学习笔记之Vuex总结(Vue状态管理)
Posted 铁锤妹妹@
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了学习笔记之Vuex总结(Vue状态管理)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、 前言
接触Vuex之前我们组件间共享数据的方式
父向子传值: v-bind属性绑定
子向父传值: v-on 事件绑定
兄弟组件之间共享数据: EventBus
1) $emit 发送数据的那个组件
2) $on 接收数据的那个组件
上面这三种共享数据方式,只适合小范围的数据共享,如果需要频繁的或大范围的来实现数据的共享,这三种方式就有点力不从心了,这时候,Vuex诞生了!
二、初识Vuex
2.1 Vuex是什么?
Vuex是实现组件全局状态(数据)管理的一种机制,可以方便的实现组件之间数据的共享。
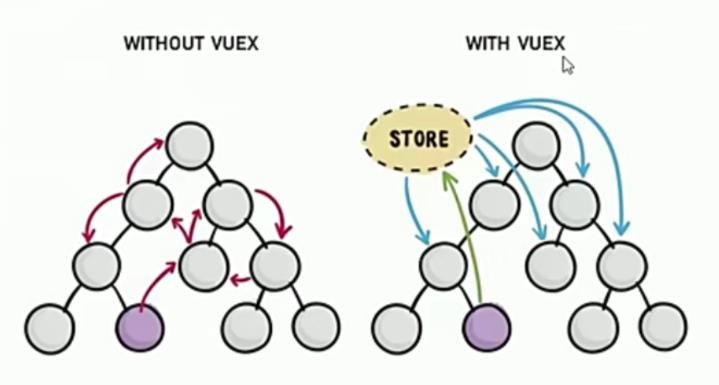
把数据存在store中,别的组件需要的话直接去store里取
2.2 使用Vuex统一管理状态的好处
1)能够在Vuex中集中管理共享的数据,易于开发和后期维护
2)能够高效地实现组件之间的数据共享,提高开发效率
3)存储在Vuex中的数据都是响应式的,能够实时保持数据与页面的同步
2.3 什么样的数据适合存储到Vuex中?
一般情况下,只有组件之间共享的数据,才有必要存储到Vuex中;对于组件中的私有数据,依旧存储在组件自身的data中
2.4 什么时候应该用Vuex?
1)这个问题因人而异,如果你不需要开发大型的单页应用,此时你完全没有必要使用Vuex,
比如页面就两三个,使用Vuex后增加的文件比你现在的页面还要多,那就没这个必要了。
2)假如你的项目达到了中大型应用的规模,此时你很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex将会成为自然而然的选择。
2.5 Vuex基本使用
- 安装Vuex依赖包
npm i vuex --save
- 在项目的根目录下新增一个store文件夹,在该文件夹内创建index.js
此时你的项目的src文件夹应当是这样的
│ App.vue
│ main.js
│
├─assets
│ logo.png
│
├─components
│ HelloWorld.vue
│
├─router
│ index.js
│
└─store
index.js
3) 初始化store下index.js中的内容
import Vue from 'vue'; //首先引入vue
import Vuex from 'vuex'; //引入vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
// state 类似 data
//这里面写入数据
},
getters:{
// getters 类似 computed
// 在这里面写个方法
},
mutations:{
// mutations 类似 methods
// 写方法对数据做出更改(同步操作)
},
actions:{
// actions 类似 methods
// 写方法对数据做出更改(异步操作)
}
})
//可能有的地方书写的风格不是这样的,如果需要的了解的可以百度看看其他人的
4)main.js中将store挂载到当前项目的Vue实例当中去
在main.js中使用我们的index.js(这里是为了防止在各个组件中引用,因为main.js中,有我们的new Vue 实例啊!)
//main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store, //store:store 和router一样,将我们创建的Vuex实例挂载到这个vue实例中;所有的组件,可以直接从 store 中获取全局数据了
render: h => h(App)
})
5)最后修改App.vue:
<template>
<div id='app'>
name:
<h1>{{ $store.state.count}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
或者在组件方法中使用
...,
methods:{
add(){
//使用this.$store.state.xxx可直访问到仓库中的状态
console.log(this.$store.state.count)
}
},
...
注意,不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 (commit) mutation。这样使得我们可以方便的跟踪每一个状态的变化。
三、VueX中的核心内容
Vuex中的主要核心概念如下:
state 存放状态
getters 加工state成员给外界
mutations state成员同步操作
actions 异步操作
modules 模块化状态管理
3.1 state
state 提供唯一的公共数据源,所有共享的数据都要统一放到store的state中进行存储。
//创建store数据源,提供唯一公共数据
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
3.1.1 组件访问state数据的两种方式
- 组件访问state中数据的
第一种方式:
// vue模板中不要使用this
this.$store.state.全局数据名称
- 组件访问state中数据的
第二种方式:
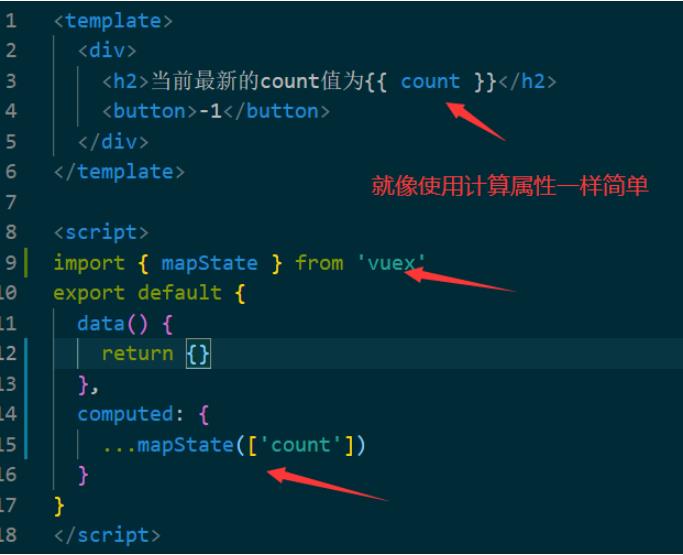
// 1. 从 vuex 中按需导入 mapState 函数
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
通过刚才导入的 mapState 函数,将当前组件需要的全局数据,映射为当前组件的 computed 计算属性:
// 2. 将全局数据,映射为当前组件的计算属性
computed:{
...mapState (['count'])
//如果使用的名称和index.js中的一样,直接写成上面数组的形式就行,
// 如果想改变下名字,写法如下
...mapState({
newCount: state => state.count
})
三个点…是展开运算符,意思是把全局里面的数据映射为当前组件的计算属性,在使用全局数据的时候,就像用一个计算属性一样简单;可认为当前count就是一个计算属性,希望将计算属性的值显示在页面上。
3.2 getters
getter 用于对 store 中的数据进行加工处理形成的数据。
1)getter 类似 Vue的计算属性;它的返回值会根据它的依赖被缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生了改变才会被重新计算。
2)store 中数据发生变化,getter的数据也会跟着变化。
3.2.1 getters基本使用
getters中的方法有两个默认参数
1)state 永远都是自身的state,state代表全局的数据对象;
2)getters 当前getters对象,用于将getters下的其他getter拿来用
例如
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
getters:{
showNum(state){
return "当前最新的数量是【'+ state.count +'】"
},
fullNum(state,getters){
return getters.showNum +'增加1:'+ state.count++
}
}
//组件中调用
this.$store.getters.fullNum
官方建议:
是不是每次都写this.$store.getters.XXX让你感到厌烦,你实在不想写这个东西怎么办,官方建议我们可以使用mapGetters去解构到计算属性中,就像使用mapState一样,就可以直接使用this调用了,就像下面3.2.2 方法2 这样:
3.2.2 使用getters 的两种方式
- 使用 getters 的
第一种方式:
this.$store.getters.名称
- 使用 getters 的
第二种方式:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed:{
...mapGetters (['fullNum'])
//组件中使用 跟计算属性一样调用
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前最新的count值为{{ fullNum }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
3.3 Mutations
3.3.1 为什么用Mutations??
用 `this.$store.state.count` 这种方式,不利于我们知道到底是谁修改了store全局数据, 不利于后期维护;
如果是用mutations修改,有问题可直接找mutations,找到对应的mutations就能找到问题了,方便后期维护;
通过这种方式虽然操作起来稍微繁琐些,但是可以集中监控所有数据的变化。
3.3.2 Mutations基本使用
mutations方法都有默认的形参:
([state] ,[payload])
1) state 必传的默认参数;永远都是自身的state,state代表全局的数据对象;
2)payload 载荷;是该方法在被调用时传递额外参数使用的

3.3.3 触发mutations时候携带参数
在大多数情况下,载荷应该是一个对象,这样可以包含多个字段并且记录的 mutation 会更易读:
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
addCount(state) {
state.count = 5;
},
addCountIsWhat(state, payload) { // 增加一个带参数的mutations方法,并且官方建议payload为一个对象
state.count = payload.count;
},
},
});
export default store;
组件中使用:
<script>
export default {
mounted() {
this.$store.commit('addCountIsWhat', {count:10}); // 调用的时候也需要传递一个对象
}
}
</script>
3.3.4 使用mutations的两种方式
- 使用 mutations 的
第一种方式:
this.$store.commit('mutations 中的方法名')
- 使用 mutations 的
第二种方式:
<script>
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex';
export default {
mounted() {
this.addCountIsWhat({count:20});
},
methods: { // 注意,mapMutations是解构到methods里面的,而不是计算属性了
...mapMutations(['addCountIsWhat']),
},
}
</script>
3.3.5 Mutation 需遵守 Vue 的响应规则
既然 Vuex 的 store 中的状态是响应式的,那么当我们变更状态时,监视状态的 Vue 组件也会自动更新。这也意味着 Vuex 中的 mutation 也需要与使用 Vue 一样遵守一些注意事项:
1) 最好提前在你的 store 中初始化好所有所需属性。
2) 当需要在对象上添加新属性时,你应该使用Vue.set(obj, 'newProp', 123);
或者以新对象替换老对象。例如,利用对象展开运算符我们可以这样写state.obj = { ...state.obj, newProp: 123 }
3) Vue.delete 删除成员Vue.delete(obj,'newProp')
3.4 Actions
Action 用于处理异步任务。
如果通过异步操作变更数据,必须通过 Action,而不能使用Mutation,但是 Action 中还是要通过触发 Mutation的方式间接变更数据。
只有通过actions => mumations => state,这个流程进行数据变更操作。
3.4.1 Actions基本使用
Actions方法都有默认的形参:
1) context 上下文对象(相当于一个与 store 实例具有相同方法和属性的 context 对象,
因此你可以调用 context.commit 提交一个 mutation,或者通过 context.state 和 context.getters 来获取 state 和 getters。);
2)payload 是该方法在被调用时额外传递参数使用的
例如:
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
//只有 mutations 中定义的函数,才有权利修改 state 中的数据
mutations: {
addCountIsWhat(state,payload){
state.count = payload.count
}
},
actions: {
setCount(context,payload){ //默认第一个参数是context,其值是复制的一份store
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('addCountIsWhat',payload)
},1000)
}
})
组件中调用:
this.$store.dispath('setCount',{count:300})
实践中,我们会经常用到 ES2015 的 参数解构来简化代码(特别是我们需要调用 commit 很多次的时候):
actions: {
setCount({ commit },payload) {
commit('addCountIsWhat',payload)
}
}
改进:
由于是异步操作,所以我们可以为我们的异步操作封装为一个Promise对象
setCount(context,payload){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('addCountIsWhat',payload)
resolve()
},1000)
})
}
3.4.2 Action处理异步的正确使用方式
想要使用action处理异步工作很简单,只需要将异步操作放到action中执行(如上面代码中的setTimeout)。
要想在异步操作完成后继续进行相应的流程操作,有两种方式:
1. store.dispatch返回相应action的执行结果,而action的处理函数返回的就是Promise,所以store.dispatch仍然返回一个Promise。
actions: {
actionA ({ commit }) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('addCountIsWhat')
resolve()
}, 1000)
})
}
}
现在可以写成:
store.dispatch('actionA').then(() => {
// ...
})
在另外一个 action 中也可以:
actions: {
// ...
actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
return dispatch('actionA').then(() => {
commit('addCountIsWhat')
})
}
}
2. 利用 async/await 进行组合action。代码更加简洁。
// 假设 getData() 和 getOtherData() 返回的是 Promise
actions: {
async actionA ({ commit }) {
commit('gotData', await getData())
},
async actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
await dispatch('actionA') // 等待 actionA 完成
commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData())
}
}
一个 store.dispatch 在不同模块中可以触发多个 action 函数。在这种情况下,只有当所有触发函数完成后,返回的 Promise 才会执行。
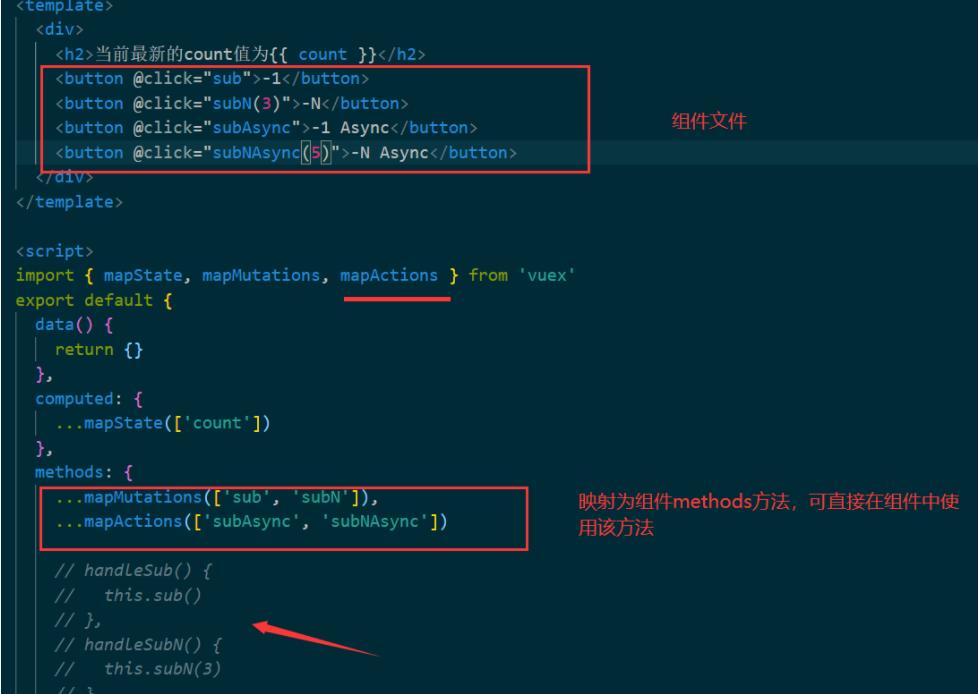
3.4.3 使用 Actions 的两种方式
- 使用 Actions 的
第一种方式:
this.$store.dispath('Actions 中的方法名')
- 使用 Actions 的
第二种方式:
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
methods:{
...mapActions (['addAsync','addNasync'])
Action部分个人觉得文档讲解的挺不错,我刚接触也能看的懂,可参考下这部分:
https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/actions.html#%E7%BB%84%E5%90%88-action
3.4.4 组件中直接调用映射的methods方法
3.5 modules
modules,可以让每一个模块拥有自己的state、mutation、action、getters,使得结构非常清晰,方便管理;如果所有的状态或者方法都写在一个store里面,将会变得非常臃肿,难以维护。
3.5.1 怎么用module?
一般结构:
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB})
模块内部的数据:
1) 模块内部的 state 是局部的,是被限制到模块的命名空间下,需要命名空间才能访问,也就是模块私有的比如 moduleA.js 模块
state 中的 count 数据,我们要通过 this.$store.state.moduleA.count 获取。
2)但actions 和mutations, 其实还有 getters 却没有被限制,在默认情况下,它们是注册到全局命名空间下的,所谓的注册到全局命名空间下,
其实就是我们访问它们的方式和原来没有module 的时候是一样的。
比如没有 module 的时候,this.$store.dispatch(“actions”);现在有了modules, actions 也写在了module 下面,
我们仍然可以这么写,this.$store.dispatch(“changeName”);组件中的getters,也是通过this.$store.getters.xxx来获取
注意,这个时候我们写$store.getters的时候,就不用写成$store.getters.a.fullNum了;
因为程序会默认先从初始的store中的getters寻找有没有fullNum这个方法,如果没有,就会去新的模块moduleA中寻找;
这就意味着,在开发时,一定不要写重复名字的方法
结合案例学习下
- 在src 目录下新建一个store文件夹,在里面建module文件夹 =》login.js,用于存放login 模块的状态。 为了简单起见,把模块下的state, actions,mutations, getters 全放在login.js文件中。
先简单给它增加一个状态,userName: “sam”
const state = {
useName: "sam"
};
const mutations = {
};
const actions = {
};
const getters = {
};
// 不要忘记把state, mutations等暴露出去。
export default {
state,
mutations,
actions,
getters
}
- 在store文件夹下,新建一个index.js作为根store,他通过modules属性引入 login 模块。
import Vue from "vue";
import Vuex from "vuex";
Vue.use(Vuex);
// 引入login 模块
import login from "./login"
export default new Vuex.Store({
// 通过modules属性引入login 模块。
modules: {
login: login
}
})
- 在main.js中引入store, 并注入到vue 根实例中。
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
// 引入store
import store from "./store"
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store, // 注入到根实例中。
render: h => h(App)
})
- 在组件中通过computed属性获取到login下的state. 这里要注意,在没有modules 的情况下,
组件中通过this.store.state.属性名,有了 modules 之后,state被限制到login的命名空间下,所有属性名前必须加命名空间,在这里是this.$store.state.login.userName
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{useName}}</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// computed属性,从store 中获取状态state,不要忘记login命名空间。
computed: {
useName: function() {
return this.$store.state.login.useName
}
}
}
</script>
项目目录如下:
- 通过actions, mutations 改变名字, 这就涉及到dispatch action, commit mutations, mutations 改变state.
先在 modules 文件夹login.js中添加changeName action 和 change_name mutations.
const mutations = {
change_name (state, anotherName) {
state.useName = anotherName;
}
};
const actions = {
changeName ({commit},anotherName) {
commit("change_name", anotherName)
}
};
在组件 中添加一个按钮:<button> change to json</button>, 点击时,dispatch 一个 action. 那在组件中怎么dispatch actions 呢?
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<h1>{{useName}}</h1>
<!-- 添加按钮 -->
<div>
<button @click="changeName"> change to json</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
// computed属性,从store 中获取状态state,不要忘记login命名空间。
computed: {
useName: function() {
return this