8. spark源码分析(基于yarn cluster模式)- Task执行,Map端写入实现
Posted Leo Han
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了8. spark源码分析(基于yarn cluster模式)- Task执行,Map端写入实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本系列基于spark-2.4.6
通过上一节分析,我们知道,task提交之后通过launchTasks来具体执行任务,这一章节我们看下其具体实现.
private def launchTasks(tasks: Seq[Seq[TaskDescription]]) {
for (task <- tasks.flatten) {
val serializedTask = TaskDescription.encode(task)
if (serializedTask.limit() >= maxRpcMessageSize) {
Option(scheduler.taskIdToTaskSetManager.get(task.taskId)).foreach { taskSetMgr =>
try {
var msg = "Serialized task %s:%d was %d bytes, which exceeds max allowed: " +
"spark.rpc.message.maxSize (%d bytes). Consider increasing " +
"spark.rpc.message.maxSize or using broadcast variables for large values."
msg = msg.format(task.taskId, task.index, serializedTask.limit(), maxRpcMessageSize)
taskSetMgr.abort(msg)
} catch {
case e: Exception => logError("Exception in error callback", e)
}
}
}
else {
val executorData = executorDataMap(task.executorId)
executorData.freeCores -= scheduler.CPUS_PER_TASK
logDebug(s"Launching task ${task.taskId} on executor id: ${task.executorId} hostname: " +
s"${executorData.executorHost}.")
executorData.executorEndpoint.send(LaunchTask(new SerializableBuffer(serializedTask)))
}
}
}
第一步判断序列化后的task是否大于maxRpcMessageSize,如果大于,直接报任务失败异常,退出执行当前任务,如果没有的话,则会发送LaunchTask指令给Executor去执行。接下来就要看Executor中是怎么执行的了。
通过前面的分析,我们知道,executor中消息到来会在org.apache.spark.rpc.netty.Inbox中进行处理:
def process(dispatcher: Dispatcher): Unit = {
var message: InboxMessage = null
inbox.synchronized {
if (!enableConcurrent && numActiveThreads != 0) {
return
}
message = messages.poll()
if (message != null) {
numActiveThreads += 1
} else {
return
}
}
while (true) {
safelyCall(endpoint) {
message match {
case RpcMessage(_sender, content, context) =>
try {
endpoint.receiveAndReply(context).applyOrElse[Any, Unit](content, { msg =>
throw new SparkException(s"Unsupported message $message from ${_sender}")
})
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
context.sendFailure(e)
throw e
}
case OneWayMessage(_sender, content) =>
endpoint.receive.applyOrElse[Any, Unit](content, { msg =>
throw new SparkException(s"Unsupported message $message from ${_sender}")
})
case OnStart =>
endpoint.onStart()
if (!endpoint.isInstanceOf[ThreadSafeRpcEndpoint]) {
inbox.synchronized {
if (!stopped) {
enableConcurrent = true
}
}
}
case OnStop =>
val activeThreads = inbox.synchronized { inbox.numActiveThreads }
dispatcher.removeRpcEndpointRef(endpoint)
endpoint.onStop()
case RemoteProcessConnected(remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onConnected(remoteAddress)
case RemoteProcessDisconnected(remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onDisconnected(remoteAddress)
case RemoteProcessConnectionError(cause, remoteAddress) =>
endpoint.onNetworkError(cause, remoteAddress)
}
}
inbox.synchronized {
if (!enableConcurrent && numActiveThreads != 1) {
numActiveThreads -= 1
return
}
message = messages.poll()
if (message == null) {
numActiveThreads -= 1
return
}
}
}
}
实际在CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend进行处理:
case LaunchTask(data) =>
if (executor == null) {
exitExecutor(1, "Received LaunchTask command but executor was null")
} else {
val taskDesc = TaskDescription.decode(data.value)
logInfo("Got assigned task " + taskDesc.taskId)
executor.launchTask(this, taskDesc)
}
def launchTask(context: ExecutorBackend, taskDescription: TaskDescription): Unit = {
val tr = new TaskRunner(context, taskDescription)
runningTasks.put(taskDescription.taskId, tr)
threadPool.execute(tr)
}
将接收到的task封装成一个TaskRunner然后提交到线程池中执行:
override def run(): Unit = {
threadId = Thread.currentThread.getId
Thread.currentThread.setName(threadName)
val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean
val taskMemoryManager = new TaskMemoryManager(env.memoryManager, taskId)
val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime
} else 0L
Thread.currentThread.setContextClassLoader(replClassLoader)
val ser = env.closureSerializer.newInstance()
logInfo(s"Running $taskName (TID $taskId)")
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.RUNNING, EMPTY_BYTE_BUFFER)
var taskStartTime: Long = 0
var taskStartCpu: Long = 0
startGCTime = computeTotalGcTime()
try {
Executor.taskDeserializationProps.set(taskDescription.properties)
updateDependencies(taskDescription.addedFiles, taskDescription.addedJars)
task = ser.deserialize[Task[Any]](
taskDescription.serializedTask, Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
task.localProperties = taskDescription.properties
task.setTaskMemoryManager(taskMemoryManager)
val killReason = reasonIfKilled
if (killReason.isDefined) {
throw new TaskKilledException(killReason.get)
}
if (!isLocal) {
logDebug("Task " + taskId + "'s epoch is " + task.epoch)
env.mapOutputTracker.asInstanceOf[MapOutputTrackerWorker].updateEpoch(task.epoch)
}
// Run the actual task and measure its runtime.
taskStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
taskStartCpu = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime
} else 0L
var threwException = true
val value = Utils.tryWithSafeFinally {
val res = task.run(
taskAttemptId = taskId,
attemptNumber = taskDescription.attemptNumber,
metricsSystem = env.metricsSystem)
threwException = false
res
} {
val releasedLocks = env.blockManager.releaseAllLocksForTask(taskId)
val freedMemory = taskMemoryManager.cleanUpAllAllocatedMemory()
if (freedMemory > 0 && !threwException) {
val errMsg = s"Managed memory leak detected; size = $freedMemory bytes, TID = $taskId"
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.unsafe.exceptionOnMemoryLeak", false)) {
throw new SparkException(errMsg)
} else {
logWarning(errMsg)
}
}
if (releasedLocks.nonEmpty && !threwException) {
if (conf.getBoolean("spark.storage.exceptionOnPinLeak", false)) {
throw new SparkException(errMsg)
} else {
logInfo(errMsg)
}
}
}
task.context.fetchFailed.foreach { fetchFailure =>
}
val taskFinish = System.currentTimeMillis()
val taskFinishCpu = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime
} else 0L
task.context.killTaskIfInterrupted()
val resultSer = env.serializer.newInstance()
val beforeSerialization = System.currentTimeMillis()
val valueBytes = resultSer.serialize(value)
val afterSerialization = System.currentTimeMillis()
task.metrics.setExecutorDeserializeTime(
(taskStartTime - deserializeStartTime) + task.executorDeserializeTime)
task.metrics.setExecutorDeserializeCpuTime(
(taskStartCpu - deserializeStartCpuTime) + task.executorDeserializeCpuTime)
task.metrics.setExecutorRunTime((taskFinish - taskStartTime) - task.executorDeserializeTime)
task.metrics.setExecutorCpuTime(
(taskFinishCpu - taskStartCpu) - task.executorDeserializeCpuTime)
task.metrics.setJvmGCTime(computeTotalGcTime() - startGCTime)
task.metrics.setResultSerializationTime(afterSerialization - beforeSerialization)
// Expose task metrics using the Dropwizard metrics system.
// Update task metrics counters
executorSource.METRIC_CPU_TIME.inc(task.metrics.executorCpuTime)
executorSource.METRIC_RUN_TIME.inc(task.metrics.executorRunTime)
executorSource.METRIC_JVM_GC_TIME.inc(task.metrics.jvmGCTime)
executorSource.METRIC_DESERIALIZE_TIME.inc(task.metrics.executorDeserializeTime)
executorSource.METRIC_DESERIALIZE_CPU_TIME.inc(task.metrics.executorDeserializeCpuTime)
executorSource.METRIC_RESULT_SERIALIZE_TIME.inc(task.metrics.resultSerializationTime)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_FETCH_WAIT_TIME
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleReadMetrics.fetchWaitTime)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_WRITE_TIME.inc(task.metrics.shuffleWriteMetrics.writeTime)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_TOTAL_BYTES_READ
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleReadMetrics.totalBytesRead)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_REMOTE_BYTES_READ
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleReadMetrics.remoteBytesRead)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_REMOTE_BYTES_READ_TO_DISK
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleReadMetrics.remoteBytesReadToDisk)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_LOCAL_BYTES_READ
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleReadMetrics.localBytesRead)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_RECORDS_READ
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleReadMetrics.recordsRead)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_REMOTE_BLOCKS_FETCHED
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleReadMetrics.remoteBlocksFetched)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_LOCAL_BLOCKS_FETCHED
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleReadMetrics.localBlocksFetched)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_BYTES_WRITTEN
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleWriteMetrics.bytesWritten)
executorSource.METRIC_SHUFFLE_RECORDS_WRITTEN
.inc(task.metrics.shuffleWriteMetrics.recordsWritten)
executorSource.METRIC_INPUT_BYTES_READ
.inc(task.metrics.inputMetrics.bytesRead)
executorSource.METRIC_INPUT_RECORDS_READ
.inc(task.metrics.inputMetrics.recordsRead)
executorSource.METRIC_OUTPUT_BYTES_WRITTEN
.inc(task.metrics.outputMetrics.bytesWritten)
executorSource.METRIC_OUTPUT_RECORDS_WRITTEN
.inc(task.metrics.outputMetrics.recordsWritten)
executorSource.METRIC_RESULT_SIZE.inc(task.metrics.resultSize)
executorSource.METRIC_DISK_BYTES_SPILLED.inc(task.metrics.diskBytesSpilled)
executorSource.METRIC_MEMORY_BYTES_SPILLED.inc(task.metrics.memoryBytesSpilled)
val accumUpdates = task.collectAccumulatorUpdates()
val directResult = new DirectTaskResult(valueBytes, accumUpdates)
val serializedDirectResult = ser.serialize(directResult)
val resultSize = serializedDirectResult.limit()
val serializedResult: ByteBuffer = {
if (maxResultSize > 0 && resultSize > maxResultSize) {ze)}), " +
s"dropping it.")
ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](TaskResultBlockId(taskId), resultSize))
} else if (resultSize > maxDirectResultSize) {
val blockId = TaskResultBlockId(taskId)
env.blockManager.putBytes(
blockId,
new ChunkedByteBuffer(serializedDirectResult.duplicate()),
StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_SER)
ser.serialize(new IndirectTaskResult[Any](blockId, resultSize))
} else {
logInfo(s"Finished $taskName (TID $taskId). $resultSize bytes result sent to driver")
serializedDirectResult
}
}
setTaskFinishedAndClearInterruptStatus()
execBackend.statusUpdate(taskId, TaskState.FINISHED, serializedResult)
} catch {.......
} finally {
runningTasks.remove(taskId)
}
}
这里前面很大一部分在准备task执行的相关环境,然后调用task.run来执行,最后通过Task.runTask来实际执行任务,这是一个接口,我们以ShuffleMapTask为例进行说明:
// ShuffleMapTask
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = {
// Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable.
val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean
val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime
} else 0L
val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance()
val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])](
ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader)
_executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime
_executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) {
threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime
} else 0L
var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null
try {
val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager
writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context)
writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
writer.stop(success = true).get
} catch {
....
}
}
这里会调用Writer进行处理:
writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]])
spark中的ShuffleWriter有如下几种实现:
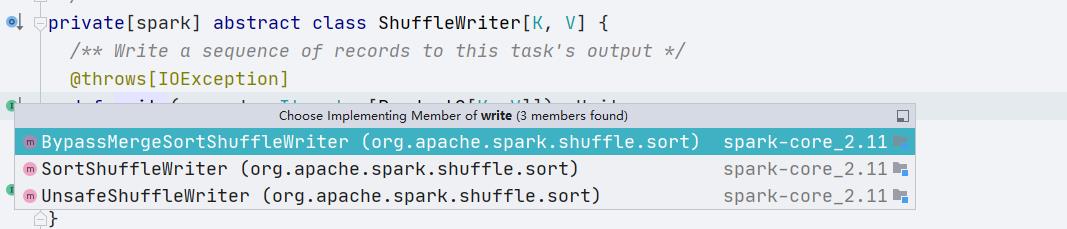
我们看下默认的SortShuffleWriter实现:
override def write(records: Iterator[Product2[K, V]]): Unit = {
sorter = if (dep.mapSideCombine) {
new ExternalSorter[K, V, C](
context, dep.aggregator, Some(dep.partitioner), dep.keyOrdering, dep.serializer)
} else {
new ExternalSorter[K, V, V](
context, aggregator = None, Some(dep.partitioner), ordering = None, dep.serializer)
}
sorter.insertAll(records)
// Don't bother including the time to open the merged output file in the shuffle write time,
// because it just opens a single file, so is typically too fast to measure accurately
// (see SPARK-3570).
val output = shuffleBlockResolver.getDataFile(dep.shuffleId, mapId)
val tmp = Utils.tempFileWith(output)
try {
val blockId = ShuffleBlockId(dep.shuffleId, mapId, IndexShuffleBlockResolver.NOOP_REDUCE_ID)
val partitionLengths = sorter.writePartitionedFile(blockId, tmp)
shuffleBlockResolver.writeIndexFileAndCommit(dep.shuffleId, mapId, partitionLengths, tmp)
mapStatus = MapStatus(blockManager.shuffleServerId, partitionLengths)
} finally {
if (tmp.exists() && !tmp.delete()) {
logError(s"Error while deleting temp file ${tmp.getAbsolutePath}")
}
}<以上是关于8. spark源码分析(基于yarn cluster模式)- Task执行,Map端写入实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章