Java常用类
Posted Wecccccccc
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java常用类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
常用类
包装类Wrapper的分类
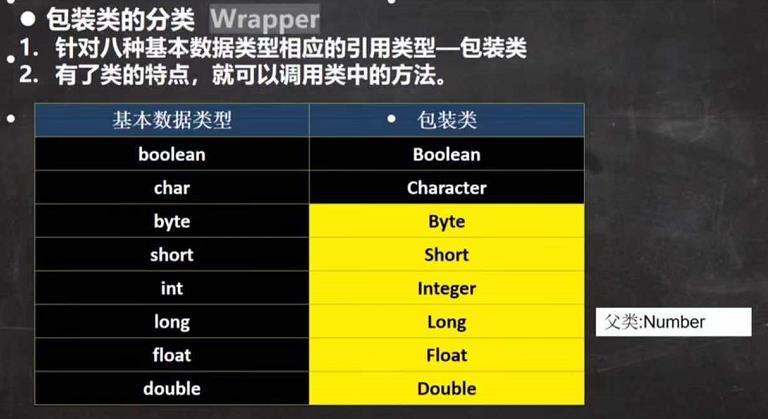
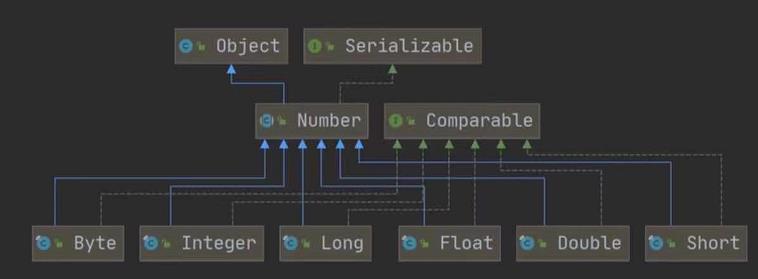
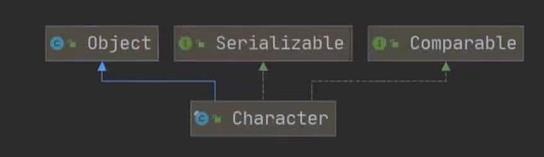
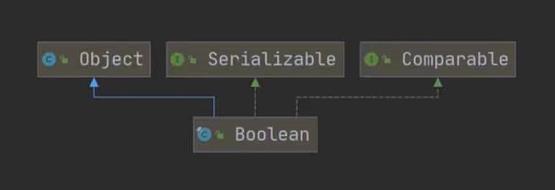
包装类和基本数据的转换

01:
package TryCatchExercise;
public class WrapperDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//手动装箱
int n1 = 100;
Integer integer = new Integer(n1);
Integer integer1 = Integer.valueOf(n1);
//手动拆箱
int i = integer.intValue();
//JKD5后,自动装箱
int n2 = 200;
Integer integer2 = n2;//底层使用的是 Integer.valueOf(n2)
//自动拆箱
int n3 = integer2;//底层仍然使用的是 intValue()方法
}
}
小练习

包装类型和String类型的相互转换

01:
package TryCatchExercise;
public class WrapperVSString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//包装类(Integer)->String
Integer i = 100;
//1.
String str1 = i+"";
//2.
String str2 = i.toString();
//3.
String str3 = String.valueOf(i);
//String -> Integer
//1.
String str4 = "12345";
Integer i1 = Integer.parseInt(str4);
//2.
Integer integer = new Integer(str4);
}
}
Integer类和Character类的常用方法

小练习

01:
package AbstractDemo01;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i = new Integer(1);
Integer j = new Integer(1);
System.out.println(i==j);
//底层Integer.valueOf()
Integer n = 1;
Integer m = 1;
System.out.println(n==m);
//底层Integer.valueOf()
Integer x = 128;
Integer y = 128;
System.out.println(x==y);
// @IntrinsicCandidate
// public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
// if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
// return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
// return new Integer(i);
// }
// false
// true
// false
}
}
02:

String类的理解和创建对象

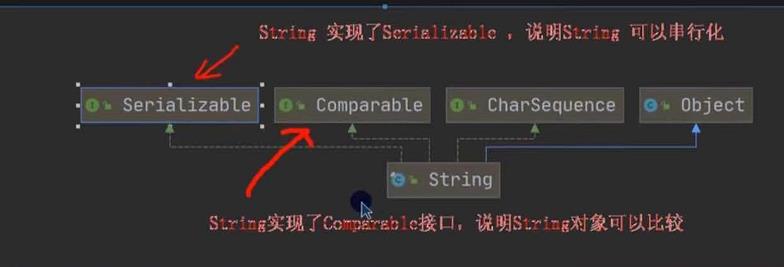
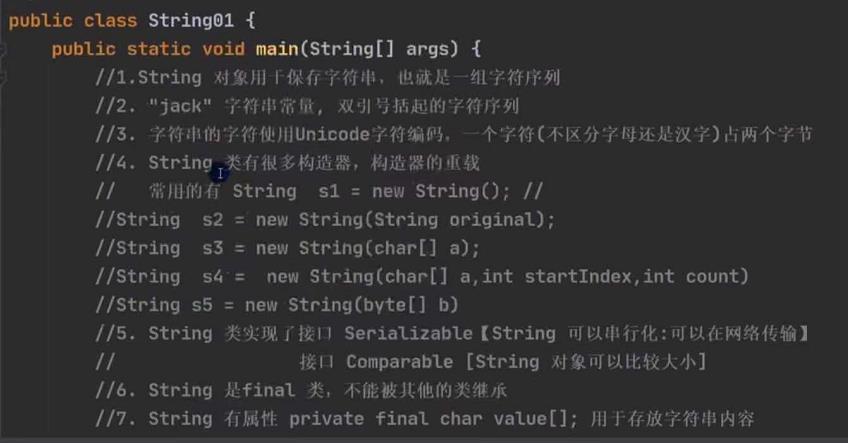
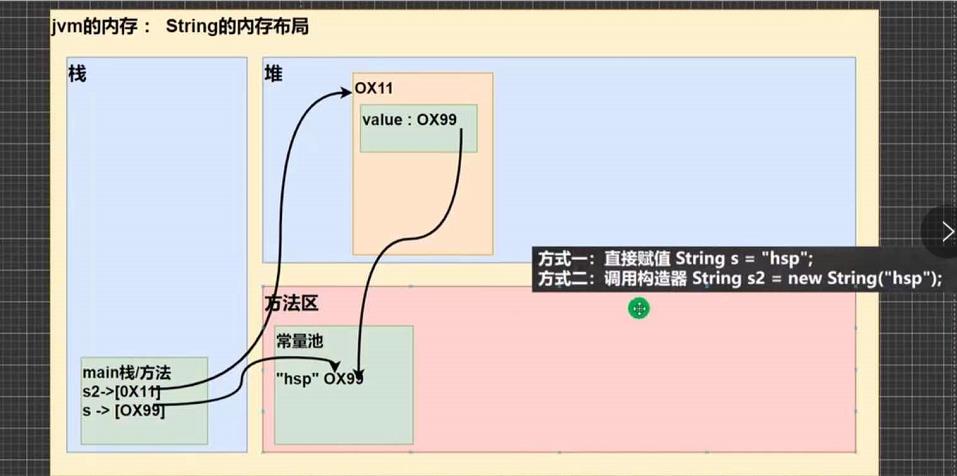
两种创建String对象的区别





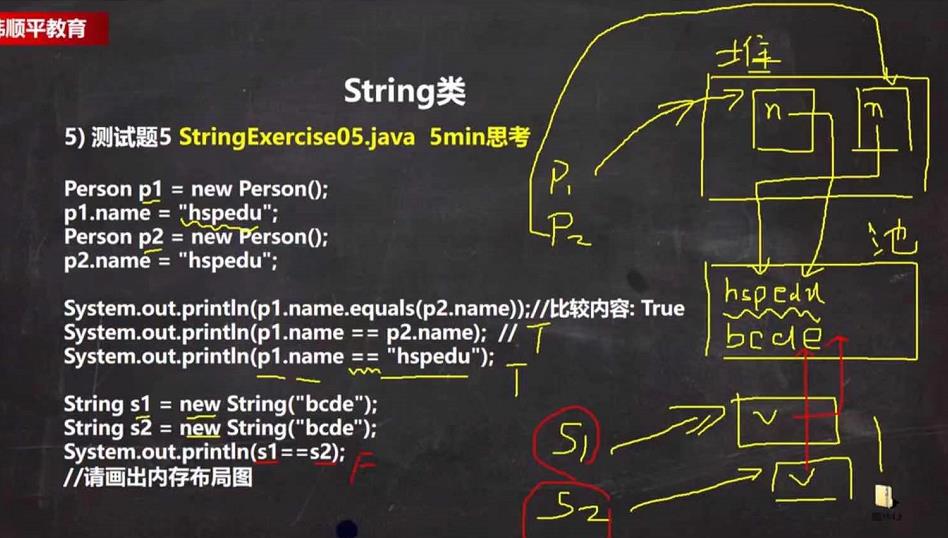
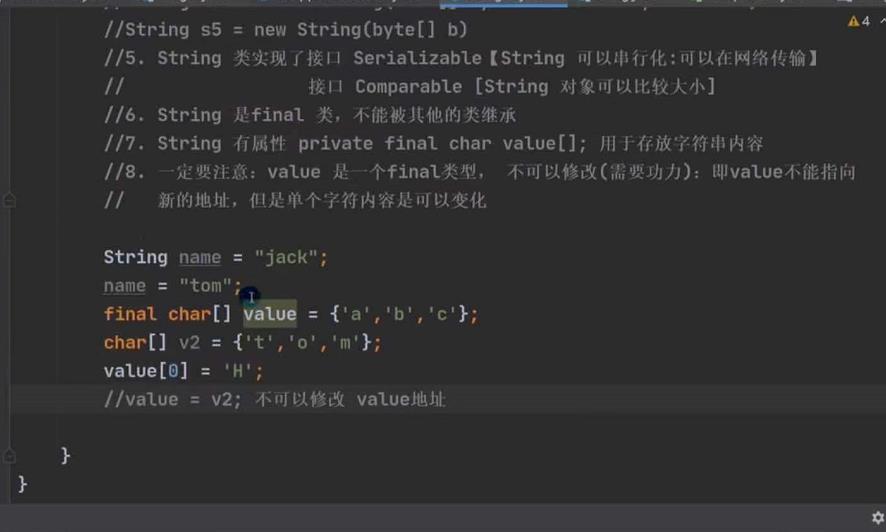
字符串的特性



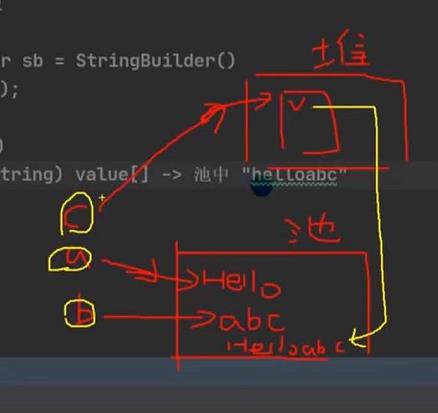
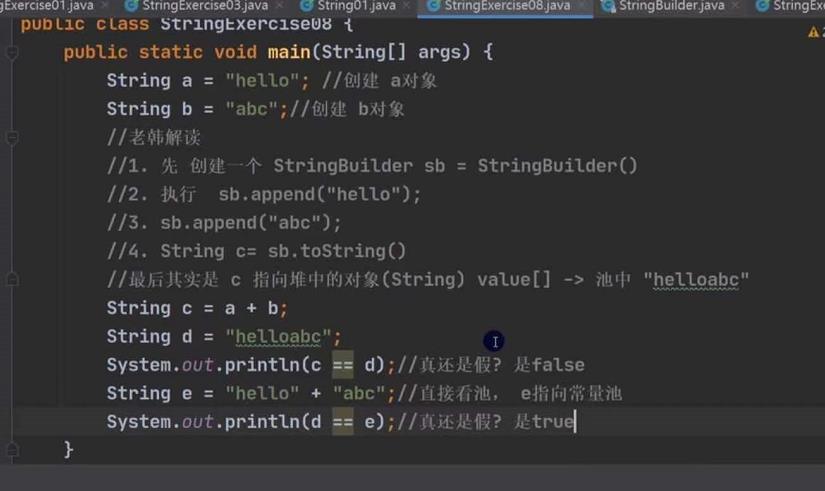


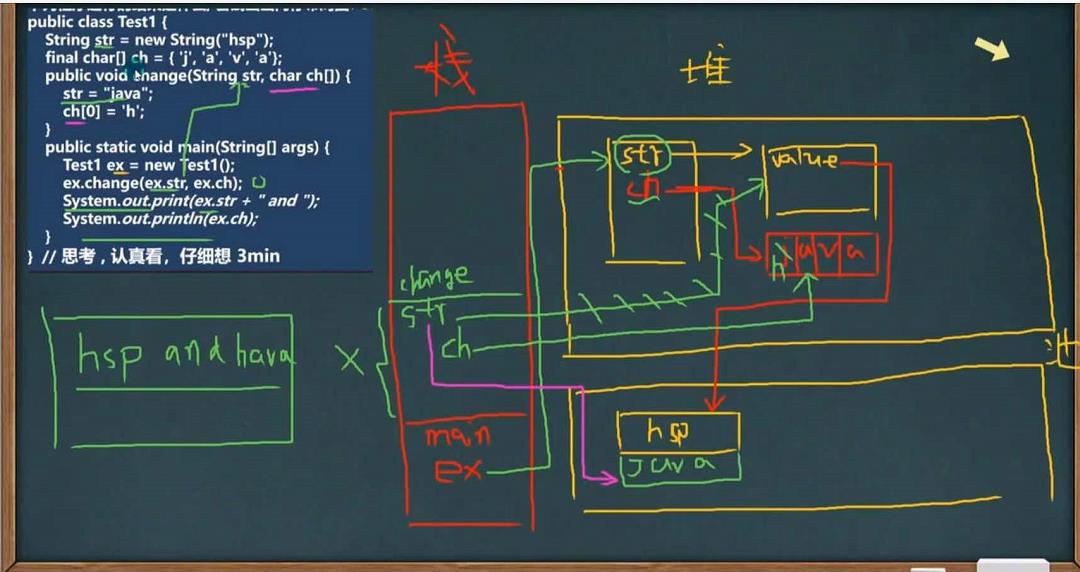
String类的常用方法







01:
package StringDemo01;
import java.util.Locale;
public class StringMethod01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "Hello";
System.out.println(str1.equals(str2));//false
String username = "join";
if ("join".equalsIgnoreCase(username))
{
System.out.println("join yes");//join yes
}
else
{
System.out.println("join no");
}
String username2 = "JoIn";
if ("join".equalsIgnoreCase(username2))
{
System.out.println("join yes");//join yes
}
else
{
System.out.println("join no");
}
System.out.println("jack".length());//4
String s1 = "wer@terwe@g";
int idx = s1.indexOf('@');
System.out.println(idx);//3
s1 = "wer@asdasda@ad";
idx = s1.lastIndexOf('@');
System.out.println(idx);//11
String name = "jackioio";
System.out.println(name.substring(6));//io
System.out.println(name.substring(0,3));//jac
String s = "hello";
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());//HELLO
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());//hello
String ss1 = "baoyu";
ss1 = s.concat("jack").concat("jxuad").concat("dasda");
System.out.println(ss1);//hellojackjxuaddasda
ss1 = "jack and mike jack";
ss1 = ss1.replace("jack","tom");
System.out.println(ss1);//tom and mike tom
String sss1 = "jack,miek,lll";
String[] split = sss1.split(",");
for (String v:split)
{
System.out.println(v);
// jack
// miek
// lll
}
String hhh = "hhkad\\\\asdas\\\\adas";
String[] hhhs = hhh.split("\\\\\\\\");
for (String v:hhhs)
{
System.out.println(v);
// hhkad
// asdas
// adas
}
String h1 = "dafsfsdf";
char [] chs = h1.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0;i< h1.length();i++)
{
System.out.println(chs[i]);
}
//1.如果长度相同,并且每个字符也相同,返回0
//2.如果长度相同或者不相同,但是在进行比较时,可以区分大小就返回
// if (c1 != c2)
// {
// return c1-c2;
// }
//3.如果前面的部分都相同,就返回str1.len-str2.len
String a = "jack";
String b = "apple";
System.out.println(b.compareTo(a));//-9
a = "jack1";
b = "jack111";
System.out.println(b.compareTo(a));//2
String studentname = "john";
int age = 10;
double score = 98.3/3;
char gender = '男';
String info = "My name is"+name+"age = "+age+"score = "+score+"gender = "+gender+"I want to make eyeryone happy";
String formatStr = "my name is%s age = %d score = %.2f gender = %c ";
String info2 = String.format(formatStr,name,age,score,gender);
System.out.println(info);
System.out.println(info2);
// My name isjackioioage = 10score = 32.766666666666666gender = 男I want to make eyeryone happy
// my name isjackioio age = 10 score = 32.77 gender = 男
}
}
StringBuffer类基本介绍
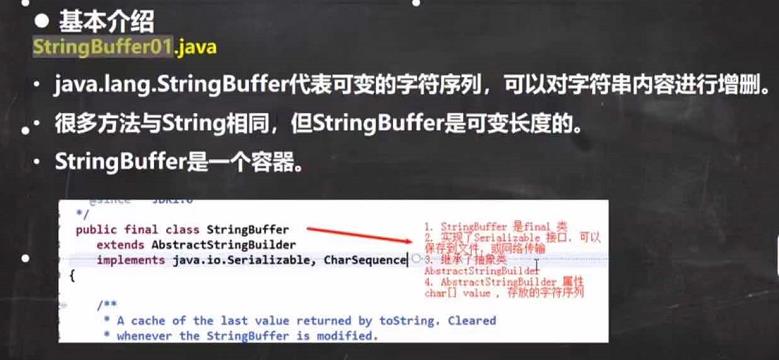
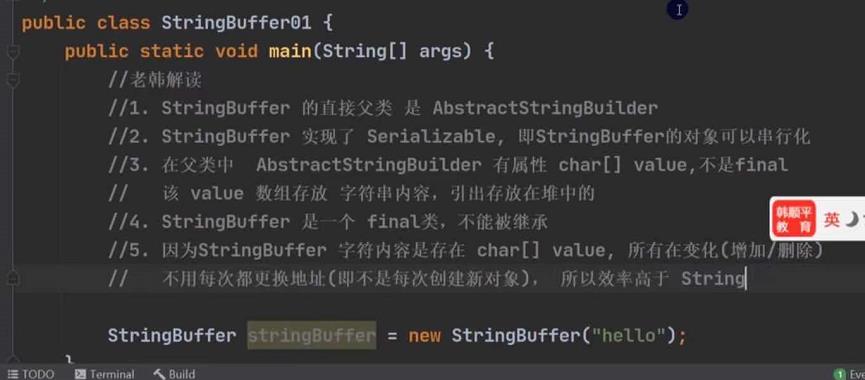
String VS StringBuffer

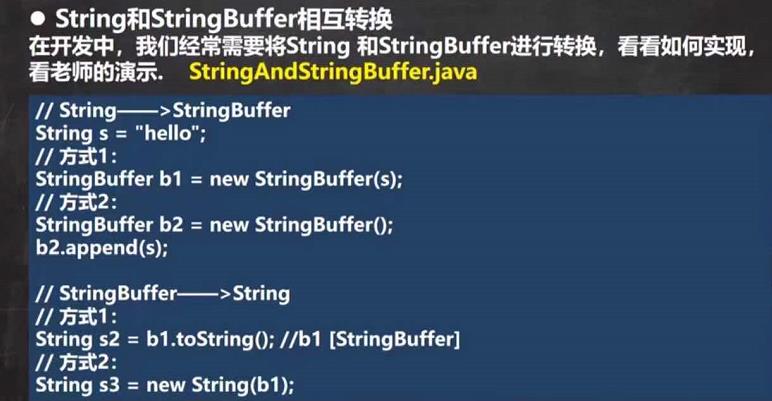
StringBuffer的构造器

01:
package StringBufferDemo01;
public class StringBufferDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建一个大小为16的char[],用于存放字符内容
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
//2.通过构造器指定char[]大小
StringBuffer stringBuffer1 = new StringBuffer(100);
//3.通过给一个String创建StringBuffer,char[]大小就是str.length()+16
String hello = new String("hello");
//String -> StringBuffer
String str = "hello tom";
//1.使用构造器
//注意:返回的才是StringBuffer对象,对str本身没有影响
StringBuffer stringBuffer2 = new StringBuffer(str);
//2.使用append方法
StringBuffer stringBuffer3 = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer append = stringBuffer3.append(str);
//StringBuffer -> String
//1.使用StringBuffer的toString方法
StringBuffer hspedu = new StringBuffer("hspedu");
String s = hspedu.toString();
//2.使用构造器
String s1 = new String(stringBuffer3);
}
}
StringBuffer类常见方法

01:
package StringBufferMethod;
public class StringBufferMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer hello = new StringBuffer("hello");
//增
hello.append(',');
hello.append("zsf");
hello.append("zhaom").append(100).append(true).append(10.5);
System.out.println(hello);
//删
hello.delete(11,14);//[11,14)
System.out.println(hello);
//改
hello.replace(9,11,"jack");//[9,11)
System.out.println(hello);
//插
hello.insert(9,"mike");//插在坐标为9的前面
System.out.println(hello);
int length = hello.length();
System.out.println(length);
}
}
小练习
01:

02:

package StringBufferMethod;
public class StringBufferExercise01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String price = "123565467894.59";
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer((price));
// int i = sb.lastIndexOf(".");
// sb = sb.insert(i-3,",");
// System.out.println(sb);
for (int i = sb.lastIndexOf(".");i-3 >0;i-=3)
{
sb = sb.insert(i-3,",");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
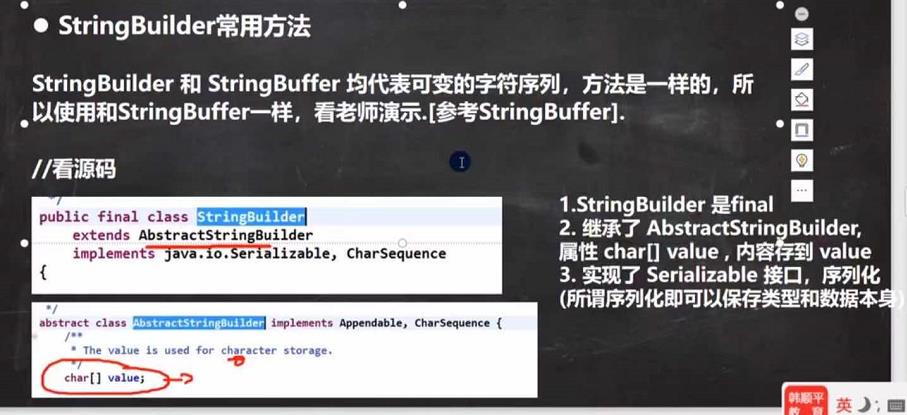
StringBuilder类结构剖析


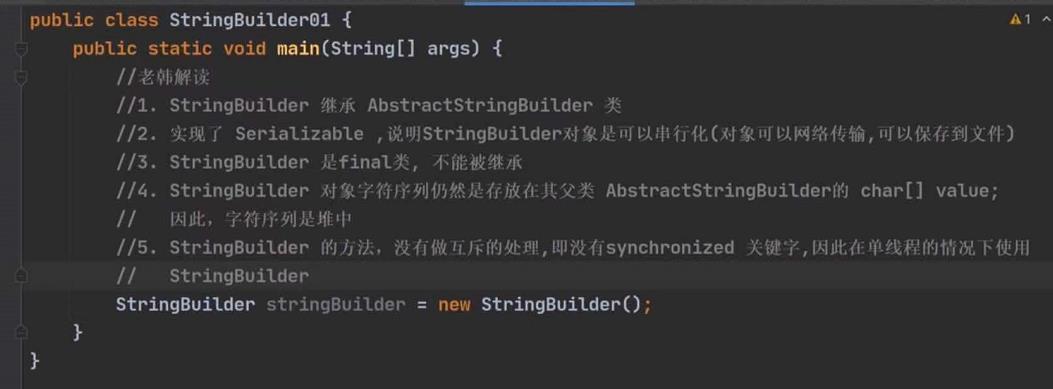



Math类


01:
package StringBufferMethod;
public class MathMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.abs 绝对值
int abs = Math.abs(9);
System.out.println(abs);
//2.pow 求幂
double pow = Math.pow(2,4);
System.out.println(pow);
//3.ceil 向上取整,返回>=该参数的最小整数
double ceil = Math.ceil(-3.0001);
System.out.println(ceil);
//4.floor 向下取整,返回<=该参数的最大整数
double floor = Math.floor(-4.999);
System.out