❤️Android 12 高斯模糊-RenderEffect❤️
Posted 帅次
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了❤️Android 12 高斯模糊-RenderEffect❤️相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
🔥 android 12 高斯模糊
新功能:更易用的模糊、彩色滤镜等特效 。
新的 API 让你能更轻松地将常见图形效果应用到视图和渲染结构上。
-
使用 RenderEffect 将模糊、色彩滤镜等效果应用于 RenderNode 或 View。
-
使用新的 Window.setBackgroundBlurRadius() API 为窗口背景创建雾面玻璃效果,
-
使用 blurBehindRadius 来模糊窗口后面的所有内容。
咱们一个一个玩。
🔥 RenderEffect
💥 实现效果
private void setBlur(){
View.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(3, 3, Shader.TileMode.REPEAT));
...
}
使用特别简单,走你。
🌀 X 轴的模糊效果图
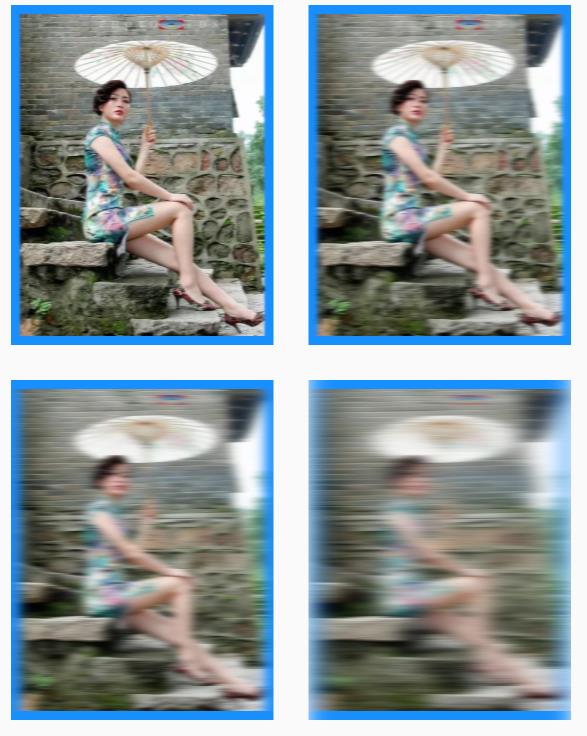

咱再看看代码
private void setBlur(){
agb.iv1.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(3, 0, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP));
agb.iv2.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(8, 0, Shader.TileMode.REPEAT));
agb.iv3.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(18, 0 ,Shader.TileMode.MIRROR));
agb.iv4.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(36, 0,Shader.TileMode.DECAL));
}
RenderEffect.createBlurEffect()的四个参数:
-
radiusX 沿 X 轴的模糊半径
-
radiusY 沿 Y 轴的模糊半径
-
inputEffect 模糊一次(传入 RenderEffect)
-
edgeTreatment 用于如何模糊模糊内核边缘附近的内容
下面两种仅看效果图。就不做代码设置了。
🌀 Y 轴的模糊效果图
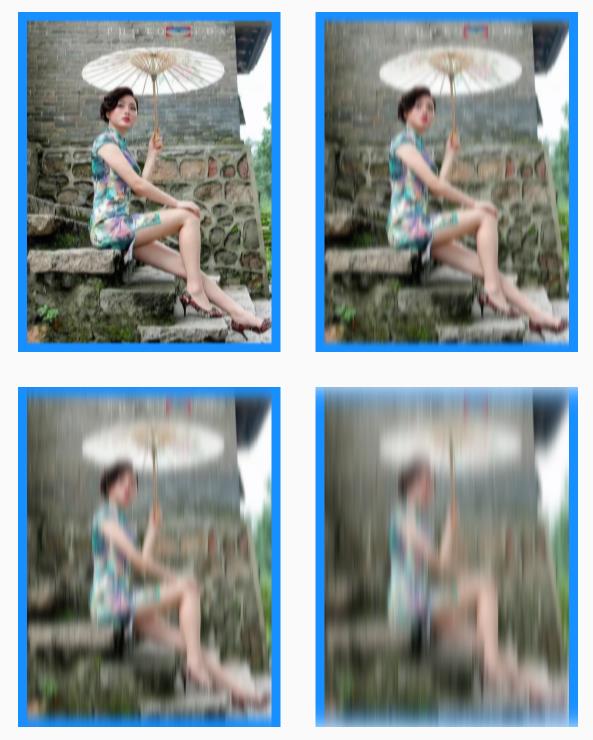

🌀 XY同时模糊效果图

第四个参数对边缘模糊,效果图如下:
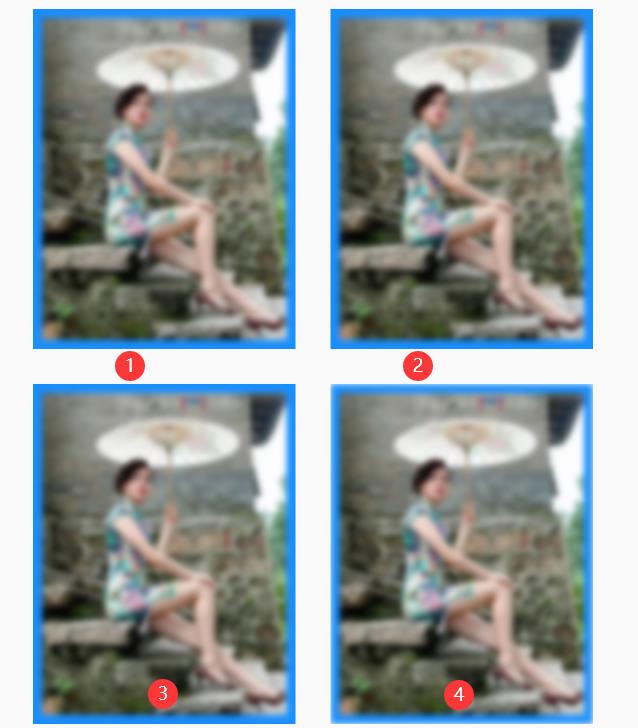

Shader.TileMode 提供了四个选项恕我没看出来。。
这里还有一堆方法等你玩。
注意:注意如此完美的画面只能在 Android 12(SDK31)及以上的设备上使用,其他版本的设备使用会导致崩溃,谨记谨记。 效果有了,下面咱们一起看看源码。
💥 源码
🌀 View.setRenderEffect()
public void setRenderEffect(@Nullable RenderEffect renderEffect) {
...
}
这个方法就是:renderEffect 应用于 View。 传入 null清除之前配置的RenderEffect 。这里咱们先看传入的 RenderEffect。
🌀 RenderEffect.createBlurEffect()
public static RenderEffect createBlurEffect(
float radiusX,
float radiusY,
@NonNull RenderEffect inputEffect,
@NonNull TileMode edgeTreatment
) {
long nativeInputEffect = inputEffect != null ? inputEffect.mNativeRenderEffect : 0;
return new RenderEffect(
nativeCreateBlurEffect(
radiusX,
radiusY,
nativeInputEffect,
edgeTreatment.nativeInt
)
);
}
两个 createBlurEffect() 方法,分别为三参(模糊一次)和四参(模糊两次)。inputEffect 先进行了一次模糊。
看效果图:

模糊程度一样,但是实现方式不同:
private void setBlur() {
RenderEffect radiusXRenderEffect = RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(10, 0, Shader.TileMode.MIRROR);
RenderEffect radiusYRenderEffect = RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(0, 10, Shader.TileMode.MIRROR);
agb.iv1.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(10, 10, Shader.TileMode.CLAMP));
agb.iv2.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(10, 10, Shader.TileMode.REPEAT));
//自身radiusY 为 0 ,传入的radiusYRenderEffect设置的radiusY为10;
agb.iv3.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(10, 0, radiusYRenderEffect, Shader.TileMode.MIRROR));
//自身radiusX 为 0 ,传入的radiusXRenderEffect设置的radiusX为10;
agb.iv4.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createBlurEffect(0, 10, radiusXRenderEffect, Shader.TileMode.DECAL));
}
这个方法返回一个 new RenderEffect(nativeCreateBlurEffect(...)。
那咱们去看看 nativeCreateBlurEffect()
🌀 nativeCreateBlurEffect()
frameworks/base/libs/hwui/jni/RenderEffect.cpp
static const JNINativeMethod gRenderEffectMethods[] = {
...
{"nativeCreateBlurEffect", "(FFJI)J", (void*)createBlurEffect},
...
};
static jlong createBlurEffect(JNIEnv* env , jobject, jfloat radiusX,
jfloat radiusY, jlong inputFilterHandle, jint edgeTreatment) {
auto* inputImageFilter = reinterpret_cast<SkImageFilter*>(inputFilterHandle);
sk_sp<SkImageFilter> blurFilter =
SkImageFilters::Blur(
Blur::convertRadiusToSigma(radiusX),
Blur::convertRadiusToSigma(radiusY),
static_cast<SkTileMode>(edgeTreatment),
sk_ref_sp(inputImageFilter),
nullptr);
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(blurFilter.release());
}
这里有两个函数来处理我们传过来的模糊的值,咱进去看看。
🌀 convertRadiusToSigma(convertSigmaToRadius)
//该常数近似于在SkBlurMask::Blur()(1/sqrt(3)中,在软件路径的"高质量"模式下进行的缩放。
static const float BLUR_SIGMA_SCALE = 0.57735f;
float Blur::convertRadiusToSigma(float radius) {
return radius > 0 ? BLUR_SIGMA_SCALE * radius + 0.5f : 0.0f;
}
float Blur::convertSigmaToRadius(float sigma) {
return sigma > 0.5f ? (sigma - 0.5f) / BLUR_SIGMA_SCALE : 0.0f;
}
🌀 sk_ref_sp(inputImageFilter)
external/skia/include/core/SkRefCnt.h
/*
* 返回包装提供的 ptr 的 sk_sp 并对其调用 ref (如果不为空)
*/
template <typename T> sk_sp<T> sk_ref_sp(T* obj) {
//sk_sp<SkImageFilter> :
return sk_sp<T>(SkSafeRef(obj));
}
//SkSafeRef:检查参数是否为非空,如果是,则调用 obj->ref() 并返回 obj。
template <typename T> static inline T* SkSafeRef(T* obj) {
if (obj) {
obj->ref();
}
return obj;
}
🌀 SkImageFilters::Blur()
#define SK_Scalar1 1.0f
#define SK_ScalarNearlyZero (SK_Scalar1 / (1 << 12))
sk_sp<SkImageFilter> SkImageFilters::Blur(
SkScalar sigmaX, SkScalar sigmaY, SkTileMode tileMode, sk_sp<SkImageFilter> input,
const CropRect& cropRect) {
if (sigmaX < SK_ScalarNearlyZero && sigmaY < SK_ScalarNearlyZero && !cropRect) {
return input;
}
return sk_sp<SkImageFilter>(
new SkBlurImageFilter(sigmaX, sigmaY, tileMode, input, cropRect));
}
附上最后的倔强
constexpr sk_sp() : fPtr(nullptr) {}
constexpr sk_sp(std::nullptr_t) : fPtr(nullptr) {}
/**
* Shares the underlying object by calling ref(), so that both the argument and the newly
* created sk_sp both have a reference to it.
*/
sk_sp(const sk_sp<T>& that) : fPtr(SkSafeRef(that.get())) {}
template <typename U,
typename = typename std::enable_if<std::is_convertible<U*, T*>::value>::type>
sk_sp(const sk_sp<U>& that) : fPtr(SkSafeRef(that.get())) {}
/**
* Move the underlying object from the argument to the newly created sk_sp. Afterwards only
* the new sk_sp will have a reference to the object, and the argument will point to null.
* No call to ref() or unref() will be made.
*/
sk_sp(sk_sp<T>&& that) : fPtr(that.release()) {}
template <typename U,
typename = typename std::enable_if<std::is_convertible<U*, T*>::value>::type>
sk_sp(sk_sp<U>&& that) : fPtr(that.release()) {}
/**
* Adopt the bare pointer into the newly created sk_sp.
* No call to ref() or unref() will be made.
*/
explicit sk_sp(T* obj) : fPtr(obj) {}
createBlurEffect() 得到 long 类型的 native 分配的的非零地址, 传入 new RenderEffect()
🌀 new RenderEffect()
/* 构造方法:仅从静态工厂方法构造 */
private RenderEffect(long nativeRenderEffect) {
mNativeRenderEffect = nativeRenderEffect;
RenderEffectHolder.RENDER_EFFECT_REGISTRY.registerNativeAllocation(
this, mNativeRenderEffect);
}
继续
/**
* @param classLoader ClassLoader 类加载器。
* @param freeFunction 类型为 nativePtr 的本机函数的地址,用于释放这种本机分配
* @return 由系统内存分配器分配的本机内存的 NativeAllocationRegistry。此版本更适合较小的对象(通常小于几百 KB)。
*/
private static class RenderEffectHolder {
public static final NativeAllocationRegistry RENDER_EFFECT_REGISTRY =
NativeAllocationRegistry.createMalloced(
RenderEffect.class.getClassLoader(), nativeGetFinalizer());
}
🌀 NativeAllocationRegistry.createMalloced()
libcore/luni/src/main/java/libcore/util/NativeAllocationRegistry.java
@SystemApi(client = MODULE_LIBRARIES)
public static NativeAllocationRegistry createMalloced(
@NonNull ClassLoader classLoader, long freeFunction, long size) {
return new NativeAllocationRegistry(classLoader, freeFunction, size, true);
}
🌀 NativeAllocationRegistry()
libcore/luni/src/main/java/libcore/util/NativeAllocationRegistry.java
private NativeAllocationRegistry(ClassLoader classLoader, long freeFunction, long size,
boolean mallocAllocation) {
if (size < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid native allocation size: " + size);
}
this.classLoader = classLoader;
this.freeFunction = freeFunction;
this.size = mallocAllocation ? (size | IS_MALLOCED) : (size & ~IS_MALLOCED);
}
既然拿到 NativeAllocationRegistry 那就继续调用其 registerNativeAllocation() 方法。
🌀 registerNativeAllocation ()
@SystemApi(client = MODULE_LIBRARIES)
@libcore.api.IntraCoreApi
public @NonNull Runnable registerNativeAllocation(@NonNull Object referent, long nativePtr) {
//当 referent 或nativePtr 为空
...
CleanerThunk thunk;
CleanerRunner result;
try {
thunk = new CleanerThunk();
Cleaner cleaner = Cleaner.create(referent, thunk);
result = new CleanerRunner(cleaner);
registerNativeAllocation(this.size);
} catch (VirtualMachineError vme /* probably OutOfMemoryError */) {
applyFreeFunction(freeFunction, nativePtr);
throw vme;
}
// Enable the cleaner only after we can no longer throw anything, including OOME.
thunk.setNativePtr(nativePtr);
// Ensure that cleaner doesn't get invoked before we enable it.
Reference.reachabilityFence(referent);
return result;
}
向 ART 注册新的 NativePtr 和关联的 Java 对象(也就是咱们设置的模糊类)。
返回的 Runnable 可用于在引用变得无法访问之前释放本机分配。如果运行时或使用 runnable 已经释放了本机分配,则 runnable 将不起作用。
RenderEffect 算是搞完了,咱们回到View.setRenderEffect()
🌀 View.setRenderEffect()
public void setRenderEffect(@Nullable RenderEffect renderEffect) {
if (mRenderNode.setRenderEffect(renderEffect)) {
//视图属性更改(alpha、translationXY 等)的快速失效。
invalidateViewProperty(true, true);
}
}
这里有个 mRenderNode.setRenderEffect(renderEffect)。咱们近距离观望一番。
🌀 mRenderNode 的创建
咱们先找找他是在什么地方创建的。
public View(Context context) {
...
//在View的构造方法中创建
mRenderNode = RenderNode.create(getClass().getName(), new ViewAnimationHostBridge(this));
...
}
🌀 RenderNode.create()
/** @hide */
public static RenderNode create(String name, @Nullable AnimationHost animationHost) {
return new RenderNode(name, animationHost);
}
private RenderNode(String name, AnimationHost animationHost) {
mNativeRenderNode = nCreate(name);
//注册 Native Allocation。
NoImagePreloadHolder.sRegistry.registerNativeAllocation(this, mNativeRenderNode);
mAnimationHost = animationHost;
}
再往下感觉也看不到啥了 跟上面类似,看.cpp动态分配类的地址还是有点懵。让我缓缓~以后补充。
以上是关于❤️Android 12 高斯模糊-RenderEffect❤️的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章