模式识别实验一:Fisher线性判别(LDA)
Posted zstar-_
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了模式识别实验一:Fisher线性判别(LDA)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Fisher线性判别也叫作LDA,它可用于降维也可用于分类,当维度降低成1维时,确定一个阈值,即可实现分类。和PCA相比,LDA是一种有监督的降维算法,局限性在于降低的维度必须小于样本类别数-1。LDA分类的核心思想是将样本的向量空间投射到一个一维直线上,使样本类内离散度尽可能小,类间离散度尽可能大。本实验通过sonar和Iris数据集,实现了三种不同方式的分类算法,并在sonar数据集上选取了部分特征,考察了特征数和分类精确度之间的关系。
pdf版的实验报告可以戳这:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq1198768105/34257333
sonar和Iris数据集下载可以戳这:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq1198768105/31613770
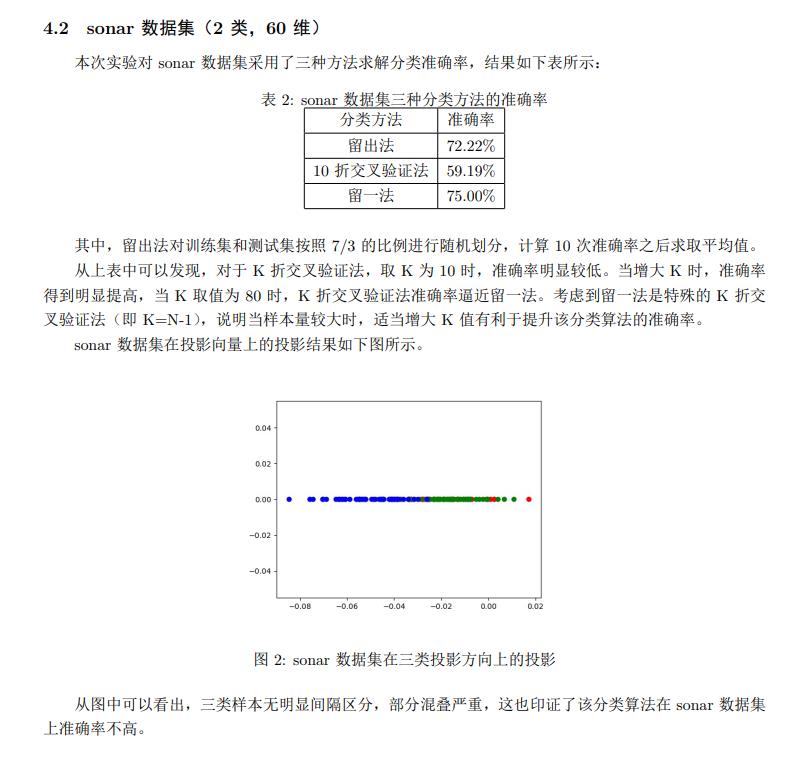
实验报告图片版








程序代码
sonar数据集分类
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, KFold, LeaveOneOut
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 正常导入数据
def load_dataset():
data = np.genfromtxt('sonar.txt', delimiter=',', usecols=np.arange(0, 60))
target = np.genfromtxt('sonar.txt', delimiter=',', usecols=(60), dtype=str)
t = np.zeros(len(target))
t[target == 'R'] = 1
t[target == 'M'] = 2
return data, t
# 自定义导入数据维度
def load_dataset_dimension(dimension):
data = np.genfromtxt('sonar.txt', delimiter=',', usecols=np.arange(0, dimension))
target = np.genfromtxt('sonar.txt', delimiter=',', usecols=(60), dtype=str)
t = np.zeros(len(target))
t[target == 'R'] = 1
t[target == 'M'] = 2
return data, t
def fisher(class1, class2):
class1 = np.mat(class1)
class2 = np.mat(class2)
# 求解每一个特征的均值,按列求解
a1 = np.mean(class1, axis=0)
a2 = np.mean(class2, axis=0)
# 直接代入公式求解类内离散度矩阵
s1 = (class1 - a1).T * (class1 - a1)
s2 = (class2 - a2).T * (class2 - a1)
sw = s1 + s2
# 这里是求解离散度矩阵的另一种思路:通过协方差公式求解,49为样本数量-1(n-1)
# s = np.cov(class0.T) * 49
# w 为最佳变换向量w*,w0为阈值
w = (a1 - a2) * np.linalg.inv(sw)
w0 = (a1 * w.T + a2 * w.T) / 2
return w, w0
# 计算分类准确率
def accuracy(pre, tar):
total = len(pre)
acc = 0
for i in range(total):
if pre[i] == tar[i]:
acc += 1
return acc / total
# 修改两个类别标签
def transform_target(data, target):
class1 = []
class2 = []
for i in range(len(data)):
if target[i] == 1:
class1.append(data[i])
elif target[i] == 2:
class2.append(data[i])
return class1, class2
# method1 留出法,随机划分训练测试集,多次平均求结果
def method1():
data, target = load_dataset()
# 使用留出法随机划分数据集,训练集/测试集=7/3, 每次划分具有随机性
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(data, target, test_size=0.30)
class1, class2 = transform_target(X_train, Y_train)
# w代表投影向量,w0代表第一类和第二类比较时的阈值。
w, w0 = fisher(class1, class2)
y = X_test * w.T
res = np.zeros(len(X_test))
for i in range(len(res)):
if y[i] > w0:
res[i] = 1
else:
res[i] = 2
# print(res)
acc = accuracy(res, Y_test)
# print("分类准确率为", acc)
return acc
# method2 k折交叉验证法
def method2():
data, target = load_dataset()
acc = 0
K = 10 # 这里设定k为10
kf = KFold(n_splits=K)
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(data):
X_train = data[train_index]
X_test = data[test_index]
Y_train = target[train_index]
Y_test = target[test_index]
class1, class2 = transform_target(X_train, Y_train)
# w代表投影向量,w0代表第一类和第二类比较时的阈值。
w, w0 = fisher(class1, class2)
y = X_test * w.T
res = np.zeros(len(X_test))
for i in range(len(res)):
if y[i] > w0:
res[i] = 1
else:
res[i] = 2
# print(res)
acc += accuracy(res, Y_test)
# print("分类准确率为", acc)
acc = acc / K
return acc
# method3 留一法
def method3():
data, target = load_dataset()
loo = LeaveOneOut()
acc = 0
for train_index, test_index in loo.split(data):
X_train = data[train_index]
X_test = data[test_index]
Y_train = target[train_index]
Y_test = target[test_index]
class1, class2 = transform_target(X_train, Y_train)
# w代表投影向量,w0代表第一类和第二类比较时的阈值。
w, w0 = fisher(class1, class2)
y = X_test * w.T
res = np.zeros(len(X_test))
for i in range(len(res)):
if y[i] > w0:
res[i] = 1
else:
res[i] = 2
# print(res)
acc += accuracy(res, Y_test)
# print("分类准确率为", acc)
acc = acc / len(data)
return acc
# dension 以留一法为基础,测试维度和准确率的关系
def dension(dimension):
data, target = load_dataset_dimension(dimension)
loo = LeaveOneOut()
acc = 0
for train_index, test_index in loo.split(data):
X_train = data[train_index]
X_test = data[test_index]
Y_train = target[train_index]
Y_test = target[test_index]
class1, class2 = transform_target(X_train, Y_train)
# w代表投影向量,w0代表第一类和第二类比较时的阈值。
w, w0 = fisher(class1, class2)
y = X_test * w.T
res = np.zeros(len(X_test))
for i in range(len(res)):
if y[i] > w0:
res[i] = 1
else:
res[i] = 2
# print(res)
acc += accuracy(res, Y_test)
# print("分类准确率为", acc)
acc = acc / len(data)
return acc
# 绘制投影图
def draw():
data, target = load_dataset()
class1, class2 = transform_target(data, target)
w, w0 = fisher(class1, class2)
y = data * w.T
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(y[0:49], np.zeros([49, 1]), 'ro')
plt.plot(y[50:99], np.zeros([49, 1]), 'go')
plt.plot(y[100:149], np.zeros([49, 1]), 'bo')
plt.savefig('./sonar.jpg')
plt.show()
def main():
# 10次计算方法一的留出法,取平均准确率作为结果(保留两位小数输出)
total_accuary1 = 0
for i in range(10):
total_accuary1 += method1()
total_accuary1 = total_accuary1 / 10
print("留出法的分类准确率为:", "{:.2%}".format(total_accuary1))
# draw()
total_accuary2 = method2()
print("K折交叉验证法的分类准确率为:", "{:.2%}".format(total_accuary2))
total_accuary3 = method3()
print("留一法的分类准确率为:", "{:.2%}".format(total_accuary3))
# 绘制维度与准确率的关系图
total_accuary = []
plt.figure(2)
for demension in range(2, 60):
total_accuary.append(dension(demension))
print(total_accuary)
plt.plot(np.arange(2, 60), total_accuary)
# 解决中文显示问题
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.xlabel("维度")
plt.ylabel("准确率")
plt.title("sonar数据集准确率随维度的变化图(留一法)")
plt.savefig('./demension.jpg')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Iris数据集分类
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, KFold, LeaveOneOut
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def load_dataset():
data = np.genfromtxt('iris.txt', delimiter=',', usecols=(0, 1, 2, 3))
target = np.genfromtxt('iris.txt', delimiter=',', usecols=(4), dtype=str)
t = np.zeros(len(target))
t[target == 'setosa'] = 1
t[target == 'versicolor'] = 2
t[target == 'virginica'] = 3
return data, t
def fisher(class1, class2):
class1 = np.mat(class1)
class2 = np.mat(class2)
# 求解每一个特征的均值,按列求解
a1 = np.mean(class1, axis=0)
a2 = np.mean(class2, axis=0)
# 直接代入公式求解类内离散度矩阵
s1 = (class1 - a1).T * (class1 - a1)
s2 = (class2 - a2).T * (class2 - a1)
sw = s1 + s2
# 这里是求解离散度矩阵的另一种思路:通过协方差公式求解,49为样本数量-1(n-1)
# s = np.cov(class0.T) * 49
# w 为最佳变换向量w*,w0为阈值
w = (a1 - a2) * np.linalg.inv(sw)
w0 = (a1 * w.T + a2 * w.T) / 2
return w, w0
# 计算分类准确率
def accuracy(pre, tar):
total = len(pre)
acc = 0
for i in range(total):
if pre[i] == tar[i]:
acc += 1
return acc / total
# 修改三个类别标签
def transform_target(data, target):
class1 = []
class2 = []
class3 = []
for i in range(len(data)):
if target[i] == 1:
class1.append(data[i])
elif target[i] == 2:
class2.append(data[i])
else:
class3.append(data[i])
return class1, class2, class3
# method1 留出法,随机划分训练测试集,多次平均求结果
def method1():
data, target = load_dataset()
# 使用留出法随机划分数据集,训练集/测试集=7/3, 每次划分具有随机性
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(data, target, test_size=0.30)
class1, class2, class3 = transform_target(X_train, Y_train)
# w12代表第一类和第二类比较的投影向量,w012代表第一类和第二类比较时的阈值,其它同理。
w12, w012 = fisher(class1, class2)
w13, w013 = fisher(class1, class3)
w23, w023 = fisher(class2, class3)
# 3分类的比较思路:两两进行比较,若两次均分类正确才算正确
y12 = X_test * w12.T
y13 = X_test * w13.T
y23 = X_test * w23.T
res = np.zeros(len(X_test))
for i in range(len(res)):
if y12[i] > w012 and y12[i] > w013:
res[i] = 1
if y12[i] < w012 and y23[i] > w023:
res[i] = 2
if y13[i] < w013 and y23[i] < w023:
res[i] = 3
# print(res)
acc = accuracy(res, Y_test)
# print("分类准确率为", acc)
return acc
# method2 k折交叉验证法
def method2():
data, target = load_dataset()
acc = 0
K = 10 # 这里设定k为10
kf = KFold(n_splits=K)
for train_index, test_index in kf.split(data):
X_train = data[train_index]
X_test = data[test_index]
Y_train = target[train_index]
Y_test = target[test_index]
class1, class2, class3 = transform_target(X_train, Y_train)
# w12代表第一类和第二类比较的投影向量,w012代表第一类和第二类比较时的阈值,其它同理。
w12, w012 = fisher(class1, class2)
w13, w013 = fisher(class1, class3)
w23, w023 = fisher(class2, class3)
# 3分类的比较思路:两两进行比较,若两次均分类正确才算正确
y12 = X_test * w12.T
y13 = X_test * w13.T
y23 = X_test * w23.T
res = np.zeros(len(X_test))
for i in range(len(res)):
if y12[i] > w012 and y12[i] > w013:
res[i] = 1
if y12[i] < w012 and y23[i] > w023:
res[i] = 2
if y13[i] < w013 and y23[i] < w023:
res[i] = 3
# print(res)
acc += accuracy(res, Y_test)
# print("分类准确率为", acc)
acc = acc / K
return acc
# method3 留一法
def method3():
data, target = load_dataset()
loo = LeaveOneOut()
acc = 0
for train_index, test_index in loo.以上是关于模式识别实验一:Fisher线性判别(LDA)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章