Python编程 模拟SQL语句 实现对员工信息的增删改查
Posted 叶庭云
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Python编程 模拟SQL语句 实现对员工信息的增删改查相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、问题描述
用 Python 模拟 sql 语句,实现对员工信息的增删改查。
- 封装函数,传入参数:文件路径和 sql 命令。
- 模拟 sql 语句实现对员工信息的现增删改查,并打印结果。
二、Python编程
导入需要的依赖库
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
"""
@Author :叶庭云
@file :实训第二次作业
@function :封装函数 根据输入的文件路径和sql命令
模拟sql语句实现对员工信息的现增删改查
"""
import re
import os
函数式编程
def sql_parse(sql_, key_list):
"""
解析sql命令字符串,按照key_lis列表里的元素分割sql得到字典形式的命令sql_dic
:param sql_:
:param key_list:
:return:
"""
sql_list = []
sql_dic = {}
for i in key_list:
b = [j.strip() for j in sql_.split(i)]
if len(b) > 1:
if len(sql_.split('limit')) > 1:
sql_dic['limit'] = sql_.split('limit')[-1]
if i == 'where' or i == 'values':
sql_dic[i] = b[-1]
if sql_list:
sql_dic[sql_list[-1]] = b[0]
sql_list.append(i)
sql_ = b[-1]
else:
sql_ = b[0]
if sql_dic.get('select'):
if not sql_dic.get('from') and not sql_dic.get('where'):
sql_dic['from'] = b[-1]
if sql_dic.get('select'):
sql_dic['select'] = sql_dic.get('select').split(',')
if sql_dic.get('where'):
sql_dic['where'] = where_parse(sql_dic.get('where'))
return sql_dic
def where_parse(where):
"""
格式化where字符串为列表where_list,用'and', 'or', 'not'分割字符串
:param where:
:return:
"""
casual_l = [where]
logic_key = ['and', 'or', 'not']
for j in logic_key:
for i in casual_l:
if i not in logic_key:
if len(i.split(j)) > 1:
ele = i.split(j)
index = casual_l.index(i)
casual_l.pop(index)
casual_l.insert(index, ele[0])
casual_l.insert(index + 1, j)
casual_l.insert(index + 2, ele[1])
casual_l = [k for k in casual_l if k]
where_list = three_parse(casual_l, logic_key)
return where_list
def three_parse(casual_l, logic_key):
"""
处理临时列表casual_l中具体的条件,'staff_id>5'-->['staff_id','>','5']
:param casual_l:
:param logic_key:
:return:
"""
where_list = []
for i in casual_l:
if i not in logic_key:
b = i.split('like')
if len(b) > 1:
b.insert(1, 'like')
where_list.append(b)
else:
key = ['<', '=', '>']
new_lis = []
opt = ''
lis = [j for j in re.split('([=<>])', i) if j]
for k in lis:
if k in key:
opt += k
else:
new_lis.append(k)
new_lis.insert(1, opt)
where_list.append(new_lis)
else:
where_list.append(i)
return where_list
def sql_action(sql_dic, titles):
"""
把解析好的sql_dic分发给相应函数执行处理
:param sql_dic:
:param titles:
:return:
"""
key = {'select': select,
'insert': insert,
'delete': delete,
'update': update}
res = []
for i in sql_dic:
if i in key:
res = key[i](sql_dic, titles)
return res
def select(sql_dic, title_):
"""
处理select语句命令
:param sql_dic:
:param title_:
:return:
"""
with open(data_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as fh:
filter_res = where_action(fh, sql_dic.get('where'), title_)
limit_res = limit_action(filter_res, sql_dic.get('limit'))
search_res = search_action(limit_res, sql_dic.get('select'), title_)
return search_res
def insert(sql_dic):
"""
处理insert语句命令
:param sql_dic:
:return:
"""
with open(data_path, 'r+', encoding='utf-8') as fp:
data_ = fp.readlines()
phone_list = [i.strip().split(',')[4] for i in data_]
ins_count = 0
if not data_:
new_id = 1
else:
last = data_[-1]
last_id = int(last.split(',')[0])
new_id = last_id + 1
record = sql_dic.get('values').split('/')
for i in record:
if i.split(',')[2] in phone_list:
print('\\033[1;31m%s 手机号已存在\\033[0m' % i)
else:
new_record = '\\n%s,%s\\n' % (str(new_id), i)
fp.write(new_record)
new_id += 1
ins_count += 1
fp.flush() # 刷新记录
return ['insert successfully!'], [str(ins_count)]
def delete(sql_dic, item):
"""
处理delete语句命令
:param sql_dic:
:param item:
:return:
"""
with open(data_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as r_file, \\
open('staff_data_bak.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as w_file:
del_count = 0
# delete from staff_data.txt where staff_id>=5 and staff_id<=10
for line in r_file.read().split("\\n")[1:]:
# print(line)
dic = dict(zip(item.split(','), line.split(',')))
# print(dic)
# delete from staff_data.txt where staff_id>=5 and staff_id<=10
print(dic)
print(sql_dic.get("where"))
# exp_1, opt, exp_2 = sql_dic.get("where")
record_list = []
try:
for item in sql_dic.get("where"):
print(item)
if type(item) is list:
exp_1, opt, exp_2 = item
print(exp_1, opt, exp_2)
flag = eval(f'{dic["staff_id"]}{opt}{exp_2}')
print(flag)
record_list.append(flag)
print(all(record_list), record_list)
if all(record_list): # 删除满足条件的
del_count += 1
pass
else:
w_file.write(line + "\\n")
except Exception as e:
print(e.args[0])
pass
w_file.flush()
# os.remove('staff_data.txt')
# os.rename('staff_data_bak.txt', 'staff_data.txt')
return ['delete successfully!'], [str(del_count)]
def update(sql_dic, title_):
"""
处理update语句命令
:param sql_dic:
:param title_:
:return:
"""
set_l = sql_dic.get('set').strip().split(',')
set_list = [i.split('=') for i in set_l]
update_count = 0
with open(data_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as r_file, \\
open('staff_data_bak.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as w_file:
for line in r_file:
dic = dict(zip(title_.split(','), line.strip().split(',')))
filter_res = logic_action(dic, sql_dic.get('where'))
if filter_res:
for i in set_list:
k = i[0]
v = i[-1]
dic[k] = v
line = [dic[i] for i in title_.split(',')]
update_count += 1
line = ','.join(line) + '\\n'
w_file.write(line)
w_file.flush()
os.remove('staff_data.txt')
os.rename('staff_data_bak.txt', 'staff_data.txt')
return ['update successfully!'], [str(update_count)]
def where_action(fh, where_list, title_):
"""
具体处理where_list里的所有条件
:param fh:
:param where_list:
:param title_:
:return:
"""
res = []
if len(where_list) != 0:
for line in fh:
dic = dict(zip(title_.split(','), line.strip().split(',')))
if dic['name'] != 'name':
logic_res = logic_action(dic, where_list)
if logic_res:
res.append(line.strip().split(','))
else:
res = [i.split(',') for i in fh.readlines()]
return res
def logic_action(dic, where_list):
"""
判断数据文件中每一条是否符合where_list条件
:param dic:
:param where_list:
:return:
"""
logic = []
# print(where_list)
# print(dic)
for exp in where_list:
# print(exp)
if type(exp) is list:
exp_k, opt, exp_v = exp
# print(exp_k, opt, exp_v)
if exp[1] == '=':
opt = '=='
logical_char = "'%s'%s'%s'" % (dic[exp_k], opt, exp_v)
# print(logical_char)
if opt != 'like':
exp = str(eval(logical_char))
else:
if exp_v in dic[exp_k]:
exp = 'True'
else:
exp = 'False'
logic.append(exp)
res = eval(' '.join(logic))
return res
def limit_action(filter_res, limit_l):
"""
用列表切分处理显示符合条件的数量
:param filter_res:
:param limit_l:
:return:
"""
if limit_l:
index = int(limit_l[0])
res = filter_res[:index]
else:
res = filter_res
return res
def search_action(limit_res, select_list, title_):
"""
处理需要查询并显示的title和相应数据
:param limit_res:
:param select_list:
:param title_:
:return:
"""
res = []
fields_list_ = title_.split(',')
if select_list[0] == '*':
res = limit_res
else:
fields_list_ = select_list
for data_ in limit_res:
dic = dict(zip(title_.split(','), data_))
r_l = []
for i in fields_list_:
r_l.append((dic[i].strip()))
res.append(r_l)
return fields_list_, res
主函数调用
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 指令关键词列表
key_lis = ['select', 'insert', 'delete', 'update', 'from', 'into', 'set', 'values', 'where', 'limit']
while True:
sql = input('请输入sql命令,退出请输入exit->>>').strip()
sql = re.sub(' ', '', sql)
if len(sql) == 0:
continue
if sql == 'exit':
break
sql_dict = sql_parse(sql, key_lis)
try:
data_path = sql_dict['from']
except KeyError:
data_path = sql_dict['into']
with open(data_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
title = f.readline().strip()
fields_list, fields_data = sql_action(sql_dict, title)
print('\\033[0;32m结果如下:\\033[0m')
print('-'.join(fields_list))
for data in fields_data:
print('-'.join(data))
三、测试结果
# 测试sql命令如下:
# select * from staff_data.txt where dept=人事
# select name,age from staff_data.txt where age > 27
# select * from staff_data.txt where enroll_date like 2017
# insert into staff_data.txt values 叶庭云,21,13198497869,算法,2018-7-12
# update into staff_data.txt set dept=算法,phone=13566677787 where staff_id=8
# delete from staff_data.txt where staff_id>=5 and staff_id<=10
# delete from staff_data.txt where staff_id>=5 and staff_id<=10
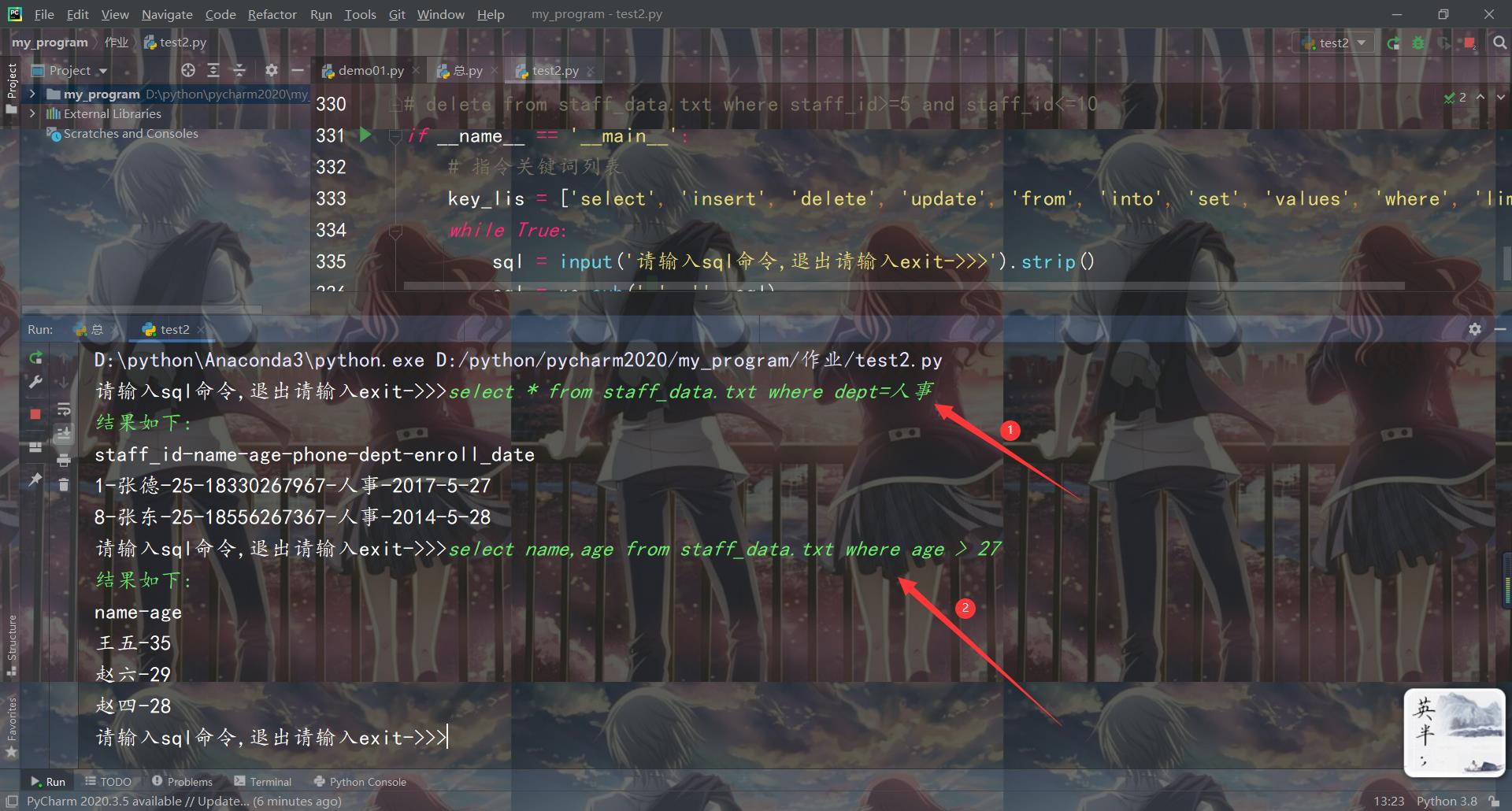
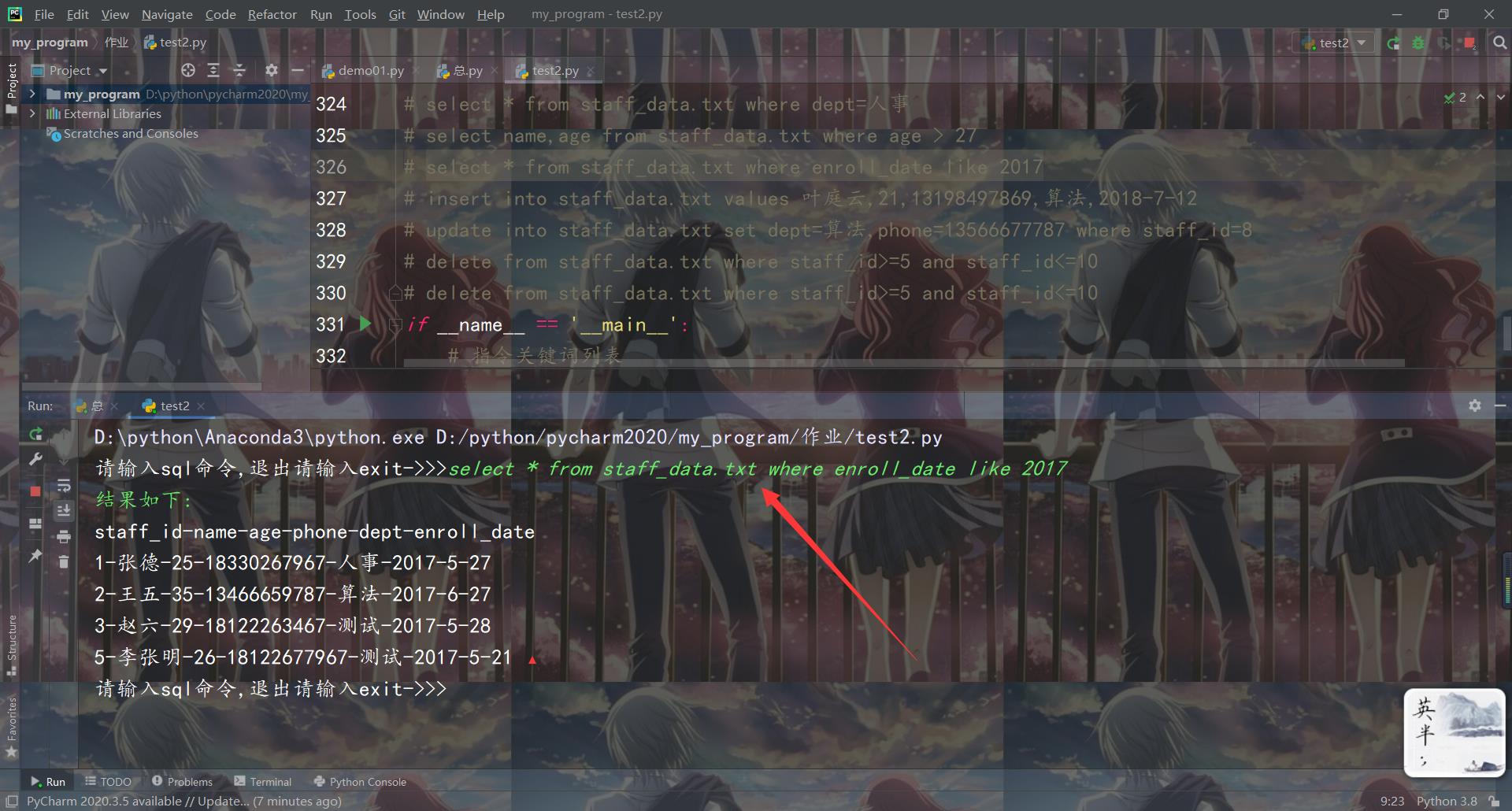
所有测试结果如下:

推荐阅读:
https://www.cnblogs.com/JayeHe/p/6846524.html
https://www.jb51.net/article/117919.htm
以上是关于Python编程 模拟SQL语句 实现对员工信息的增删改查的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章