Java无头单向非循环链表实现
Posted 宗旨飞翔
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java无头单向非循环链表实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
1.链表
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的 。
链表种类:

2.无头单向非循环链表
结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈
希桶、图的邻接表等等。
**注意:**这种链表结构的头不确定,一直在变
例如如果在开始插入节点,那么head会变

下面主要讲无头单向非循环链表
3.创建链表
首先用穷举法创建,只是暂时用,太low了
链表是一个一个节点,ListNode代表一个节点
//ListNode代表一个节点
class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}

5个节点,穷举法创建:


public ListNode head;//链表的头引用
public void createList() {
ListNode listNode1 = new ListNode(12);
ListNode listNode2 = new ListNode(23);
ListNode listNode3 = new ListNode(34);
ListNode listNode4 = new ListNode(45);
ListNode listNode5 = new ListNode(56);
listNode1.next = listNode2;
listNode2.next = listNode3;
listNode3.next = listNode4;
listNode4.next = listNode5;
this.head = listNode1;
}
4.遍历链表
用head=head.next的方式进行遍历,只要当head!=null就行。
注意条件是head!=null
不是this.head.next != null,如果是this.head.next != null最后一个节点不会打印。

但是会出现问题,head变了,所以创建变量cur=this.head,让cur移动
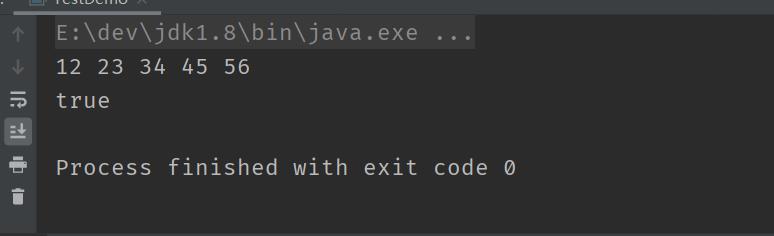
public void display() {
//this.head.next != null
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
测试:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.display();
}
}

5.功能列表
5.1查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中


首先定义ListNode cur = this.head;当cur != null,判断值是否相等,找到返回true,否则返回false:
public boolean contains(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
测试:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.display();
boolean flg = myLinkedList.contains(34);//12,56
System.out.println(flg);
}
}
5.2得到单链表的长度
//得到单链表的长度
public int size() {
int count = 0;
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
测试:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.display();
boolean flg = myLinkedList.contains(12);
System.out.println(flg);
System.out.println(myLinkedList.size());
}
}

5.3头插法
首先创建node引用:
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
例如在链表头插入1:

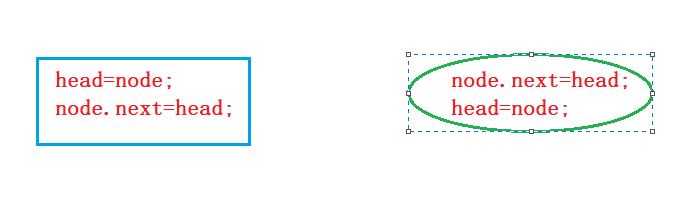
上面两种方法谁对谁错呢?
第一种错了,因为你将它的next改成自己了,后面就连不上了。
注意:绑定位置的时候,一定要先绑定后面
一个节点都没有,也可以直接插入
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
测试:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.display();
boolean flg = myLinkedList.contains(12);
System.out.println(flg);
System.out.println(myLinkedList.size());
myLinkedList.addFirst(45);
myLinkedList.display();
}
}

5.4尾插法

首先要寻找尾巴节点:

尾插法必须判空,因为为空的话,cur为空,cur.next就会报空指针异常
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node;
}
}
测试:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(76);
myLinkedList.addLast(100);
myLinkedList.addLast(340);
myLinkedList.display();
}
}

5.5任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
如果index=0,就是头插法,index=size(),就是尾插

/**
* @param index
* @Description:找到index-1位置节点的地址
* @return: ListNode
*/
public ListNode findIndex(int index) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while ((index - 1) != 0) {
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
return cur;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
System.out.println("index位置不合法!");
return;
}
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = findIndex(index);
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
}
5.6删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
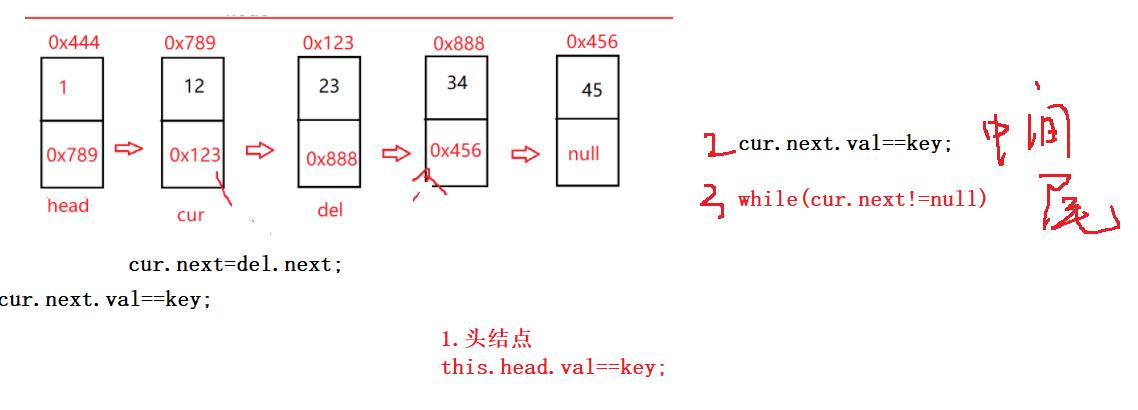
首先判断链表是否为空,然后判断头结点是否是要找的值,如果不是,后面的节点首先要找到其前驱节点cur
/**
* @param key
* @Description:找要删除节点的前驱
* @return: ListNode
*/
public ListNode searchPerv(int key) {
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == key) {
return cur;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return null;
}
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key) {
if (this.head == null) {
System.out.println("单链表为空,不能删除!");
return;
}
if (this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
ListNode cur = searchPerv(key);
if (cur == null) {
System.out.println("没有要删除的节点!");
return;
}
ListNode del = cur.next;
cur.next = del.next;
}
测试:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(76);
myLinkedList.addLast(100);
myLinkedList.addLast(340);
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.remove(34);
myLinkedList.display();
}
}

5.7删除所有值为key的节点

//删除所有值为key的节点
public ListNode removeAllKey(int key) {
if (this.head == null) return null;
ListNode perv = this.head;
ListNode cur = this.head.next;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.val == key) {
perv.next = cur.next;
cur = cur.next;
} else {
perv = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//最后处理头
if (this.head.val == key) {
this.head = this.head.next;
}
return this.head;
}
测试:删除所有的100
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(76);
myLinkedList.addLast(100);
myLinkedList.addLast(340);
myLinkedList.addFirst(100);
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.removeAllKey(100);
myLinkedList.display();
}
}

5.8清空链表

//清空链表
public void clear() {
//粗暴的 this.head==null;
while (this.head != null) {
ListNode curNext = head.next;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = curNext;
}
}
测试:
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.createList();
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.addLast(34);
myLinkedList.addLast(76);
myLinkedList.addLast(100);
myLinkedList.addLast(340);
myLinkedList.addFirst(100);
myLinkedList.display();
myLinkedList.removeAllKey(100);
System.out.println("请空前");
myLinkedList.display();
System.out.println("请空后");
myLinkedList.clear();
myLinkedList.display();
System.out.println("==========");
}
}

以上是关于Java无头单向非循环链表实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章