FreeRtos学习笔记(11)查找就绪任务中优先级最高任务原理刨析
Posted 不咸不要钱
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了FreeRtos学习笔记(11)查找就绪任务中优先级最高任务原理刨析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
FreeRtos学习笔记(11)查找就绪任务中优先级最高任务原理刨析
怎么查找就绪任务中优先级最高的?
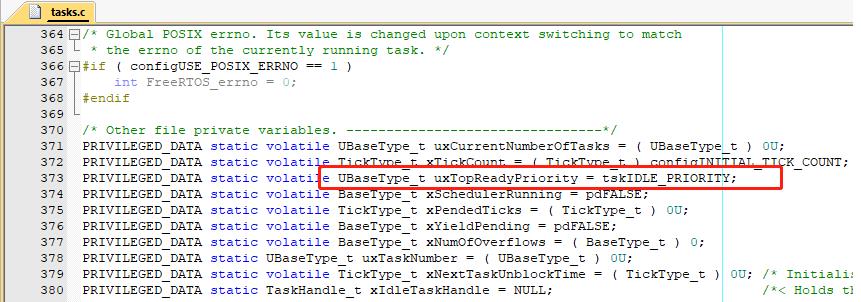
tasks.c中声明了一个全局变量 uxTopReadyPriority,任务从其他状态进入就绪态时,需要修改 uxTopReadyPriority,将就绪任务优先级信息保存在 uxTopReadyPriority 中。在FreeRtos进行剪裁时,如果最大任务优先级 configMAX_PRIORITIES 不超过32,则任务就绪时会将 uxTopReadyPriority 中任务优先级对应的位置一(例如有一个优先级为5的任务从堵塞态变为就绪态,则将uxTopReadyPriority |= 1 << 5)。
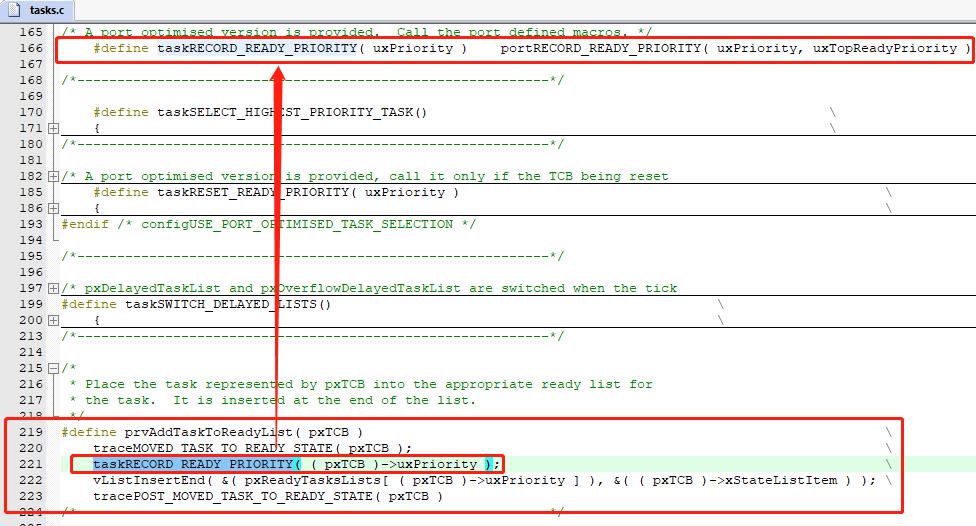
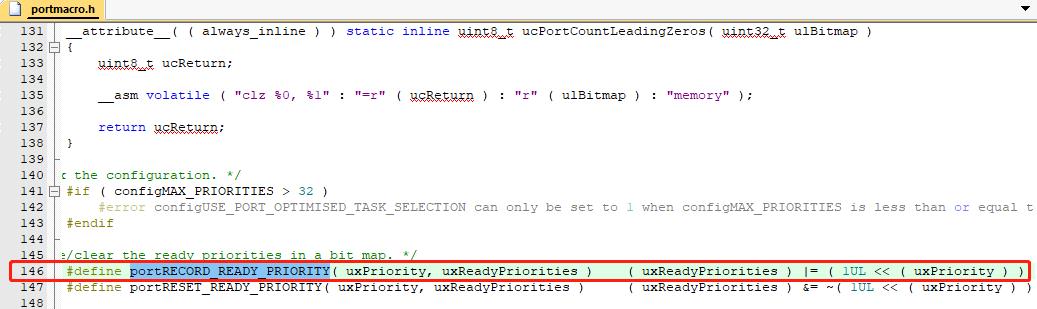
然后在任务进行切换时,根据 uxTopReadyPriority 变量的值,找到就绪任务中优先级最高的
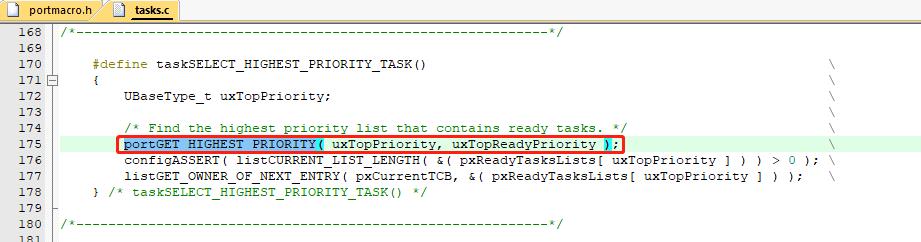
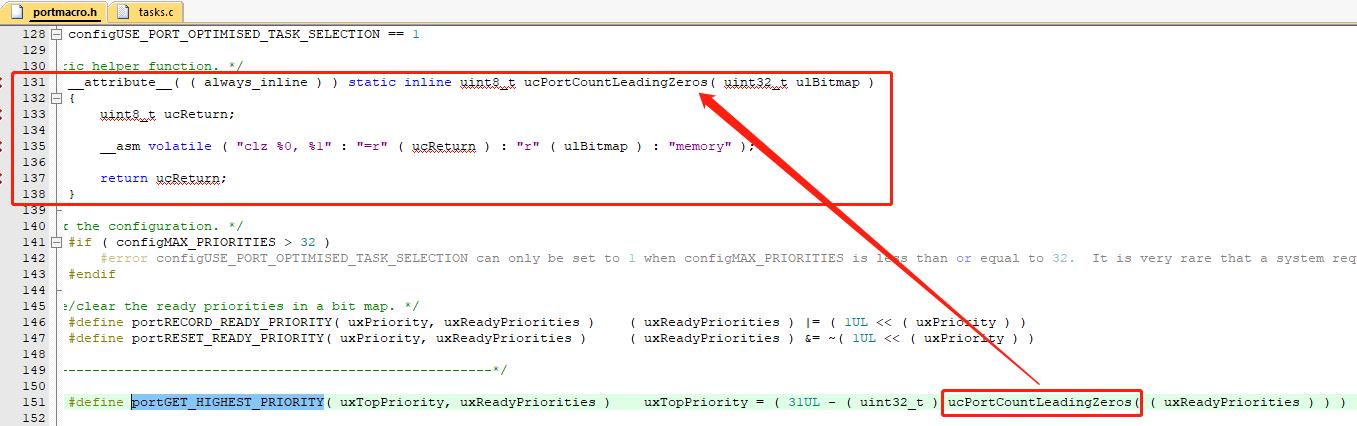
这里用到的cortex-M特有的汇编指令 clz – 计算前导零指令
比如: 一个 32 位的变量 uxTopReadyPriority, 其位 0、
位 24 和位 25 均置 1 , 其余位为 0 , 那么使用前导零指令 __CLZ
(uxTopReadyPriority)可以很快的计算出 uxTopReadyPriority 的前导零的个数为 6。

使用前导零指令 __CLZ 来查找就绪任务中优先级最高的 显然是方便快捷的,但是当遇到 最大任务优先级 configMAX_PRIORITIES 超过32 或者没有前导零指令__CLZ的内核时,需要在Free RTOSConfig.h中添加宏定义
#define configUSE_PORT_OPTIMISED_TASK_SELECTION 0
使用一种更通用的方法去查找就绪任务中优先级最高的。
链表操作
FreeRtos中有任务就绪表,任务堵塞表,任务挂起表等链表,链表操作贯穿FreeRtos整个底层,有必要了解一下FreeRtos的链表操作。这里只是大致介绍,具体代码细节可以参考野火的《FreeRTOS 内核实现与应用开发实战指南》
链表初始化
list.h中有一下三个结构体,链表节点xLIST_ITEM、链表最小节点xMINI_LIST_ITEM、链表头节点xLIST。
/*
* 链表节点
*/
struct xLIST;
struct xLIST_ITEM
{
listFIRST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */
configLIST_VOLATILE TickType_t xItemValue; /*< 节点中的值,一般排序插入时需要使用 */
struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxNext; /*< 指向下一个节点 */
struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxPrevious; /*< 指向上一个结点 */
void * pvOwner; /*< 指向该节点的任务控制块 */
struct xLIST * configLIST_VOLATILE pxContainer; /*< 指向表头 */
listSECOND_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */
};
typedef struct xLIST_ITEM ListItem_t; /* For some reason lint wants this as two separate definitions. */
struct xMINI_LIST_ITEM
{
listFIRST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */
configLIST_VOLATILE TickType_t xItemValue; /*< 节点中的值,一般排序插入时需要使用 */
struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxNext; /*< 指向下一个节点 */
struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxPrevious;/*< 指向上一个结点 */
};
typedef struct xMINI_LIST_ITEM MiniListItem_t;
/*
* 头节点
*/
typedef struct xLIST
{
listFIRST_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */
volatile UBaseType_t uxNumberOfItems; /*< 该链表中节点个数 */
ListItem_t * configLIST_VOLATILE pxIndex; /*< 指向链表第一个节点 */
MiniListItem_t xListEnd; /*< 指向固定的链表结束节点 */
listSECOND_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */
} List_t;

链表初始化其实就做了上图的几个箭头工作,将对应指针指向xListEnd尾节点,具体代码如下
void vListInitialise( List_t * const pxList )
{
/* The list structure contains a list item which is used to mark the
* end of the list. To initialise the list the list end is inserted
* as the only list entry. */
pxList->pxIndex = ( ListItem_t * ) &( pxList->xListEnd ); /*lint !e826 !e740 !e9087 The mini list structure is used as the list end to save RAM. This is checked and valid. */
/* The list end value is the highest possible value in the list to
* ensure it remains at the end of the list. */
pxList->xListEnd.xItemValue = portMAX_DELAY;
/* The list end next and previous pointers point to itself so we know
* when the list is empty. */
pxList->xListEnd.pxNext = ( ListItem_t * ) &( pxList->xListEnd ); /*lint !e826 !e740 !e9087 The mini list structure is used as the list end to save RAM. This is checked and valid. */
pxList->xListEnd.pxPrevious = ( ListItem_t * ) &( pxList->xListEnd ); /*lint !e826 !e740 !e9087 The mini list structure is used as the list end to save RAM. This is checked and valid. */
pxList->uxNumberOfItems = ( UBaseType_t ) 0U;
/* Write known values into the list if
* configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */
listSET_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_1_VALUE( pxList );
listSET_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_2_VALUE( pxList );
}
链表节点尾插入到链表尾部
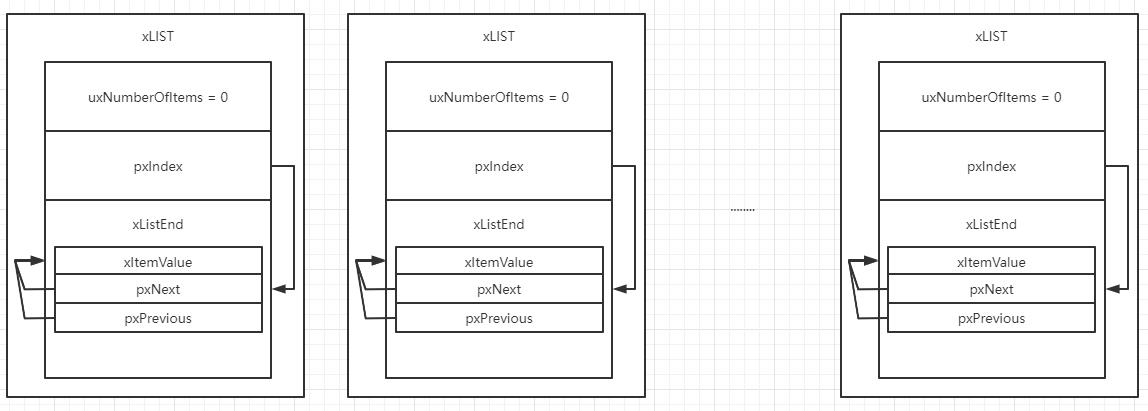
如下图所示,xLIST_ITEM 1、xLIST_ITEM 2、xLIST_ITEM 3、xListEnd这四个节点构成了一个双向循环链表。
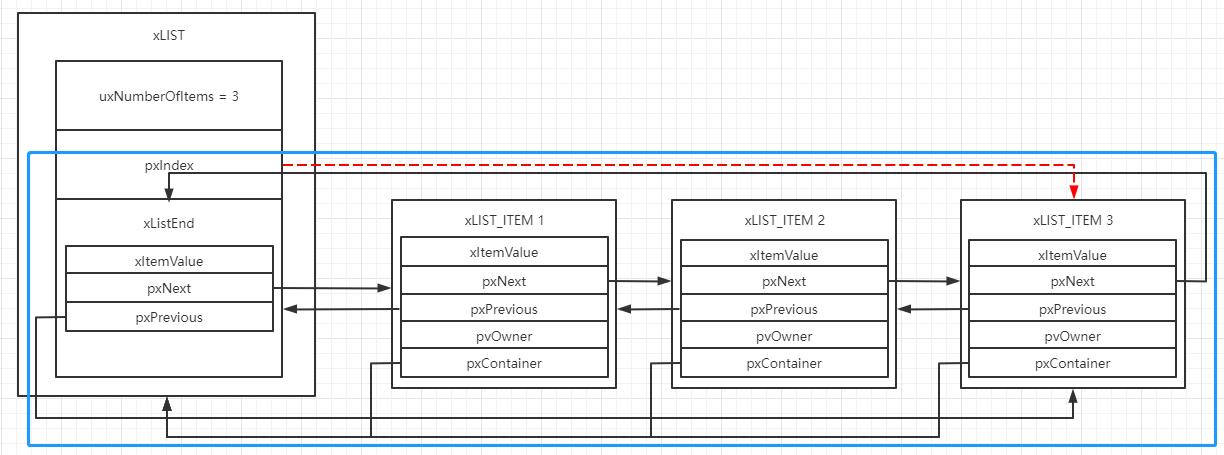
这里需要注意的是,xLIST的pxIndex项指向的节点为第一个节点,因此 vListInsertEnd 函数会将节点插入到 pxIndex指向的节点的前面,并不是插入到 xListEnd 的后面,pxIndex会不断移动,因此第一个节点不是固定的。
void vListInsertEnd( List_t * const pxList,
ListItem_t * const pxNewListItem )
{
ListItem_t * const pxIndex = pxList->pxIndex;
/* Only effective when configASSERT() is also defined, these tests may catch
* the list data structures being overwritten in memory. They will not catch
* data errors caused by incorrect configuration or use of FreeRTOS. */
listTEST_LIST_INTEGRITY( pxList );
listTEST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY( pxNewListItem );
/* Insert a new list item into pxList, but rather than sort the list,
* makes the new list item the last item to be removed by a call to
* listGET_OWNER_OF_NEXT_ENTRY(). */
pxNewListItem->pxNext = pxIndex;
pxNewListItem->pxPrevious = pxIndex->pxPrevious;
/* Only used during decision coverage testing. */
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_DELAY();
pxIndex->pxPrevious->pxNext = pxNewListItem;
pxIndex->pxPrevious = pxNewListItem;
/* Remember which list the item is in. */
pxNewListItem->pxContainer = pxList;
( pxList->uxNumberOfItems )++;
}
按值排序并插入链表节点
上面说了插入到列表末尾但是并不是插入到 xListEnd 后面,那 xListEnd 有什么作用?
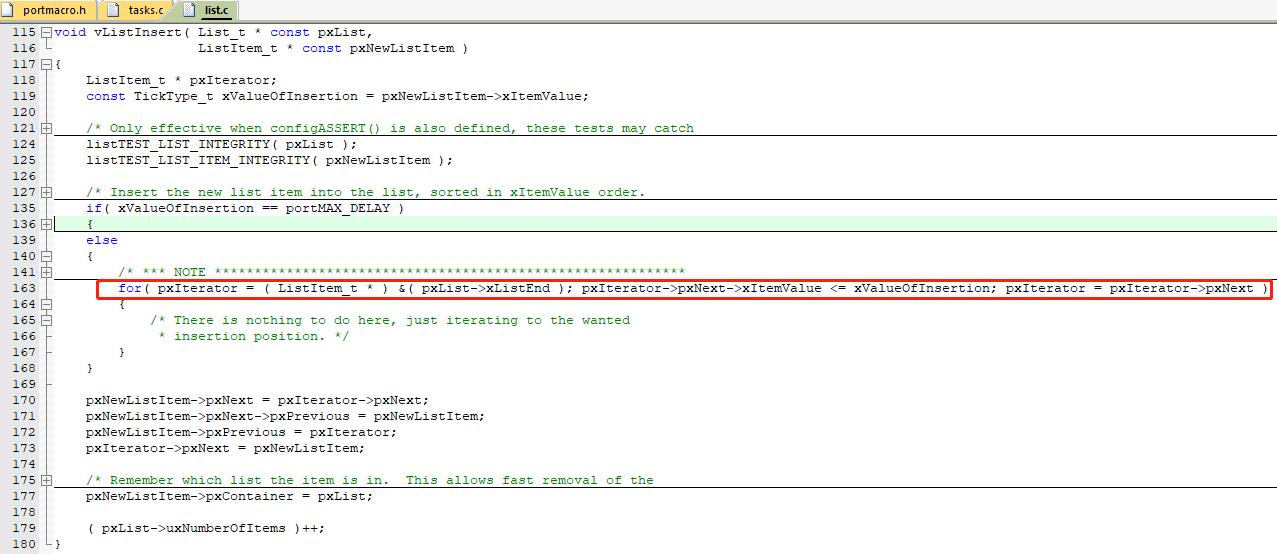
xListEnd 可以看作是一个特殊节点,节点内部的值 xItemValue 最大,方便按值排序并插入链表节点(从xListEnd开始遍历)
删除链表节点
就是将当前节点从对应链表移除。
UBaseType_t uxListRemove( ListItem_t * const pxItemToRemove )
{
/* The list item knows which list it is in. Obtain the list from the list
* item. */
List_t * const pxList = pxItemToRemove->pxContainer;
pxItemToRemove->pxNext->pxPrevious = pxItemToRemove->pxPrevious;
pxItemToRemove->pxPrevious->pxNext = pxItemToRemove->pxNext;
/* Only used during decision coverage testing. */
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_DELAY();
/* Make sure the index is left pointing to a valid item. */
if( pxList->pxIndex == pxItemToRemove )
{
pxList->pxIndex = pxItemToRemove->pxPrevious;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
pxItemToRemove->pxContainer = NULL;
( pxList->uxNumberOfItems )--;
return pxList->uxNumberOfItems;
}
任务就绪表
FreeRtos为了支持时间片调度(不同任务可以拥有相同的任务优先级),为每个任务优先级都建立了一个环形链表。因此优先级在够用的情况下尽量少。
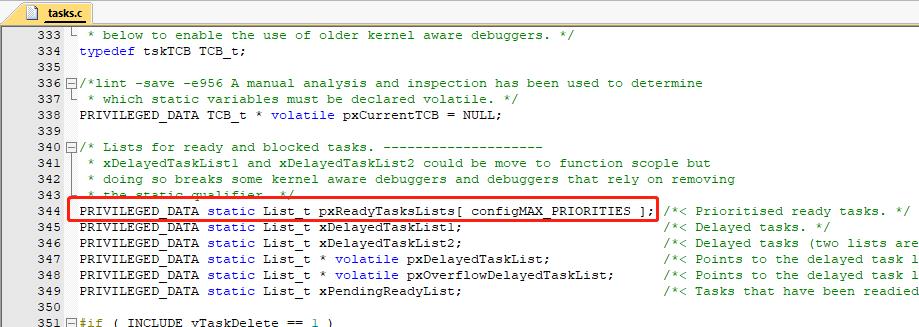
每个优先级都有一个头结点
当任务从其他状态转为就绪态时,会调用 prvAddTaskToReadyList 宏对 uxTopReadyPriority 进行修改
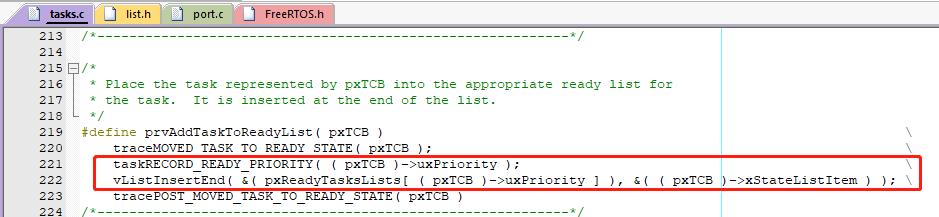
然后将任务控制块中的 xStateListItem 挂在对应优先级的头结点下。

同样,在任务从就绪态转为其他状态时,会将任务控制块中的 xStateListItem 从对应就绪列表移除。
这里需要注意一点:在禁止调度任务期间,若ISR导致了一个任务的就绪,这个任务就会放到xPendingReadyList中而不是直接加入就绪列表。


为什么不直接加入就绪列表 而要用 xPendingReadyList 做个缓冲?
任务A转为就绪态时,会将任务A的优先级和当前任务优先级做比较,如果任务A优先级高,则会立即触发PendSV中断进行任务切换。
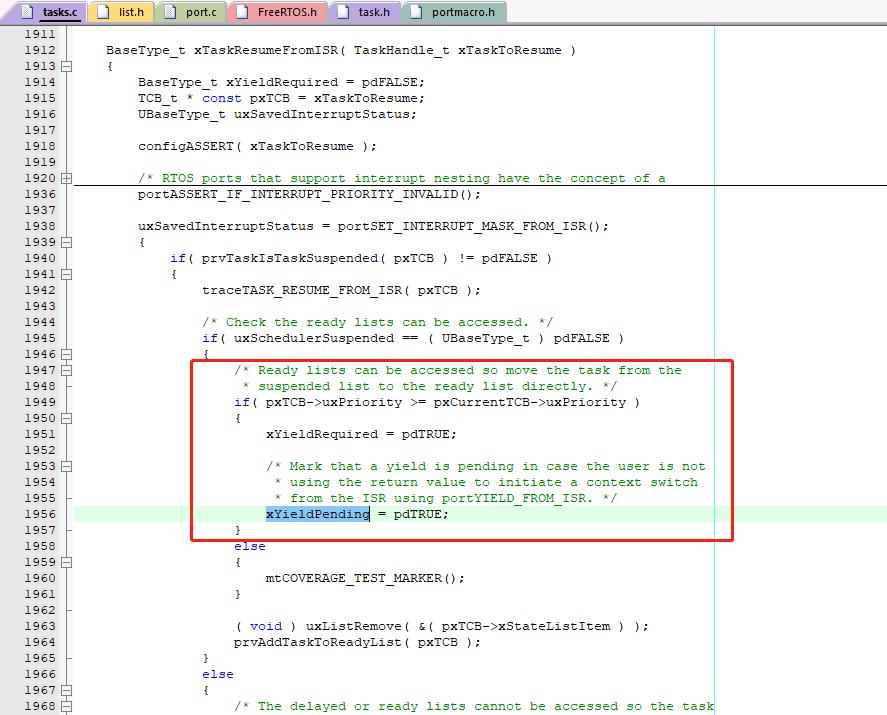
但是如果此时调度器是挂起状态,则不会进行任务切换
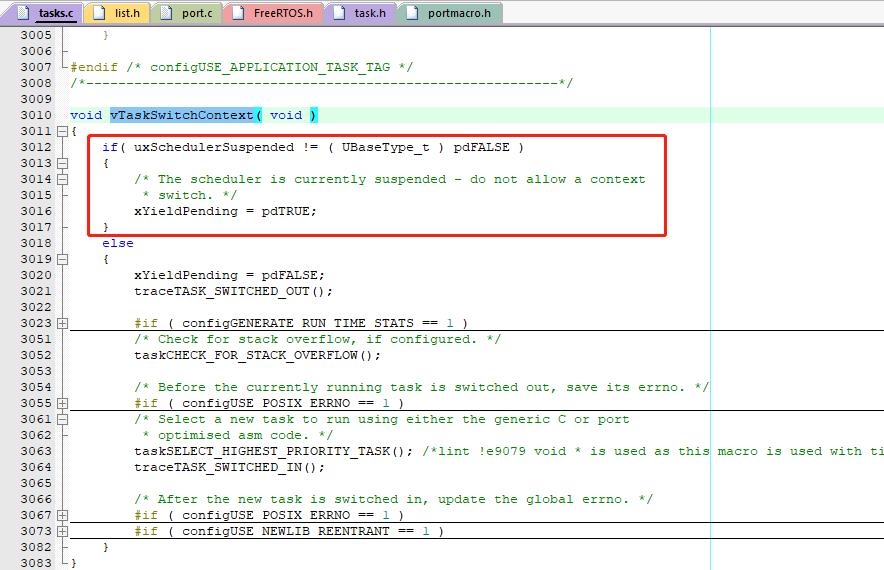
这里使用 xPendingReadyList 做了缓冲,假设任务A优先级比当前任务优先级高,在禁止调度任务期间,ISR导致了任务A就绪,任务A就会放到xPendingReadyList中,当任务调度器解挂,则会将 xPendingReadyList 中的任务A转移到对应就绪表,由于任务A优先级比当前任务优先级高,则进行任务切换。如果不使用 xPendingReadyList 则在调度器解挂后不会判断任务A和当前任务的优先级,任务A也就不会及时运行。
任务堵塞表
FreeRtos中和堵塞表相关的有下面四个变量
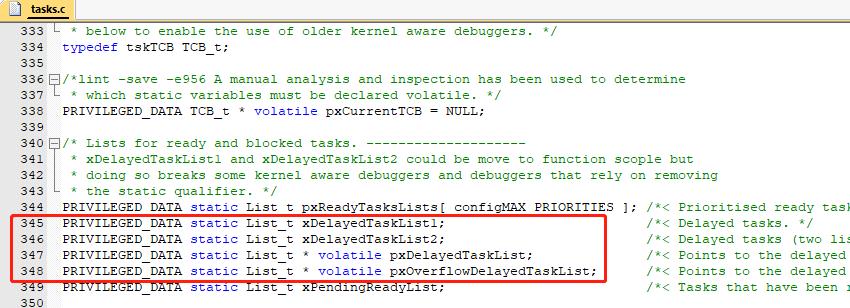
为什么有两个堵塞表?
32位内核的单片机中,FreeRtos的时间节拍类型为 uint32_t,当时间过长时就会有溢出风险。

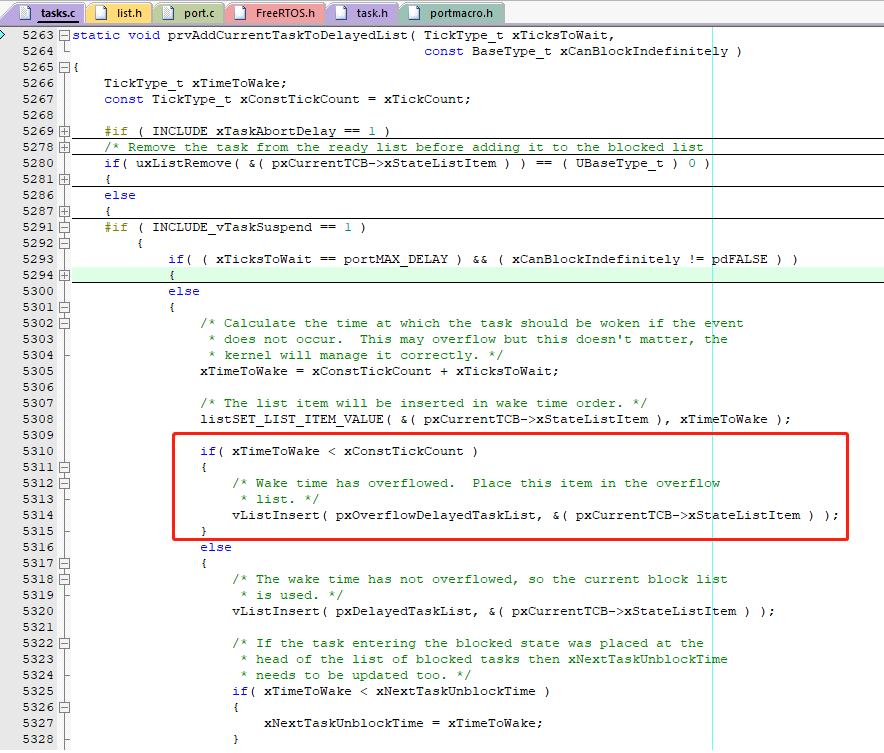
在任务转为堵塞态时,会判断当前系统时间节拍数+任务堵塞节拍数是否溢出?如果溢出就将该任务挂在溢出堵塞表中,如果不溢出就挂在堵塞表中。
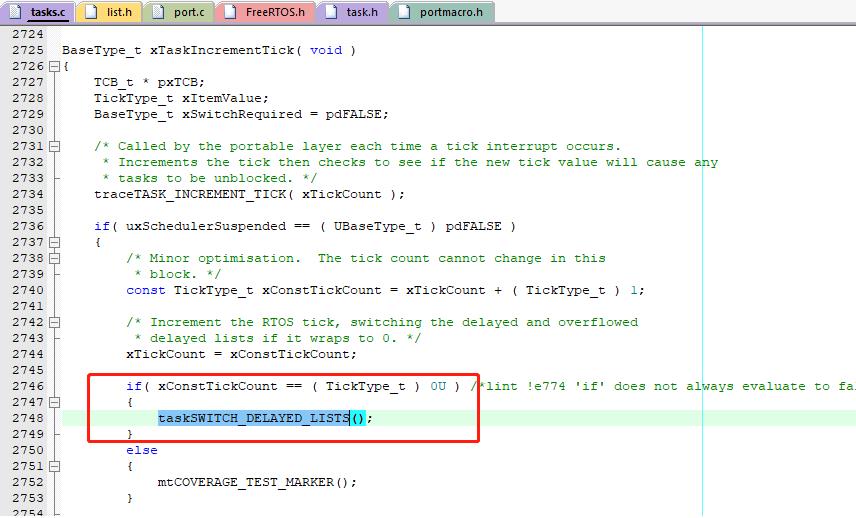
当系统时间节拍要溢出时,会将溢出堵塞表和堵塞表互换。

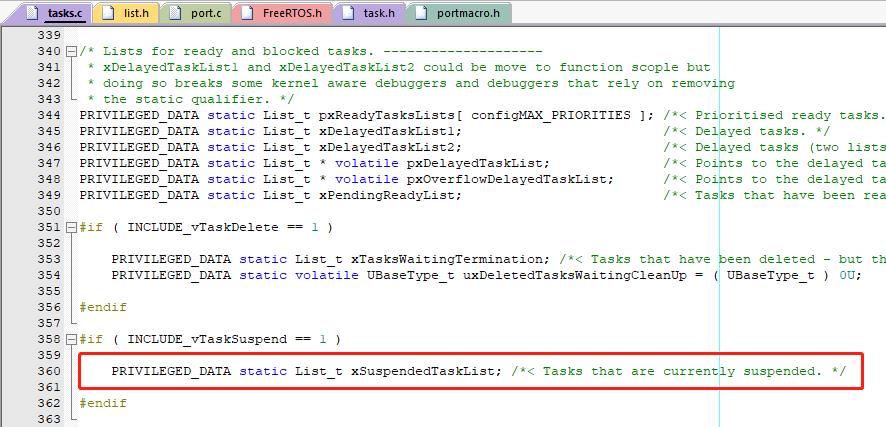
任务挂起表
理解了任务就绪表和堵塞表后,挂起表就比较简单了。当任务挂起时,会将该任务挂到挂起表中。
更新任务流程
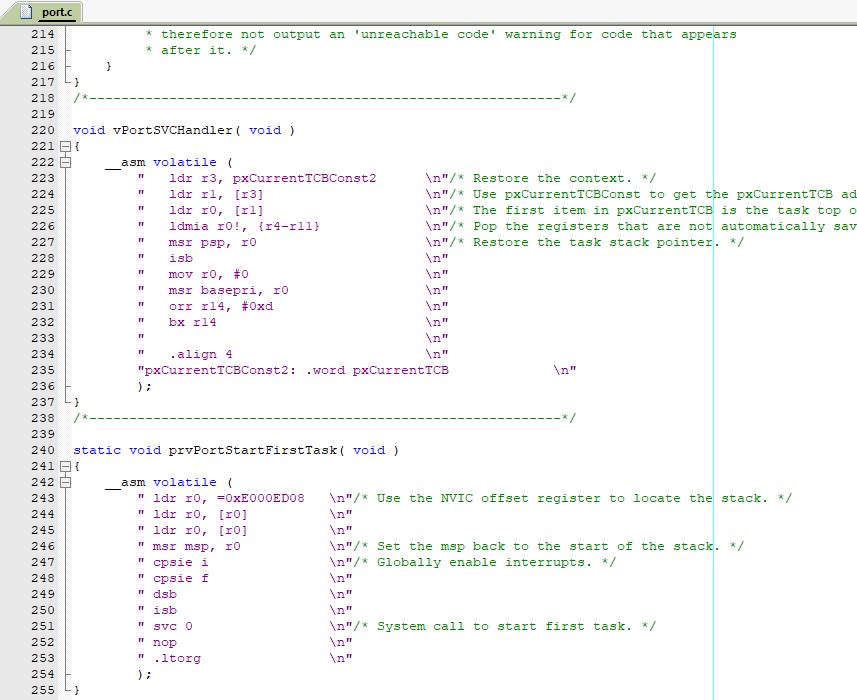
调用 vTaskStartScheduler() 启动调度器后,会触发SCV中断,在SCV中断服务函数中将堆栈指针寄存器从MSP切换成PSP,并且启动第一个任务。
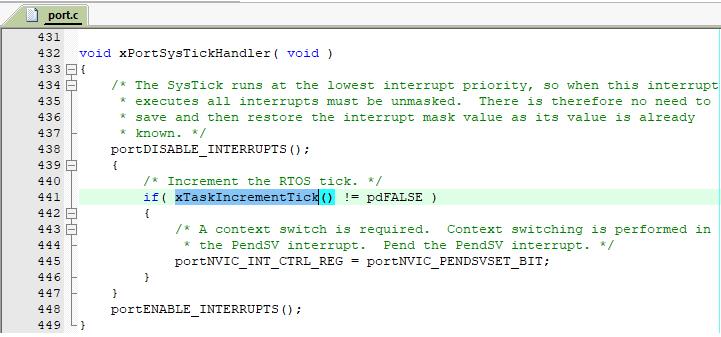
除了任务中的堵塞、挂起、手动切换任务操作,任务之间的切换主要发生在时钟节拍中断服务函数中
BaseType_t xTaskIncrementTick( void )
{
TCB_t * pxTCB;
TickType_t xItemValue;
BaseType_t xSwitchRequired = pdFALSE;
/* 调度器没有挂起 */
if( uxSchedulerSuspended == ( UBaseType_t ) pdFALSE )
{
const TickType_t xConstTickCount = xTickCount + ( TickType_t ) 1;
/* 时钟节拍自增 */
xTickCount = xConstTickCount;
if( xConstTickCount == ( TickType_t ) 0U )
{
/* 时钟节拍溢出 溢出堵塞表和堵塞表互换 */
taskSWITCH_DELAYED_LISTS();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* 当前时钟节拍大于等于堵塞列表中第一个节点堵塞时间. */
if( xConstTickCount >= xNextTaskUnblockTime )
{
for( ; ; )
{
if( listLIST_IS_EMPTY( pxDelayedTaskList ) != pdFALSE )
{
/* 堵塞列表为空 退出 */
xNextTaskUnblockTime = portMAX_DELAY;
break;
}
else
{
/* 拿出堵塞列表中第一个节点任务控制块 */
pxTCB = listGET_OWNER_OF_HEAD_ENTRY( pxDelayedTaskList );
/* 获取该任务解除堵塞的时间节拍 */
xItemValue = listGET_LIST_ITEM_VALUE( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) );
if( xConstTickCount < xItemValue )
{
/* 该任务还未到解除堵塞的时间节拍 退出 */
xNextTaskUnblockTime = xItemValue;
break;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* 将该任务从堵塞列表删除 */
( void ) uxListRemove( &( pxTCB->xStateListItem ) );
/* 如果该任务也在等信号到来,将该任务从事件列表移除. 例如如果一个任务因为等待信号量到来进入堵塞列表,等待信号量到来的最大时间为100个时钟节拍,则该任务控制块会利用 xStateListItem 将任务控制块挂在堵塞列表,利用 xEventListItem 将任务控制块挂在事件列表。 */
if( listLIST_ITEM_CONTAINER( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) ) != NULL )
{
( void ) uxListRemove( &( pxTCB->xEventListItem ) );
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
/* 添加到对应的就绪列表 */
prvAddTaskToReadyList( pxTCB );
#if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 )
{
/* 如果该任务优先级比当前任务优先级高,任务切换标志位置1 */
if( pxTCB->uxPriority >= pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority )
{
xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* configUSE_PREEMPTION */
}
}
}
/* 如果开启 支持时间片调度 功能, 当前任务优先级就绪列表中如果有多个任务,任务切换标志位置1 */
#if ( ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configUSE_TIME_SLICING == 1 ) )
{
if( listCURRENT_LIST_LENGTH( &( pxReadyTasksLists[ pxCurrentTCB->uxPriority ] ) ) > ( UBaseType_t ) 1 )
{
xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* ( ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 ) && ( configUSE_TIME_SLICING == 1 ) ) */
#if ( configUSE_TICK_HOOK == 1 )
{
/* 节拍钩子函数 */
if( xPendedTicks == ( TickType_t ) 0 )
{
vApplicationTickHook();
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* configUSE_TICK_HOOK */
#if ( configUSE_PREEMPTION == 1 )
{
/* 如果中断服务函数中有任务从挂起进入就绪态 xYieldPending 会置1,任务切换标志位 xSwitchRequired 置1 */
if( xYieldPending != pdFALSE )
{
xSwitchRequired = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
}
#endif /* configUSE_PREEMPTION */
}
else
{
++xPendedTicks;
/* The tick hook gets called at regular intervals, even if the
* scheduler is locked. */
#if ( configUSE_TICK_HOOK == 1 )
{
vApplicationTickHook();
}
#endif
}
return xSwitchRequired;
}
在 xTaskIncrementTick() 函数中分析是否需要进行任务切换,如果需要任务切换则触发PendSV中断

在PendSV中断服务函数中进行任务切换

void vTaskSwitchContext( void )
{
if( uxSchedulerSuspended != ( UBaseType_t ) pdFALSE )
{
/* 调度器挂起 */
xYieldPending = pdTRUE;
}
else
{
xYieldPending = pdFALSE;
traceTASK_SWITCHED_OUT();
#if ( configGENERATE_RUN_TIME_STATS == 1 )
{
#ifdef portALT_GET_RUN_TIME_COUNTER_VALUE
portALT_GET_RUN_TIME_COUNTER_VALUE( ulTotalRunTime );
#else
ulTotalRunTime = portGET_RUN_TIME_COUNTER_VALUE();
#endif
/* 各个任务CPU使用率统计 可以参考笔记9 */
if( ulTotalRunTime > ulTaskSwitchedInTime )
{
pxCurrentTCB->ulRunTimeCounter += ( ulTotalRunTime - ulTaskSwitchedInTime );
}
else
{
mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();
}
ulTaskSwitchedInTime = ulTotalRunTime;
}
#endif /* configGENERATE_RUN_TIME_STATS */
/* 栈溢出检查. */
taskCHECK_FOR_STACK_OVERFLOW();
/* Before the currently running task is switched out, save its errno. */
#if ( configUSE_POSIX_ERRNO == 1 )
{
pxCurrentTCB->iTaskErrno = FreeRTOS_errno;
}
#endif
/* 找到优先级最高的就绪列表,并切换任务控制块. */
taskSELECT_HIGHEST_PRIORITY_TASK();
/* After the new task is switched in, update the global errno. */
#if ( configUSE_POSIX_ERRNO == 1 )
{
FreeRTOS_errno = pxCurrentTCB->iTaskErrno;
}
#endif
#if ( configUSE_NEWLIB_REENTRANT == 1 )
{
/* Switch Newlib's _impure_ptr variable to point to the _reent
* structure specific to this task.
* See the third party link http://www.nadler.com/embedded/newlibAndFreeRTOS.html
* for additional information. */
_impure_ptr = &( pxCurrentTCB->xNewLib_reent );
}
#endif /* configUSE_NEWLIB_REENTRANT */
}
}
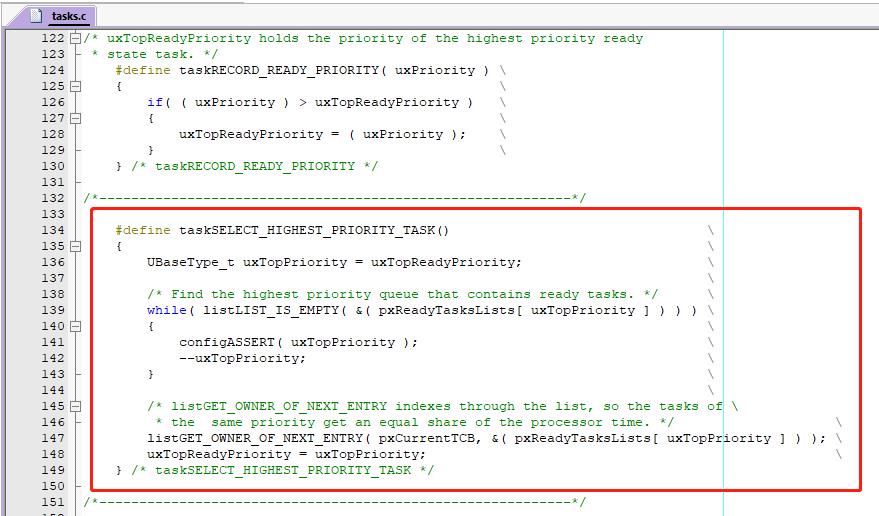
其中任务切换的核心就是 taskSELECT_HIGHEST_PRIORITY_TASK();
以上是关于FreeRtos学习笔记(11)查找就绪任务中优先级最高任务原理刨析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章