前端开发Array.prototype.reduce()的详细解析&使用
Posted 李猫er
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了前端开发Array.prototype.reduce()的详细解析&使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
reduce() 的高级用法
Array.prototype.reduce()
reduce() 方法为数组中的每一个元素执行回调函数,并将其回调的的结果值作为返回值。
语法:
arr.reduce(callback(priviousValue,currentValue,currentIndex,sourceArray),[initValue])
reduce 函数接收四个参数:
-
callback:reduce得回调函数,接收四个参数:
- priviousValue:累加器,即上一次回调返回的值,或者提供的初始值(initValue)
- currentValue:数组中当前正在被处理的值
- currentIndex: 数组中当前元素的索引(可选)
- sourceArray:reduce的源数组(可选)
-
initValue:作为第一次调用callback得第一个参数的初始值。(可选)
-
返回值
回调函数累计处理的结果
reduce() 执行过程
从MDN文档描述中:
回调函数第一次执行时,priviousValue 和currentValue的取值有两种情况:如果调用reduce()时提供了initValue,priviousValue取值为initValue,currentValue取数组中的第一个值;如果没有提供 initValue,那么priviousValue取数组中的第一个值,currentValue取数组中的第二个值。
解释:也就是说如果没有我们没有给出初始值,开始执行时,数组中被处理的取值索引是1,而不是从0开始的。这会导致数组中第一个元素(即索引为0没有被处理,因为数组的元素索引是从0开始的)
大白话显得苍白无力,实践出真知。我们来实践一下:
实例解析initValue 参数
第一个例子:没有initValue 时
let array = [1,2,3,4,5];
let sum = array.reduce((preValue,curValue,curIndex,array) => {
console.log(preValue,curValue,curIndex);
return preValue + curValue;
})
console.log(array,sum);
打印结果:
1 2 1
3 3 2
6 4 3
10 5 4
[1,2,3,4,5] 15
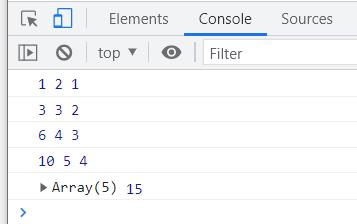
从打印的结果来看,我的数组长度是5,但是reduce()循环打印的次数只有4次,函数开始执行的数组索引是从index为1开始的,第一次的preValue值是数组的第一个值1
第二个例子:有initValue 时:
我们在第一个例子的基础上,修改一下:
let array = [1,2,3,4,5];
let sum = array.reduce((preValue,curValue,curIndex,array) => {
console.log(preValue,curValue,curIndex);
return preValue + curValue;
},0) //与上个例子相比,这里设置初始值0
console.log(array,sum);
这时候的打印结果:
0 1 0
1 2 1
3 3 2
6 4 3
10 5 4
[1,2,3,4,5] 15
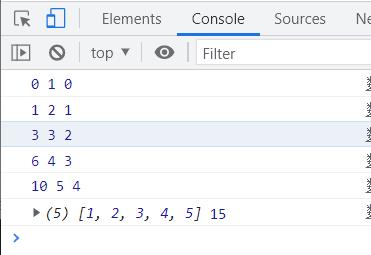
这时候的函数的执行是从index为0开始的,第一次执行回调函数时,preValue的值是我们设置的初始值0,回调函数执行5次,数组长度为5.
总之:如果没有提供initValue,reduce 会从索引1的地方开始执行 callback 函数,直接跳过第一个索引。如果提供initialValue,从索引0开始。
还有一个值得注意的是:
如果没有提供初始值,可能会有下面这四种输出的可能:
var maxCallback = ( acc, cur ) => Math.max( acc.x, cur.x );
var maxCallback2 = ( max, cur ) => Math.max( max, cur );
// reduce() 没有初始值
[ { x: 2 }, { x: 22 }, { x: 42 } ].reduce( maxCallback ); // NaN
[ { x: 2 }, { x: 22 } ].reduce( maxCallback ); // 22
[ { x: 2 } ].reduce( maxCallback ); // { x: 2 }
[ ].reduce( maxCallback ); // TypeError
// map/reduce; 这是更好的方案,即使传入空数组或更大数组也可正常执行
[ { x: 22 }, { x: 42 } ].map( el => el.x )
.reduce( maxCallback2, -Infinity );
如果数组为空且没有提供initialValue,会抛出TypeError 。如果数组仅有一个元素(无论位置如何)并且没有提供initialValue, 或者有提供initialValue但是数组为空,那么此唯一值将被返回并且callback不会被执行。因此提供初始值通常更安全。
reduce的运用
(1)计算数组中每个元素出现的次数
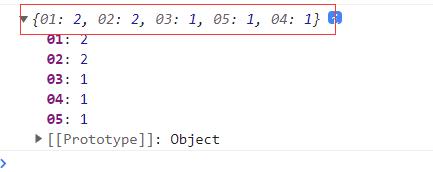
// 计算数组中每个元素出现的次数
let nums = ["01","02","03","01","05","04","02"];
let count = nums.reduce((preV,currentV) => {
if (currentV in preV) {
preV[currentV] ++
} else {
preV[currentV] = 1
}
return preV
},{})
console.log(count);
(2) 数组去重
// 数组去重
let nums = ["01","02","03", ,"04","02","01","05"];
let newArr = nums.reduce((preV,currentV) => {
if (!preV.includes(currentV)) {
return preV.concat(currentV)
} else {
return preV
}
},[])
console.log(newArr);

(3)数组扁平化:将多维数组转化为一维数组:
// 数组扁平化运用:将二维数组转化为一维
let arr = [[0,1],[2,3,4],[5,6,7,8]]
let newArr = arr.reduce((preV,currentV) => {
return preV.concat(currentV)
},[])
console.log(newArr);
打印结果:

(4)对象里的属性求和
// 对象里的属性求和
let items = [
{
id: 1,
name: 'python',
count: 20
},
{
id: 2,
name: 'javascript',
count: 30
},
{
id: 3,
name: 'java',
count: 50
}
];
let total = items.reduce((preV,currentV) => {
return currentV.count +preV;
},0);
console.log("总统计人数:" + total)
打印结果:

以上是关于前端开发Array.prototype.reduce()的详细解析&使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章