二叉搜索树与简单递归98108530701450669501538
Posted qq_40707462
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二叉搜索树与简单递归98108530701450669501538相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
98、验证二叉搜索树
给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
- 节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
- 节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
- 所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。

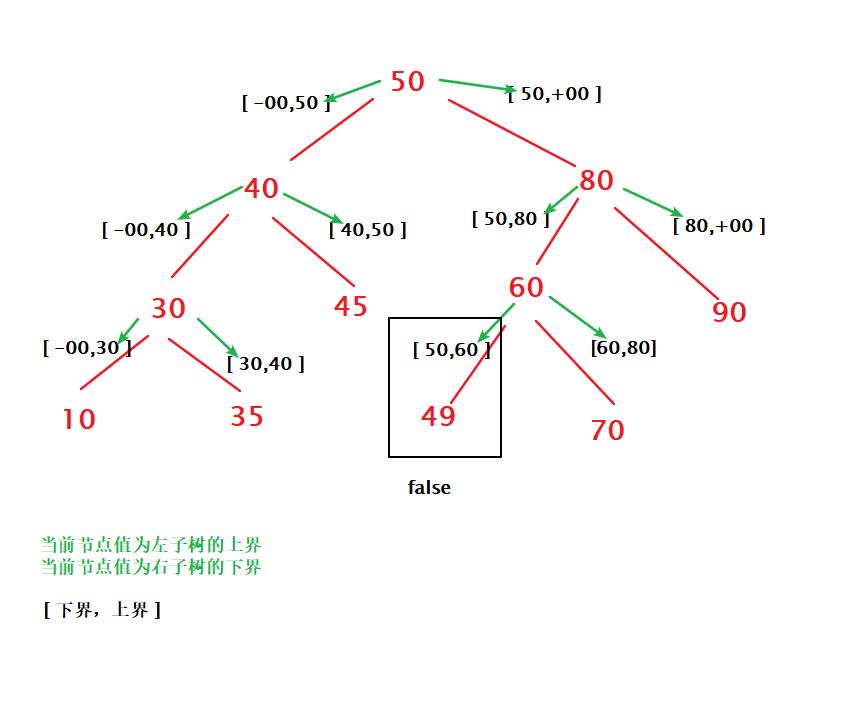
思路一:递归
不能单纯判断当前节点与左右的大小,比如
5
4 6
3 7
这个3比4小,是不可以的。所以:
- 对于左节点,当前节点及之后节点的最大值是他的父节点;
- 对于右节点,当前节点及之后节点的最小值是他的父节点;
import math
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
def dfs(root,maxval,minval):
if not root:
return True
if root.val>=maxval or root.val<=minval:
return False
return dfs(root.left,root.val,minval) and dfs(root.right,maxval,root.val)
return(dfs(root,math.inf,-math.inf))
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root,Long.MIN_VALUE,Long.MAX_VALUE);
}
public boolean dfs(TreeNode root,long min,long max){
if(root==null) return true;
if(root.val>=max || root.val<=min) return false;
return dfs(root.left,min,root.val) && dfs(root.right,root.val,max);
}
}
思路二:中序遍历
若中序遍历的结果是严格递增的,则符合题意,用n记录前一个数的大小
中序遍历
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
stack=[]
n=-math.inf
while stack or root:
if root:
stack.append(root)
root=root.left
else:
temp=stack.pop()
if temp.val<=n:
return False
n=temp.val
root=temp.right
return True
108、将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
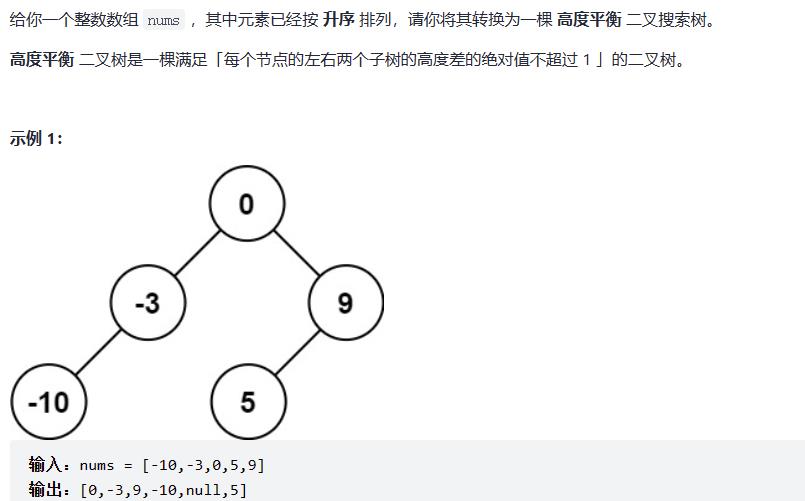
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==0) return null;
return dfs(nums,0,nums.length-1);
}
public TreeNode dfs(int[] nums,int left,int right){
if(left>right) return null;
int mid=(left+right)/2;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left=dfs(nums,left,mid-1);
root.right=dfs(nums,mid+1,right);
return root;
}
}
530、二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
给你一棵所有节点为非负值的二叉搜索树,请你计算树中任意两节点的差的绝对值的最小值。

思路一:中序遍历存入列表,列表递增,相邻值之间差最小
class Solution {
List<Integer>list=new ArrayList<>();
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
int res=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i=1;i<list.size();i++){
res=Math.min(res,list.get(i)-list.get(i-1));
}
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
dfs(root.left);
list.add(root.val);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
思路二:递归中序遍历
在递归中途更新最小值
class Solution {
int res=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
TreeNode pre;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return res;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
dfs(root.left);
if(pre!=null) res=Math.min(res,root.val-pre.val);
pre=root;
dfs(root.right);
}
}
701、二叉搜索树中的插入操作
给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和要插入树中的值,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
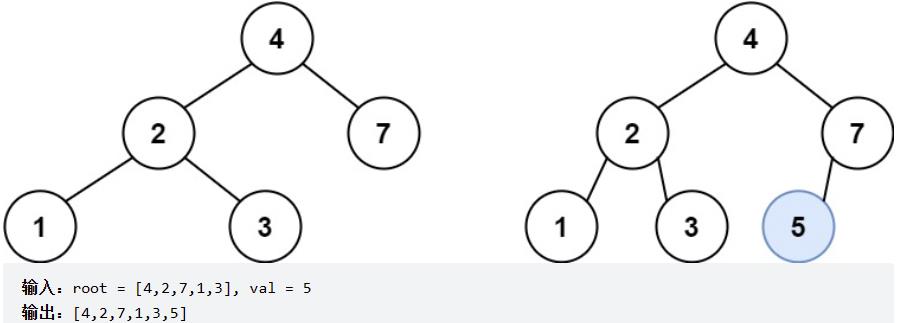
注意!!一定可以插在树的叶子上
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
//一定可以插在树的叶子上
if(root==null){
TreeNode node=new TreeNode(val);
return node;
}
if(root.val>val) root.left=insertIntoBST(root.left,val);
if(root.val<val) root.right=insertIntoBST(root.right,val);
return root;
}
}
450、删除二叉搜索树中的节点

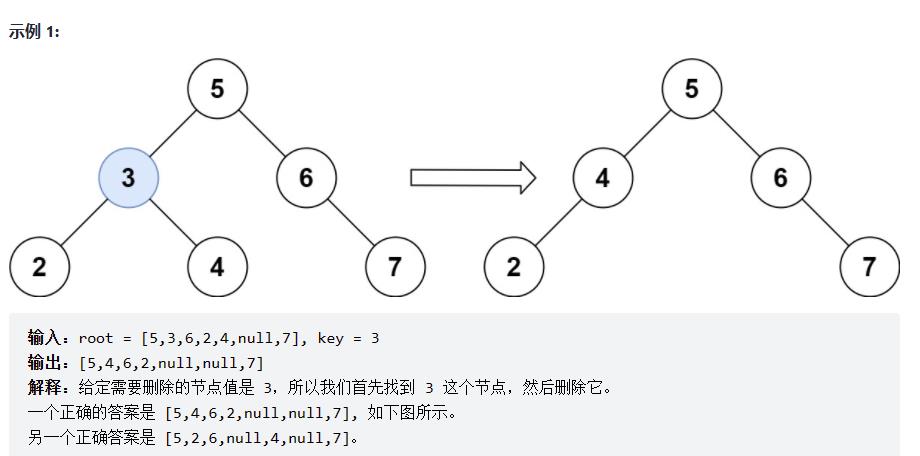
思路:
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root==null) return null;
if(root.val==key){
单层逻辑
}
if(root.val>key) root.left=deleteNode(root.left,key);
if(root.val<key) root.right=deleteNode(root.right,key);
return root;
}
递三步:
①终止条件
②单层逻辑
③处理左右
每一层有以下五种情况:
- 第一种情况:没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了 找到删除的节点
- 第二种情况:左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),直接删除节点, 返回NULL为根节点
- 第三种情况:删除节点的左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位,返回右孩子为根节点
- 第四种情况:删除节点的右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点
- 第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左孩子,放到删除节点的右子树的 最左面节点 的左孩子上,返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点。
eg 5放在8下,9接替7的位置
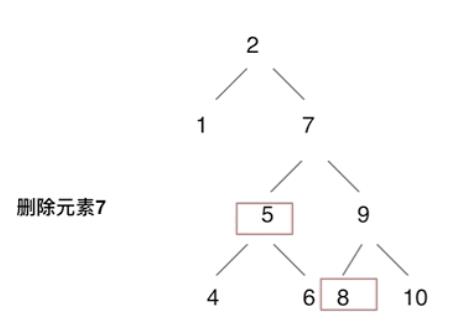
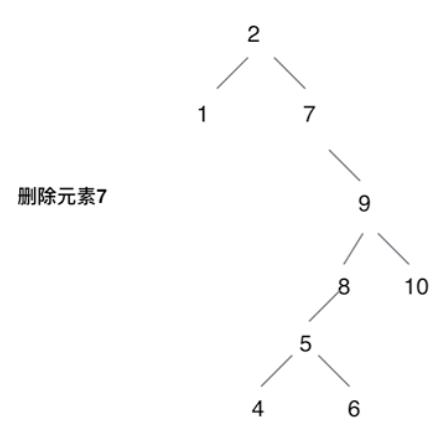
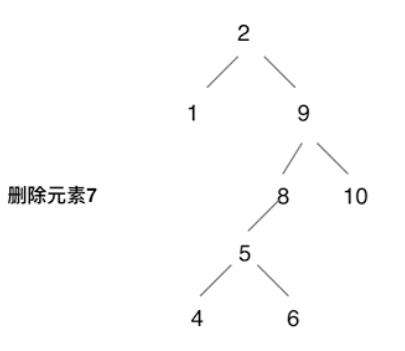
class Solution {
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root==null) return null;//一
if(root.val==key){
//二三四
if(root.left==null) return root.right;
else if(root.right==null) return root.left;
//五,都不为空
else{
TreeNode node=root.right;//找到右子树最左边的节点
while(node.left!=null) node=node.left;
node.left=root.left;//root的左节点搬下来
root=root.right;//替换root
return root;
}
}
if(root.val>key) root.left=deleteNode(root.left,key);
if(root.val<key) root.right=deleteNode(root.right,key);
return root;
}
}
669、修剪二叉搜索树

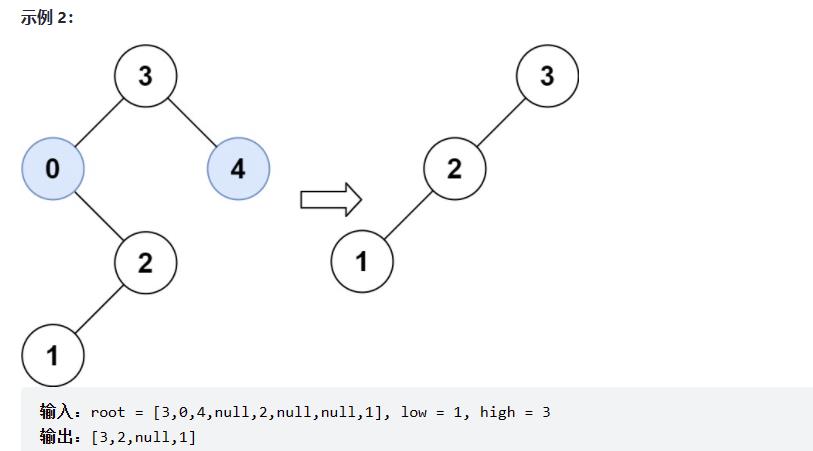
class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if(root==null) return null;
if(root.val<low) {
TreeNode rnode=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return rnode;
}
if(root.val>high){
TreeNode lnode=trimBST(root.left,low,high);
return lnode;
}
root.left=trimBST(root.left,low,high);
root.right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return root;
}
}
501、二叉搜索树中的众数
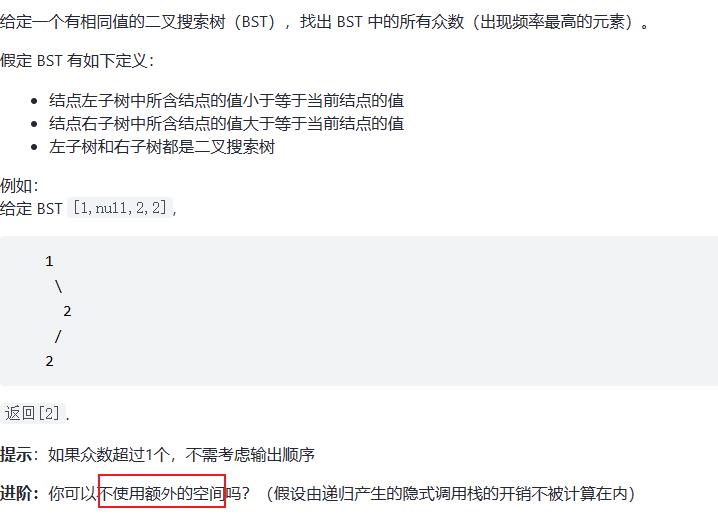
思路:
正常来说,中序遍历得到非递减数组,然后求数组众数即可,但消耗额外空间;
已知遍历顺序肯定是非递减,如果有相同的数肯定连在一起,可以在遍历途中维护一个表示当前数字出现几次的count,当前出现最对的次数maxCount,和记录前一个节点pre
cur==pre; count++;- 否则,清空count
- 如果
count>maxCount,清空res,重新开始记录
class Solution {
List<Integer>res=new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode pre=null;
int count=0;
int maxCount=0;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
find(root);
return res.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
}
public void find(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
find(root.left);
int cur=root.val;
//计数
if(pre==null || root.val!=pre.val) count=1;//重新开始计数
else count++;
//检查是否max
if(count==maxCount){
res.add(root.val);
}else if(count>maxCount){
res.clear();
res.add(root.val);
maxCount=count;
}
pre=root;
find(root.right);
}
}
538、把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
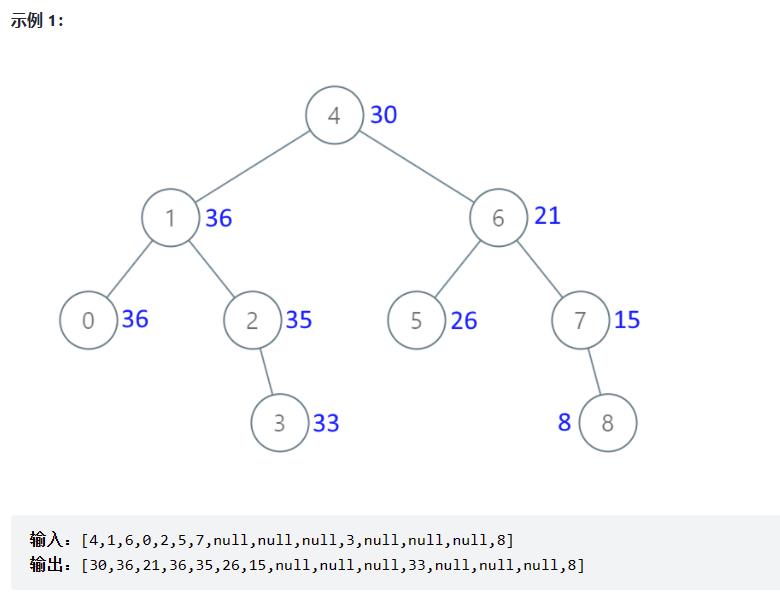
按【右中左】的顺序累加,就是一个有序数组[2, 5, 13],求从后到前的累加数组,也就是[20, 18, 13]
class Solution {
int pre=0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return null;
convertBST(root.right);
root.val+=pre;
pre=root.val;
convertBST(root.left);
return root;
}
}
以上是关于二叉搜索树与简单递归98108530701450669501538的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章