Java栈[数组,单链表],队列数组,链表和循环队列的实现
Posted 面向丈母娘编程
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java栈[数组,单链表],队列数组,链表和循环队列的实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 栈
1.1 概念
一种特殊的线性表,说明了具有前驱和后继关系。只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
栈中的数据元素遵循后进先出 LIFO 原则【Last In First Out】
压栈:栈的插入/进栈/压栈,入数据在栈顶
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据也在栈顶
后进先出【类似于浏览器的回退,只会返回上一个浏览后的页面而不是返回第一个打开的页面;弹夹中的子弹】

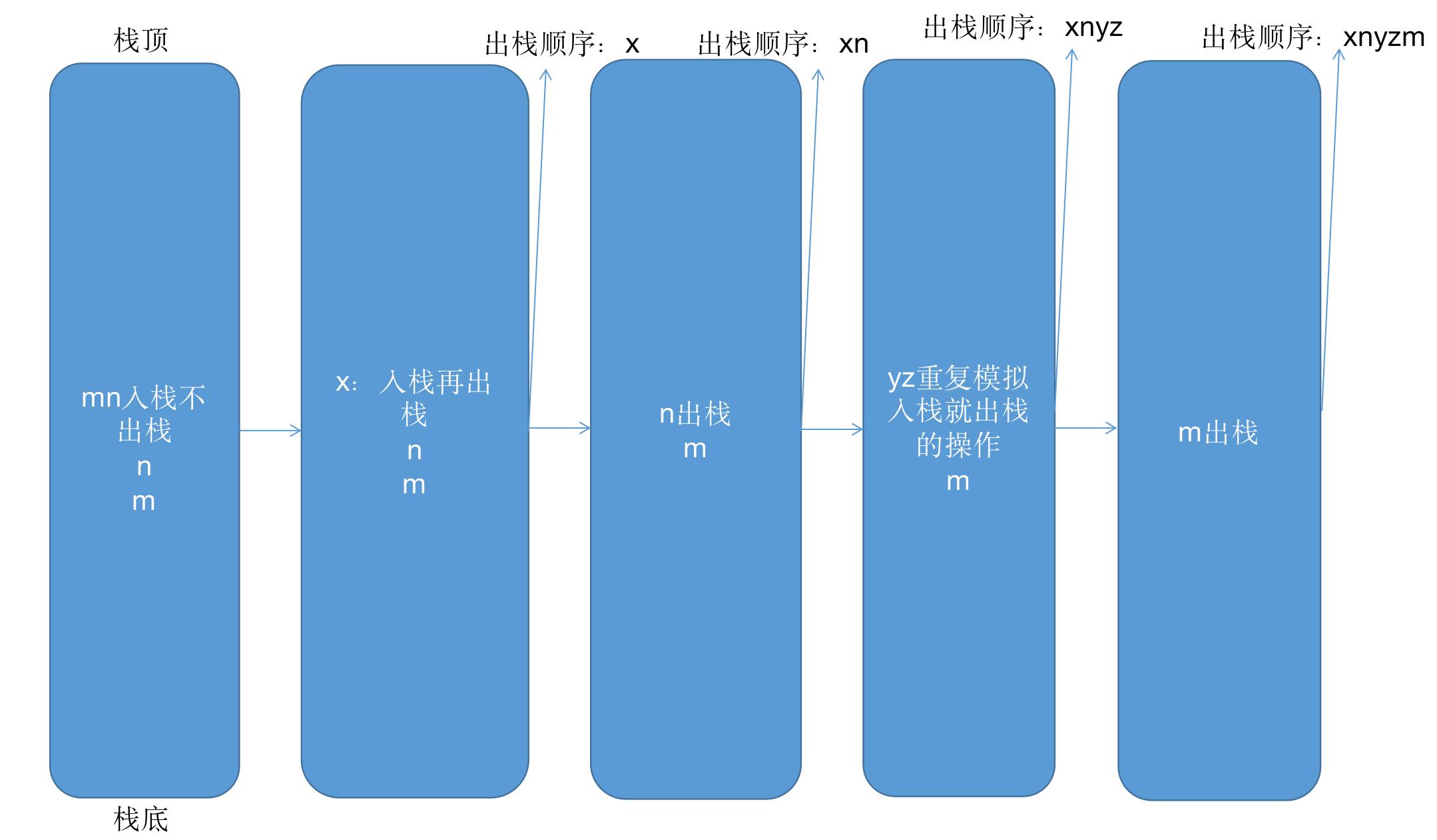
邪恶的小技巧:合理的出栈顺序(画栈图)
已知一个栈的入栈序列是m, n, x, y, z.则不可能出现的出栈顺序是: C
A mnxyz
B xnyzm
C nymxz
D nmyzx
A

B
C

m要想出栈必须让x出栈才行,所以是不可能的出栈顺序
D
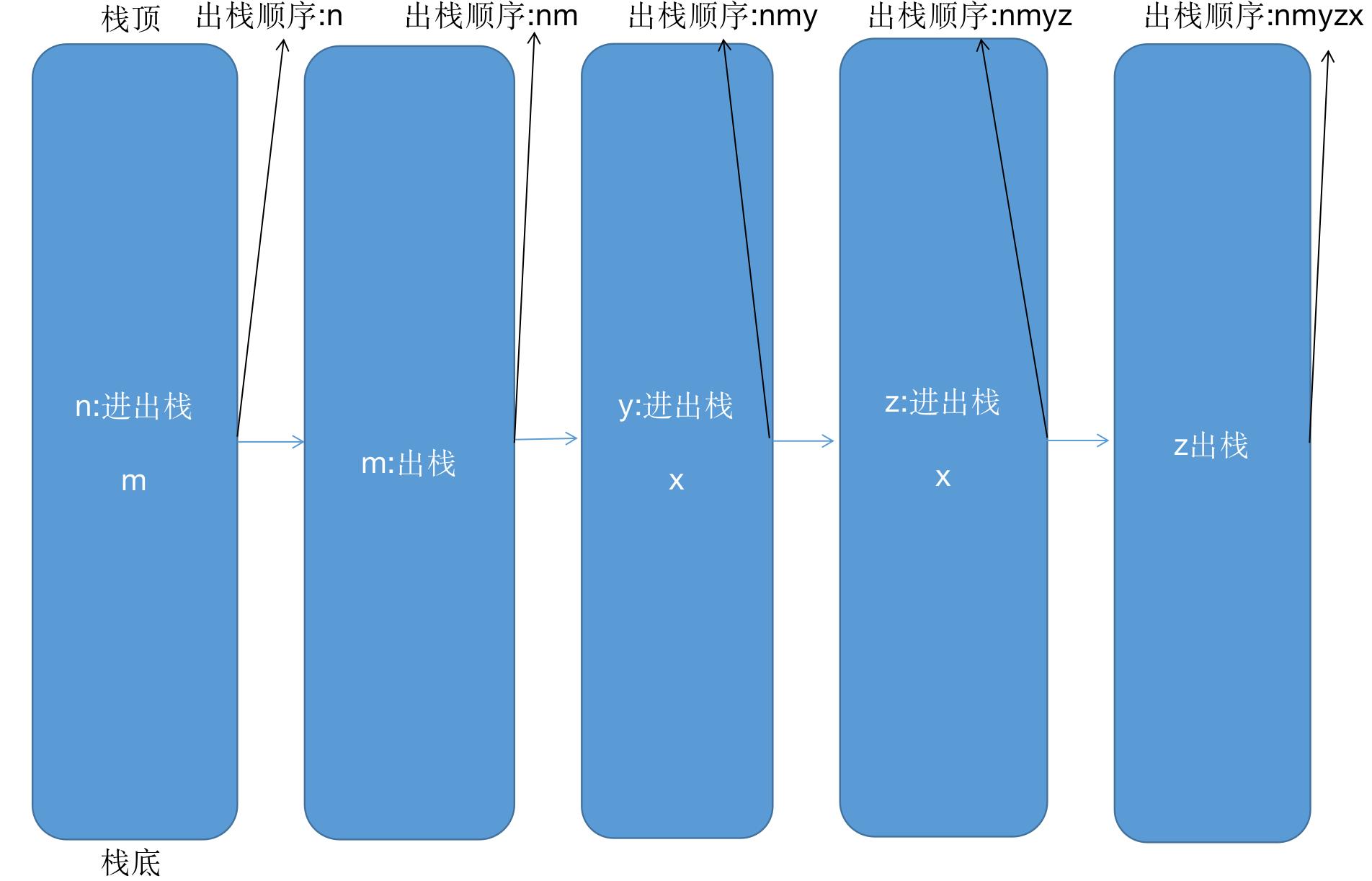
邪恶的小技巧:中缀表达式转后缀表达式
有一个中缀表达式为a*(b-(c+d)),它的后缀表达式可以是什么: A
A abcd+-*
B abc+d-*
C ab-cd+*
D abd+c-*
前缀表达式: 把运算符放前边
中缀表达式:a*(b-(c+d)
后缀表达式: 把运算符放后边
按照运算优先级给操作符号放在括号外边
a*(b-(c+d))确定优先级
(a*(b-(c+d))) 打括号
+ 先算
(a*(b- ( cd )+ ))移动符号
(a* ( b(cd)+ )- )
( a(b(cd)+)- )*
后缀表达式: abcd+-*
这样就不用像第一题那样每次都画操作栈
方法总结:从左往右,根据运算符的优先级(注意括号问题),额外加括号,把每个对应的运算符移到对应的括号外面。去除所有的括号,结果就是对应的前后缀表达式【后缀放后边,前缀放前边即可】
2*3(4+5)-6
(2*3(4+5)-6)
(2*3(45)+-6)
(2*(345)+*-6)
(2((345)+*)-6)
((2((345)+*))-6)
((2((345)+*))*6)-
2345 +**6-
应用
int func(后缀表达式)
1.2 实现
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(1);// 增加元素
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
System.out.println(stack.peek());// 获取栈顶元素但不删除 3
System.out.println(stack.pop());// 弹出栈顶元素 删除3
System.out.println(stack.peek());// 获取栈顶元素但不删除2
System.out.println(stack.empty());// 栈自带的 empty 方法
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());// 继承 vector 的方法
System.out.println(stack.search(2));// 查找下标
System.out.println(stack.search(3));// 没有就返回 -1
}
3
3
2
false
false
1
-1
Stack 源码

发现只有
push,peek,pop,empty,search方法
为何可以使用isEmpty呢?
为何可以使用 isEmpty 方法呢。

因为
Stack继承Vector,所以可以使用父类的isEmpty方法
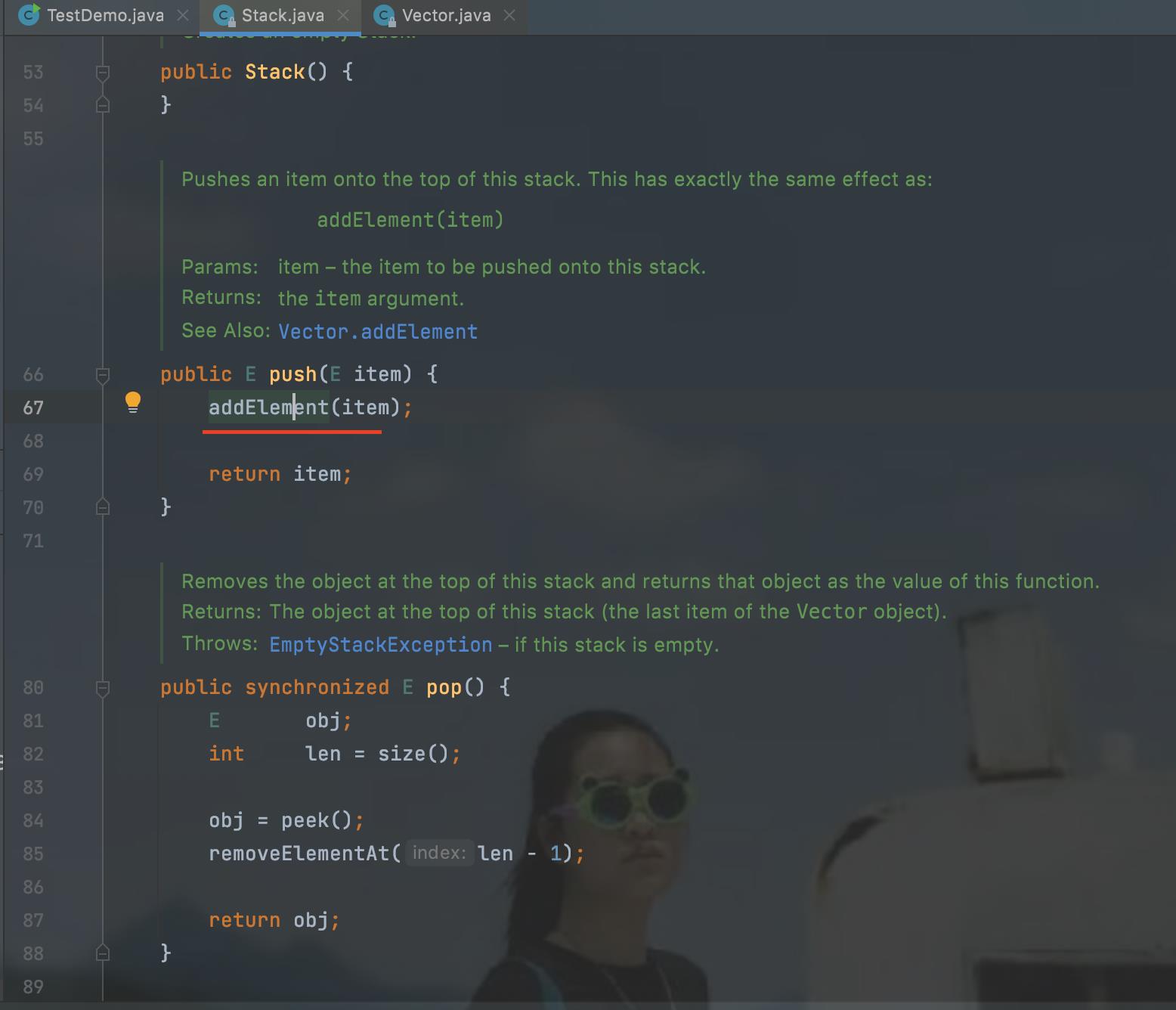
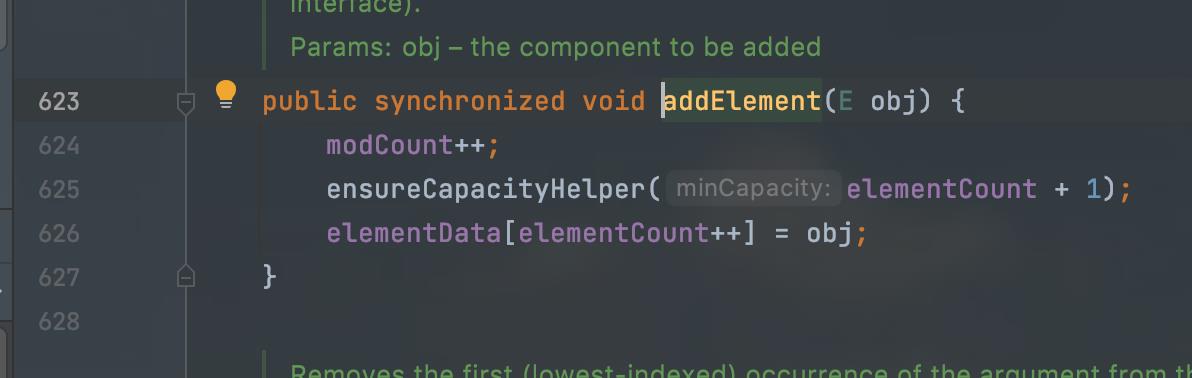
分析一下push压栈操作,来查看它的底层是如何实现的
查看addElementr方法
如果不清楚源代码内容的可以查看我的博客——List的使用中add方法一步步源码解析,了解栈的底层数组如何扩容如何增加元素
我们查看一下 Stack 继承和实现

发现这个体系是:Stack 类继承 Veator 类, Vector 类继承 AbstractList 类, AbstractList 类继承自 AbstractCollection 类, AbstractCollection 类实现 Collection 接口, Collection 接口继承 Iterable 接口
1.2.1 数组实现Stack
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyStackList<E> {
// public static void main1(String[] args) {
// Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
// stack.push(1);// 增加元素
// stack.push(2);
// stack.push(3);
// System.out.println(stack.peek());// 获取栈顶元素但不删除 3
// System.out.println(stack.pop());// 弹出栈顶元素 删除3
// System.out.println(stack.peek());// 获取栈顶元素但不删除2
// System.out.println(stack.empty());// 栈自带的 empty 方法
// System.out.println(stack.isEmpty());// 继承 vector 的方法
// System.out.println(stack.search(2));// 查找下标
// System.out.println(stack.search(3));// 没有就返回 -1
// }
private E[] elem;
private int usedSize = 0;
private int capacity = 4;
MyStackList() {
this.elem = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
// 扩容
private void checkCapacity() {
if (this.usedSize == this.capacity) {
this.capacity *= 2;
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem, this.capacity);
}
}
E push(E e) {
checkCapacity();
this.elem[this.usedSize++] = e;
return this.elem[this.usedSize - 1];
}
E pop() {
if (this.usedSize == 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("Stack is empty !!!");
} else {
return this.elem[--this.usedSize];
}
}
E peek() {
if (this.usedSize == 0) {
return null;
} else {
return this.elem[this.usedSize - 1];
}
}
boolean empty() {
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
void display() {
for (int i = this.usedSize-1; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
private static void testPush() {
MyStackList stack = new MyStackList();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.print(stack.push(i) + " ");
}
}
private static void testPop() {
System.out.println("Push:");
MyStackList stack = new MyStackList();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
stack.push(i);
}
stack.display();
System.out.println("Pop:");
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
System.out.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
System.out.println("Residue: ");
stack.display();
}
private static void testPeek() {
MyStackList stack = new MyStackList();
System.out.println("Push:");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
stack.push(i);
}
stack.display();
System.out.println("Peek:");
for (int i = 5; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.print(stack.peek() + " ");
}
System.out.println("Residue:");
stack.display();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 放置测试用例
testPop();
}
}
数组实现栈, 为了提高效率该如何插入删除数据呢?
- 尾插尾删: 避免了数组元素的移动, 时间复杂度O(1)
- 头插头删: 还要移动数据, 时间复杂度O(N)
1.2.2 单链表实现Stack
class Node<E> {
private E val;
private Node next;
public Node(E val) {
this.val = val;
}
Node head;
E push(E val) {
Node node = new Node(val);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
return (E) head.val;
} else {
node.next = head;
head = node;
return (E) head.val;
}
}
E pop() {
if (head == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NULL !!!");
} else {
E ret = (E) head.val;
head = head.next;
return ret;
}
}
E peek() {
if (head == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NULL !!!");
} else {
return (E) head.val;
}
}
void display() {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
}
}
public class MyStackLinked<E> {
private static void testPush() {
Node node = new Node(null);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
System.out.print(node.push(i) + " ");
}
}
private static void testPop() {
Node node = new Node(null);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
node.push(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.print(node.pop() + " ");
}
}
private static void testPeek() {
Node node = new Node(null);
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
node.push(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.print(node.peek() + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testPeek();
}
}
单链表实现栈, 为了提高效率该如何插入删除数据呢?
- 头插头删: 时间复杂度O(1)
- 尾插尾删: 不带尾节点单链表时间是复杂度O(N);带尾节点尾结点
tail可以把入栈push操作的时间复杂度降到O(1)但是无法把出栈pop时间复杂度降到O(1)【需要找尾节点的前一个节点,所以是O(N)】
2. 队列
2.1 概念
只允许一端进行数据插入操作,另一端进行数据删除操作的特殊线性表.队列具有先进先出功能FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列: 进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列: 进行删除操作的一端称为对头

先进先出【操作系统的程序点开执行顺序,客服电话,键盘的输入,记事本的输出】
2.2 实现

发现 Queue 只有方框中的方法
Queue 接口继承了 Collection 接口, Collection 接口继承 Iterable 接口【实现过程比 Stack 简单许多】
数组实现Queue
数组实现队列有没有什么问题呢?
因为是先进先出的, 所以会导致先出空间的内容造成浪费。而不是像栈那样一直处于一端操作,不会造成空间浪费。如果元素移动的话来决解空间问题的话,时间复杂度会变为O(N)效率太低

因此数组的话可以通过“循环”的方式实现队列
什么是“循环队列”呢?
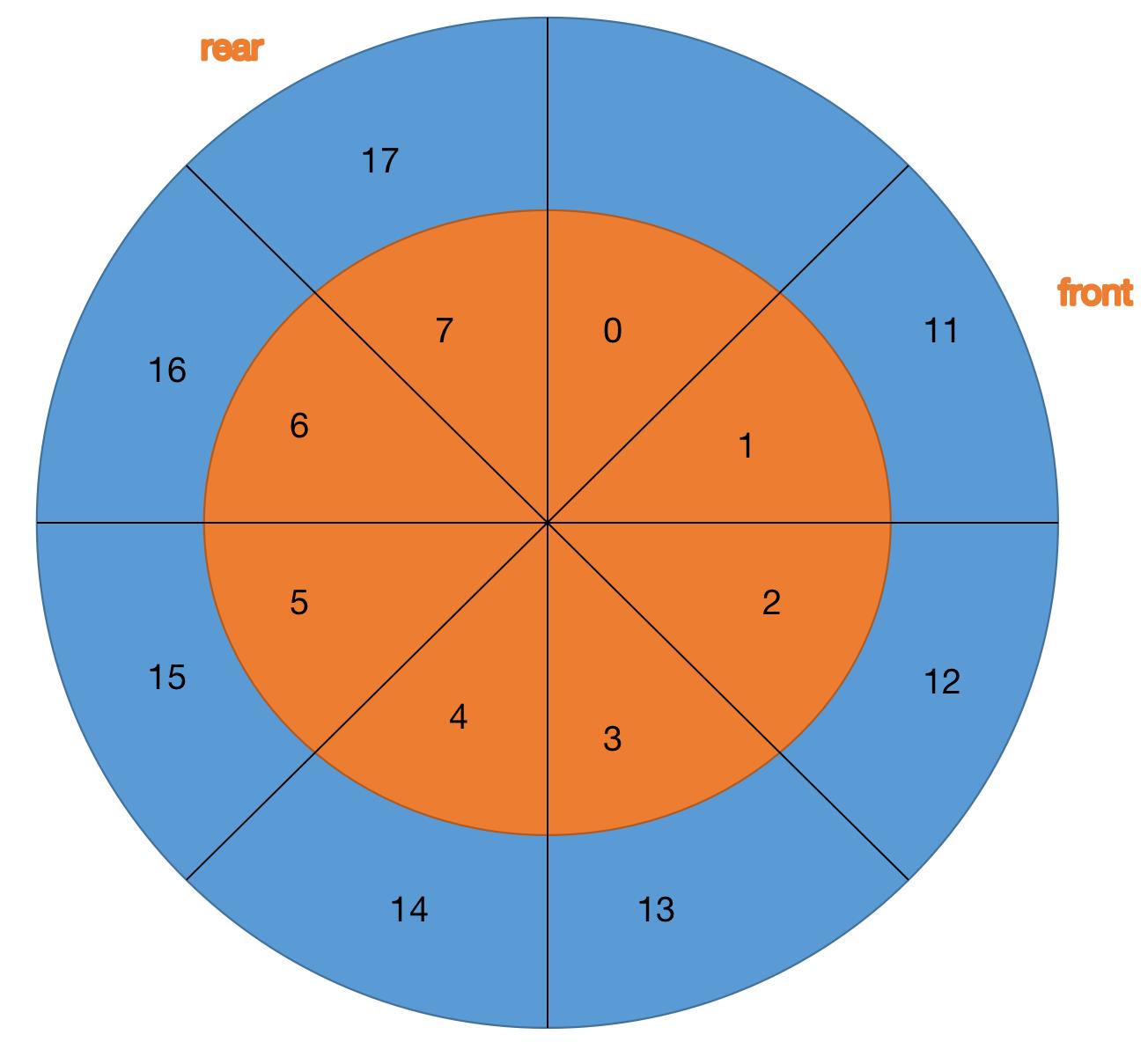
分析解释环形图
- 0~7: 数组的引用
- 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17存储的元素值
- rear:指向插入元素的引用【带插入元素的下一个索引】,图中代表的是刚插入元素17还未移动rear下标,此时插入元素操作完毕后的rear应该移动到下一个索引0处
- front:指向对头元素的索引,每次出队列一个元素就移动一次front
思考: 何时代表队列满了, 何时代表队列空?
- 当
front==rear的时候,有两种可能: 要么队列满要么队列空- 如果 rear 的下一个是 front 就代表满了【现在可以区
front==rear】的两种情况了
思考: rear走到数组末尾,该如何跳转到数组0下标开头呢?
最简单的方法就是 if 判断
if (re a r== elem.length-1){// 走到了队尾
rear = 0;
}
这时候如果利用取余运算呢? 会发现有不同的运算效果
假设一边有插入一边有删除,那么这个时候即可实现循环操作对立达到堆空间的利用的同时复杂度还是O(1)
| 队列长度为8, rear+1 | 取余结果 |
|---|---|
| 1%8 | 1 |
| 2%8 | 2 |
| 3%8 | 3 |
| 4%8 | 0 |
| 5%8 | 5 |
| 6%8 | 8 |
| 7%8 | 8 |
| 8%8 | 0 |
| 9%8: 不会出现这种情况,rear+1==front的话就已经是满队列 | 1 |


2.2.1 数组实现循环队列
这是一个 OJ 链接
方案1会浪费一个位置的队列空间,代码如下:
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] elem;
private int front, rear;
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
this.elem = new int[k+1];
}
/**
* 入队列
*
* @param value 值
* @return
*/
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if ((this.rear + 1) % this.elem.length == this.front) {
return false;//满了
} else {
this.elem[this.rear] = value;
this.rear = (this.rear + 1) % this.elem.length;
return true;
}
}
/**
* 出队列
*
* @return
*/
public boolean deQueue() {
if (this.front == this.rear) {
return false;
} else {
int val = this.elem[this.front];
// this.front = (this.front + 1) % this.elem.length;// 因为是循环,所以不能直接 front+1
return true;
}
}
/**
* 取队头元素【相当于 peek 】
*
* @return
*/
public int Front() {
if (this.front == this.rear) {
return -1;// leetcode 抛异常会认为是你的代码错误,所以不能抛异常
} else {
int val = this.elem[this.front];
return val;
}
}
/**
* 取队尾元素
* rear处于0位置则返回this.elem.length-1
* 所以不能直接进行 -1 操作
*
* @return
*/
public int Rear() {
if (this.rear == this.以上是关于Java栈[数组,单链表],队列数组,链表和循环队列的实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章