iOS-深拷贝和浅拷贝
Posted MinggeQingchun
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了iOS-深拷贝和浅拷贝相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、深拷贝(Deep Copy) 和 浅拷贝(Shallow Copy)
1、深拷贝(Deep Copy):内容拷贝,拷贝数据到一块新内存区域,指针指向拷贝的数据区
(另外创造一个一模一样的对象,新对象跟原对象不共享内存,修改新对象不会改到原对象)
2、浅拷贝(Shallow Copy):指针拷贝,复制一个新的指针,指针指向同一块内存区域。实际内存并没有发生拷贝
(只复制指向某个对象的指针,而不复制对象本身,新旧对象还是共享同一块内存)
1、对不可变对象执行copy操作,是浅拷贝(指针拷贝,内容相同),都指向同一片存储空间,源数据被修改,副本数据也会被修改
2、对不可变字符串执行mutCopy操作,是深拷贝(对象拷贝),两者指向不同的存储空间
3、可变字符串执行copy或mutCopy都是深拷贝
4、可变容器类执行copy或mutcopy或者不可变容器执行mutCopy都是不完全深拷贝,即只是容器对象指向不同的内存空间,内部的元素则指向同一个内存
5、可变数组执行copy(NSMutableArray执行copy后返回的NSArray),在使用过程回出现crash的问题
6、数组完全深拷贝需要执行initWithArray:copyItems: 方法
NSArray *deepCopy = [[NSArray alloc] initWithArray:array copyItems:YES];参考苹果官方原图:苹果官网文档
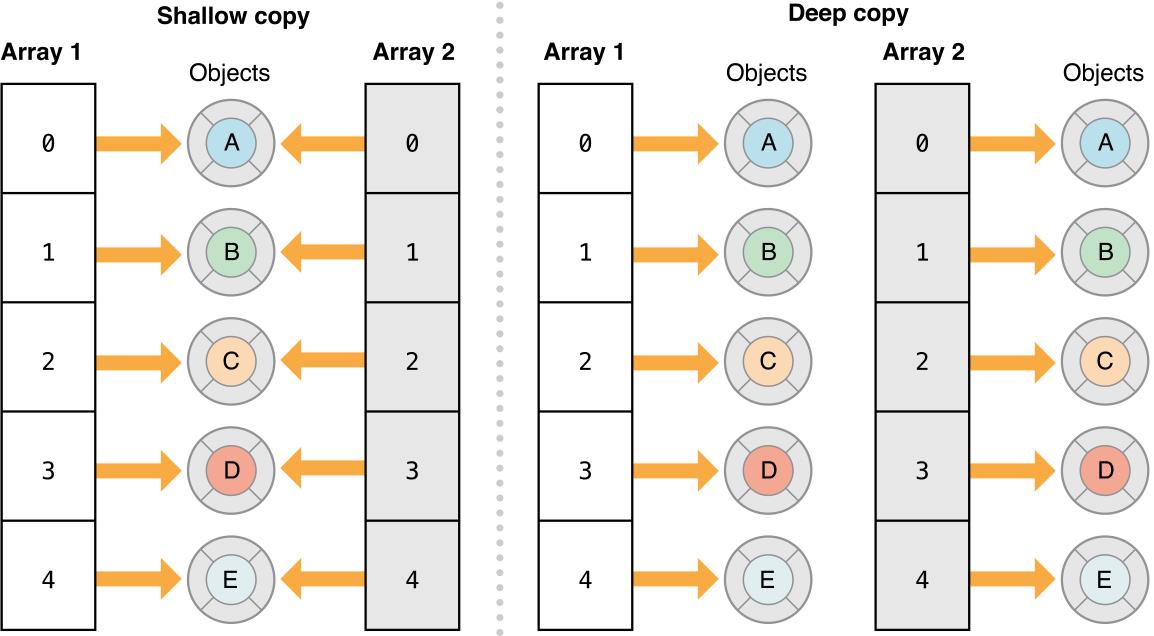
深拷贝参考下图:

浅拷贝参考下图:

在Objective-C中并不是所有的对象都支持Copy,MutableCopy,遵守NSCopying协议的类才可以发送Copy消息,遵守NSMutableCopying 协议的类才可以发送MutableCopy消息.
二、对非集合对象的copy和mutableCopy
以NSString类型举例:
NSLog(@"--不可变NSString--");
NSString *string = @"123";
NSString *stringCopy = [string copy];
NSLog(@"--不可变NSString--copy--");
NSLog(@"string的地址:%p,stringCopy的地址:%p",string,stringCopy);
NSMutableString *stringMCopy = [string mutableCopy];
NSLog(@"--不可变NSString--mutableCopy--");
NSLog(@"stringMCopy的地址:%p",stringMCopy);
// string = @"123456";
// NSLog(@"string:%@ stringCopy:%@ stringMCopy:%@",string,stringCopy,stringMCopy);
NSLog(@"");
NSLog(@"--可变NSMutableString--");
NSMutableString * mString = [NSMutableString stringWithString:@"123"];
NSString *mStringCopy = [mString copy];
NSLog(@"--可变NSMutableString--copy--");
NSLog(@"mString的地址:%p,mStringCopy的地址:%p",mString,mStringCopy);
NSMutableString *mStringMCopy = [mString mutableCopy];
NSLog(@"--可变NSMutableString--mutableCopy--");
NSLog(@"mStringMCopy的地址:%p",mStringMCopy);输出结果

通过查看内存,可以看到 stringCopy 和 string 的地址是一样,进行了指针拷贝;而 stringMCopy 的地址和 string 不一样,进行了内容拷贝;
可以看到 mStringCopy 和 mString 的地址是一样,进行了内容拷贝;而 mStringMCopy 的地址和 mString 不一样,进行了内容拷贝;
因此,得出结论:
非集合对象(immutableObject)的copy和mutableCopy
对immutable对象进行copy操作,是指针拷贝,mutableCopy操作时内容拷贝;对mutable对象进行copy和mutableCopy都是内容拷贝。
[immutableObject copy] //浅拷贝
[immutableObject mutableCopy] //深拷贝
[mutableObject copy] //深拷贝
[mutableObject mutableCopy] //深拷贝
三、对集合对象的copy和mutableCopy
集合对象指的是NSArray,NSDictionary,NSSet等类的对象。
NSLog(@"--不可变NSArray--");
NSArray *array = @[@1, @2, @3, @4];
NSArray *arrayCopy = [array copy];
NSMutableArray *arrayMCopy = [array mutableCopy];
NSLog(@"--不可变NSArray--copy--");
NSLog(@"array的地址:%p; arrayCopy的地址:%p; arrayMCopy的地址:%p",array,arrayCopy,arrayMCopy);
NSLog(@"--不可变NSArray--mutableCopy--");
NSLog(@"array的第一个元素地址:%p; arrayCopy的第一个元素地址:%p; arrayMCopy的第一个元素地址:%p",array[0],arrayCopy[0],arrayMCopy[0]);
NSLog(@"");
NSLog(@"--可变NSMutableArray--");
NSMutableArray *mArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithObjects:@1, @2, @3, @4, nil];
NSArray *mArrayCopy = [mArray copy];
NSMutableArray *mArrayMCopy = [mArray mutableCopy];
NSLog(@"--可变NSMutableArray--copy--");
NSLog(@"mArray的地址:%p; mArrayCopy的地址:%p; mArrayMCopy的地址:%p",mArray,mArrayCopy,mArrayMCopy);
NSLog(@"--可变NSMutableArray--mutableCopy--");
NSLog(@"mArray的第一个元素地址:%p; mArrayCopy的第一个元素地址:%p; mArrayMCopy的第一个元素地址:%p",mArray[0],mArrayCopy[0],mArrayMCopy[0]);输出结果

查看内容,可以看到arrayCopy和array的地址是一样的,而arrayMCopy和array的地址是不同的。说明copy操作进行了指针拷贝,mutableCopy进行了内容拷贝。但需要强调的是:此处的内容拷贝,仅仅是拷贝array这个对象,array集合内部的元素仍然是指针拷贝。
mArrayCopy、mArrayMCopy和mArray的内存地址都不一样,说明mArrayCopy、mArrayMCopy都对mArray进行了内容拷贝,mArray集合内部的元素仍然是指针拷贝。
因此,在集合类对象中,对immutable对象进行copy,是指针拷贝,mutableCopy是内容拷贝;对mutable对象进行copy和mutableCopy都是内容拷贝。但是:集合对象的内容拷贝仅限于对象本身,对象元素仍然是指针拷贝。
[immutableObject copy] // 浅拷贝
[immutableObject mutableCopy] //单层深拷贝
[mutableObject copy] //单层深拷贝
[mutableObject mutableCopy] //单层深拷贝
四、集合单层深拷贝(one-level-deep copy)
我们在上面NSArray和NSMutableArray不管是进行copy也好,还是mutableCopy也好,其实对象元素都是浅拷贝(指针拷贝),这种情况是属于深拷贝,还是浅拷贝?苹果官网文档有这样原话描述:
Deep Copies
There are two ways to make deep copies of a collection. You can use the collection’s equivalent of initWithArray:copyItems: with YES as the second parameter. If you create a deep copy of a collection in this way, each object in the collection is sent a copyWithZone: message. If the objects in the collection have adopted the NSCopying protocol, the objects are deeply copied to the new collection, which is then the sole owner of the copied objects. If the objects do not adopt the NSCopying protocol, attempting to copy them in such a way results in a runtime error. However, copyWithZone: produces a shallow copy. This kind of copy is only capable of producing a one-level-deep copy. If you only need a one-level-deep copy, you can explicitly call for one as in Listing 2.
Listing 2 Making a deep copy
NSArray *deepCopyArray=[[NSArray alloc] initWithArray:someArray copyItems:YES];
This technique applies to the other collections as well. Use the collection’s equivalent of initWithArray:copyItems: with YES as the second parameter.
If you need a true deep copy, such as when you have an array of arrays, you can archive and then unarchive the collection, provided the contents all conform to the NSCoding protocol. An example of this technique is shown in Listing 3.
Listing 3 A true deep copy
NSArray* trueDeepCopyArray = [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithData:
[NSKeyedArchiver archivedDataWithRootObject:oldArray]];

关于浅拷贝、深拷贝、单层深拷贝做了概念区分:
浅拷贝(shallow copy): 在浅拷贝操作时,对于被拷贝对象的每一层都是指针拷贝。
深拷贝(one-level-deep copy):在深拷贝操作时,对于被拷贝对象,至少有一层是深拷贝。
完全拷贝(real-deep copy):在完全拷贝操作时,对于被拷贝对象的每一层都是对象拷贝。
我们要想对数组中的对象也进行深拷贝,要做到如下:
首先创建Person.h和Person.m,需要实现<NSCopying>协议,不然汇报如下错误:
*** Terminating app due to uncaught exception 'NSInvalidArgumentException', reason: '-[Person copyWithZone:]: unrecognized selector sent to instance 0x6000015084c0'
//Person.h 文件
@interface Person : NSObject<NSCopying>
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@end
//Person.m 文件
@implementation Person
//实现copyWithZone方法
- (id)copyWithZone:(NSZone *)zone {
Person *p = [[self class] allocWithZone:zone];
p.name = [self name];
return p;
}
@end实现如下:
/*--------数组元素拷贝-------*/
NSLog(@"");
NSLog(@"--不可变NSArray--元素拷贝--");
Person *person = [[Person alloc] init];
[person setName:@"one"];
NSArray *array1 = [[NSArray alloc] initWithObjects:person, nil];
//注意仅仅是这里更改为了[[NSArray alloc] initWithArray:array1 copyItems:YES];
NSArray *array2 = [[NSArray alloc] initWithArray:array1 copyItems:YES];
Person *p = array2[0];
[p setName:@"two"];//尝试更改name的值
//获取两个数组里的各自Person对象
Person *p1 = [array1 objectAtIndex:0];
Person *p2 = [array2 objectAtIndex:0];
NSLog(@"array1:%p",array1);
NSLog(@"array2:%p",array2);
NSLog(@"p1:%p",p1);
NSLog(@"p2:%p",p2);
NSLog(@"p1.name:%@",p1.name);
NSLog(@"p2.name:%@",p2.name);
NSLog(@"");
NSLog(@"--可变NSMutableArray--元素拷贝--");
Person *per = [[Person alloc] init];
[per setName:@"one11"];
NSMutableArray *array111 = [[NSMutableArray alloc] initWithObjects:person, nil];
//注意仅仅是这里更改为了[[NSArray alloc] initWithArray:array1 copyItems:YES];
NSMutableArray *array222 = [[NSMutableArray alloc] initWithArray:array111 copyItems:YES];
Person *pp = array222[0];
[pp setName:@"two22"];//尝试更改name的值
//获取两个数组里的各自Person对象
Person *p11 = [array111 objectAtIndex:0];
Person *p22 = [array222 objectAtIndex:0];
NSLog(@"array111:%p",array111);
NSLog(@"array222:%p",array222);
NSLog(@"p11:%p",p11);
NSLog(@"p22:%p",p22);
NSLog(@"p11.name:%@",p11.name);
NSLog(@"p22.name:%@",p22.name);输出结果:
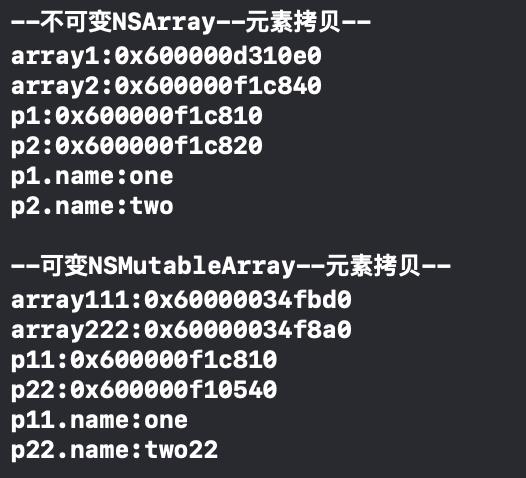
我们可以看出,不但array1和array2的内存地址发生改变,连array2里面的Person对象也发生改变,生成了另外一个Person对象,即使属于array1的Person对象的元素name发生改变也不会影响到array2里的Person对象。
参考文章
以上是关于iOS-深拷贝和浅拷贝的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章