AI数学用梯度下降算法优化线性回归方程(含代码)
Posted 木盏
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了AI数学用梯度下降算法优化线性回归方程(含代码)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
众所周知,线性回归(Linear Regression)是最常见的机器学习算法之一,简单但超级实用。线性回归旨在用线性方程来拟合数据分布,在数据量小计算速度要求高的地方是神经网络的最佳替代品。
LR的一般表现形式为:
y
=
w
⃗
T
x
⃗
+
b
y = \\vec{w}^T\\vec{x} + b
y=wTx+b
通常,LR优化方式可以通过构建均方误差损失函数,得到一个凸函数,计算导数为0的位置来确定
w
⃗
\\vec{w}
w和
b
b
b,如周志华老师西瓜书里描述的那样。
在工程上,我们可以把LR当做一个简易的神经网络来对待,用梯度下降算法就可以优化。本文提供一个梯度下降算法优化LR的实验例子,有助于加深大家对LR以及梯度下降的理解。
实验意图:
假设有一个绝对正确的函数
y
=
f
(
x
⃗
;
w
⃗
,
b
)
=
w
⃗
T
x
⃗
+
b
y=f(\\vec{x};\\vec{w},b)=\\vec{w}^T\\vec{x}+b
y=f(x;w,b)=wTx+b,每输入一个
x
⃗
\\vec{x}
x都可以得到一个准确的
y
y
y。那么,咱们只需要得到最真实的
w
⃗
\\vec{w}
w和
b
b
b即可。假设最真实的
w
⃗
=
[
3
,
1
,
4
,
1
,
5
,
9
,
2
,
6
]
\\vec{w}=[3,1,4,1,5,9,2,6]
w=[3,1,4,1,5,9,2,6],最真实的
b
=
3.7
b=3.7
b=3.7。
初始化
w
⃗
\\vec{w}
w和
b
b
b为随机数,通过大量样本的梯度反传来修正
w
⃗
\\vec{w}
w和
b
b
b到真实的值。
推导过程:

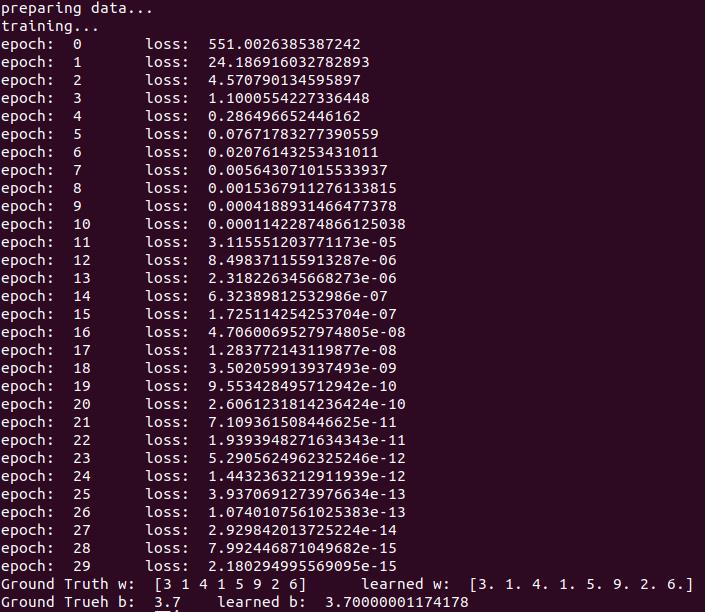
实验环境:
python3.7
numpy >=1.15.1
先申明,以下代码为本人原创,借用最好在评论中告知我。
########################################################
# @author: MuZhan
# @contact: levio.pku@gmail.com
# experiment: using GD to optimize Linear Regression
# To fit `y=w*x+b`, where x and w are multi-dim vectors.
########################################################
import numpy as np
# initial setting
np.random.seed(10)
epochs = 30
lr = .1 # learning rate
w_ = np.array([3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6]) # the ground truth w
b_ = 3.7 # the ground truth b
SAMPLE_NUM = 100
x_dim = len(w_)
# preparing random (x, y) pairs
print('preparing data...')
x_list = []
y_list = []
for i in range(SAMPLE_NUM):
x = np.random.rand(x_dim)
y = w_.dot(x) + b_
x_list.append(x)
y_list.append(y)
# init w
np.random.seed(10)
w = np.random.rand(x_dim)
# init b
b = 1
# training
print('training...')
for e in range(epochs):
print('epoch: ', e, end='\\t')
sum_loss = 0
for i in range(len(x_list)):
x = x_list[i]
y_ = y_list[i]
y = w.dot(x) + b
loss = (y - y_) ** 2
sum_loss += loss
# use Gradient Descent to update parameters
w = w - 2 * lr * (y - y_) * x
b = b - 2 * lr * (y - y_)
print('loss: ', sum_loss)
print('Ground Truth w: ', w_, end='\\t')
print('learned w: ', w)
print('Ground Trueh b: ', b_, end='\\t')
print('learned b: ', b)
c++:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdlib>
#define SAMPLES_NUM 10000
#define EPOCHS 20
#define LEARNING_RATE 0.001
using namespace std;
float dot(float* x, float* w, int length){
float res = 0;
for(int i=0; i<length; ++i){
res += x[i] * w[i];
}
return res;
}
float get_random(){
return (rand() % 1000) / 100.0;
}
void update_weights(float* x, float* w, int length, float sqrt_loss)
{
for(int i=0; i<length; ++i){
w[i] -= 2 * LEARNING_RATE * sqrt_loss * x[i];
}
}
int main(){
float x[8] = {1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4};
float w_[8] = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6}; // Ground Truth w
float b_ = 3.7; // Ground Truth b
int length = int(sizeof(w_)/sizeof(w_[0]));
float y;
// collect samples
vector<vector<float>> samples;
vector<float> tmp;
for(int i=0; i<=length; ++i) tmp.push_back(0);
for(int i=0; i<SAMPLES_NUM; ++i){
for(int j=0; j<length; ++j){
tmp[j] = get_random();
x[j] = tmp[j];
}
y = dot(x, w_, length) + b_;
tmp[length] = y;
samples.push_back(tmp);
}
// init w, b
float w[8] = {1, 2, 3};
float b = 1.0f;
// training
float x_tmp[length];
float y_tmp, loss;
for(int e=0; e<EPOCHS; ++e){
for(int i=0; i<samples.size(); ++i){
vector<float> sample = samples[i];
copy(sample.begin(), sample.end(), x_tmp);
y_tmp = sample[length];
y = dot(x_tmp, w, length) + b;
loss = (y - y_tmp) * (y - y_tmp);
// update parameters
update_weights(x_tmp, w, length, (y - y_tmp));
b -= 2 * LEARNING_RATE * (y - y_tmp);
}
cout<<loss<<endl;
}
for(int i=0; i<length; ++i){
cout<<w[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
cout<<b<<endl;
return 0;
}
以上是关于AI数学用梯度下降算法优化线性回归方程(含代码)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章