Notes5剑指offer_21-40题
Posted 码农编程录
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Notes5剑指offer_21-40题相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
21.调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面

class Solution {
public int[] exchange(int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while(left < right)
{
//从左往右找偶数 找到偶数 停止
while(left < right && nums[left] % 2 == 1) left ++;
//从右往左找奇数 找到奇数停止
while(left < right && nums[right] % 2 == 0) right --;
if(left < right)
{
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
}
}
return nums;
}
}
22.链表中倒数第k个节点

class Solution {
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
//单个指针 走到头 len
//从头走 len - k
//双指针
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = head;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i ++)
{
//k 大于链表长度
if(first == null) return null;
first = first.next;
}
while(first != null)
{
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
return second;
}
}
23.链表中环的入口结点

class Solution {
public ListNode entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode head) {
/*
//hash表 从头到尾遍历
Set<ListNode> hash = new HashSet<>();
while(head != null)
{
if(!hash.add(head))
return head;
head = head.next;
}
return null;
*/
//快慢指针
ListNode slow = head;//走一步
ListNode fast = head;//走两步
while(fast != null)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if(fast == slow)
{
slow = head;
while(slow != fast)
{
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
}
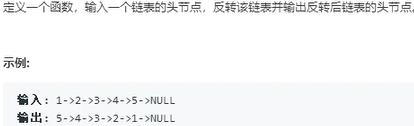
24.反转链表
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while(cur != null)
{
//让cur指向 pre
//然后 pre cur 都往后走一个
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
25.合并两个排序的链表

class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
//归并排序思想
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while(l1 != null && l2 != null)
{
if(l1.val <= l2.val)
{
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
else
{
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(l1 != null)
{
cur.next = l1;
}
if(l2 != null)
{
cur.next = l2;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
26.树的子结构

class Solution {
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
//递归
//A根 B根
//A左子树 B
//A右子树 B
if(A == null || B == null) return false;
return (issubtree(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B)|| isSubStructure(A.right, B));
}
public boolean issubtree(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
//true
if(B == null) return true;
//false
if(A == null || A.val != B.val) return false;
return issubtree(A.left, B.left) && issubtree(A.right, B.right);
}
}
27.二叉树的镜像

class Solution {
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
//左右子树交换
if(root == null) return null;
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(temp);
return root;
}
}
28.对称的二叉树

class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return true;
return dfs(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean dfs(TreeNode left, TreeNode right)
{
if(left == null && right == null) return true;
if(left == null || right == null || left.val != right.val) return false;
return dfs(left.left, right.right) && dfs(left.right, right.left);
}
}
29.顺时针打印矩阵

class Solution {
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
//判断边界
if(matrix.length == 0)
return new int[0];
//右下左上
int left = 0, right = matrix[0].length -1, up = 0, down = matrix.length - 1;
int num = 0;
int[] res = new int[(right + 1) * (down + 1)];
while(true)
{
//右
for(int i = left; i <= right; i ++)
res[num ++] = matrix[up][i];
if(++ up > down) break;
//下
for(int i = up; i <= down; i ++)
res[num ++] = matrix[i][right];
if(-- right < left ) break;
//左
for(int i = right; i >= left; i --)
res[num ++] = matrix[down][i];
if(-- down < up) break;
//上
for(int i = down; i >= up; i --)
res[num ++] = matrix[i][left];
if(++ left > right) break;
}
return res;
}
}
30.包含min函数的栈

class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> A, B;//A正常的栈 B记录最小元素的栈
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
A = new Stack<>();
B = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
//判断当前元素 和栈内最小的元素 对比
A.add(x);
if(B.empty() || B.peek() >= x)
B.add(x);
}
public void pop() {
//栈顶元素 是不是 最小的
//if(A.pop().equals(B.peek()))
// B.pop();
if(A.peek().equals(B.peek()))//不能用 == 必须用 equals
B.pop();
A.pop();
}
public int top() {
//直接写
return A.peek();
}
public int min() {
//找到栈内最小的元素 直接写
return B.peek();
}
}
31.栈的压入、弹出序列

class Solution {
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack<Integer> temp = new Stack<>();
int i = 0;
for(int num : pushed)
{
temp.push(num);//入栈
//模拟出栈
while(!temp.isEmpty() && temp.peek() == popped[i])
{
temp.pop();
i ++;
}
}
return temp.isEmpty();
}
}
32.从上到下打印二叉树

class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new int[0];
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
//队列操作 保存根节点
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
//根结点
TreeNode r = q.poll();
ans.add(r.val);
//左子树
if(r.left != null) q.add(r.left);
//右子树
if(r.right != null) q.add(r.right);
}
int[] res = new int[ans.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i ++)
res[i] = ans.get(i);
return res;
}
}
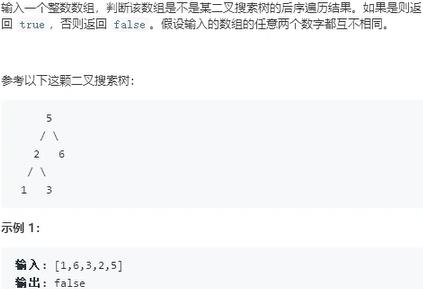
33.二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
class Solution {
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
//左<根<右 二叉检索树
//后序遍历
//左右根
//递归
return dfs(postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
public boolean dfs(int[] arr, int l, int r)
{
if(l >= r) return true;//遍历到最后 都是true
//r对应 当前子树 根节点
//找到左右子树的临界点
int p = l;
while(arr[p] < arr[r]) p ++;
int m = p;
while(arr[p] > arr[r]) p ++;
return (p == r) && dfs(arr, l, m - 1) && dfs(arr, m, r - 1);
}
}
34.二叉树中和为某一值的路径


class Solution {
//前序遍历 根左右
LinkedList<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();//所有路径
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();//单条路径
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
//递归函数
recur(root, sum);
return res;
}
void recur(TreeNode root, int target){
//找到 target = 0时候的叶节点
if(root == null) return;
path.add(root.val);
target -= root.val;
if(target == 0 &&以上是关于Notes5剑指offer_21-40题的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章