数据结构--栈
Posted 你帅你先说.
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构--栈相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
●🧑个人主页:你帅你先说.
●📃欢迎点赞👍关注💡收藏💖
●📖既选择了远方,便只顾风雨兼程。
●🤟欢迎大家有问题随时私信我!
●🧐版权:本文由[你帅你先说.]原创,CSDN首发,侵权必究。
🕶️1.栈
🎩1.1栈的概念
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
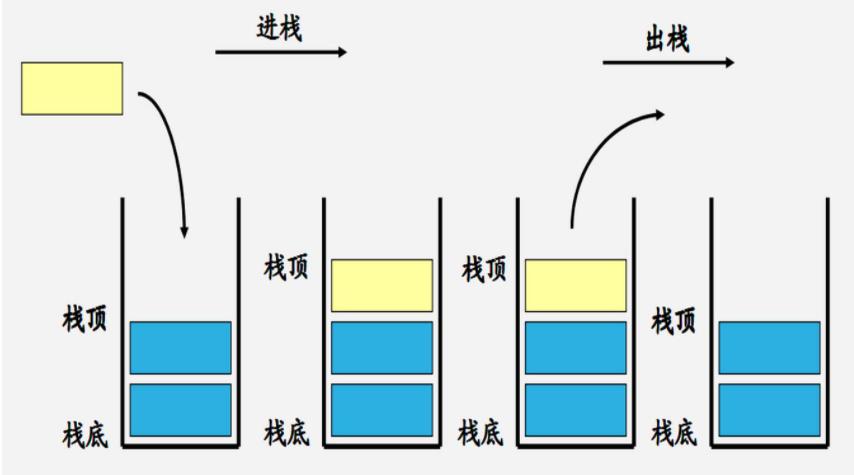
👑1.2栈的实现
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
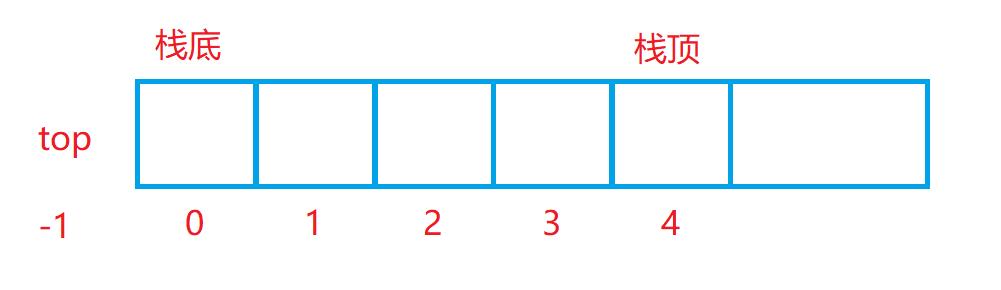
📱1.2.1栈的初始化
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = -1;
}
💻1.2.2判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
if (ps->top == -1)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
🖱️1.2.3进栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->capacity == ps->top+1)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = realloc(ps->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newCapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->top++;
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
}
🏷️1.2.4出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
📌1.2.5取栈顶元素
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(!StackEmpty(ps));
return ps->a[ps->top];
}
🔑1.2.5销毁栈
void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = 0;
ps->top = -1;
}
相信学完链表的你,栈对你来说是小菜一碟

这样的文章你还不快 点赞👍关注💡收藏💖
悄悄告诉你📢:长按👍可一键三连
以上是关于数据结构--栈的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章