开始使用Spring Cloud实战微服务
Posted shi_zi_183
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了开始使用Spring Cloud实战微服务相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
开始使用Spring Cloud实战微服务
Spring Cloud 实战前提
Spring Cloud不一定适合所有人。学习之前需要了解需要具备什么样的技术能力,以及实战中会使用到哪些工具。
技术储备
Spring Cloud并不是面向零基础开发人员的,它有一定的学习曲线。
- 语言基础:Spring Cloud是一个基于Java语言的工具套件,所以学习他需要一定的Java基础。当然,Spring Cloud同样也支持使用Scala、Groovy等语言进行开发。
- Spring Boot:Spring Cloud是基于Spring Boot构建的,因此它延续了Spring Boot的契约模式以及开发方式。如果大家对Spring Boot不熟悉,建议花一点时间入门。
- 项目管理与构建工具:目前业界比较主流的项目管理与构建工具有Maven和Gradle等,本书采用的是目前相对主流的Maven。大家也可使用Gradle管理与构建项目。并且,Maven与Gradle项目可以互换转换,例如,使用以下命令即可将Maven项目转换为Gradle项目。
gradle init --type pom
工具及软件版本
JDK:Spring Cloud官方建议使用JDK 1.8。
Spring Boot:本书使用Spring Boot1.5.9.RELEASE
Spring Boot:本书使用Spring Cloud Edgware RELEASE
IDE:IntelliJ IDEA
Maven:Maven3.39构建项目。和Spring Boot、Spring Cloud一样,Maven3.3.x默认也是运行在JDK1.8以上的。
服务提供者与服务消费者
使用微服务构建的是分布式系统,微服务之间通过网络进行通信。我们使用服务提供者与服务消费者来描述微服务之间的调用关系。
| 名词 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 服务提供者 | 服务的被调用方(即:为其他服务提供服务的服务) |
| 服务消费者 | 服务的调用方(即:依赖其他服务的服务) |
我们继续以电影售票系统为例。哟弄个胡向电影微服务发起了一个购票的请求。在进行购票的业务操作前,电影微服务需要调用用户微服务的接口,查询当前用户的余额是多少,是不是符合购票标准等。在这种场景下,用户微服务就是一个服务提供者,电影微服务则是一个服务消费者。
编写服务提供者
编写一个服务提供者(用户微服务),该服务可通过主键查询用户信息。为便于测试,使用Spring Data JPA作为持久层框架,使用H2作为数据库。
手动编写项目
1) 创建一个Maven项目,它的ArtifacId是microservice-simple-provider-user,pom.xml的内容如下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>microservice-simple-provider-use</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<!--引入spring boot的依赖-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--引入spring cloud的依赖-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>Edgware.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
其中,spring-boot-starter-web提供了Spring MVC的支持;spring-boot-starter-data-jpa提供了Spring Data JPA的支持。
准备好建表语句,在项目的classpath下创建sql文件夹并在其下建立schema.sql、data.sql
schema.sql
drop table user if exists;
create table user(id bigint generated by default as identity ,username varchar(40),name varchar(20),age int(3),balance decimal(10,2),primary key (id));
data.sql
insert into user(id,username,name,age,balance) values (1,'account1','张三',20,100.00);
insert into user(id,username,name,age,balance) values (2,'account2','李四',28,180.00);
insert into user(id,username,name,age,balance) values (3,'account3','王五',32,280.00);
在项目下创建entity包创建用户实体类
User.java
package com.example.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
@Entity
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
@Column
private String username;
@Column
private String name;
@Column
private Integer age;
@Column
private BigDecimal balance;
//省略setter、getter、tostring
}
创建dao包并在其下创建UserRepository.java
package com.example.dao;
import com.example.entity.User;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User,Long> {
}
创建controller包并在其下创建UserController
package controller;
import dao.UserRepository;
import entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public User findById(@PathVariable Long id) {
User findOne = this.userRepository.findOne(id);
return findOne;
}
}
Controller中用到的@GetMapping是Spring4.3提供的新注解。它是一个组合注解,等价于@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET),用于简化开发。同理还有@PostMapping、@PutMapping、@DeleteMapping、@PatchMapping等。
编写启动类,在类上使用@SpringBootApplication声明这是一个Spring Boot项目。
ProvideUserApplication.java
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class ProviderUserApplication {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(ProviderUserApplication.class,args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication是一个组合注解,它整合了@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan注解,并开启了Spring Boot程序的组件扫描和自动配置功能。在开发Spring Boot程序的过程中,常常会组合使用@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan等注解,所以Spring Boot提供了@SpringBootApplication,来简化开发。
编写配置文件,命名为application.yml
server:
port: 8000
spring:
jpa:
generate-ddl: false
show-sql: true
hibernate:
ddl-auto: none
datasource: #指定数据源
platform: h2 #指定数据源类型
schema: classpath:sql/schema.sql #指定h2数据库的建表脚本
data: classpath:sql/data.sql #指定h2数据库的数据脚本
logging: #配置日志级别,让hibernate打印执行的SQL
level:
root: INFO
org.hibernate: INFO
org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicBinder: TRACE
org.hibernate.type.descriptor.sql.BasicExtractor: TRACE
在传统的Web开发中,常使用properties格式文件作为配置文件。Spring Boot以及Spring Cloud支持使用properties或者yml格式的文件作为配置文件。
yml文件格式是YAML(Yet Another Markup Language)编写的文件格式,YAML和properties格式的文件可互相转换。
但是,YAML比properties结构清晰;可读性、可维护性也更强,并且语法简捷,也更支持中文汉字(UTF-8)。yml有严格的缩进,并且key与value之间使用’:'分隔,冒号后的空格不能少,需要注意。
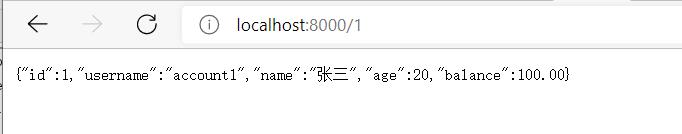
测试
访问http://localhost:8000/1,获得结果。

使用Spring Initializr快速创建Spring Boot项目
之前是手动创建项目的。事实上,也可使用Spring Initializr快速创建项目。虽然Spring Initializr不能生成应用程序的业务代码,但它可生成基本的项目结构。这样可以把更多精力放在具体的业务代码上,无须过分关注项目搭建的过程。
编写服务消费者
前文编写了一个服务提供者(用户微服务)。本节来编写一个服务消费者(电影微服务)。该服务非常简单,它使用RestTemplate调用微服务的API,从而查询指定ID的用户信息。
1)创建一个Spring Initializr项目,ArtifactId是microsevice-simple-consumer-movie。
2)选择web依赖
3)创建用户实体类,该类是一个POJO
User.java
package com.example.entity;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String username;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private BigDecimal banlance;
//省略setter、getter、tostring
}
4)修改启动类
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MicroseviceSimpleConsumerMovieApplication {
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MicroseviceSimpleConsumerMovieApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Bean是一个方法注解,作用是实例化一个Bean并使用该方法的名称命名。在本例中,添加@Bean注解的restTemplate()方法,等价于RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
5)创建controller包并在其下创建一个MovieController控制类
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.entity.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
public class MovieController {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public User findById(@PathVariable Long id){
return this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8000/"+id,User.class);
}
}
6)配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 8010
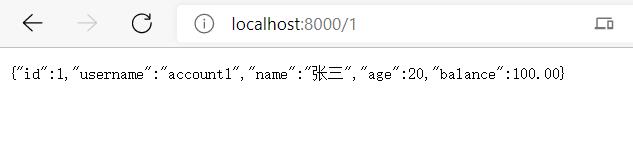
测试
访问http://localhost:8010/user/1

为项目整合Spring Boot Actuator
Spring Boot Actuator提供了很多监控断点。可使用http://{ip}:{post}/{endpoint}的形式访问这些端点,从而了解应用程序的运行状况。
| 端点 | 描述 | HTTP方法 | 是否敏感 |
|---|---|---|---|
| autoconfig | 显示自动配置的信息 | GET | 是 |
| beans | 显示应用程序上下文所有的Spring bean | GET | |
| configprops | 显示所有@ConfigurationProperties的配置属性列表 | GET | 是 |
| dump | 显示线程活动的快照 | GET | 是 |
| env | 显示应用的环境变量 | GET | 是 |
| health | 显示应用程序的健康指标,这些值由HealthIndicator的实现类提供。当应用开启安全保护时,对于未经用户认证的请求,只会显示简单的状态;如已认证,则会显示健康详情 | ||
| info | 显示应用的信息,可使用info.*属性自定义info端点公开的数据 | GET | 否 |
| mappings | 显示所有@RequestMapping的路径列表 | GET | 是 |
| metrics | 显示应用的度量标准信息 | GET | 是 |
| shutdown | 关闭应用(默认情况下不启用,如需启用,需设置endpoints.shutdown.enabled=true) | POST | 是 |
| trace | 显示跟踪信息(默认情况下为最近100个HTTP请求) | GET | 是 |
为项目添加以下依赖
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
这样就整合好Actuator了。
测试
/health端点
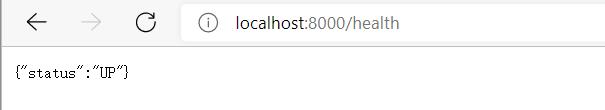
此时,可展示当前应用的健康状况。其中,UP表示运行正常,除UP外,还有DOWN、OUT_OF_SERVICE/UNKNOWN等状态。此时,只显示了一个概要情况,如需展示详情,可为应用添加spring-boot-starter-security或设置management.security.enable=false.
设置management.security.enable=false再次访问。
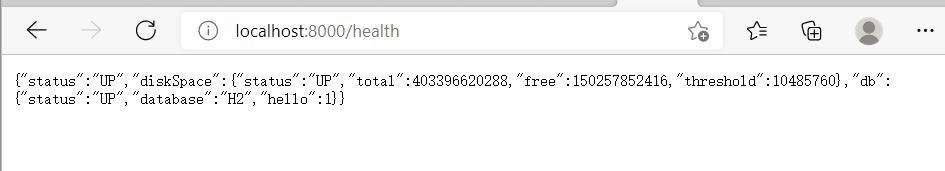
由结果可知,/health的本质,通过检查Spring Boot应用资源,来判断应用是否正常。
测试二
/info端口
访问http://localhost:8000/info,可以看到以下内容。
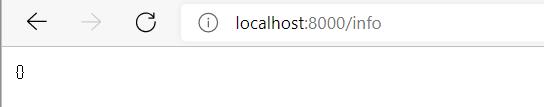
由结果可知,info端点并没有返回任何数据给我们。可使用info.*属性来自定义info端点公开的数据。
info:
app:
name: @project.artifactId@
encoding: @project.build.sourceEncoding@
java:
source: @java.version@
target: @java.version@
重启,重新访问
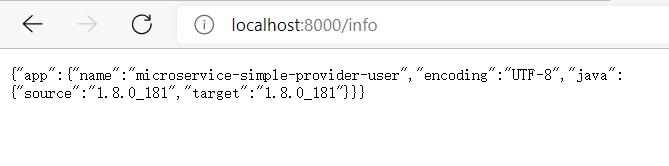
其他端点可以自行测试。
Spring Boot出于安全考虑,从Spring Boot1.5开始,对于敏感路径,默认不允许访问(直接访问将看到错误页面,HTTP错误码为401)。
硬编码有哪些问题
MovieController.java中
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public User findById(@PathVariable Long id){
return this.restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8000/"+id,User.class);
}
由代码可知,我们是把提供者的网络地址(IP和端口等)硬编码在代码中的,当然,也可将其提取到配置文件中去。
user:
userServiceUrl: http://localhost:8000/
代码改为
@Value("${user.userServiceUrl}")
private String userServiceUrl;
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public User findById(@PathVariable Long id){
return this.restTemplate.getForObject(this.userServiceUrl+id,User.class);
}
在传统的应用程序中,一般都是这么做的。然而,这种方式有很多问题。
- 使用场景有局限:如果服务提供者的网络地址(ip和端口)发生改变,会影响服务消费者。例如,用户微服务的网络地址发生变化,就需要修改电影微服务的配置,并重新发布。这显然是不可取的。
- 无法动态伸缩:在生产环境中,每个微服务一般都会部署多个实例,从而实现容灾和负载均衡。在微服务框架的系统中,还需要系统具备自动伸缩的能力,例如动态增减节点等。硬编码无法适应这种需求。
以上是关于开始使用Spring Cloud实战微服务的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章