Flutter 手势GestureDetector解析
Posted mercyT
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Flutter 手势GestureDetector解析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
对于移动端的开发者来说,手势是一个非常重要的模块,基本上做任何App都会遇到各种各样的手势问题,而手势也是移动的一个不算小的模块吧,要彻底搞得还是得费一些时间的,如果之前对android或者ios的手势或者说点击事件的原理有所了解的,那么了解其它语言的手势原理相对来说帮助还是挺大的。
好了,切入正题。在Flutter中,对于Flutter有一定了解的人都知道,可以通过GestureDetector来给不具有点击事件或者手势回调的Widget添加手势回调。然后为了点击水波纹的点击效果,大多数开发者可能会使用InkWell widget来包装一个需要添加点击事件的控件。
前戏部分: InkWell 和 GestureDetector的区别
对Flutter有一一些深入了解的人可能知道,InkWell就是对GestureDetector的一个封装。看图:
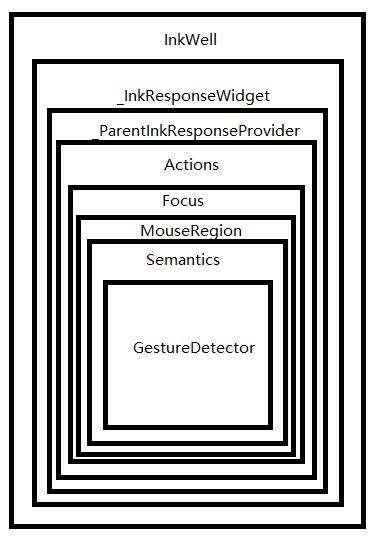
- InkWell是继承于InkResponse,
- InkResponse是集成于StatelessWidget类,
- 在onBuild中返回了_InkResponseStateWidget
由于以上这部分代码没有什么逻辑,为了减少篇幅我就不贴源码了。
_InkResponseStateWidget中的核心代码如下:
return _ParentInkResponseProvider(
state: this,
child: Actions(
actions: _actionMap,
child: Focus(
focusNode: widget.focusNode,
canRequestFocus: _canRequestFocus,
onFocusChange: _handleFocusUpdate,
autofocus: widget.autofocus,
child: MouseRegion(
cursor: effectiveMouseCursor,
onEnter: _handleMouseEnter,
onExit: _handleMouseExit,
child: Semantics(
onTap: widget.excludeFromSemantics || widget.onTap == null ? null : _simulateTap,
onLongPress: widget.excludeFromSemantics || widget.onLongPress == null ? null : _simulateLongPress,
child: GestureDetector(//InkWell手势的来源
onTapDown: enabled ? _handleTapDown : null,
onTap: enabled ? _handleTap : null,
onTapCancel: enabled ? _handleTapCancel : null,
onDoubleTap: widget.onDoubleTap != null ? _handleDoubleTap : null,
onLongPress: widget.onLongPress != null ? _handleLongPress : null,
behavior: HitTestBehavior.opaque,
excludeFromSemantics: true,
child: widget.child,
),
),
),
),
),
);
通过上述代码可以看出,GestureDetector是Flutter中手势的一个最基本类,我们可以直接用,也可以给予GestureDetector来做一些列的自定义封装
切入正题
一、 GestureDetector简介
class GestureDetector extends StatelessWidget {
// 省略代码
}
/// A widget that detects gestures.
///
/// Attempts to recognize gestures that correspond to its non-null callbacks.
///
/// If this widget has a child, it defers to that child for its sizing behavior.
/// If it does not have a child, it grows to fit the parent instead.
///
/// By default a GestureDetector with an invisible child ignores touches;
/// this behavior can be controlled with [behavior].
这个是官方简介,我理解的大概意思就是说GestureDetector是一个小控件,事件的点击区域会以子控件为准,如果子控件为不可见或者没有子控件,则会去适应父控件,而这个行为可以通过behavior属性来控制。这块内容不是今天的重点,我们先看重点吧。
二、GestureDetector功能解析
既然是Widiget,那么核心代码肯定在onBuild中,我们直接先看看一下源码。
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final Map<Type, GestureRecognizerFactory> gestures = <Type, GestureRecognizerFactory>{};
if (onTapDown != null ||
onTapUp != null ||
onTap != null ||
onTapCancel != null ||
onSecondaryTap != null ||
onSecondaryTapDown != null ||
onSecondaryTapUp != null ||
onSecondaryTapCancel != null||
onTertiaryTapDown != null ||
onTertiaryTapUp != null ||
onTertiaryTapCancel != null
) {
gestures[TapGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<TapGestureRecognizer>(
() => TapGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(TapGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onTapDown = onTapDown
..onTapUp = onTapUp
..onTap = onTap
..onTapCancel = onTapCancel
..onSecondaryTap = onSecondaryTap
..onSecondaryTapDown = onSecondaryTapDown
..onSecondaryTapUp = onSecondaryTapUp
..onSecondaryTapCancel = onSecondaryTapCancel
..onTertiaryTapDown = onTertiaryTapDown
..onTertiaryTapUp = onTertiaryTapUp
..onTertiaryTapCancel = onTertiaryTapCancel;
},
);
}
if (onDoubleTap != null) {
gestures[DoubleTapGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<DoubleTapGestureRecognizer>(
() => DoubleTapGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(DoubleTapGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onDoubleTapDown = onDoubleTapDown
..onDoubleTap = onDoubleTap
..onDoubleTapCancel = onDoubleTapCancel;
},
);
}
if (onLongPress != null ||
onLongPressUp != null ||
onLongPressStart != null ||
onLongPressMoveUpdate != null ||
onLongPressEnd != null ||
onSecondaryLongPress != null ||
onSecondaryLongPressUp != null ||
onSecondaryLongPressStart != null ||
onSecondaryLongPressMoveUpdate != null ||
onSecondaryLongPressEnd != null) {
gestures[LongPressGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<LongPressGestureRecognizer>(
() => LongPressGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(LongPressGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onLongPress = onLongPress
..onLongPressStart = onLongPressStart
..onLongPressMoveUpdate = onLongPressMoveUpdate
..onLongPressEnd = onLongPressEnd
..onLongPressUp = onLongPressUp
..onSecondaryLongPress = onSecondaryLongPress
..onSecondaryLongPressStart = onSecondaryLongPressStart
..onSecondaryLongPressMoveUpdate = onSecondaryLongPressMoveUpdate
..onSecondaryLongPressEnd = onSecondaryLongPressEnd
..onSecondaryLongPressUp = onSecondaryLongPressUp;
},
);
}
if (onVerticalDragDown != null ||
onVerticalDragStart != null ||
onVerticalDragUpdate != null ||
onVerticalDragEnd != null ||
onVerticalDragCancel != null) {
gestures[VerticalDragGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<VerticalDragGestureRecognizer>(
() => VerticalDragGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(VerticalDragGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onDown = onVerticalDragDown
..onStart = onVerticalDragStart
..onUpdate = onVerticalDragUpdate
..onEnd = onVerticalDragEnd
..onCancel = onVerticalDragCancel
..dragStartBehavior = dragStartBehavior;
},
);
}
if (onHorizontalDragDown != null ||
onHorizontalDragStart != null ||
onHorizontalDragUpdate != null ||
onHorizontalDragEnd != null ||
onHorizontalDragCancel != null) {
gestures[HorizontalDragGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<HorizontalDragGestureRecognizer>(
() => HorizontalDragGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(HorizontalDragGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onDown = onHorizontalDragDown
..onStart = onHorizontalDragStart
..onUpdate = onHorizontalDragUpdate
..onEnd = onHorizontalDragEnd
..onCancel = onHorizontalDragCancel
..dragStartBehavior = dragStartBehavior;
},
);
}
if (onPanDown != null ||
onPanStart != null ||
onPanUpdate != null ||
onPanEnd != null ||
onPanCancel != null) {
gestures[PanGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<PanGestureRecognizer>(
() => PanGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(PanGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onDown = onPanDown
..onStart = onPanStart
..onUpdate = onPanUpdate
..onEnd = onPanEnd
..onCancel = onPanCancel
..dragStartBehavior = dragStartBehavior;
},
);
}
if (onScaleStart != null || onScaleUpdate != null || onScaleEnd != null) {
gestures[ScaleGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<ScaleGestureRecognizer>(
() => ScaleGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(ScaleGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onStart = onScaleStart
..onUpdate = onScaleUpdate
..onEnd = onScaleEnd
..dragStartBehavior = dragStartBehavior;
},
);
}
if (onForcePressStart != null ||
onForcePressPeak != null ||
onForcePressUpdate != null ||
onForcePressEnd != null) {
gestures[ForcePressGestureRecognizer] = GestureRecognizerFactoryWithHandlers<ForcePressGestureRecognizer>(
() => ForcePressGestureRecognizer(debugOwner: this),
(ForcePressGestureRecognizer instance) {
instance
..onStart = onForcePressStart
..onPeak = onForcePressPeak
..onUpdate = onForcePressUpdate
..onEnd = onForcePressEnd;
},
);
}
return RawGestureDetector(
gestures: gestures,
behavior: behavior,
excludeFromSemantics: excludeFromSemantics,
child: child,
);
}
代码相当的长,看着很复杂,其实逻辑非常的简单。就是注册手势的识别器。
final Map<Type, GestureRecognizerFactory> gestures = <Type, GestureRecognizerFactory>{};
将逻辑细分一下:
- 创建一个Map容器gestures
- 添加单击识别器
- 添加双击识别器
- 添加纵向(y轴方向)滑动识别器
- 添加横向(x轴方向)滑动识别器
- 添加双向(y轴和x轴)同时滑动识别器
- 添加缩放手势识别器
- 添加带有力传感器的识别器
- 最后根据这些参数创建一个RawGestureDetector控件。
当然,添加这些手势识别器的前提条件就是有回调需求,也就是if中的那些判断。因此通过上述代码可以总结出我们通过使用GestureDetector的功能可以理解为再有需要的情况下注册手势识别器的监听,那么既然有监听,肯定就有地方将事件发送出来。
三、手势事件分发跟踪
因为flutter中的很多方法都是回调的方式,而且很多源码都是接口的形式去调用的,直接扒源码比较难,因此我们通过打断点观察方法调用栈的形式来追踪手势的传递过程。
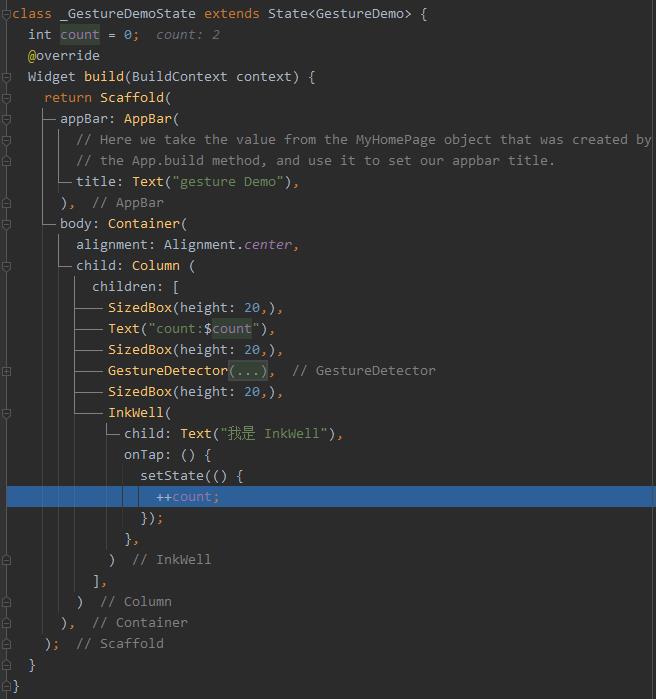
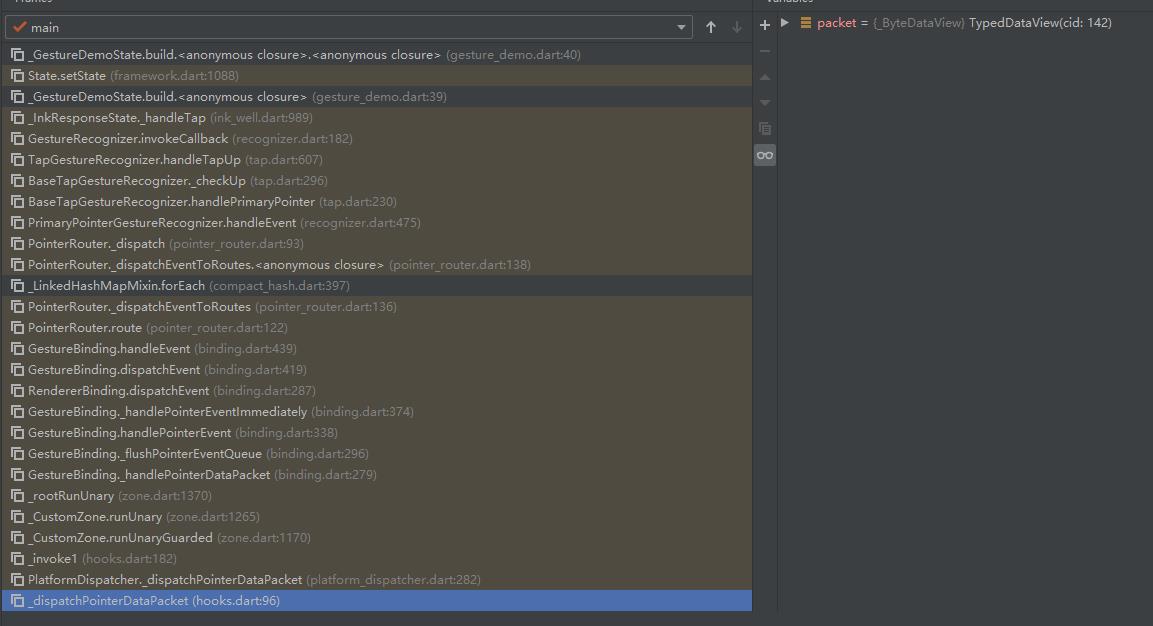
上面两个截图,一个是通过InkWell来注册一个手势回调,第二个截图则是方法调用栈。从这个断点可以看到,点击手势的最终来源于Honks.dart文件中的_dispatchPointerDataPacket方法
@pragma('vm:entry-point')
// ignore: unused_element
void _dispatchPointerDataPacket(ByteData packet) {
PlatformDispatcher.instance._dispatchPointerDataPacket(packet);
}
源码比较简单,就是从引擎VM中获取到点击屏幕的一个ByteData数据包,拿到之后就丢给PlatformDispatcher中的方法去处理。
再看PlatformDispathcer._dispatchPointerDataPacket方法
// Called from the engine, via hooks.dart
void _dispatchPointerDataPacket(ByteData packet) {
if (onPointerDataPacket != null) {
_invoke1<PointerDataPacket>(
onPointerDataPacket,
_onPointerDataPacketZone,
_unpackPointerDataPacket(packet),
);
}
}
上面这部分不是核心代码,只是一个方法的调用,核心代码_unpackPointerDataPacket方法中的逻辑,如下:
static PointerDataPacket _unpackPointerDataPacket(ByteData packet) {
const int kStride = Int64List.bytesPerElement;
const int kBytesPerPointerData = _kPointerDataFieldCount * kStride;
final int length = packet.lengthInBytes ~/ kBytesPerPointerData;
assert(length * kBytesPerPointerData == packet.lengthInBytes);
final List<PointerData> data = <PointerData>[];
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
int offset = i * _kPointerDataFieldCount;
data.add(PointerData(
embedderId: packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
timeStamp: Duration(microseconds: packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian)),
change: PointerChange.values[packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian)],
kind: PointerDeviceKind.values[packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian)],
signalKind: PointerSignalKind.values[packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian)],
device: packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
pointerIdentifier: packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
physicalX: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
physicalY: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
physicalDeltaX: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
physicalDeltaY: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
buttons: packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
obscured: packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian) != 0,
synthesized: packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian) != 0,
pressure: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
pressureMin: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
pressureMax: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
distance: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
distanceMax: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
size: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
radiusMajor: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
radiusMinor: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
radiusMin: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
radiusMax: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
orientation: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
tilt: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
platformData: packet.getInt64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
scrollDeltaX: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
scrollDeltaY: packet.getFloat64(kStride * offset++, _kFakeHostEndian),
));
assert(offset == (i + 1) * _kPointerDataFieldCount);
}
return PointerDataPacket(data: data);
}
这块代码的计算逻辑比较复杂,如果不细看,只是了解大概逻辑的话,还是比较好理解的。就是从引擎获取到的Bytedata中解析出PointerData。这个PointerData中包含了屏幕的物理触摸位置相关的数据。
根据最开始的那张方法调用栈可以看到,接下来调用的是
GestureBinding._handlePointerDataPacket (binding.dart:279)
_rootRunUnary (zone.dart:1370)
_CustomZone.runUnary (zone.dart:1265)
_CustomZone.runUnaryGuarded (zone.dart:1170)
_invoke1 (hooks.dart:182)
这5个方法,由于前4个方法(从下往上)基本上没啥业务逻辑,都是callback回调,这就不细讲了,重点关注一下GestureBinding._handlePointerDataPacket 这个方法,从方法名可以猜到,就是处理PointerData的方法。
void _handlePointerDataPacket(ui.PointerDataPacket packet) {
// We convert pointer data to logical pixels so that e.g. the touch slop can be
// defined in a device-independent manner.
_pendingPointerEvents.addAll(PointerEventConverter.expand(packet.data, window.devicePixelRatio));
if (!locked)
_flushPointerEventQueue();
}
从这个方法的内容可以看出,这个方法主要做的事情
- PointerData数据解析成PointerEvent
- 将PointerEvent添加到_pendingPointerEvents队列中
- 处理完之后再从队列里取出这些数据。
看一下转化过程的源代码,大概了解一下逻辑就好了。
static Iterable<PointerEvent> expand(Iterable