RabbitMq一文彻底弄懂RabbitMq的四种交换机原理及springboot实战应用
Posted 干饭两斤半
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了RabbitMq一文彻底弄懂RabbitMq的四种交换机原理及springboot实战应用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
四大交换机工作原理及实战应用
交换机概念
交换机可以理解成具有路由表的路由程序,仅此而已。每个消息都有一个称为路由键(routing key)的属性,就是一个简单的字符串。
最新版本的RabbitMQ有四种交换机类型,分别是Direct exchange、Fanout exchange、Topic exchange、Headers exchange。
交换机的作用: 生产者向broker(rabbitmq服务器)发送消息,交换机通过生产者绑定的路由键,将消息推送到不同的消息队列中。而消费者,只绑定队列,从队列中获取消息。
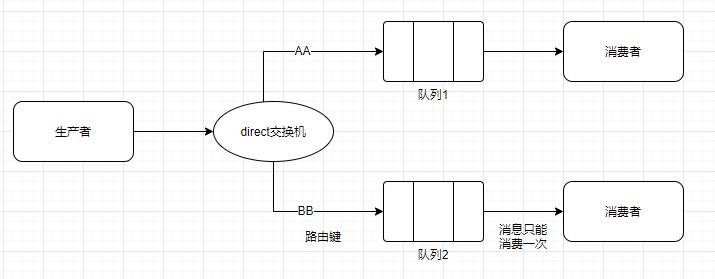
direct 直连交换机
工作模式图解
生产者发送的消息;交换机会根据不同的路由键,发送到对应的队列;
springboot代码
MQ配置类,声明交换机、队列,路由键绑定
/**
* 声明交换机、队列、路由键绑定
* /
@Configuration
puvlic class RabbitConfig {
/**
* 创建直连交换机
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange createExchange() {
// 交换机名字;是否持久化;是否自动删除
return new DirectExchange("testE", true, false);
}
/**
* 创建队列
*/
@Bean
public Queue createQueue() {
// 交换机名字;是否持久化;是否自动删除
return new Queue ("testQ", true, false, false);
}
/**
* 通过路由键绑定交换机和队列
*/
@Bean
public Binding createBinding() {
// 交换机名字;是否持久化;是否自动删除
return BindingBuilder
.bind(this.createQueue())
.to(this.createExchange())
.with("testR");
}
}
生产者
/**
* 消息生产者
*/
@Service
public class ProduceMsg {
@Autowire
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMsg(Object msg){
// 消息唯一标识
CorrelationData correlationData= new CorrelationData();
correlationData.setId(msg.getId());
rabbitTemplate.converAndSend("testE", "testR", msg, correlationData);
}
}
消费者
@Conponent
public class ConsumeMsg {
/**
* 消费者监听队列
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "testQ")
public void sendMsg(String msg){
log.info("接收到消息:{}", msg);
// ......业务逻辑消费消息;
}
}
Fanout扇出交换机
工作模式图解
生产者发送到交换机的消息;会发送到绑定到该交换机的所有队列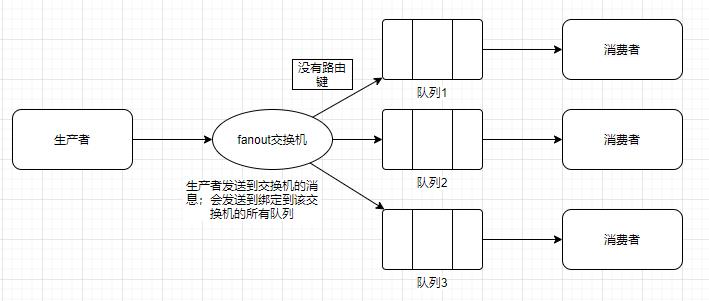
springboot代码
MQ配置类,声明交换机、队列,绑定
/**
* RabbitMQ配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMqConfig {
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueA()
{
return new Queue("queueA", true, false, false);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueB()
{
return new Queue("queueB", true, false, false);
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueueC()
{
return new Queue("queueC", true, false, false);
}
@Bean
FanoutExchange fanoutExchange()
{
return new FanoutExchange("exchangeFanout");
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeA()
{
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueA()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeB()
{
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueB()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeC()
{
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueueC()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
}
生产者
/**
* 消息生产者
*/
@Service
public class ProduceMsg {
@Autowire
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMsg(Object msg){
// 消息唯一标识
CorrelationData correlationData= new CorrelationData();
correlationData.setId(msg.getId());
rabbitTemplate.converAndSend("exchangeFanout", "", msg, correlationData);
}
}
消费者
@Conponent
public class ConsumeMsg {
/**
* 消费者监听队列
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = "testQ")
public void sendMsg(String msg){
log.info("接收到消息:{}", msg);
// ......业务逻辑消费消息;
}
}
Topic主题交换机
topic模式跟direct的区别是,topic模式可以用通配符的方式,对路由键进行绑定;达到更灵活路由消息的效果。
交换机的routingKey不能随意写;必须是以点号分隔;如aa.bb; cc.dd.ee等形式
*号代表一个单词;#号代表0个或多个单词
工作模式图解
图中队列1绑定的路由键是 *.*.routeA
图中队列2绑定的路由键是 routeA.#
生产者向该交换机的routeA.xxx.routeA路由键发送消息;那么队列1和2都会收到消息

springboot代码
MQ配置类,声明交换机、队列,绑定
@Configuration
public class TopicRabbitMqConfig
{
/**
* 队列A
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueA() {
return new Queue("topic_queue_A", true, false, false);
}
/**
* 队列B
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueB() {
return new Queue("topic_queue_B", true, false, false);
}
/**
* Topic交换器
*/
@Bean
TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange("topic_exchange", true, false);
}
/**
* 绑定A
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeQueueA() {
//将队列和交换机绑定, 并设置用于匹配键:routingKey
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueA()).to(exchange()).with("*.*.routeKey");
}
/**
* 绑定B
*/
@Bean
Binding bindingExchangeQueueB(Queue topicQueueB, TopicExchange exchange) {
//将队列和交换机绑定, 并设置用于匹配键:routingKey
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueB()).to(exchange()).with("routeKey.#");
}
}
生产者
/**
* 消息生产者
*/
@Service
public class ProduceMsg {
@Autowire
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendMsg(Object msg){
// 消息唯一标识
CorrelationData correlationData= new CorrelationData();
correlationData.setId(msg.getId());
rabbitTemplate.converAndSend("topic_exchange", "routeKey.test.routeKey",
msg, correlationData);
}
}
这个生产者发送的消息;队列topic_queue_A和topic_queue_B都会接收到该生产者发送的消息
header交换机
该交换机不同于其他机制,且实际开发不常用,此处不作讲解
以上是关于RabbitMq一文彻底弄懂RabbitMq的四种交换机原理及springboot实战应用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章