裸机开发框架构建之---点灯大师
Posted 菜鸟江多多
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了裸机开发框架构建之---点灯大师相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
实际设计代码,
总共分四层:硬件层—硬件接口层—设备管理层—应用层面
面向对象编程步骤:
3.设备管理层
1.首先对对象进行描述,有什么属性,任务要求可以实现什么功能,
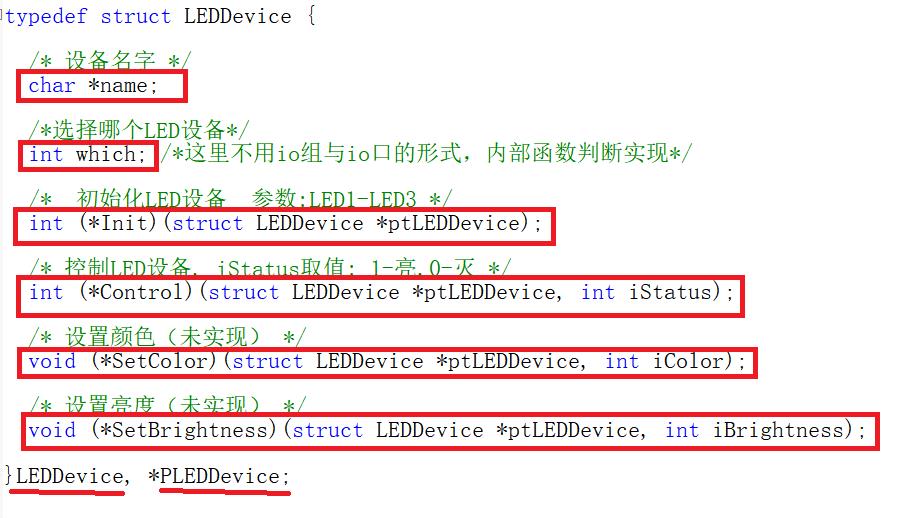
拿LED来说:使用需要初始化函数,可能有相同的多个设备,我们要准确控制哪一个设备的开关状态,颜色??亮度??根据项目需求可以自己设计,写法一般是把设备所有实现的功能抽象出一个结构体,实现函数啥的全部放到结构体里面,如下:
这里描述了设备名字,选择哪一个LED,初始化函数,控制LED的开关函数,设置LED颜色,亮度等等,这里的参数为结构体指针的形式
抽象出结构体
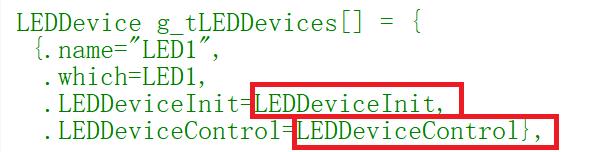
初始化结构体
结构体的初始化看相同设备的数量,如果数量比较多的话就用结构体数组,如果只是单个设备就用结构体变量,这里的初始化可以用两种形式,第一种c89标准下,这里描述相同设备比较多,使用结构体数组的形式
第一种初始化方法(c89标准)

第二种初始化方法(C99标准)
第二种c99以上标准,此种方法代码可读性更高(MDK下使用需要勾选C99标准)

这一层的函数还没实现
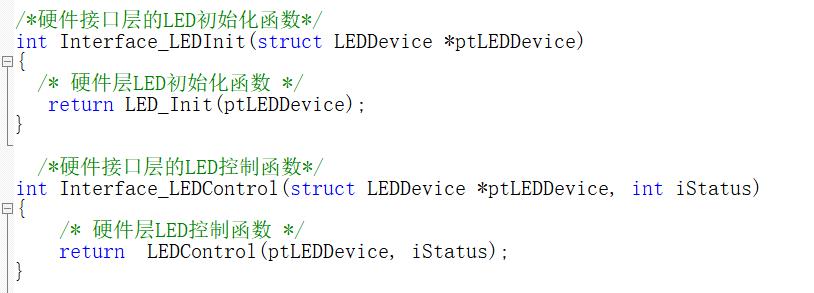
实现如下:可以看到,调用了硬件接口层的函数

接下来就实现硬件接口层的函数
2.硬件接口层
这一层仅仅是对硬件层的函数进行封装,比较简单
可以看到,就是一层包装而已,实现应用层和硬件层的分离
1.硬件层
这一层就是直接对硬件的操作,根据库不同和板子不同会有不同的写法,但是最终这个函数实现的,都将被硬件接口层封装
硬件LED层初始化函数
int LED_Init(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice)
{
static char ucLed=0;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct;
if (!ptLEDDevice) /* 防御式编程:判断为空指针 */
return -1;
switch (ptLEDDevice->which) /*选择使能哪个LED*/
{
case LED1:
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_8;
break;
}
case LED2:
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_9;
break;
}
case LED3:
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_10;
break;
}
default:
return -1;
}
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOD, ENABLE);/*锁存器时钟*/
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_2MHz;
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP;
GPIO_Init(GPIOC, &GPIO_InitStruct); //数据引脚
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_2;
GPIO_Init(GPIOD, &GPIO_InitStruct); //锁存引脚
GPIO_Write(GPIOC, ~ucLed <<8);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
return 0;
}
硬件层LED控制函数
int LEDControl(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iStatus)
{
BitAction pinstate;
if (!ptLEDDevice)
return -1;
pinstate = iStatus ? Bit_RESET : Bit_SET;
switch (ptLEDDevice->which)
{
case LED1:
{
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8,pinstate);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);/*锁存器引脚*/
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
break;
}
case LED2:
{
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_9,pinstate);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
break;
}
case LED3:
{
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_10,pinstate);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
break;
}
default:
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
这里有三个设备,如何使用某一个LED设备,这里在设备管理层还写了这么一个函数
定义一个指针函数,这里传输的参数是witch,通过输入witch值确定哪一个数组
PLEDDevice GetLEDDevice(int which)
{
if (which >= LED1 && which <= LED3)
return &g_tLEDDevices[which];
else
return NULL;
}
4.应用层
最后应用测试代码
void Led_test(void)
{
PLEDDevice PLED1 = GetLEDDevice(LED1);
PLEDDevice PLED2 = GetLEDDevice(LED2);
PLEDDevice PLED3 = GetLEDDevice(LED3);
PLED1->Init(PLED1);
PLED2->Init(PLED2);
PLED3->Init(PLED3);
PLED1->Control(PLED1, 0); /*打开设备*/
PLED2->Control(PLED2, 0);
PLED3->Control(PLED3, 0);
}
整体源代码(mdk4下调试编译通过,主控STM32F103RB)
硬件层
led.c
#include "led.h"
/*硬件层LED函数的初始化,返回值:-1失败,0:成功*/
int LED_Init(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice)
{
static char ucLed=0;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct;
if (!ptLEDDevice) /* 防御式编程:判断为空指针 */
return -1;
switch (ptLEDDevice->which) /*选择使能哪个LED*/
{
case LED1:
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_8;
break;
}
case LED2:
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_9;
break;
}
case LED3:
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOC, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_10;
break;
}
default:
return -1;
}
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOD, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_2MHz;
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_Out_PP;
GPIO_Init(GPIOC, &GPIO_InitStruct); //数据引脚
GPIO_InitStruct.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_2;
GPIO_Init(GPIOD, &GPIO_InitStruct); //锁存引脚
GPIO_Write(GPIOC, ~ucLed <<8);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
return 0;
}
int LEDControl(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iStatus)
{
BitAction pinstate;
if (!ptLEDDevice)
return -1;
pinstate = iStatus ? Bit_RESET : Bit_SET;
switch (ptLEDDevice->which)
{
case LED1:
{
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_8,pinstate);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);/*锁存器*/
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
break;
}
case LED2:
{
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_9,pinstate);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
break;
}
case LED3:
{
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIOC,GPIO_Pin_10,pinstate);
GPIO_SetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
GPIO_ResetBits(GPIOD,GPIO_Pin_2);
break;
}
default:
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
led.h
#ifndef __LED_H
#define __LED_H
#include "stm32f10x.h"
#include "bsp_interface_led.h"
#include "bsp_device_led.h"
int LEDControl(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iStatus);/*LED控制函数*/
int LED_Init(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice);
#endif
硬件接口层
bsp_interface_led.c
#include "bsp_interface_led.h"
#include "bsp_device_led.h"
#include "led.h"
/*硬件接口层的LED初始化函数*/
int Interface_LEDInit(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice)
{
/* 硬件层LED初始化函数 */
return LED_Init(ptLEDDevice);
}
/*硬件接口层的LED控制函数*/
int Interface_LEDControl(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iStatus)
{
/* 硬件层LED控制函数 */
return LEDControl(ptLEDDevice, iStatus);
}
bsp_interface_led.h
#ifndef __BSP_LED_INTERFACE_H
#define __BSP_LED_INTERFACE_H
#include "bsp_device_led.h"
int Interface_LEDInit(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice);
int Interface_LEDControl(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iStatus);
#endif /* __BSP_LED_INTERFACE_H */
设备管理层
bsp_device_led.c
#include "bsp_device_led.h"
#include "bsp_interface_led.h"
/*设备管理层的LED初始化函数*/
int LEDDeviceInit(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice)
{
/*硬件接口层的LED初始化函数*/
return Interface_LEDInit(ptLEDDevice);
}
/*设备管理层的LED控制函数*/
int LEDDeviceControl(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iStatus)
{
/*硬件接口层的LED控制函数*/
return Interface_LEDControl(ptLEDDevice,iStatus);
}
LEDDevice g_tLEDDevices[] = {
{"LED1",LED1, LEDDeviceInit, LEDDeviceControl},
{"LED2",LED2, LEDDeviceInit, LEDDeviceControl},
{"LED3",LED3, LEDDeviceInit, LEDDeviceControl},
};
/* C99标准可写成以下形式
LEDDevice g_tLEDDevices[] = {
{.name="LED1",
.which=LED1,
.LEDDeviceInit=LEDDeviceInit,
.LEDDeviceControl=LEDDeviceControl},
{.name="LED2",
.which=LED2,
.LEDDeviceInit=LEDDeviceInit,
.LEDDeviceControl=LEDDeviceControl},
{.name="LED3",
.which=LED3,
.LEDDeviceInit=LEDDeviceInit,
.LEDDeviceControl=LEDDeviceControl},
};
*/
PLEDDevice GetLEDDevice(int which)
{
if (which >= LED1 && which <= LED3)
return &g_tLEDDevices[which];
else
return NULL;
}
bsp_device_led.c
#ifndef __BSP_LED_DEVICE_H
#define __BSP_LED_DEVICE_H
#ifndef NULL
#define NULL (void *)0
#endif
#define LED1 0
#define LED2 1
#define LED3 2
typedef struct LEDDevice {
/* 设备名字 */
char *name;
/*选择哪个LED设备*/
int which; /*这里不用io组与io口的形式,内部函数判断实现*/
/* 初始化LED设备 参数:LED1-LED3 */
int (*Init)(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice);
/* 控制LED设备, iStatus取值: 1-亮,0-灭 */
int (*Control)(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iStatus);
/* 设置颜色(未实现) */
void (*SetColor)(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iColor);
/* 设置亮度(未实现) */
void (*SetBrightness)(struct LEDDevice *ptLEDDevice, int iBrightness);
}LEDDevice, *PLEDDevice;
PLEDDevice GetLEDDevice(int which);
#endif /* __BSP_LED_DEVICE_H */
应用层
void Led_test(void)
{
PLEDDevice PLED1 = GetLEDDevice(LED1);
PLEDDevice PLED2 = GetLEDDevice(LED2);
PLEDDevice PLED3 = GetLEDDevice(LED3);
PLED1->Init(PLED1);
PLED2->Init(PLED2);
PLED3->Init(PLED3);
PLED1->Control(PLED1, 1); /*打开设备*/
PLED2->Control(PLED2, 1);
PLED3->Control(PLED3, 1);
}
源工程下载链接
git地址:https://gitee.com/he-dejiang/framework.git
以上是关于裸机开发框架构建之---点灯大师的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章