《Depth from Videos in the Wild:Unsupervised Monocular Depth Learning from Unknown Cameras》论文笔记
Posted m_buddy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《Depth from Videos in the Wild:Unsupervised Monocular Depth Learning from Unknown Cameras》论文笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
参考代码:depth_from_video_in_the_wild
1. 概述
导读:在这篇文章中提出了一种自监督深度估计算法,总体上看文章的算法是与monodepth2方法存在一定程度关联性,它们都是采用视频帧之间的相关性来建立自监督关系的。文章的方法经过凝练主要的工作主要体现为如下几点:
1)将相机位姿(旋转和平移矩阵)与相机内参(如果想的话可预测畸变参数)均通过网络预测的形式进行表达,增加对输入数据的适应性;
2)采用几何特性(也就是两帧像素计算光度重构损失的时候选择深度最小的为有效像素点)避免遮挡带来的影响;
3)为了应对目标运动带来的影响,文章经过实验表明通过粗糙的bbox-rect的形式也能获得不错的效果,减少了对先验知识为mask的依赖,简化工作;
4)针对归一化操作过程中存在均值方差漂移问题,文章在深度估计网络的编码器中对均值和方差两个变量认为引入噪声;
综上,经过文章在上面4点工作,文章的算法表现出了较为强大的鲁棒性以及较好的深度估计能力,下图是文章方法得到的示例:
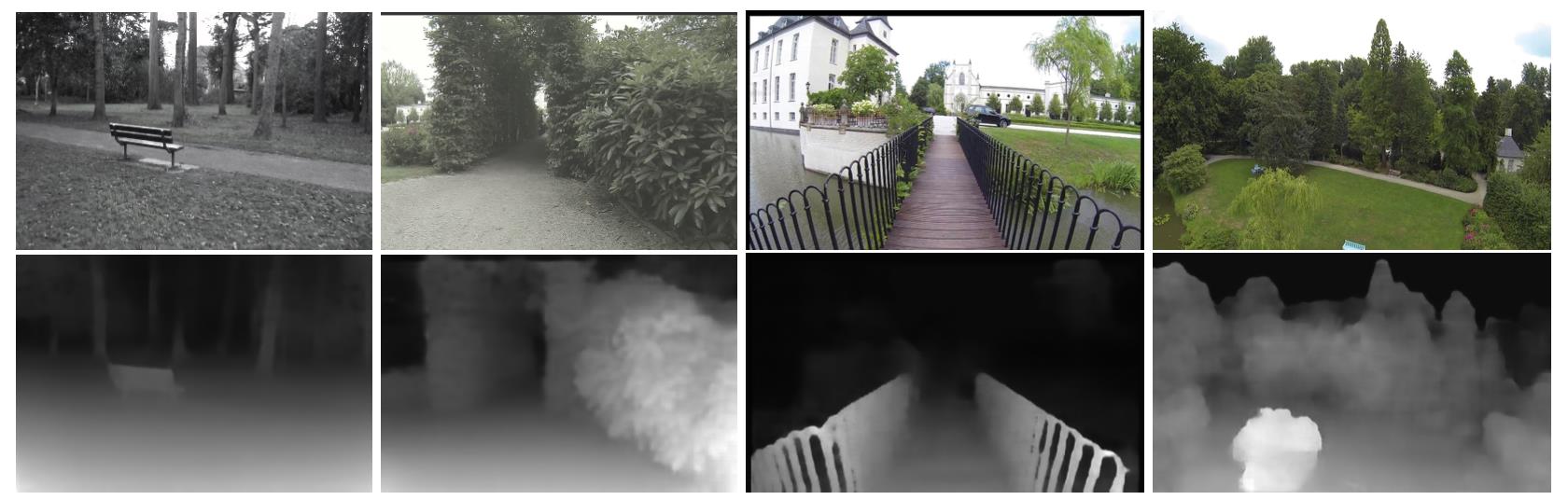

2. 方法设计
对于文章算法的输入是如下格式的:

从上图中可以看出其是由3个连续帧拼接起来的,对于每一帧需要标注出其中运动的物体也就是下图:

除此之外,相机的内参为选择输入项,毕竟网络具有相机内参预测功能。
2.1 深度估计与相机参数估计
2.1.1 深度估计网络
文章采用的深度估计网络是典型的U型网络(带shortcut连接),只不过在U型网络的编码器阶段会对归一化之后的结果添加扰动,从而保证网络在train和infer的时候性能不会存在大的偏差,其使用的归一化函数为:
# /model.py#L202
def _normalizer_fn(x, is_train, name='bn'): # 融合了噪声的归一化操作
return randomized_layer_normalization.normalize(
x, is_train=is_train, name=name, stddev=noise_stddev)
对于其中添加噪声的部分可以参考:
# randomized_layer_normalization.py#L32
def normalize(x, is_train, name='bn', stddev=0.5):
...
进而对于整体深度估计网络部分的实现可以参考:
# depth_prediction_net.py#L100
def depth_prediction_resnet18unet(images, is_training, decoder_weight_reg=0.0,
normalizer_fn=None, reflect_padding=True):
...
2.1.2 相机参数估计
这里相机参数的估计包含了相机内参和外参,其中对于相机外参的估计是与monodepth2
中相机参数估计是一致的,可以参考:
# motion_prediction_net.py#L80
def motion_field_net(images, weight_reg=0.0):
...
rotation = background_motion[:, 0, 0, :3] # 旋转分量
translation = background_motion[:, :, :, 3:] # 平移分量
...
这里需要注意的是平移矩阵是全局的,在此基础上文章中采用级联的形式,并且在不同尺度下去估计平移矩阵的偏移,为的是排除目标移动对平移矩阵带来的影响,则平移矩阵经过矫正公式:
t
(
x
,
y
)
=
t
0
+
m
(
x
,
y
)
δ
(
x
,
y
)
t(x,y)=t_0+m(x,y)\\delta(x,y)
t(x,y)=t0+m(x,y)δ(x,y)
其中,
t
0
t_0
t0是网络预测出来的初始平移矩阵,
m
(
x
,
y
)
m(x,y)
m(x,y)是运动目标的掩膜(为1的地方为运动区域),
δ
(
x
,
y
)
\\delta(x,y)
δ(x,y)是平移矩阵的偏移。则对于偏移的预测实现可以参考:
# motion_prediction_net.py#L61
residual_translation = _refine_motion_field(translation, conv7) # 使用不同层次的特征对平移分量进行优化(公式4)
residual_translation = _refine_motion_field(residual_translation, conv6)
residual_translation = _refine_motion_field(residual_translation, conv5)
residual_translation = _refine_motion_field(residual_translation, conv4)
residual_translation = _refine_motion_field(residual_translation, conv3)
residual_translation = _refine_motion_field(residual_translation, conv2)
residual_translation = _refine_motion_field(residual_translation, conv1)
residual_translation = _refine_motion_field(residual_translation, images)
那么,对应的按照上述的公式对全局平移矩阵进行校准,也就是:
# model.py#L280
trans += trans_res * dilate(self.seg_stack[:, :, :, j:j + 1]) # 文章公式4
inv_trans += inv_trans_res * dilate(self.seg_stack[:, :, :, i:i + 1])
这里额外添加的是对于相机内参的估计,可以参考:
# motion_prediction_net.py#L176
intrinsic_mat = add_intrinsics_head(bottleneck, image_height, image_width) # 使用网络去预测相机内参
2.2 运动目标的掩膜确定
在上文中提到了运动目标掩膜 m ( x , y ) m(x,y) m(x,y),它是通过分割进行确定的,对应在代码中通过下面的函数进行确定的:
# model.py#L163
def process_obj_mask(obj_id): # 从分割mask确定object motion mask
...
下图中的上图就是通过上述方式获取的运动目标掩膜,下图展示的是按照深度z维度进行方向划分之后不同像素的运动情况:
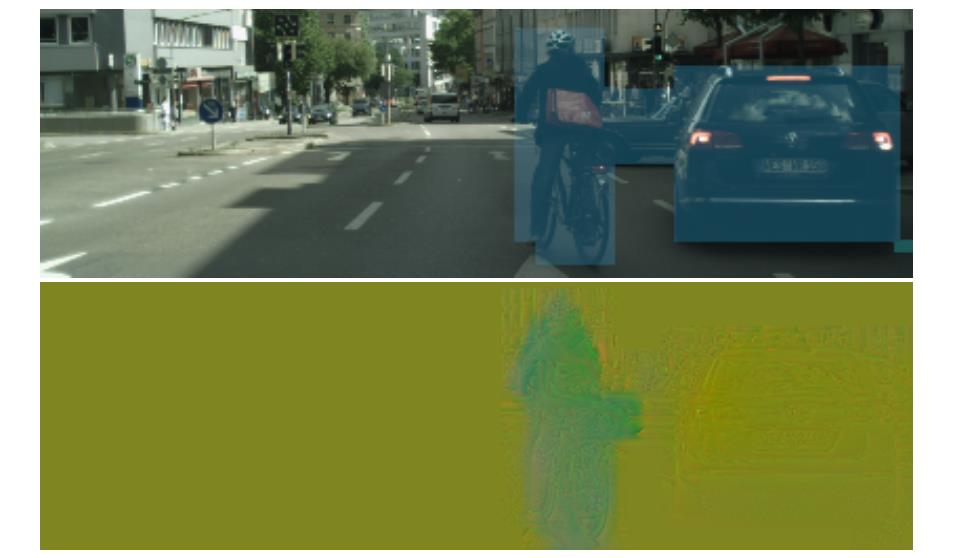

2.3 遮挡问题处理
在相机的运动过程中会存在一些像素不可见的情况,可以参考下图的示意:
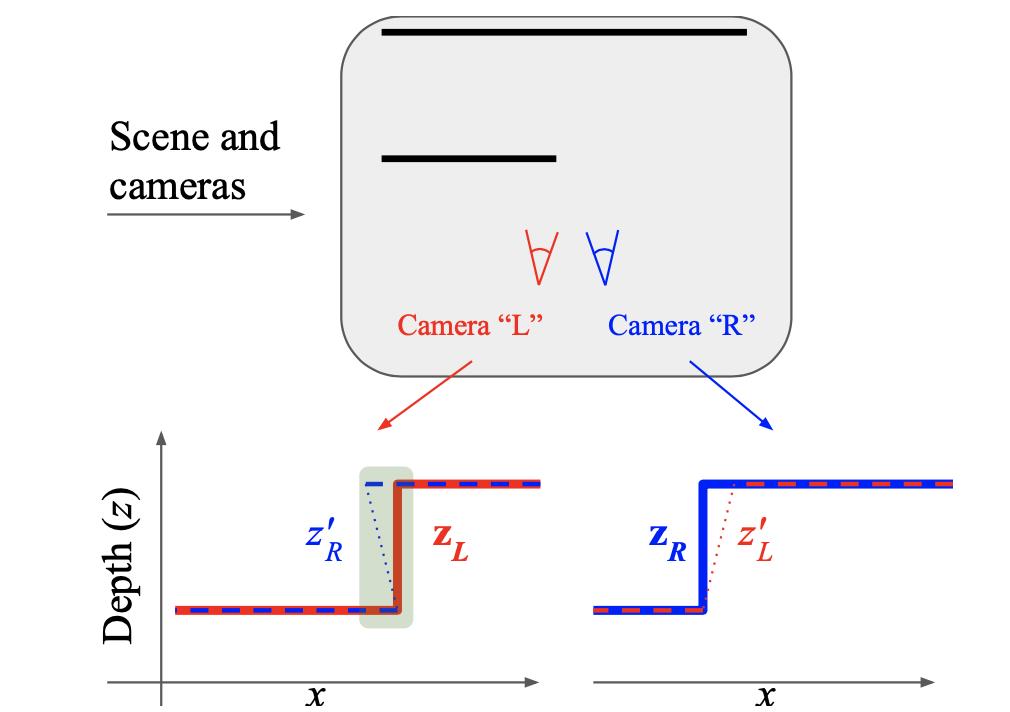
那么对于上述问题的处理,文章是选择重映射之后深度的最小作为像素有效性判别的,也就是下面代码中的tf.less()项:
# consistency_losses.py#L80
frame1_closer_to_camera = tf.to_float( # 按照4.3节的内容按照最小距离排除遮挡区域,并且为有效区域
tf.logical_and(
frame1transformed_depth.mask,
tf.less(frame1transformed_depth.depth, frame2depth_resampled)))
2.4 损失函数
文章中的损失函数是采用相邻帧上做来回映射的形式实现的,其损失函数实现为:
# consistency_losses.py#L204
def rgbd_and_motion_consistency_loss(frame1transformed_depth, frame1rgb,
frame2depth, frame2rgb, rotation1,
translation1, rotation2, translation2):
"""A helper that bundles rgbd and motion consistency losses together."""
# 深度+图像重映射L1 Loss,以及重映射图像对的SSIM相似度损失
endpoints = rgbd_consistency_loss(frame1transformed_depth, frame1rgb,
frame2depth, frame2rgb)
# We calculate the loss only for when frame1transformed_depth is closer to the
# camera than frame2 (occlusion-awareness). See explanation in
# rgbd_consistency_loss above.
# 平移旋转矩阵重映射之后的一致性损失
endpoints.update(motion_field_consistency_loss(
frame1transformed_depth.pixel_xy, endpoints['frame1_closer_to_camera'],
rotation1, translation1, rotation2, translation2))
return endpoints
在上述SSIM损失中为了避免重映射之后采样带来像素不连续问题(会给SSIM带来较大影响),文章中对SSIM计算过程中窗口中的像素进行加权操作:
# consistency_losses.py#L98
depth_error_second_moment = _weighted_average( # 为SSIM损失计算周围像素的权值
tf.square(frame2depth_resampled - frame1transformed_depth.depth),
frame1_closer_to_camera) + 1e-4
depth_proximity_weight = (
depth_error_second_moment /
(tf.square(frame2depth_resampled - frame1transformed_depth.depth) +
depth_error_second_moment) * tf.to_float(frame1transformed_depth.mask))
2.5 消融实验

3. 实验结果
KITTI数据集上的性能比较(其中Godard为monodepth2):

以上是关于《Depth from Videos in the Wild:Unsupervised Monocular Depth Learning from Unknown Cameras》论文笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章