L - Two Ants Gym - 102823L
Posted Jozky86
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了L - Two Ants Gym - 102823L相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
题意:
有两个线段A,B,两个线段不会超过一个公共点,
你站在线段B上,整个平面你看不到的区域的面积(如图中S所在区域)
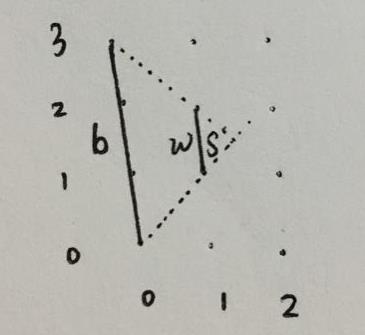
题解:
计算几何,恶心题。调了一个小时还是不对,吐了
基本思路:很明显S所在区域是一个三角形,其中两点是线段w的两端,那我们求出第三个点即可
基本思路是正确的,但是本题要处理的细节很多:
如图,此时面积为inf

如图,此时面积为inf

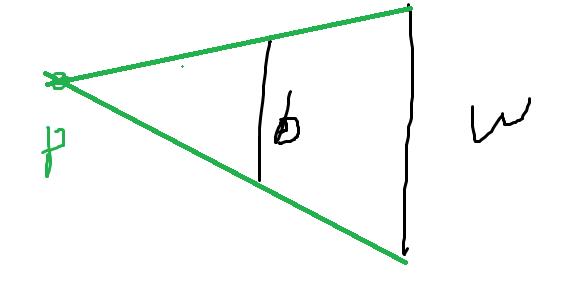
如图,此时面积为0.00
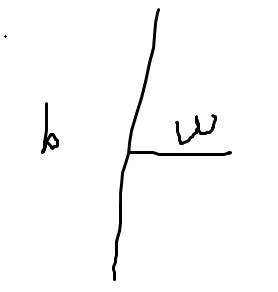
如图,此时情况为inf
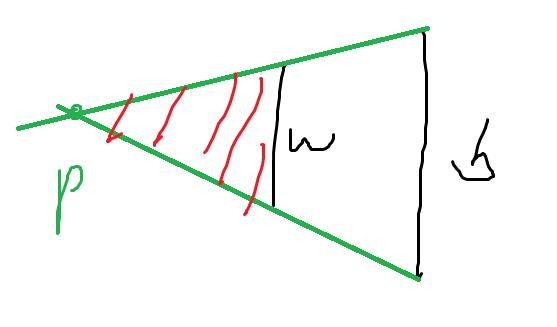
此时面积为红色区域
情况非常多,总结下:
线段W退化成点,答案为0
线段B退化成点,答案为inf
两线段规范相交,答案为0
两线段非规范相交:
若有共线答案为0。
否则即交点在端点,答案为inf
两线段不相交:
B线段的两点在W线段的两侧,答案为0.
否则:
两个线段端点彼此之间的连线,若有交点,判断其相对位置,如果相对于W线段不与黑色线段同侧,则计算该点与W线段构成的面积即是答案。
若没有交点(平行),或者交点都在B线段同侧,则答案为inf.
代码:
AC代码,代码网上的,真的改不动了
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// `计算几何模板`
const double eps = 1e-14;
const double inf = 1e20;
const double pi = acos(-1.0);
const int maxp = 1010;
//`Compares a double to zero`
int sgn(double x)
{
if (fabs(x) < eps) { return 0; }
else { return x < 0 ? -1 : 1; }
}
//square of a double
inline double sqr(double x) {return x * x;}
struct Point {
double x, y;
Point() {}
Point(double _x, double _y)
{
x = _x;
y = _y;
}
void input()
{
scanf("%lf%lf", &x, &y);
}
void output()
{
printf("%.2f %.2f\\n", x, y);
}
bool operator == (Point b)const
{
return sgn(x - b.x) == 0 && sgn(y - b.y) == 0;
}
bool operator < (Point b)const
{
return sgn(x - b.x) == 0 ? sgn(y - b.y) < 0 : x < b.x;
}
Point operator -(const Point &b)const
{
return Point(x - b.x, y - b.y);
}
//叉积
double operator ^(const Point &b)const
{
return x * b.y - y * b.x;
}
//点积
double operator *(const Point &b)const
{
return x * b.x + y * b.y;
}
//返回长度
double len()
{
return hypot(x, y); //库函数
}
//返回长度的平方
double len2()
{
return x * x + y * y;
}
//返回两点的距离
double distance(Point p)
{
return hypot(x - p.x, y - p.y);
}
Point operator +(const Point &b)const
{
return Point(x + b.x, y + b.y);
}
Point operator *(const double &k)const
{
return Point(x * k, y * k);
}
Point operator /(const double &k)const
{
return Point(x / k, y / k);
}
//`计算pa 和 pb 的夹角`
//`就是求这个点看a,b 所成的夹角`
//`测试 LightOJ1203`
double rad(Point a, Point b)
{
Point p = *this;
return fabs(atan2( fabs((a - p) ^ (b - p)), (a - p) * (b - p) ));
}
//`化为长度为r的向量`
Point trunc(double r)
{
double l = len();
if (!sgn(l)) { return *this; }
r /= l;
return Point(x * r, y * r);
}
//`逆时针旋转90度`
Point rotleft()
{
return Point(-y, x);
}
//`顺时针旋转90度`
Point rotright()
{
return Point(y, -x);
}
//`绕着p点逆时针旋转angle`
Point rotate(Point p, double angle)
{
Point v = (*this) - p;
double c = cos(angle), s = sin(angle);
return Point(p.x + v.x * c - v.y * s, p.y + v.x * s + v.y * c);
}
};
struct Line {
Point s, e;
Line() {}
Line(Point _s, Point _e)
{
s = _s;
e = _e;
}
bool operator ==(Line v)
{
return (s == v.s) && (e == v.e);
}
//`根据一个点和倾斜角angle确定直线,0<=angle<pi`
Line(Point p, double angle)
{
s = p;
if (sgn(angle - pi / 2) == 0) {
e = (s + Point(0, 1));
} else {
e = (s + Point(1, tan(angle)));
}
}
//ax+by+c=0
Line(double a, double b, double c)
{
if (sgn(a) == 0) {
s = Point(0, -c / b);
e = Point(1, -c / b);
} else if (sgn(b) == 0) {
s = Point(-c / a, 0);
e = Point(-c / a, 1);
} else {
s = Point(0, -c / b);
e = Point(1, (-c - a) / b);
}
}
void input()
{
s.input();
e.input();
}
void adjust()
{
if (e < s) { swap(s, e); }
}
//求线段长度
double length()
{
return s.distance(e);
}
//`返回直线倾斜角 0<=angle<pi`
double angle()
{
double k = atan2(e.y - s.y, e.x - s.x);
if (sgn(k) < 0) { k += pi; }
if (sgn(k - pi) == 0) { k -= pi; }
return k;
}
//`点和直线关系`
//`1 在左侧`
//`2 在右侧`
//`3 在直线上`
int relation(Point p)
{
int c = sgn((p - s) ^ (e - s));
if (c < 0) { return 1; }
else if (c > 0) { return 2; }
else { return 3; }
}
// 点在线段上的判断
bool pointonseg(Point p)
{
return sgn((p - s) ^ (e - s)) == 0 && sgn((p - s) * (p - e)) <= 0;
}
//`两向量平行(对应直线平行或重合)`
bool parallel(Line v)
{
return sgn((e - s) ^ (v.e-v.s)) == 0;
}
//`两线段相交判断`
//`2 规范相交`
//`1 非规范相交`
//`0 不相交`
int segcrossseg(Line v)
{
int d1 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.s - s));
int d2 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.e-s));
int d3 = sgn((v.e-v.s) ^ (s - v.s));
int d4 = sgn((v.e-v.s) ^ (e - v.s));
if ( (d1 ^ d2) == -2 && (d3 ^ d4) == -2 ) { return 2; }
return (d1 == 0 && sgn((v.s - s) * (v.s - e)) <= 0) ||
(d2 == 0 && sgn((v.e-s) * (v.e-e)) <= 0) ||
(d3 == 0 && sgn((s - v.s) * (s - v.e)) <= 0) ||
(d4 == 0 && sgn((e - v.s) * (e - v.e)) <= 0);
}
//`直线和线段相交判断`
//`-*this line -v seg`
//`2 规范相交`
//`1 非规范相交`
//`0 不相交`
int linecrossseg(Line v)
{
int d1 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.s - s));
int d2 = sgn((e - s) ^ (v.e-s));
if ((d1 ^ d2) == -2) { return 2; }
return (d1 == 0 || d2 == 0);
}
//`两直线关系`
//`0 平行`
//`1 重合`
//`2 相交`
int linecrossline(Line v)
{
if ((*this).parallel(v)) {
return v.relation(s) == 3;
}
return 2;
}
//`求两直线的交点`
//`要保证两直线不平行或重合`
Point crosspoint(Line v)
{
double a1 = (v.e-v.s) ^ (s - v.s);
double a2 = (v.e-v.s) ^ (e - v.s);
return Point((s.x * a2 - e.x * a1) / (a2 - a1), (s.y * a2 - e.y * a1) / (a2 - a1));
}
//点到直线的距离
double dispointtoline(Point p)
{
return fabs((p - s) ^ (e - s)) / length();
}
//点到线段的距离
double dispointtoseg(Point p)
{
if (sgn((p - s) * (e - s)) < 0 || sgn((p - e) * (s - e)) < 0) {
return min(p.distance(s), p.distance(e));
}
return dispointtoline(p);
}
//`返回线段到线段的距离`
//`前提是两线段不相交,相交距离就是0了`
double dissegtoseg(Line v)
{
return min(min(dispointtoseg(v.s), dispointtoseg(v.e)), min(v.dispointtoseg(s), v.dispointtoseg(e)));
}
//`返回点p在直线上的投影`
Point lineprog(Point p)
{
Point v = e - s;
return s + ( (v * (v * (p - s))) / (v.len2()) );
}
//`返回点p关于直线的对称点`
Point symmetrypoint(Point p)
{
Point q = lineprog(p);
return Point(2 * q.x - p.x, 2 * q.y - p.y);
}
};
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
Line w, b;
int cas = 0;
Line l1, l2, l3, l4;
Point cp;
int sg;
double ans;
while (T--) {
++cas;
w.input();
b.input();
if (w.s == w.e) {
printf("Case %d: 0.000\\n", cas);
} else if (b.s == b.e) {
printf("Case %d: inf\\n"