C++初阶---vector的使用及模拟实现 (待写。。)。
Posted 4nc414g0n
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++初阶---vector的使用及模拟实现 (待写。。)。相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
vector使用及模拟实现
vector
vector介绍
template < class T, class Alloc = allocator<T> > class vector; // generic template① : vector是表示可以改变大小的数组的序列容器
②: 就像数组一样,vector也采用的连续存储空间来存储元素。也就是意味着可以采用下标对vector的元素进行访问,和数组一样高效。但是又不像数组,它的大小是可以动态改变的,而且它的大小会被容器自动处理
③:本质讲,vector使用动态分配数组来存储它的元素。当新元素插入时候,这个数组需要被重新分配大小为了增加存储空间。其做法是,分配一个新的数组,然后将全部元素移到这个数组。就时间而言,这是一个相对代价高的任务,因为每当一个新的元素加入到容器的时候,vector并不会每次都重新分配大小
④ :vector分配空间策略:vector会分配一些额外的空间以适应可能的增长,因为存储空间比实际需要的存储空间更大。不同的库采用不同的策略权衡空间的使用和重新分配。但是无论如何,重新分配都应该是对数增长的间隔大小,以至于在末尾插入一个元素的时候是在常数时间的复杂度完成的
⑤: vector占用了更多的存储空间,为了获得管理存储空间的能力,并且以一种有效的方式动态增长
⑥:与其它动态序列容器相比(deques, lists and forward_lists), vector在访问元素的时候更加高效,在末尾添加和删除元素相对高效。对于其它不在末尾的删除和插入操作,效率更低。比起lists和forward_lists统一的迭代器和引用更好——————————————————————————翻译自:vector -C++ Reference
vector使用
详细请参考:cplusplus -vector
①vector构造函数
1.构造一个空容器,没有元素
explicit vector (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());2.构造一个包含 n 个元素的容器。每个元素都是 val 的副本
explicit vector (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type(), const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());3.构造一个包含与范围 [first,last) 一样多的元素的容器,每个元素都由该范围内的对应元素以相同的顺序构造
template <class InputIterator> vector (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());4.以相同的顺序构造一个容器,其中包含 x 中每个元素的副本
vector (const vector& x);
示例代码:// constructing vectors #include <iostream> #include <vector> int main () { //四种构造方式 std::vector<int> first;// int类型的空vector std::vector<int> second (4,100);// 四个整数,值为 100 std::vector<int> third (second.begin(),second.end()); // 迭代second std::vector<int> fourth (third);// third的拷贝 // 迭代器构造函数也可用于从数组构造: int myints[] = {16,2,77,29}; std::vector<int> fifth (myints, myints + sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int) ); std::cout << "The contents of fifth are:"; for (std::vector<int>::iterator it = fifth.begin(); it != fifth.end(); ++it) std::cout << ' ' << *it; std::cout << '\\n'; return 0; }
输出:
The contents of fifth are: 16 2 77 29
②vector的访问及遍历操作
vector和string相似,迭代器也是指针:具体参考C++初阶—STL入门+(string)的iterator部分
注意:
rbegin和rend就不是原生指针指向数组的指针是天然的迭代器
| 名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
begin | 迭代器返回到开头 |
end | 迭代器返回到结尾 |
cbegin | const重载 |
cend | const重载 |
rbegin | 反向迭代器返回到开头 |
rend | 反向迭代器返回到结尾 |
crbegin | const重载 |
crend | const重载 |
③vector常见容量操作
| 名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
size | 返回大小 |
max_size | (用处不大) |
resize | 类似string的resize,只是char缺省值是‘\\0’,int缺省值为‘0’ |
reserve | 类似string的reserve |
capacity | 容量 |
empty | 判空 |
③vector访问操作
注意:
operator[]会检查下标是否小于size,越界大于就assert终止程序报错,而at是抛异常
reserve后未初始化的空间不能访问,resize默认会初始化,可以访问
迭代器区间都是左闭右开
| 名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
operator[] | 取得元素 |
at | 取得元素 |
front | 取首元素 |
back | 取尾元素 |
④vector修改操作
vector没有find成员函数
find函数模板是std下的
实现:template<class InputIterator, class T> InputIterator find (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const T& val) { while (first!=last) { if (*first==val) return first; ++first; } return last; }返回迭代区间 [first,last)的第一个值为val的元素(指相当于指针)
| 名称 | 功能 |
|---|---|
assign | 分配vector内容 |
push_back | 尾插 |
pop_back | 尾删 |
insert | 插入元素 |
erase | 删除元素 |
insert | 插入元素 |
swap | 交换元素 |
assign:
template <class InputIterator>
void assign (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);void assign (size_type n, const value_type& val);std::vector<int> first; std::vector<int> second; std::vector<int> third; first.assign (7,100); // 7个值为100的整形 std::vector<int>::iterator it; it=first.begin()+1; second.assign (it,first.end()-1); // 5个first中间的元素 int myints[] = {1776,7,4}; third.assign (myints,myints+3); // 从数组assign std::cout << "Size of first: " << int (first.size()) << '\\n'; std::cout << "Size of second: " << int (second.size()) << '\\n'; std::cout << "Size of third: " << int (third.size()) << '\\n';
输出:
Size of first: 7
Size of second: 5
Size of third: 3
vector模拟实现
C++语言使用的标准模板库v30版本,作为一份源码来说易于剖析和学习-Standard Template Library v30 uses language version C++
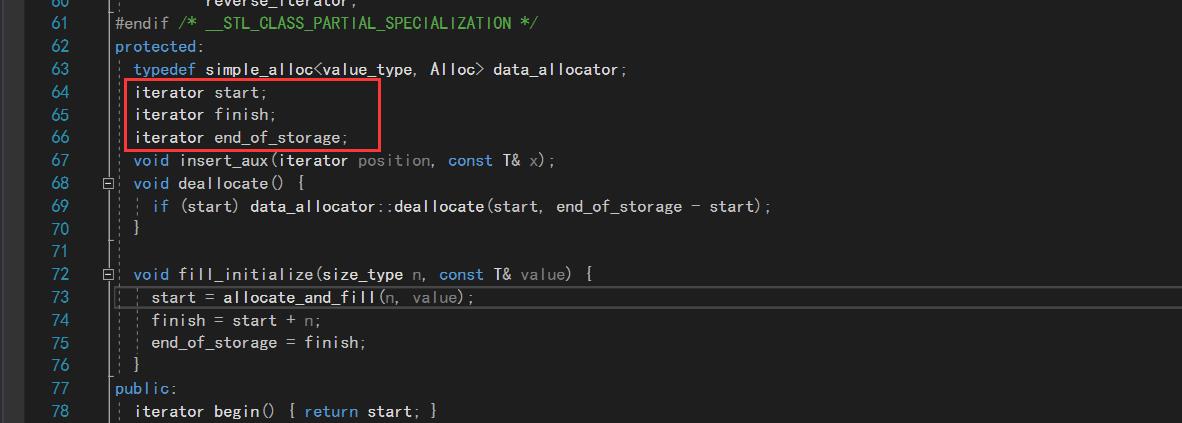
我们找到stl_vector.h,会看到被protect修饰的三个迭代器成员变量,结合之前string在定义的_str,_size,_capacity,
这里推测应该是指向首元素,末尾元素,容量位置的三个指针,iterator是typedef T* iterator出来的,也就是指针
下面.h中实现的构造函数印证了我们的想法
以上是关于C++初阶---vector的使用及模拟实现 (待写。。)。的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章