关于Linux运维中监控方面的一些笔记
Posted 山河已无恙
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了关于Linux运维中监控方面的一些笔记相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
写在前面
- 笔记是报班学习后整理的,适合温习,不适合新手。蹭着国庆长假整理了一份,希望对小伙伴有帮助.
- 生活加油,天天开心!博文主要围绕以几个方面:
- 监控的基本知识
- zabbix 的安装部署教程,
- 多节点监控实战
可能不是不喜欢了,而是累了,可能不是之前的喜欢都是假的,只是这个世界本来就很苍白
一、监控概述
1.1 监控的目的
| 监控的目的 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 报告系统运行状况 | 每一部分必须同时监控,内容包括吞吐量、反应时间、使用率等 |
| 提前发现问题 | 进行服务器性能调整前,知道调整什么,找出系统的瓶颈在什么地方 |
1.1.1 监控的资源类别
| 监控的资源类别 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 公开数据 | Web、FTP、SSH、数据库等应用服务,TCP或UDP端口 |
| 私有数据 | CPU、内存、磁盘、网卡流量等使用信息,用户、进程等运行信息 |
1.2 监控软件
| 命令 | 描述 |
|---|---|
ps | 查看进程信息 |
uptime | 查看CPU的负载 |
free | 查看系统内存信息 |
swapon -s | 查看交换分区信息 |
df -h | 查看文件系统挂载情况 |
ifconfg | 查看网卡信息 |
netstat或ss | 查看网络连接状态信息 (端口等) |
ping | 测试网络延迟 (是否可以通信) |
traceroute | 跟踪路由 |
iostat | 查询磁盘读写的性能 |
sar | 综合命令,可以查询cpu、磁盘、网络 , 查询历史或实时数据 |
查看进程信息
######查看进程信息
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ ps -aux | less
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
root 1 0.0 0.0 43264 3708 ? Ss 17:49 0:04 /usr/lib/systemd/systemd --switched-root --system --deserialize 21
root 2 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [kthreadd]
root 3 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [ksoftirqd/0]
root 5 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:49 0:00 [kworker/0:0H]
root 7 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [migration/0]
root 8 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [rcu_bh]
root 9 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:01 [rcu_sched]
root 10 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [watchdog/0]
root 11 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [watchdog/1]
root 12 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [migration/1]
root 13 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [ksoftirqd/1]
root 15 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:49 0:00 [kworker/1:0H]
root 17 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [kdevtmpfs]
root 18 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:49 0:00 [netns]
root 19 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:49 0:00 [khungtaskd]
root 20 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:49 0:00 [writeback]
root 21 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:49 0:00 [kintegrityd]
root 22 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:49 0:00 [bioset]
root 23 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:49 0:00 [kblockd]
root 24 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:49 0:00 [md]
root 26 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? R 17:49 0:02 [kworker/1:1]
root 31 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 17:50 0:00 [kswapd0]
root 32 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? SN 17:50 0:00 [ksmd]
root 33 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? SN 17:50 0:00 [khugepaged]
root 34 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:50 0:00 [crypto]
root 42 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:50 0:00 [kthrotld]
root 44 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 17:50 0:00 [kmpath_rdacd]
:
查看cpu负载
#######查看cpu负载
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ uptime
19:09:58 up 1:20, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
查看内存使用信息
#######查看内存使用信息
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ free -h
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3.8G 202M 3.3G 16M 322M 3.4G
Swap: 9G 0B 9G
查看交换分区设备信息
#######查看交换分区设备信息
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ swapon -s
Filename Type Size Used Priority
/dev/sda2 partition 10485756 0 -1
查看设备文件系统挂载信息
#######查看设备文件系统挂载信息
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda1 150G 2.7G 148G 2% /
devtmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev
tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 2.0G 17M 2.0G 1% /run
tmpfs 2.0G 0 2.0G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
tmpfs 394M 0 394M 0% /run/user/0
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
查看网卡信息, 需安装 net-tools软件包
########查看网卡信息, 需安装 net-tools软件包
#RX packets 指进站的总流量(从开机开始计算)
#TX packets 指出站的总流量(从开机开始计算)
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ ifconfig ens32
ens32: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.26.55 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.26.255
inet6 fe80::20c:29ff:fec9:6fae prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:c9:6f:ae txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 754 bytes 72467 (70.7 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 562 bytes 64846 (63.3 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
查看端口信息和对应的协议,与grep结合使用
######查看端口信息和对应的协议,与grep结合使用
##netsat 功能相同
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ ss -ntulpa
Netid State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port
udp UNCONN 0 0 127.0.0.1:323 *:* users:(("chronyd",pid=586,fd=1))
udp UNCONN 0 0 ::1:323 :::* users:(("chronyd",pid=586,fd=2))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* users:(("sshd",pid=935,fd=3))
tcp LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:*
users:(("master",pid=1050,fd=13))
tcp ESTAB 0 0 192.168.26.55:22 192.168.26.1:2326
users:(("sshd",pid=1203,fd=3))
tcp ESTAB 0 0 192.168.26.55:22 192.168.26.1:11634
users:(("sshd",pid=12072,fd=3))
tcp LISTEN 0 128 :::22 :::*
users:(("sshd",pid=935,fd=4))
tcp LISTEN 0 100 ::1:25 :::*
users:(("master",pid=1050,fd=14))
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
测试网络延迟 (是否可以通信)
#########测试网络延迟 (是否可以通信)
##time=0.519 ms 为网络延迟时间,时间越小,网络延迟越短
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ ping 127.0.0.1
PING 127.0.0.1 (127.0.0.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.406 ms
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.090 ms
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.130 ms
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.124 ms
^C
--- 127.0.0.1 ping statistics ---
4 packets transmitted, 4 received, 0% packet loss, time 3005ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 0.090/0.187/0.406/0.127 ms
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
traceroute可以跟踪路由,查看到目标主机经过哪些路由
########traceroute可以跟踪路由,查看到目标主机经过哪些路由
[root@proxy ~]# yum -y install traceroute
[root@proxy ~]# traceroute 192.168.2.254
traceroute to 192.168.2.254 (192.168.2.254), 30 hops max, 60 byte packets
1 192.168.2.254 (192.168.2.254) 0.929 ms * *
iostat 查询磁盘的读写性能,需要安装软件包sysstat
########iostat 查询磁盘的读写性能,需要安装软件包sysstat
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ iostat
Linux 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 (liruilongs.github.io) 09/30/2021 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
avg-cpu: %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
0.16 0.01 0.18 0.11 0.00 99.54
##kB_read/s 磁盘每秒读的数据大小(KB)
##kB_wrtn/s 磁盘每秒写入的数据大小(KB)
##kB_read 磁盘读的总数据大小(KB)
##kB_wrtn 磁盘写入的总数据大小(KB)
Device: tps kB_read/s kB_wrtn/s kB_read kB_wrtn
sda 1.59 59.74 11.22 360970 67798
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
sar查看CPU的信息,第一个数字:指每隔几秒读取数据; 第二个数字: 指取几次CPU的数据
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ sar 1 2
Linux 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 (liruilongs.github.io) 09/30/2021 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
###%idle 指CPU的空闲率
08:59:07 PM CPU %user %nice %system %iowait %steal %idle
08:59:08 PM all 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
08:59:09 PM all 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
Average: all 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 100.00
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
使用sar查看所有网卡的实时流量信息
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$ sar -n DEV 1 2
#############使用sar查看所有网卡的实时流量信息
#第一个数字1:指每隔1秒查看一次网络数据流量; 第二个数字2: 指查看两次
Linux 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 (liruilongs.github.io) 09/30/2021 _x86_64_ (2 CPU)
#rxkB/s 指每秒接收数据的流量(KB);
#txkB/s 指每秒发送数据的流量 (KB);
09:00:26 PM IFACE rxpck/s txpck/s rxkB/s txkB/s rxcmp/s txcmp/s rxmcst/s
09:00:27 PM ens32 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
09:00:27 PM lo 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
09:00:27 PM docker0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
09:00:27 PM IFACE rxpck/s txpck/s rxkB/s txkB/s rxcmp/s txcmp/s rxmcst/s
09:00:28 PM ens32 1.00 1.00 0.06 0.47 0.00 0.00 0.00
09:00:28 PM lo 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
09:00:28 PM docker0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
Average: IFACE rxpck/s txpck/s rxkB/s txkB/s rxcmp/s txcmp/s rxmcst/s
Average: ens32 0.50 0.50 0.03 0.23 0.00 0.00 0.00
Average: lo 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
Average: docker0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
┌──[root@liruilongs.github.io]-[~]
└─$
1.3 自动化监控系统
| Cacti | 特点:将监控到的数据,绘制成各种图形 | 基于SNMP协议 (网络管理协议) 的监控软件,强大的绘图能力 |
| Nagios | 特点:状态检查和报警机制 (例如:内存不足或CPU负载高时,及时的给管理员发送报警信息(邮件报警,短信报警等) ) | 基于Agent监控,强大的状态检查与报警机制,插件极多,自己写监控脚本嵌入到Nagios非常方便 |
| Zabbix | 特点:支持多种报警机制,支持分布式监控,支持数据绘图 | 基于多种监控机制,支持分布式监控 |
1.3.1 Zabbix简介
Zabbix 是一个高度集成的监控解决方案,可以实现企业级的开源分布式监控,
Zabbix 通过 C/S模式采集监控数据
C/S (client/server):客户端/服务器
客户端程序负载采集要监控的数据,然后发送给监控服务器;
监控服务器对客户发送过来的数据进行存储和处理;
Zabbix通过B/S模式实现Web管理
B/S (browser/server): 浏览器/服务器
管理员可以通过浏览器,访问监控服务器web页面,并可以查看和管理监控系统
1.3.2 监控拓扑
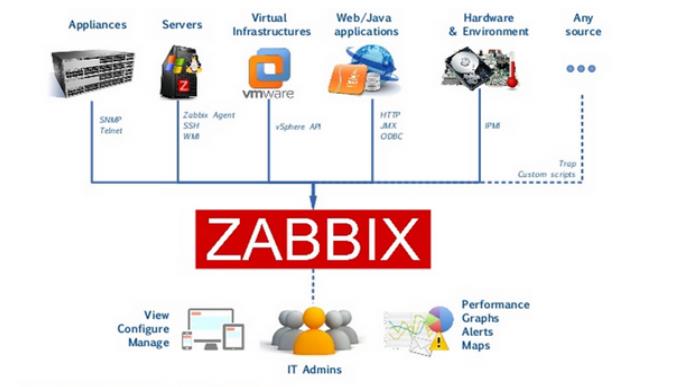
| Zabbix监控原理: |
|---|
| 部署一个Zabbix监控服务器, 用于存储和处理监控数据; |
| 如果被监控的是Linux或Windows主机,需要安装客户端程序agent来采集监控数据; |
| 如果被监控的是网络设备(交换机,路由器等),通过SNMP协议进行监控; |
| 最后Zabbix监控服务器,将客户端收集来的数据存储到数据库中,通过web页面来管理 |
| 监控角色 |
|---|
| 监控服务器 |
| 监控服务器可以通过SNMP (网络管理协议)或Agent采集数据 |
| 数据可以写入mysql、Oracle等数据库中 |
| 服务器使用LNMP实现web前端的管理 |
| 被监控主机 |
| 被监控主机需要安装Agent |
| 常见的网络设备一般支持SNMP (网络管理协议) |
二、LNMP环境准备
这里的话,因为zabbix web系统使用的是php,所以需要配置LNMP环境。
nginx是一款小巧而高效的Web服务器软件,可帮您在Linux系统下快速方便地搭建出LNMP Web服务环境。在ECS实例上搭建LNMP环境,其中LNMP分别代表Linux、Nginx、MySQL和PHP。
2.1 部署LNMP
这里小伙伴可以参考这个:手动部署LNMP环境(CentOS 7)
2.1.1 安装前准备
- 监控服务器(需要使用Web页面操作,因此需要先部署LNMP)
- 设置主机名(zabbixserver)
- 设置IP地址(192.168.26.15)
- 关闭防火墙、SELinux
- 监控客户端 (2.100和2.200)
- 主机web1(192.168.26.14)
- 主机web2(192.168.26.13)
- 关闭防火墙、SELinux
虚拟机环境准备(克隆centos7 模板机): ——> 关闭防火墙和SELinux,嗯,因为需要多个机器,所以我们用
ansible,方便一点,这里,192.168.26.15为控制机,192.168.26.14,192.168.26.13 为节点机
| 主机名 | IP地址 |
|---|---|
| zabbixserver | 192.168.26.15 |
| web1 | 192.168.26.14 |
| web2 | 192.168.26.13 |
配置到物理机的SSH免密
┌──(liruilong㉿Liruilong)-[/mnt/e/docker]
└─$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.26.13
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/home/liruilong/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.26.13 (192.168.26.13)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:1F/T20FjhEaLDtutI1rXCwOFGZ5nPs3hFzHyjsnAs3Q.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.26.13's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.26.13'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
┌──(liruilong㉿Liruilong)-[/mnt/e/docker]
└─$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.26.14
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/home/liruilong/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.26.14 (192.168.26.14)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:cfpb8zAi+otnaU0YIoRb76iaOYiFDI4JHyU9N0LmNkY.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.26.14's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.26.14'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
┌──(liruilong㉿Liruilong)-[/mnt/e/docker]
└─$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.26.15
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/home/liruilong/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.26.15 (192.168.26.15)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Ix6WxiXXJVdMFdSqiXLaPYdg+khbzkjuYO4raDDnih0.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no/[fingerprint])? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.26.15's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.26.15'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
┌──(liruilong㉿Liruilong)-[/mnt/e/docker]
└─$
ansible环境准备
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/]
└─$ mkdir ansible;cd ansible;vim ansible.cfg
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ cat ansible.cfg
[defaults]
# 主机清单文件,就是要控制的主机列表
inventory=inventory
# 连接受管机器的远程的用户名
remote_user=root
# 角色目录
roles_path=roles
# 设置用户的su 提权
[privilege_escalation]
become=True
become_method=sudo
become_user=root
become_ask_pass=False
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ vim inventory
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ cat inventory
[web]
192.168.26.13
192.168.26.14
[zabbix]
192.168.26.13
192.168.26.14
127.0.0.1
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$
配置控制机到节点机的SSH免密
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.26.13
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: ERROR: failed to open ID file '/root/.pub': No such file or directory
(to install the contents of '/root/.pub' anyway, look at the -f option)
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.26.14
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: ERROR: failed to open ID file '/root/.pub': No such file or directory
(to install the contents of '/root/.pub' anyway, look at the -f option)
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:/wLemqRJd5tsIWj/hxole6EpNTZ9M2lDooVGnYTx3I4 root@zabbixserver
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| o=.. |
| ..+o. |
| o = o |
| . + = . |
| .S E O |
| oooX.+ + |
| .ooB++o |
| . *o*=+. |
| o +==o. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.26.14
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.26.14 (192.168.26.14)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:cfpb8zAi+otnaU0YIoRb76iaOYiFDI4JHyU9N0LmNkY.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:35:32:02:28:b3:2f:9b:11:3c:d9:16:29:ab:2f:75:73.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.26.14's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.26.14'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.26.13
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.26.13 (192.168.26.13)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:1F/T20FjhEaLDtutI1rXCwOFGZ5nPs3hFzHyjsnAs3Q.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:b3:c9:31:0e:08:31:5b:7b:25:dd:a3:a7:f1:db:ac:7a.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.26.13's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.26.13'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ ssh-copy-id root@192.168.26.15
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
root@192.168.26.15's password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh 'root@192.168.26.15'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
测试ansible
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$ ansible all -m ping
192.168.26.13 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.26.14 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
127.0.0.1 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
┌──[root@zabbixserver]-[/ansible]
└─$
检查防火墙和selinux
┌──以上是关于关于Linux运维中监控方面的一些笔记的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章