DeepRacer 根据路线计算Action Space RaceLine_Speed_ActionSpace
Posted 架构师易筋
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了DeepRacer 根据路线计算Action Space RaceLine_Speed_ActionSpace相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 说明
1.0.0.1 第 1 部分:从最佳赛车线计算最佳速度
本笔记本的第 1 部分采用了最佳赛车线,可以使用 Race-Line-Calculation.ipynb ( GitHub ) 生成,并为赛车线上的每个点生成最佳速度
输入:.py 文件,带有包含最佳赛车线的 2D 数组:2 列 (x,y)
输出:带有二维数组的 .py 文件:4 列(x、y、速度、预期时间)。这个数组可以插入到奖励函数中
注:赛车线的最后一个点被删除,因为它与第一个点相同
1.0.0.2 第 2 部分:计算动作空间
本笔记本的第 2 部分采用最佳赛车路线和速度,并使用 K-Means 和高斯噪声注入数据,计算动作空间
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from scipy import stats
import math
# Ignore deprecation warnings we have no power over
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# Path of the optimal racing line (.npy file)
fpath = "./racelines/reInvent2019_track-1000-4-2019-11-09-113228.npy"
# Change manually (this is only so that output files are named correctly)
TRACK_NAME = "reInvent2019_track"
racing_track = np.load(fpath)
# Convert np array to list and remove last point because it is the same point as the first one
racing_track = racing_track.tolist()[:-1]
2 Part 1 和 Part 2 的辅助函数
# Uses previous and next coords to calculate the radius of the curve
# so you need to pass a list with form [[x1,y1],[x2,y2],[x3,y3]]
# Input 3 coords [[x1,y1],[x2,y2],[x3,y3]]
def circle_radius(coords):
# Flatten the list and assign to variables (makes code easier to read later)
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 = [i for sub in coords for i in sub]
a = x1*(y2-y3) - y1*(x2-x3) + x2*y3 - x3*y2
b = (x1**2+y1**2)*(y3-y2) + (x2**2+y2**2)*(y1-y3) + (x3**2+y3**2)*(y2-y1)
c = (x1**2+y1**2)*(x2-x3) + (x2**2+y2**2)*(x3-x1) + (x3**2+y3**2)*(x1-x2)
d = (x1**2+y1**2)*(x3*y2-x2*y3) + (x2**2+y2**2) * \\
(x1*y3-x3*y1) + (x3**2+y3**2)*(x2*y1-x1*y2)
# In case a is zero (so radius is infinity)
try:
r = abs((b**2+c**2-4*a*d) / abs(4*a**2)) ** 0.5
except:
r = 999
return r
# Returns indexes of next index and index+lookfront
# We need this to calculate the radius for next track section.
def circle_indexes(mylist, index_car, add_index_1=0, add_index_2=0):
list_len = len(mylist)
# if index >= list_len:
# raise ValueError("Index out of range in circle_indexes()")
# Use modulo to consider that track is cyclical
index_1 = (index_car + add_index_1) % list_len
index_2 = (index_car + add_index_2) % list_len
return [index_car, index_1, index_2]
def optimal_velocity(track, min_speed, max_speed, look_ahead_points):
# Calculate the radius for every point of the track
radius = []
for i in range(len(track)):
indexes = circle_indexes(track, i, add_index_1=-1, add_index_2=1)
coords = [track[indexes[0]],
track[indexes[1]], track[indexes[2]]]
radius.append(circle_radius(coords))
# Get the max_velocity for the smallest radius
# That value should multiplied by a constant multiple
v_min_r = min(radius)**0.5
constant_multiple = min_speed / v_min_r
print(f"Constant multiple for optimal speed: {constant_multiple}")
if look_ahead_points == 0:
# Get the maximal velocity from radius
max_velocity = [(constant_multiple * i**0.5) for i in radius]
# Get velocity from max_velocity (cap at MAX_SPEED)
velocity = [min(v, max_speed) for v in max_velocity]
return velocity
else:
# Looks at the next n radii of points and takes the minimum
# goal: reduce lookahead until car crashes bc no time to break
LOOK_AHEAD_POINTS = look_ahead_points
radius_lookahead = []
for i in range(len(radius)):
next_n_radius = []
for j in range(LOOK_AHEAD_POINTS+1):
index = circle_indexes(
mylist=radius, index_car=i, add_index_1=j)[1]
next_n_radius.append(radius[index])
radius_lookahead.append(min(next_n_radius))
max_velocity_lookahead = [(constant_multiple * i**0.5)
for i in radius_lookahead]
velocity_lookahead = [min(v, max_speed)
for v in max_velocity_lookahead]
return velocity_lookahead
# For each point in racing track, check if left curve (returns boolean)
def is_left_curve(coords):
# Flatten the list and assign to variables (makes code easier to read later)
x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3 = [i for sub in coords for i in sub]
return ((x2-x1)*(y3-y1) - (y2-y1)*(x3-x1)) > 0
# Calculate the distance between 2 points
def dist_2_points(x1, x2, y1, y2):
return abs(abs(x1-x2)**2 + abs(y1-y2)**2)**0.5
3 改变LOOK_AHEAD_POINTS以影响算法向前看多少点(越高,汽车越早开始坏掉)
- 改变MIN_SPEED和MAX_SPEED适应轨道和模型!
LOOK_AHEAD_POINTS = 1
MIN_SPEED = 1.4
MAX_SPEED = 4
# Calculate optimal speed
velocity = optimal_velocity(track=racing_track,
min_speed=MIN_SPEED, max_speed=MAX_SPEED, look_ahead_points=LOOK_AHEAD_POINTS)
3.0.0.1
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
x = [i[0] for i in racing_track]
y = [i[1] for i in racing_track]
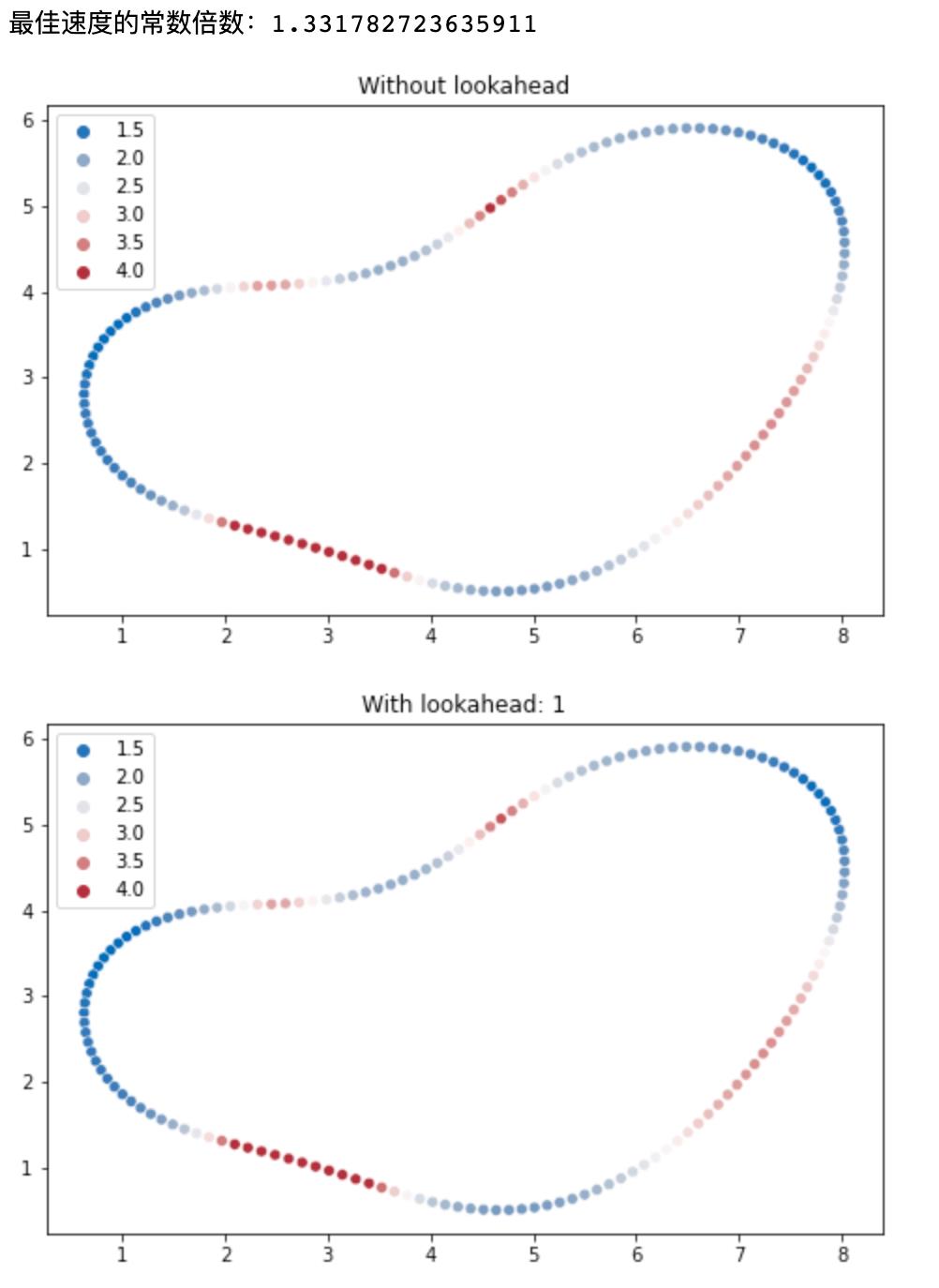
# Without lookahead
velocity_no_lookahead = optimal_velocity(track=racing_track,
min_speed=MIN_SPEED, max_speed=MAX_SPEED, look_ahead_points=0)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 5))
ax = sns.scatterplot(x=x, y=y, hue=velocity_no_lookahead,
palette="vlag").set_title("Without lookahead")
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 5))
ax = sns.scatterplot(x=x, y=y, hue=velocity, palette="vlag").set_title(
f"With lookahead: {LOOK_AHEAD_POINTS}")
3.0.0.2
distance_to_prev = []
for i in range(len(racing_track)):
indexes = circle_indexes(racing_track, i, add_index_1=-1, add_index_2=0)[0:2]
coords = [racing_track[indexes[0]],racing_track[indexes[1]]]
dist_to_prev = dist_2_points(x1=coords[0][0], x2=coords[1][0], y1=coords[0][1], y2=coords[1][1])
distance_to_prev.append(dist_to_prev)
time_to_prev = [(distance_to_prev[i]/velocity[i]) for i in range(len(racing_track))]
total_time = sum(time_to_prev)
print(f"Total time for track, if racing line and speeds are followed perfectly: {total_time} s")
如果完全遵循赛车路线和速度,赛道总时间:9.211515584763472 s
3.1
# Now we have list with columns (x,y,speed,distance,time)
racing_track_everything = []
for i in range(len(racing_track)):
racing_track_everything.append([racing_track[i][0],
racing_track[i][1],
velocity[i],
time_to_prev[i]])
# Round to 5 decimals
racing_track_everything = np.around(racing_track_everything, 5).tolist()
# Write to txt file
with open(f'optimals_newest_{TRACK_NAME}.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write("[")
for line in racing_track_everything:
f.write("%s" % line)
if line != racing_track_everything[-1]:
f.write(",\\n")
f.write("]")
4
# Calculate the radius for every point of the racing_track
radius = []
for i in range(len(racing_track)):
indexes = circle_indexes(racing_track, i, add_index_1=-1, add_index_2=1) # CHANGE BACK? 1;2
coords = [racing_track[indexes[0]],
racing_track[indexes[1]], racing_track[indexes[2]]]
radius.append(circle_radius(coords))
# Calculate curve direction
left_curve = []
for i in range(len(racing_track)):
indexes = circle_indexes(racing_track, i, add_index_1=-1, add_index_2=1)
coords = [racing_track[indexes[1]],
racing_track[indexes[0]], racing_track[indexes[2]]]
left_curve.append(is_left_curve(coords))
# Calculate radius with + and - for direction (+ is left, - is right)
radius_direction = []
for i in range(len(racing_track)):
radius_with_direction = radius[i]
if left_curve[i] == False:
radius_with_direction *= -1
radius_direction.append(radius_with_direction)
# Calculate steering with + and -
dist_wheels_front_back = 0.165 # meters
steering = []
for i in range(len(racing_track)):
steer = math.degrees(math.asin(dist_wheels_front_back/radius_direction[i]))
steering.append(steer)
# Merge relevant lists into dataframe
all_actions = pd.DataFrame({"velocity":velocity,
"steering":steering})
min(radius)
# Visualize action space
ax = sns.scatterplot(data=all_actions, x="steering", y="velocity")
ax.invert_xaxis()
ax.set_title(f"With lookahead: {LOOK_AHEAD_POINTS}")
可视化空间
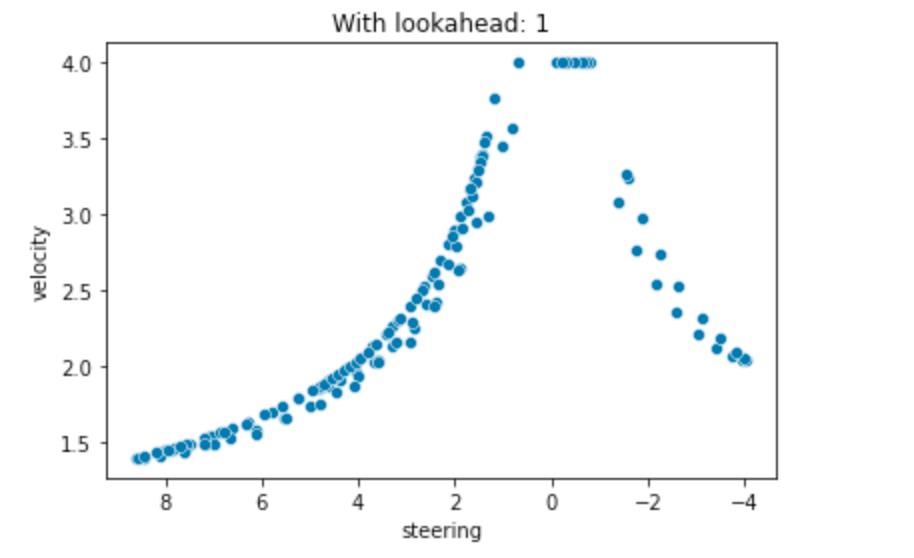
4.1 可视化所有动作
# Visualize all actions
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
sns.lineplot(data=all_actions["velocity"], color="r")
ax2 = plt.twinx()
sns.lineplot(data=all_actions["steering"], color="g", ax=ax2)
plt.axhline(0, ls='--', color="g")
a = plt.title("Speed (red), Steering (green; positive=left)")
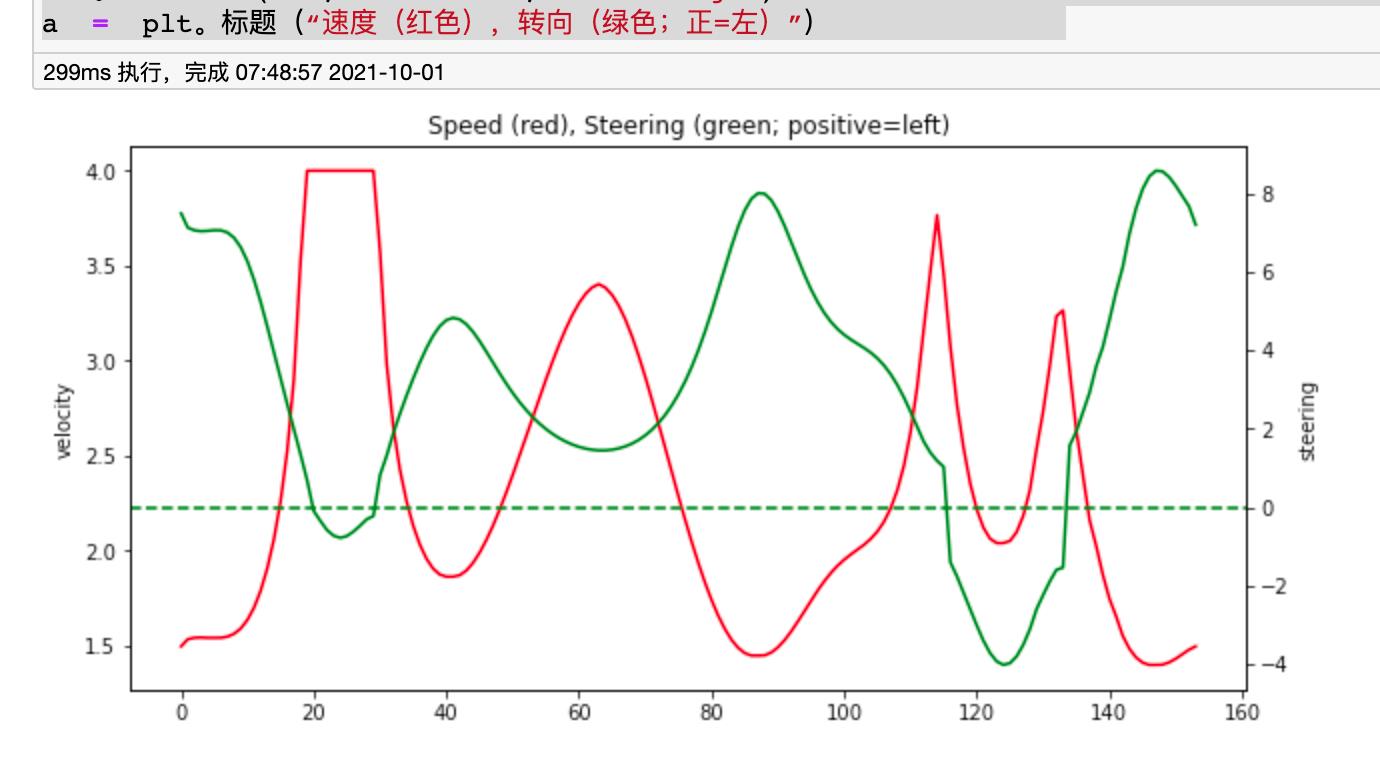
4.0.0.1
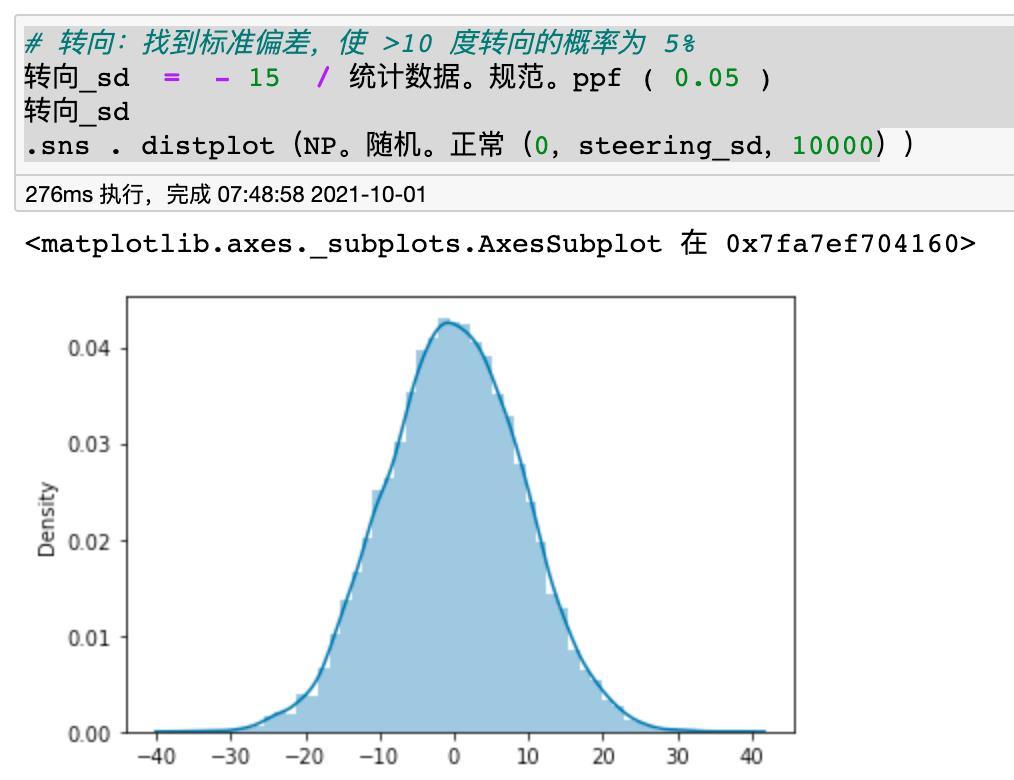
# Steering: Find standard deviation so that probability of >10 degrees steering is 5%
steering_sd = -15 / stats.norm.ppf(0.05)
steering_sd
sns.distplot(np.random.normal(0,steering_sd,10000))
# Velocity: Find standard deviation so that probability of >0.25m/s deviation is 0%
# Note: Here, probability is set to 0%, so no noise regarding velocity
velocity_sd = -0.25 / stats.norm.ppf(0.00)
velocity_sd
sns.distplot(np.random.normal(0,velocity_sd,10000))
all_actions_norm = all_actions.copy()
all_actions_norm_len = len(all_actions_norm)
resample_size = 1000
# Add gaussian noise to action space
for i in range(all_actions_norm_len):
v_true = all_actions_norm.iloc[i]["velocity"]
s_true = all_actions_norm.iloc[i]["steering"]
v_norm = np.random.normal(loc=v_true, scale=velocity_sd, size=resample_size)
s_norm = np.random.normal(loc=s_true, scale=steering_sd, size=resample_size)
vs_norm = pd.DataFrame(np.column_stack([v_norm,s_norm]), columns=["velocity","steering"])
all_actions_norm = pd.concat([all_actions_norm,vs_norm], axis=0, ignore_index=True)
# Take out actions with max speed, so that they are not affected by gaussian noise
# We do this because there are disproportionally many points with max speed, so
# K-Means will focus too much on these
all_actions_norm = all_actions_norm[all_actions_norm["velocity"] < MAX_SPEED]
# Add initial actions to action space (to make clustering more focused on initial actions)
add_n_initial_actions = int(resample_size / 8)
add_initial_actions = pd.DataFrame()
for i in range(add_n_initial_actions):
add_initial_actions = pd.concat([add_initial_actions,all_actions], axis=0, ignore_index=True)
all_actions_norm = pd.concat([all_actions_norm,add_initial_actions], axis=0, ignore_index=True)
# Display actions shape
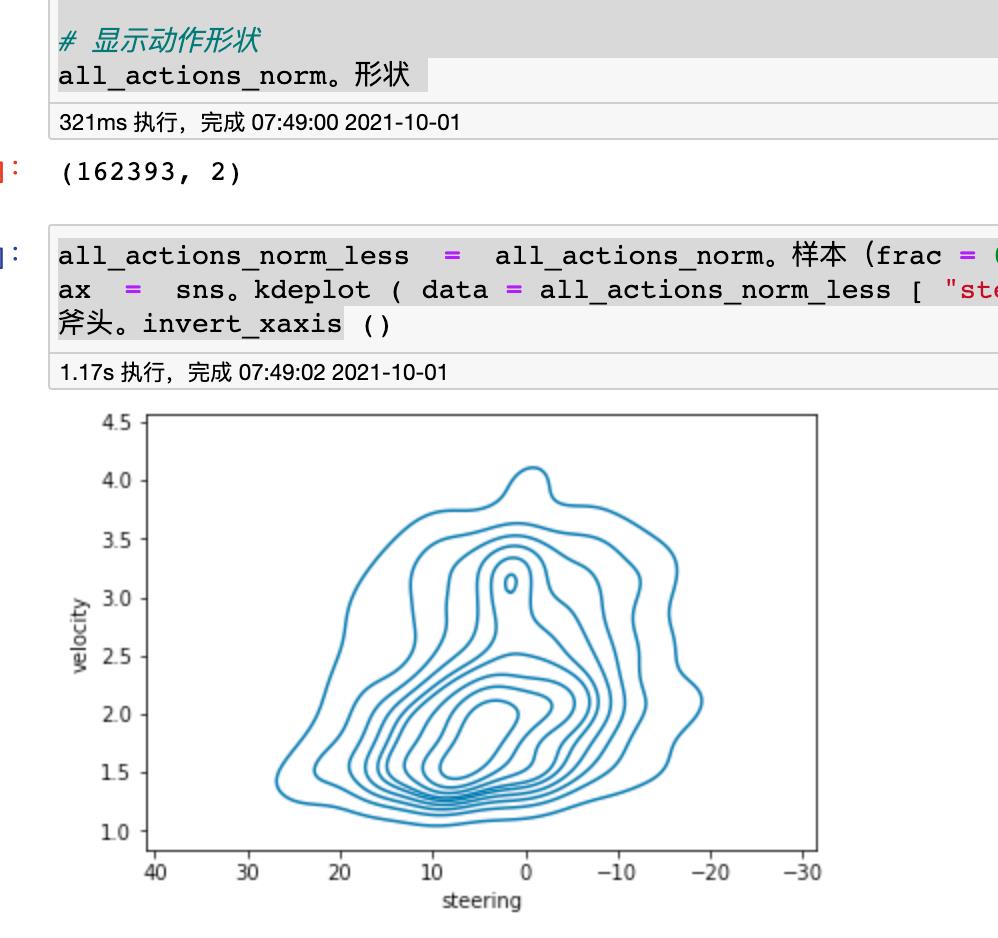
all_actions_norm.shape
all_actions_norm_less = all_actions_norm.sample(frac=0.01).reset_index(drop=True) # sample bc less compute time
ax = sns.kdeplot(data=all_actions_norm_less["steering"],data2=all_actions_norm_less["velocity"])
ax.invert_xaxis()
X = all_actions_norm
# Calculate action space with KMeans
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from sklearn.cluster import MiniBatchKMeans
# Rescale data with minmax
minmax_scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_minmax = pd.DataFrame(minmax_scaler.fit_transform(X),
columns=["velocity","steering"])
# KMeans
# remove 2 actions from KMeans so that low speed & high steering actions can be manually included
n_clusters = 21-2
model = MiniBatchKMeans(n_clusters=n_clusters).fit(X_minmax)
# Centroids (interpretable)
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
minmax_scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_minmax_fit = minmax_scaler.fit(X)
X_centroids = pd.DataFrame(X_minmax_fit.inverse_transform(model.cluster_centers_),
columns=["velocity","steering"])
# Add 2 manual actions
# Reason: When car starts new episode, it does not start on or direction of racing line, 以上是关于DeepRacer 根据路线计算Action Space RaceLine_Speed_ActionSpace的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章