop
for (int i = 2; i < loop; i += 2) {
sign *= -1;
power *= x2;
facter *= i * (i - 1);
sum += sign * power / facter;
}
return sum + 1;
}
随机数优化
#include <ctime>
typedef unsigned int u32;
class LCG {
public:
LCG(u32 seed) : mSeed(seed) {}
u32 operator()() {
mSeed = mSeed * 214013U + 2531011U;
return (mSeed >> 16U) & 0x7FFFU;
}
private:
u32 mSeed;
};
GCC 编译器优化
开启 -ffast-math 选项来加速浮点数运算;
开启 -march=native 来让编译器做本地处理器架构优化;
开启最高等级优化选项 -O3,O3 和 fast-math 可以合写成 -Ofast
以上是关于DSP Math加速优化整理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章