JUC并发编程 共享模式之工具 JUC CountdownLatch(倒计时锁) -- CountdownLatch应用(等待多个线程准备完毕( 可以覆盖上次的打印内)等待多个远程调用结束)(代码片段
Posted Z && Y
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JUC并发编程 共享模式之工具 JUC CountdownLatch(倒计时锁) -- CountdownLatch应用(等待多个线程准备完毕( 可以覆盖上次的打印内)等待多个远程调用结束)(代码片段相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 等待多个线程准备完毕(\\r可以覆盖上次的打印内)
玩王者荣耀时,有十个玩家(相当于十个线程),只有等这十个玩家的进度条都为100%时才会开始游戏,现在我们使用CountdownLarch倒计时锁模拟这个过程
示例代码:
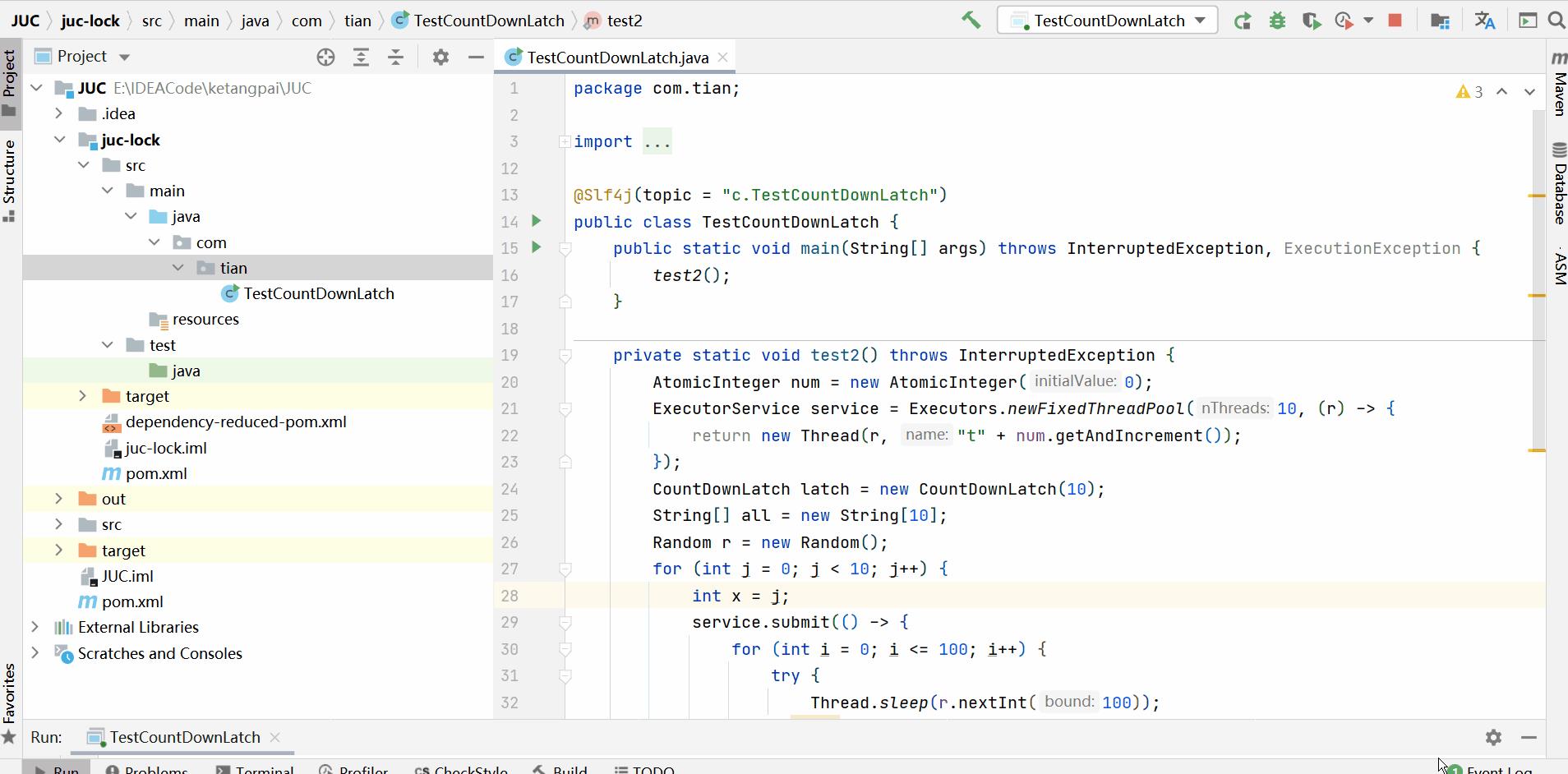
package com.tian;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestCountDownLatch")
public class TestCountDownLatch {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
test2();
}
private static void test2() throws InterruptedException {
AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10, (r) -> {
return new Thread(r, "t" + num.getAndIncrement());
});
// 初始倒计时为10
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);
String[] all = new String[10];
Random r = new Random();
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
int x = j;
service.submit(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(r.nextInt(100));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
all[x] = Thread.currentThread().getName() + "(" + (i + "%") + ")";
System.out.print("\\r" + Arrays.toString(all));
}
// 每次有一个线程到达100% 倒计时减1
latch.countDown();
});
}
// 等待倒计时为0
latch.await();
System.out.println("\\n游戏开始...");
service.shutdown();
}
}
运行结果:
2. 等待多个远程调用结束
线程Controller需要等待接口调用成功后才会执行下面的逻辑,怎么保证
多个远程调用结束结束呢?下面介绍2种方法。
2.1 需要返回结果 使用Future
private static void test3() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
log.debug("begin");
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future<Map<String, Object>> f1 = service.submit(() -> {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/order/{1}", Map.class, 1);
});
Future<Map<String, Object>> f2 = service.submit(() -> {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/product/{1}", Map.class, 1);
});
// 等待线程1的结果 阻塞在这里
System.out.println(f1.get());
// 等待线程2的结果 阻塞在这里
System.out.println(f2.get());
// 执行到这里时 已经成功获取到f1和f2的结果了
log.debug("执行完毕");
service.shutdown();
}
2.2 不需要返回值结果 使用CountdownLatch
private static void test3() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
log.debug("begin");
ExecutorService service = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 初始倒计时为2
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(2);
service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> response = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/order/{1}", Map.class, 1);
// 倒计时减1
latch.countDown();
});
service.submit(() -> {
Map<String, Object> response1 = restTemplate.getForObject("http://localhost:8080/product/{1}", Map.class, 1);
// 倒计时减1
latch.countDown();
});
// 等待倒计时为0
latch.await();
log.debug("执行完毕");
service.shutdown();
}
以上是关于JUC并发编程 共享模式之工具 JUC CountdownLatch(倒计时锁) -- CountdownLatch应用(等待多个线程准备完毕( 可以覆盖上次的打印内)等待多个远程调用结束)(代码片段的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章