BMP格式函数分析器java语言数学分析项目
Posted 九死九歌
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了BMP格式函数分析器java语言数学分析项目相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、项目简介:
先给大家看一下这个小项目的效果:

运行后生成的pic.bmp图片
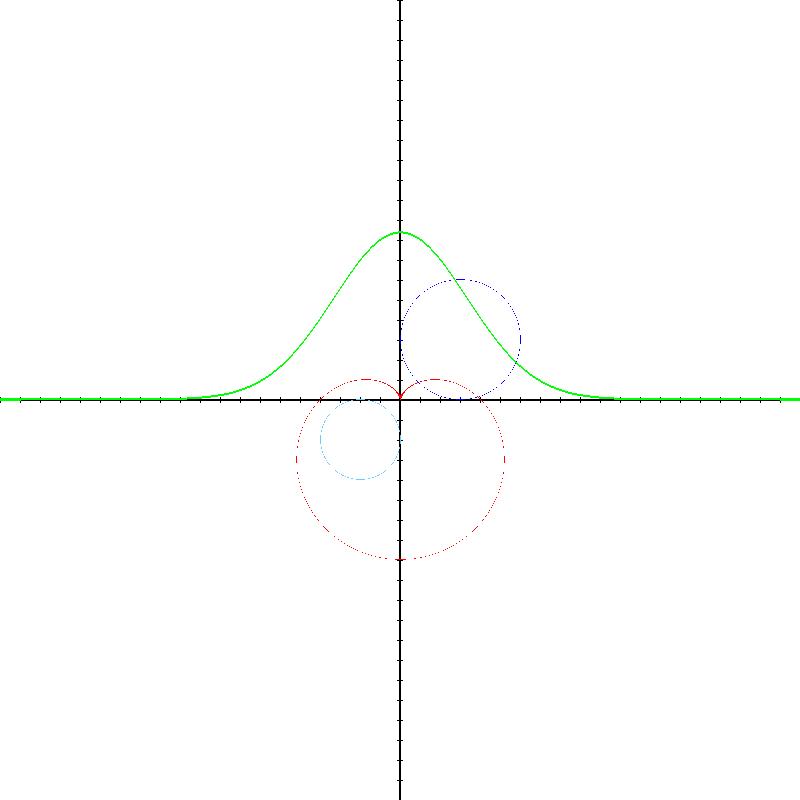
没错,这个项目的主要功能就是通过函数生成对应的图像。
主要是用到的技术有:IO流、BMP格式分析、面向对象程序设计。
项目结构如下:
Main类主要用来测试,剩下的三个类我会在下面一一介绍。
二、项目内容:
① Color类
众所周知,图片其实就是由像素组成的二维矩阵,那我们肯定就要构建一个Color类表示像素了,图片信息的存储就是一个Color类型二维数组存储。
package www.spd.pic;
public class Color {
public static final Color BLACK = new Color((byte)0x00, (byte)0x00, (byte)0x00);
public static final Color RED = new Color((byte)0xff, (byte)0x00, (byte)0x00);
public static final Color GREEN = new Color((byte)0x00, (byte)0xff, (byte)0x00);
public static final Color BLUE = new Color((byte)0x00, (byte)0x00, (byte)0xff);
byte red;
byte green;
byte blue;
/**
* 三个参数分别是三种三原色对应的数值
* @param red 红色
* @param green 绿色
* @param blue 蓝色
*/
public Color(byte red, byte green, byte blue) {
this.red = red;
this.green = green;
this.blue = blue;
}
/**
* 继承{@link Object#toString()}方法,以实现方便输出
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
int r = red >= 0 ? red : (red + 0x100);
int g = green >= 0 ? green : (green + 0x100);
int b = blue >= 0 ? blue : (blue + 0x100);
return String.format("#%02x%02x%02x", r, g, b);
}
/**
* 将颜色信息转换成字节数组
* @return
*/
public byte[] toByteArray() {
byte[] arr = new byte[3];
arr[0] = blue;
arr[1] = green;
arr[2] = red;
return arr;
}
}
② BMP类:
对于BMP的文件格式分析详见这篇博文,写的很详细,我的项目就是参考了这篇博文:位图(bmp)文件格式分析。
package www.spd.pic;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class BMP {
//文件名
String name;
//整个BMP文件的大小
int bfSize;
//位图的宽度,单位是像素
int biWidth;
//位图的高度,单位是像素
int biHeight;
//位图全部像素占用的字节数,BI_RGB时可设为0
int biSizeImage;
//因为32位的Windows操作系统处理4个字节(32位)的速度比较快,所以BMP的每一行颜色占用的字节数规定为4的整数倍。
//如果一行颜色有两个像素,共占用6字节,如果要补齐4*2=8字节,就要再加两个0字节。
//经计算,appendBit = biWidth % 4;
int appendBytes;
//表示一行像素真正占多少字节,即本身要占的字节加上补齐字节
int widthBytes;
//图片的像素信息
Color[][] pixelsMatrix;
public BMP(String path) {
this(new File(path));
}
/**
* 通过传参{@link java.io.File}获得图片的各种信息(即所有的成员变量)
* @param file BMP文件
*/
public BMP(File file) {
/* 获得文件名称并通过后缀名利用正则表达式判断是不是标准的bmp图片文件 */
name = file.getName();
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(".*\\\\.bmp");
Matcher m = p.matcher(name);
if (!m.find()) throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件后缀不正确!!");
/* 获得字节数组 */
byte[] arr = getByteArray(file);
if (arr == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件为空文件!!");
/* bmp文件前两字节是“bm”即0x4d42,用来做标识,若前两位不是该字节则抛出异常 */
int bfType = byteArrayToInteger(arr, 1, 0);
if (bfType != 0x4d42) throw new IllegalArgumentException("文件受损!!");
bfSize = byteArrayToInteger(arr, 0x5, 0x2);
biWidth = byteArrayToInteger(arr, 0x15, 0x12);
biHeight = byteArrayToInteger(arr, 0x19, 0x16);
/* 1c到1f位表示一个像素占多少位,24位则是常用的十六进制颜色表示所对应的,两位就是黑白图片 */
int biBitCount = byteArrayToInteger(arr, 0x1f, 0x1c);
if (biBitCount != 24) throw new IllegalArgumentException("图片不是24位真色彩位图!!");
biSizeImage = byteArrayToInteger(arr, 0x27, 0x24);
appendBytes = biWidth % 4;
widthBytes = biWidth * 3 + appendBytes;
pixelsMatrix = new Color[biHeight][biWidth];
/* 双层for循环获取像素信息 */
for (int i = 0; i < biHeight; i++) {
int pixelEnd = (biHeight - i - 1) * widthBytes + 0x36;
for (int j = 0; j < biWidth; j++) {
pixelsMatrix[i][j] = new Color(arr[pixelEnd + 2], arr[pixelEnd + 1], arr[pixelEnd]);
pixelEnd += 3;
}
}
}
/**
* 获得某种颜色的图片
* @param color 若传参红则为一张只有红色的图片。以此类推
* @param name 文件名
* @param width 图片宽度
* @param height 图片高度
*/
public BMP(Color color, String name, int width, int height) {
this.name = name;
biWidth = width;
biHeight = height;
appendBytes = biWidth % 4;
widthBytes = biWidth * 3 + appendBytes;
pixelsMatrix = new Color[biHeight][biWidth];
/* 遍历矩阵把color传参给每一个像素 */
for (int i = 0; i < biHeight; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < biWidth; j++) {
pixelsMatrix[i][j] = color;
}
}
biSizeImage = widthBytes * height;
bfSize = biSizeImage + 0x36;
}
public BMP(String name, int width, int height) {
this(new Color((byte)0xff, (byte)0xff, (byte)0xff), name, width, height);
}
public BMP(Color color, int width, int height) {
this(color, "pic.bmp", width, height);
}
public BMP(int width, int height) {
this("pic.bmp", width, height);
}
/**
* 继承{@link Object#toString()}实现打印图片信息
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
return "BMP{" +
"\\n\\tname=\\"" + name +
"\\", \\n\\tbfSize=" + bfSize +
", \\n\\tbiWidth=" + biWidth +
", \\n\\tbiHeight=" + biHeight +
", \\n\\tbiSizeImage=" + biSizeImage +
", \\n\\tappendBytes=" + appendBytes +
", \\n\\twidthBytes=" + widthBytes +
"\\n}";
}
/**
* 通过传参{@link java.io.File} 并利用缓冲流{@link java.io.BufferedInputStream}获得其字节流
* @param file bmp文件
* @return 图片文件的字节流
*/
private static byte[] getByteArray(File file) {
try(BufferedInputStream bis =
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream(file));
ByteArrayOutputStream baos =
new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
int len = -1;
byte[] flush = new byte[1024];
while ((len = bis.read(flush)) != -1) {
baos.write(flush, 0, len);
baos.flush();
}
return baos.toByteArray();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.err.println("文件不存在!!");
return null;
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("IO操作出现异常!!");
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 该方法与{@link #integerToByteArray(int, int)}相反<br/>
* 获得字节数组的某几位对应的整型数<br/>
* 主要在中{@link #BMP(File)}中调用
* @param arr 字节数组
* @param begin 开始索引
* @param end 结束索引
* @return 对应的整型数
*/
private int byteArrayToInteger(byte[] arr, int begin, int end) {
int ans = 0;
int temp;
if (begin <= end) {
for (int i = begin; i <= end; i++) {
ans *= 0x100;
temp = arr[i] >= 0 ? arr[i] : (arr[i] + 128);
ans += temp;
}
}
if (begin > end) {
for (int i = begin; i >= end; i--) {
ans *= 0x100;
temp = arr[i] >= 0 ? arr[i] : (arr[i] + 128);
ans += temp;
}
}
return ans;
}
/**
* 该方法与{@link #byteArrayToInteger(byte[], int, int)}相反<br/>
* 获得整型数对应的字节数组
* 重要在{@link #toByteArray()}中调用
* @param size 返回的数组占几个字节
* @param num 整型数的值
* @return 返回的字节数组
*/
private byte[] integerToByteArray(int size, int num) {
byte[] arr = new byte[size];
int i = 0;
while (num > 0) {
byte temp = (byte) (num % 0x100);
num /= 0x100;
try {
arr[i] = temp;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("数字数值大于2^"+size);
}
i++;
}
return arr;
}
/**
* 把图片文件整个转化成字节流
* @return 图片文件对应的字节流
*/
public byte[] toByteArray() {
try(ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
baos.write("BM".getBytes());
baos.write(integerToByteArray(4, bfSize));
baos.write(new byte[4]);
baos.write(integerToByteArray(4, 0x36));
baos.flush();
baos.write(integerToByteArray(4, 40));
baos.write(integerToByteArray(4, biWidth));
baos.write(integerToByteArray(4, biHeight));
baos.write(integerToByteArray(2, 1));
baos.write(integerToByteArray(2, 24));
baos.write(new byte[4]);
baos.write(integerToByteArray(4, biSizeImage));
baos.write(new byte[16]);
baos.flush();
byte[] append = new byte[appendBytes];
for (int i = biHeight - 1; i >= 0 ; i--) {
for (int j = 0; j < biWidth; j++) {
baos.write(pixelsMatrix[i][j].toByteArray());
}
baos.write(append);
baos.flush();
}
return baos.toByteArray();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("IO操作出现异常!!");
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 把图片文件的字节流通过输出流{@link java.io.FileOutputStream}写入到外部文件中去
*/
public void createFile() {
byte[] arr = toByteArray();
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(name)) {
fos.write(arr);
fos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("将图像对象写入成图像时出线IO异常!!");
}
}
}
③ getPicByFunc类:
从字面意义上来看:“从函数获得图像类”,它的下面有一个内部接口Functial,即可作为函数的,一个内部类Function,里面有一个Functial对象,和一个Color对象,表示的是一个带颜色的函数。
package www.spd.pic;
public class getPicByFunc {
public static BMP getPic(Function func, int size) {
return getPic("pic.bmp", func, size);
}
public static BMP getPic(String name, Function func, int size) {
return getPic(name, new Function[]{func}, size);
}
public static BMP getPic(Function[] functions, int size) {
return getPic("pic.bmp", functions, size);
}
/**
*
* @param name 写出的文件名
* @param functions 几个函数
* @param size 图片尺寸
* @return 返回图片
*/
public static BMP getPic(String name, Function[] functions, int size) {
BMP pic = new BMP(name, size * 40, size * 40以上是关于BMP格式函数分析器java语言数学分析项目的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章