SinGAN一张照片即可生成同样的照片(附简化版代码)
Posted AI信仰者
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SinGAN一张照片即可生成同样的照片(附简化版代码)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、摘要
本文主要讲解:SinGAN-一张照片即可生成一模一样的照片(附简化版代码)
主要思路:
- 先由一个Z_N输入到G_N的生成器得到生成图像(这一步是单纯由噪声生成,其他生成器的输入都是由随机噪声图像z_n和上一层生成的 上采样到当前生成器尺寸组成)。
- 接着利用生成图像的图像块(每一层图像块的大小不一样,按照由粗糙到精细、由大到小)和当前层的图像块(由训练数据下采样得到)放入判别器中进行判断,直到两者不能被判别器区分。
- 通过这种一层一层、由下往上的训练过程,得到最终的结果。
2、相关技术
SinGAN架构
一种基于层级的patch-GAN模型(Markovian discriminator)。如下图所示,模型的每个部分负责输入图像的不同尺度捕获图像块分布。这种层级GAN模型感受野小和有限的功能,可以防止网络记住整图的信息。虽然类似的网络结构被应用过,但这是首次应用在一张图像的内部学习上。
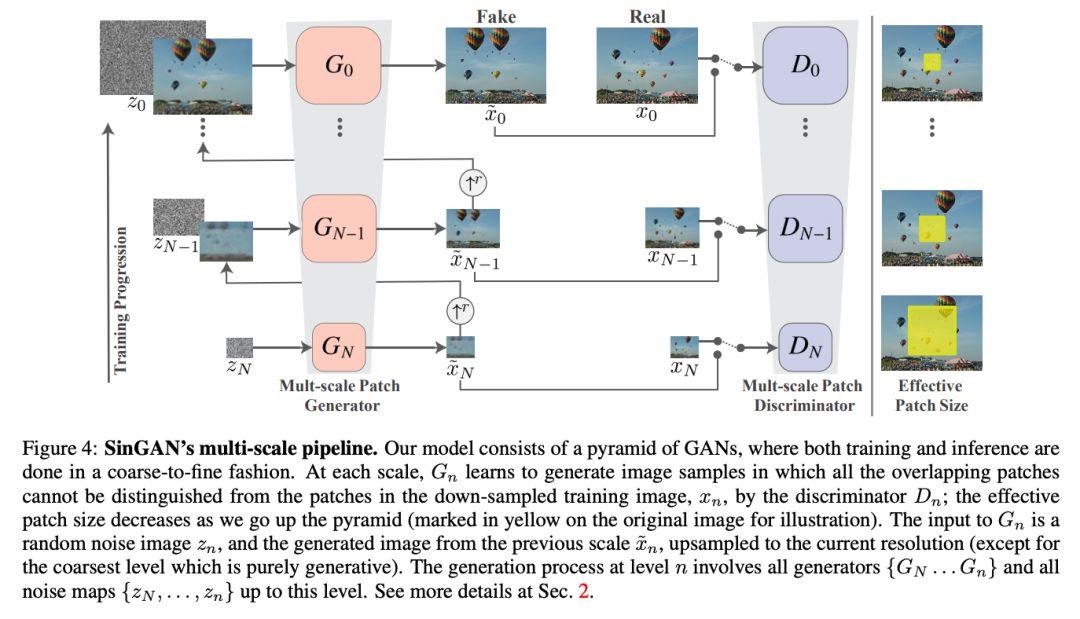
模型是由金字塔形式大小的生成器 组成,训练数据 也是金字塔形式大小组成,训练数据是由一个 因子控制,一些r>0。根据每层 的图像块分布,相应层的生成器 产生真实的图像实例。然后通过对抗学习,判别器 通过对生成器 产生的图像块(生成图像的某一部分)进行判别,达到相对较好的状态(以目前来说达不到最终的纳什均衡点),最后完成训练过程。
从刚刚的图中我们可以看到,每个尺度注入噪声后,先由粗糙的尺度开始生成图像,然后按照相应的顺序传递到相对应的生成器,最终生成精细的尺度;某一层的所有生成器和判别器有着相同的感受野,随着由下往上的生成过程,因此可以捕获尺度减小的结构信息。
3、完整代码和步骤
算法训练的效果如此视频:
SinGAN训练过程
主运行程序入口
import os
from SinGAN.run_train import functions
from SinGAN.run_train.manipulate import SinGAN_generate
from SinGAN.run_train.training import train
from SinGAN.run_train.config import get_arguments
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = get_arguments()
parser.add_argument('--input_dir', help='input image dir', default='../Input/Images')
parser.add_argument('--input_name', help='input image name', default='food.jpg')
parser.add_argument('--mode', help='task to be done', default='train')
opt = parser.parse_args()
#
opt = functions.post_config(opt)
Gs = []
Zs = []
reals = []
NoiseAmp = []
dir2save = functions.generate_dir2save(opt)
if (os.path.exists(dir2save)):
print('trained model already exist')
else:
try:
os.makedirs(dir2save)
except OSError:
pass
# 将图片读取成torch版的数据
real = functions.read_image(opt)
# 将图片适配尺寸
functions.adjust_scales2image(real, opt)
# 开始训练模型 opt 手动输入的参数
train(opt, Gs, Zs, reals, NoiseAmp)
# 根据模型生成图片 生成具有任意大小和比例的新图像
SinGAN_generate(Gs, Zs, reals, NoiseAmp, opt)
training.py
import os
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.utils.data
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from SinGAN.run_train import functions, models
from SinGAN.run_train.imresize import imresize
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def train(opt, Gs, Zs, reals, NoiseAmp):
real_ = functions.read_image(opt)
in_s = 0
scale_num = 0
# 计算局部权重 调整大小
real = imresize(real_, opt.scale1, opt)
# 创造真实图片的锥体
reals = functions.creat_reals_pyramid(real, reals, opt)
nfc_prev = 0
# 全卷积GANs组成的金字塔
while scale_num < opt.stop_scale + 1:
opt.nfc = min(opt.nfc_init * pow(2, math.floor(scale_num / 4)), 128)
opt.min_nfc = min(opt.min_nfc_init * pow(2, math.floor(scale_num / 4)), 128)
opt.out_ = functions.generate_dir2save(opt)
opt.outf = '%s/%d' % (opt.out_, scale_num)
try:
os.makedirs(opt.outf)
except OSError:
pass
plt.imsave('%s/in.png' % (opt.out_), functions.convert_image_np(real), vmin=0, vmax=1)
plt.imsave('%s/original.png' % (opt.out_), functions.convert_image_np(real_), vmin=0, vmax=1)
plt.imsave('%s/real_scale.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(reals[scale_num]), vmin=0, vmax=1)
D_curr, G_curr = init_models(opt)
if (nfc_prev == opt.nfc):
# 加载训练好的模型
G_curr.load_state_dict(torch.load('%s/%d/netG.pth' % (opt.out_, scale_num - 1)))
D_curr.load_state_dict(torch.load('%s/%d/netD.pth' % (opt.out_, scale_num - 1)))
z_curr, in_s, G_curr = train_single_scale(D_curr, G_curr, reals, Gs, Zs, in_s, NoiseAmp, opt)
# 是否固定部分参数进行网络训练
G_curr = functions.reset_grads(G_curr, False)
G_curr.eval()
D_curr = functions.reset_grads(D_curr, False)
D_curr.eval()
Gs.append(G_curr)
Zs.append(z_curr)
NoiseAmp.append(opt.noise_amp)
torch.save(Zs, '%s/Zs.pth' % (opt.out_))
torch.save(Gs, '%s/Gs.pth' % (opt.out_))
torch.save(reals, '%s/reals.pth' % (opt.out_))
torch.save(NoiseAmp, '%s/NoiseAmp.pth' % (opt.out_))
scale_num += 1
nfc_prev = opt.nfc
del D_curr, G_curr
return
def train_single_scale(netD, netG, reals, Gs, Zs, in_s, NoiseAmp, opt, centers=None):
real = reals[len(Gs)]
opt.nzx = real.shape[2] # +(opt.ker_size-1)*(opt.num_layer)
opt.nzy = real.shape[3] # +(opt.ker_size-1)*(opt.num_layer)
opt.receptive_field = opt.ker_size + ((opt.ker_size - 1) * (opt.num_layer - 1)) * opt.stride
pad_noise = int(((opt.ker_size - 1) * opt.num_layer) / 2)
pad_image = int(((opt.ker_size - 1) * opt.num_layer) / 2)
if opt.mode == 'animation_train':
opt.nzx = real.shape[2] + (opt.ker_size - 1) * (opt.num_layer)
opt.nzy = real.shape[3] + (opt.ker_size - 1) * (opt.num_layer)
pad_noise = 0
# 对Tensor使用0进行边界填充
m_noise = nn.ZeroPad2d(int(pad_noise))
m_image = nn.ZeroPad2d(int(pad_image))
alpha = opt.alpha
fixed_noise = functions.generate_noise([opt.nc_z, opt.nzx, opt.nzy], device=device)
# 返回一个大小为fill_value的张量
z_opt = torch.full(fixed_noise.shape, 0, device=device)
z_opt = m_noise(z_opt)
# setup optimizer
optimizerD = optim.Adam(netD.parameters(), lr=opt.lr_d, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
optimizerG = optim.Adam(netG.parameters(), lr=opt.lr_g, betas=(opt.beta1, 0.999))
# 按需调整学习率
schedulerD = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer=optimizerD, milestones=[1600], gamma=opt.gamma)
schedulerG = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer=optimizerG, milestones=[1600], gamma=opt.gamma)
errD2plot = []
errG2plot = []
D_real2plot = []
D_fake2plot = []
z_opt2plot = []
# 它是从噪声生成图像的
for epoch in range(opt.niter):
if (Gs == []) & (opt.mode != 'SR_train'):
z_opt = functions.generate_noise([1, opt.nzx, opt.nzy], device=device)
z_opt = m_noise(z_opt.expand(1, 3, opt.nzx, opt.nzy))
noise_ = functions.generate_noise([1, opt.nzx, opt.nzy], device=device)
noise_ = m_noise(noise_.expand(1, 3, opt.nzx, opt.nzy))
else:
noise_ = functions.generate_noise([opt.nc_z, opt.nzx, opt.nzy], device=device)
noise_ = m_noise(noise_)
############################
# (1) Update D network: maximize D(x) + D(G(z))
###########################
# Dsteps 'Discriminator inner steps',default=3
for j in range(opt.Dsteps):
# train with real
netD.zero_grad()
output = netD(real).to(device)
# D_real_map = output.detach()
errD_real = -output.mean() # -a
errD_real.backward(retain_graph=True)
D_x = -errD_real.item()
# train with fake
if (j == 0) & (epoch == 0):
if (Gs == []) & (opt.mode != 'SR_train'):
prev = torch.full([1, opt.nc_z, opt.nzx, opt.nzy], 0, device=device)
in_s = prev
prev = m_image(prev)
z_prev = torch.full([1, opt.nc_z, opt.nzx, opt.nzy], 0, device=device)
z_prev = m_noise(z_prev)
opt.noise_amp = 1
elif opt.mode == 'SR_train':
z_prev = in_s
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
RMSE = torch.sqrt(criterion(real, z_prev))
opt.noise_amp = opt.noise_amp_init * RMSE
z_prev = m_image(z_prev)
prev = z_prev
else:
prev = draw_concat(Gs, Zs, reals, NoiseAmp, in_s, 'rand', m_noise, m_image, opt)
prev = m_image(prev)
z_prev = draw_concat(Gs, Zs, reals, NoiseAmp, in_s, 'rec', m_noise, m_image, opt)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
RMSE = torch.sqrt(criterion(real, z_prev))
opt.noise_amp = opt.noise_amp_init * RMSE
z_prev = m_image(z_prev)
else:
prev = draw_concat(Gs, Zs, reals, NoiseAmp, in_s, 'rand', m_noise, m_image, opt)
prev = m_image(prev)
if opt.mode == 'paint_train':
prev = functions.quant2centers(prev, centers)
plt.imsave('%s/prev.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(prev), vmin=0, vmax=1)
if (Gs == []) & (opt.mode != 'SR_train'):
noise = noise_
else:
noise = opt.noise_amp * noise_ + prev
fake = netG(noise.detach(), prev)
output = netD(fake.detach())
errD_fake = output.mean()
errD_fake.backward(retain_graph=True)
D_G_z = output.mean().item()
gradient_penalty = functions.calc_gradient_penalty(netD, real, fake, opt.lambda_grad, device)
gradient_penalty.backward()
errD = errD_real + errD_fake + gradient_penalty
optimizerD.step()
errD2plot.append(errD.detach())
############################
# (2) Update G network: 最大化 D(G(z))
###########################
for j in range(opt.Gsteps):
netG.zero_grad()
output = netD(fake)
D_fake_map = output.detach()
errG = -output.mean()
# errG.backward(retain_graph=True)
if alpha != 0:
loss = nn.MSELoss()
if opt.mode == 'paint_train':
z_prev = functions.quant2centers(z_prev, centers)
plt.imsave('%s/z_prev.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(z_prev), vmin=0, vmax=1)
Z_opt = opt.noise_amp * z_opt + z_prev
rec_loss = alpha * loss(netG(Z_opt.detach(), z_prev), real)
rec_loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
rec_loss = rec_loss.detach()
else:
Z_opt = z_opt
rec_loss = 0
optimizerG.step()
errG2plot.append(errG.detach() + rec_loss)
D_real2plot.append(D_x)
D_fake2plot.append(D_G_z)
z_opt2plot.append(rec_loss)
if epoch % 25 == 0 or epoch == (opt.niter - 1):
print('scale %d:[%d/%d]' % (len(Gs), epoch, opt.niter))
if epoch % 500 == 0 or epoch == (opt.niter - 1):
plt.imsave('%s/fake_sample.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(fake.detach()), vmin=0, vmax=1)
plt.imsave('%s/G(z_opt).png' % (opt.outf),
functions.convert_image_np(netG(Z_opt.detach(), z_prev).detach()), vmin=0, vmax=1)
# plt.imsave('%s/D_fake.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(D_fake_map))
# plt.imsave('%s/D_real.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(D_real_map))
# plt.imsave('%s/z_opt.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(z_opt.detach()), vmin=0, vmax=1)
# plt.imsave('%s/prev.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(prev), vmin=0, vmax=1)
# plt.imsave('%s/noise.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(noise), vmin=0, vmax=1)
# plt.imsave('%s/z_prev.png' % (opt.outf), functions.convert_image_np(z_prev), vmin=0, vmax=1)
torch.save(z_opt, '%s/z_opt.pth' % (opt.outf))
schedulerD.step()
schedulerG.step()
functions.save_networks(netG, netD, z_opt, opt)
return z_opt, in_s, netG
def draw_concat(Gs, Zs, reals, NoiseAmp, in_s, mode, m_noise, m_image, opt):
G_z = in_s
if len(Gs) > 0:
if mode == 'rand'以上是关于SinGAN一张照片即可生成同样的照片(附简化版代码)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章