CS224W摘要11.Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs
Posted oldmao_2000
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了CS224W摘要11.Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
CS224W: Machine Learning with Graphs
公式输入请参考: 在线Latex公式
本节课将介绍知识图谱上的推理任务(就是QA任务)。
主要思路如下:
1.基本概念
2.单跳查询(问答)
3.多跳查询
4.在不完整的KG上进行路径查询(借鉴TransE)
5.联合查询
6.在不完整的KG上进行联合查询(使用Query2Box)
7.Query2Box推广到更一般的形式
本节课用到的一个医学知识图谱。
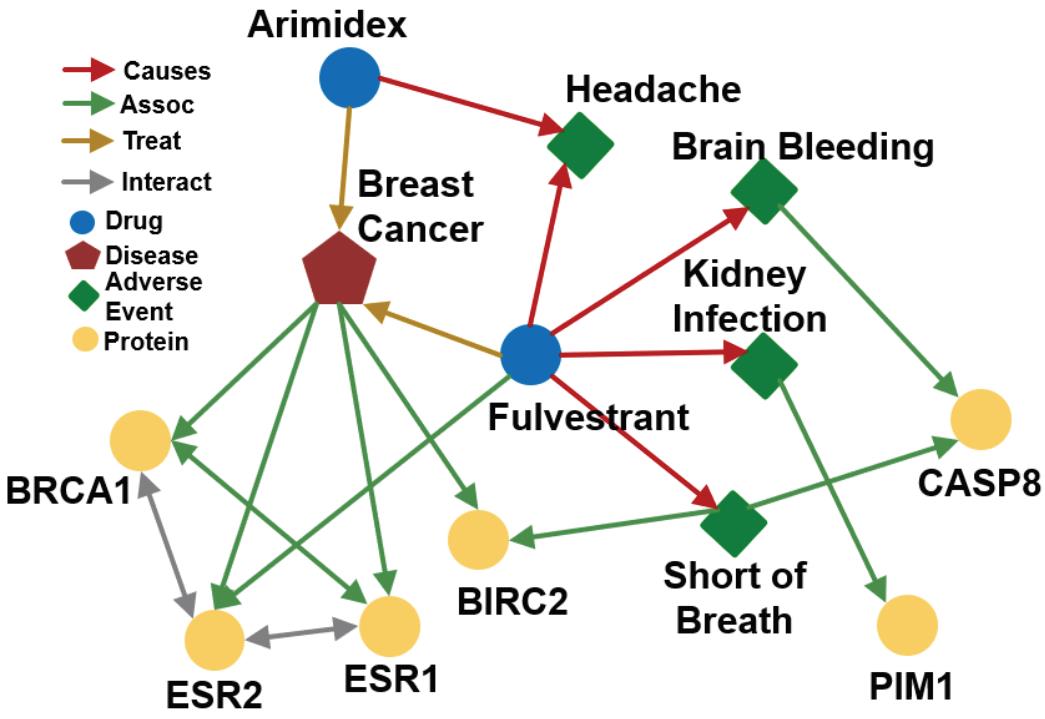
Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs
Predictive Queries on KG
给出几个例子:
| Query Types | Examples | |
|---|---|---|
| One-hop Queries | What adverse event is caused by Fulvestrant? (e:Fulvestrant, (r:Causes)) | 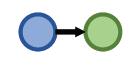 |
| PathQueries | What protein is associated with the adverse event caused by Fulvestrant? (e:Fulvestrant, (r:Causes, r:Assoc)) | 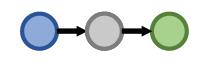 |
| Conjunctive Queries | What is the drug that treats breast cancer and caused headache? ((e:BreastCancer, (r:TreatedBy)), (e:Migraine, (r:CausedBy)) | 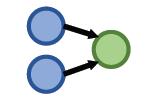 |
从One-hop query到path queries(完整KG)
对于单跳查询,可以说非常简单,因为在KG里面已经有
(
h
,
r
,
t
)
(h,r,t)
(h,r,t)的三元组了,这个时候的单跳查询相当于:问题
(
h
,
(
r
)
)
(h,(r))
(h,(r))的答案是
t
t
t吗。
For example: What side effects are caused by drug Fulvestrant?
例如:张三的爸爸是谁?
然后可以把单跳查询扩展到多跳查询,就是加多个关系进行计算,多个关系就会形成路径(path)
q
=
(
v
a
,
(
r
1
,
⋯
,
r
n
)
)
q=(v_a,(r_1,\\cdots,r_n))
q=(va,(r1,⋯,rn))
其中
v
a
v_a
va是开始实体(anchor entity),后面那些就是路径。
答案可以记为:
[
[
q
]
]
G
[[q]]_G
[[q]]G
图形化后:
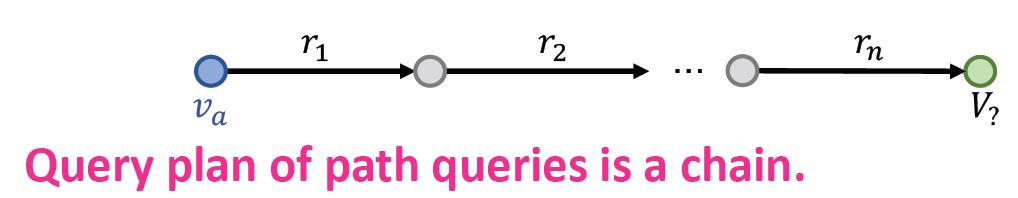
例子:燕小六的七舅姥爷的三外孙女
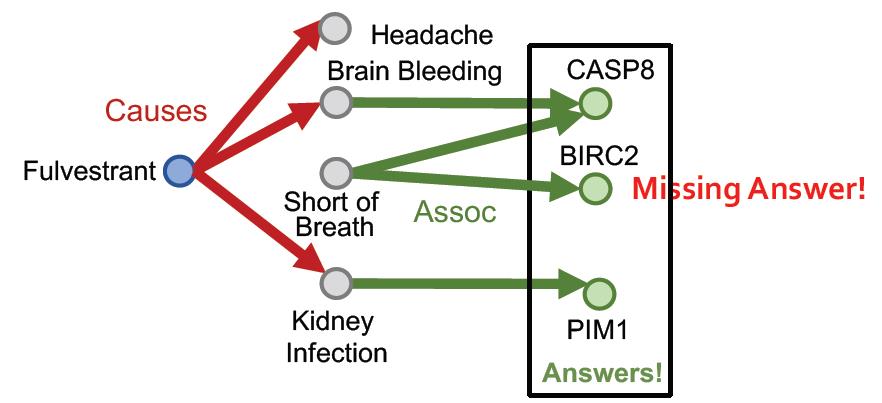
“What proteins are associated with adverse events caused by Fulvestrant?”
v
a
v_a
va is e:Fulvestrant
𝑟
1
,
𝑟
2
𝑟_1, 𝑟_2
r1,r2 is (r:Causes, r:Assoc)
Query:(e:Fulvestrant, (r:Causes, r:Assoc))
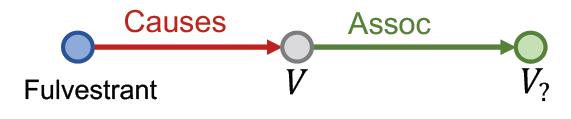
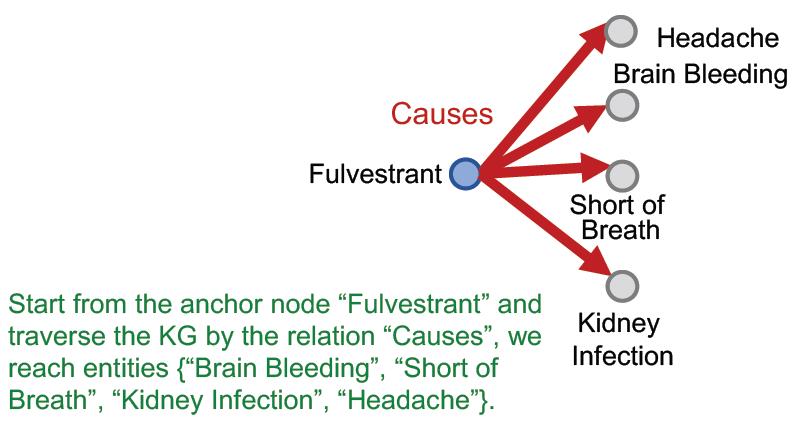
做这个查询就是用图的遍历即可,先遍历第一步
r
1
r_1
r1:
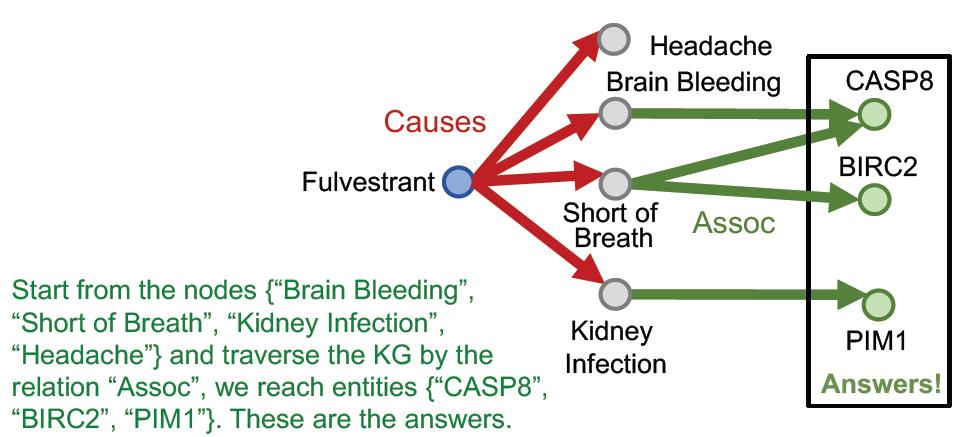
遍历第二步
r
2
r_2
r2:
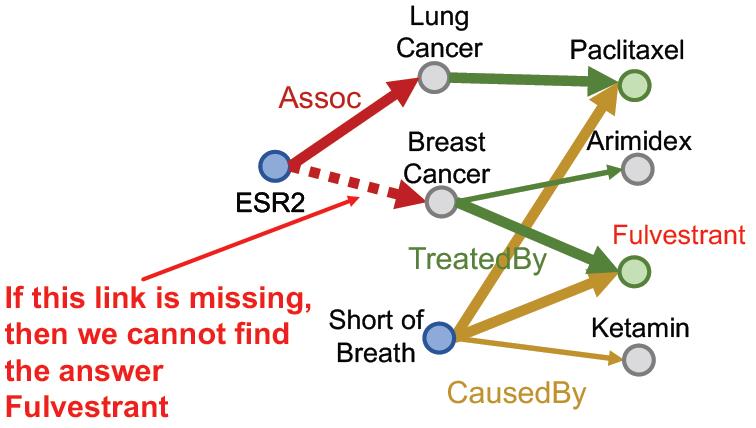
但是实际上没有这么简单,因为KG是不完整的。
例如:如果Fulvestrant和Short of Breath之间少了一个关系,那么会导致最后结果少了一个。
为什么不先做KG Completion
根据上节学习到的知识,我们知道可以做知识图谱补全任务,是不是补全了之后再来做推理就完美了?
答案:不是的
因为在知识图谱补全任务中,得到的补全的结果是一个非常稠密的图,补全任务中得到的关系是一个概率,所以大多数节点都会有一定概率出现关系(边)。
Time complexity of traversing a dense KG is exponential as a function of the path length 𝐿:
O
(
d
m
a
x
L
)
O(d^L_{max})
O(dmaxL)
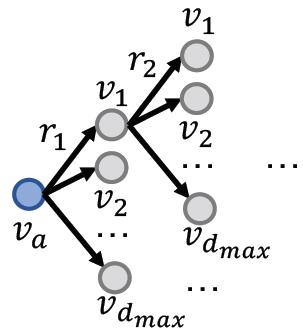
可以看到遍历操作是指数级别的复杂度,玩不起。下面看解决方案。
Answering Predictive Queries on Knowledge Graphs
Task: Predictive Queries
要在缺失信息(边)的情况下作出回答,相当于:Generalization of the link
prediction task
核心思路:
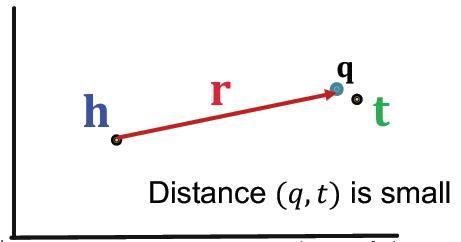
根据TransE的socore函数:
f
r
(
h
,
t
)
=
−
∣
∣
h
+
r
−
t
∣
∣
f_r(h,t)=-||h+r-t||
fr(h,t)=−∣∣h+r−t∣∣
可以把查询的表征理解为:
q
=
h
+
r
q=h+r
q=h+r
那么Predictive Queries的目标就是要使得查询的表征与答案的表征越近越好。
f
q
(
t
)
=
−
∣
∣
q
−
t
∣
∣
f_q(t)=-||q-t||
fq(t)=−∣∣q−t∣∣
同样套路,先看单跳查询:
如果是多跳查询:
q
=
(
v
a
,
(
r
1
,
⋯
,
r
n
)
)
q=(v_a,(r_1,\\cdots,r_n))
q=(va,(r1,⋯,rn))
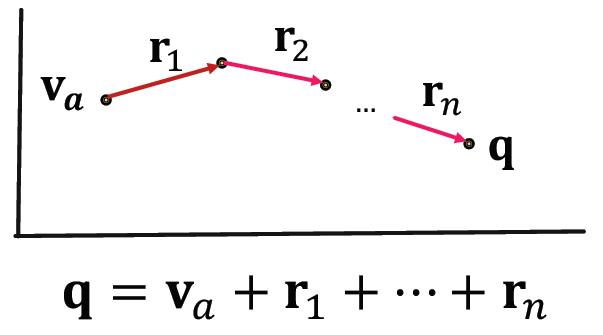
这样做的好处:
The embedding process only involves vector addition, (向量的加法)
independent of # entities
\\color{red}\\text{independent of \\# entities}
independent of # entities in the KG!
看例子:“What proteins are associated with adverse events caused by Fulvestrant?”
查询表示为: (e:Fulvestrant, (r:Causes , r:Assoc))
| 步骤 | Query Plan | Embedding Process |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  |
| 2 |  | 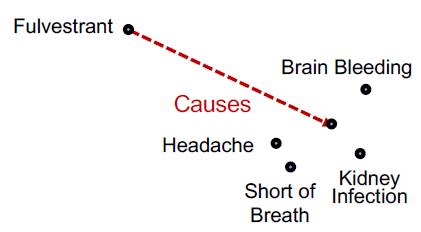 |
| 3 |  | 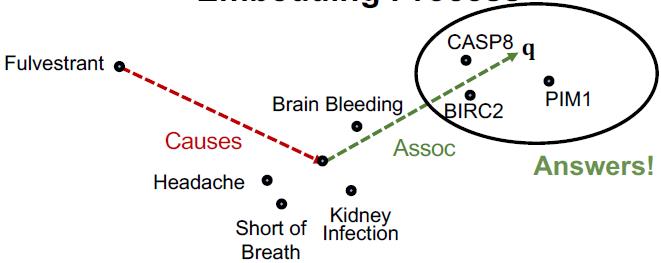 |
这里要补充1点:由于几个KG补全模型中,只有TransE能处理composition
relations,TransR / DistMult / ComplEx则不行。
Conjunctive Queries(完全图)
对于更加复杂的Conjunctive Queries,上面的模型就不好用了,看例子:
“What are drugs that cause Short of Breath and treat diseases associated with protein ESR2?”
查询:((e:ESR2, (r:Assoc, r:TreatedBy)), (e:Short of Breath, (r:CausedBy))
Query plan:
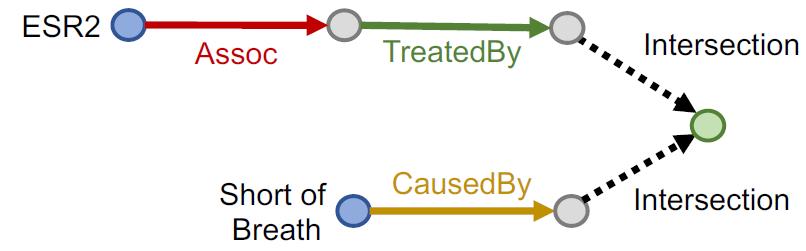
按KG traversal的思路,把这个Conjunctive Queries分解为两个Path Queries,然后求公共区域(不是求交):
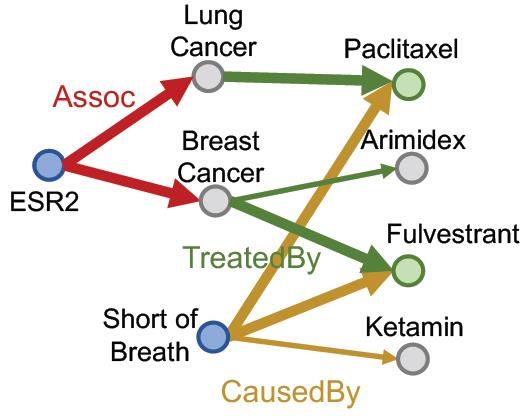
这也是在完全图的视角下完成的,如果缺少某个边,那么还是不行:
Query2box: Reasoning over KGs Using Box Embeddings

再回过头来看这个图,实际上这里面的灰色三个点实际上可能包含多个实体,解决这个表达 就要用框。
Box Embedding
Embed queries with hyper-rectangles (boxes)
𝐪
=
(
𝐶
𝑒
𝑛
𝑡
𝑒
𝑟
(
𝑞
)
,
𝑂
𝑓
𝑓
𝑠
𝑒
𝑡
(
𝑞
)
)
𝐪 = (𝐶𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟(𝑞) , 𝑂𝑓𝑓𝑠𝑒𝑡(𝑞))
q=(Center(q),Offset(q))
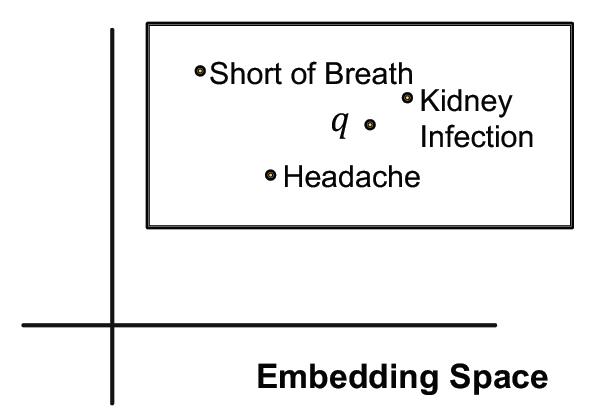
如果玩过数据库的QR Tree索引就会比较好理解,就是用一个矩形框来表征几个实体,例如:we can embed the adverse events of Fulvestrant with a box that enclose all the answer entities.
对于一些特殊的表示:
1.单个实体可以看做offset为0的矩形框,就是一个点。
2.每个关系会产生一个新的矩形框
3.多个矩形框可以做交集操作,得到的仍然是一个框(可以是空)
看上面的例子:
“What are drugs that cause Short of Breath and treat diseases
associated with protein ESR2?”
查询:((e:ESR2, (r:Assoc, r:TreatedBy)), (e:Short of Breath, (r:CausedBy))
再次看:

| Query Plan | Embedding Space | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 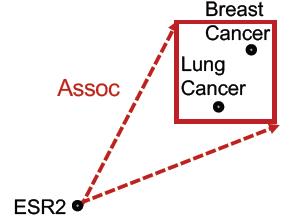 |
| 2 | 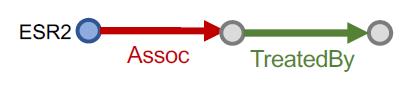 | 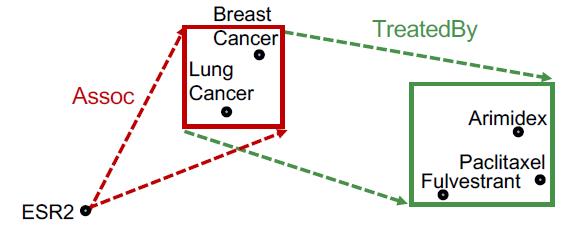 |
| 3 | 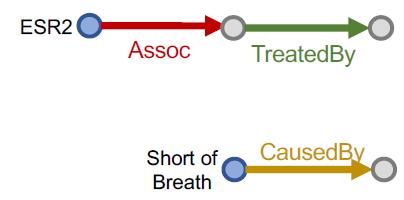 | 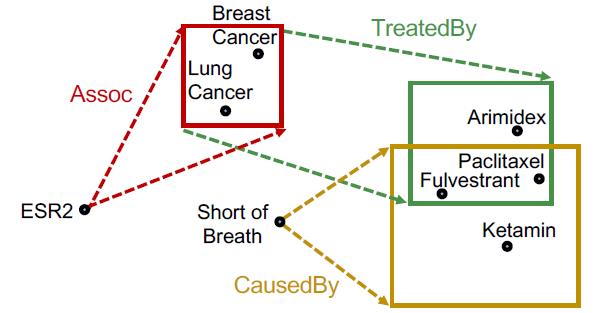 |
Projection 和Intersection
这里补充一下从点(或者矩形框)通过关系得到新box的操作:Projection Operator
P
\\mathcal{P}
P
Box × Relation → Box
𝐶
𝑒
𝑛
(
𝑞
′
)
=
𝐶
𝑒
𝑛
(
𝑞
)
+
𝐶
𝑒
𝑛
(
𝑟
)
𝑂
𝑓
𝑓
(
𝑞
′
)
=
𝑂
𝑓
𝑓
(
𝑞
)
+
𝑂
𝑓
𝑓
(
𝑟
)
𝐶𝑒𝑛 (𝑞') = 𝐶𝑒𝑛 (𝑞) + 𝐶𝑒𝑛 (𝑟)\\\\ 𝑂𝑓𝑓 (𝑞') = 𝑂𝑓𝑓 (𝑞) + 𝑂𝑓𝑓(𝑟)
Cen(q′)=Cen(q)+Cen(r)Off(q′)=Off(q)+Off(r)
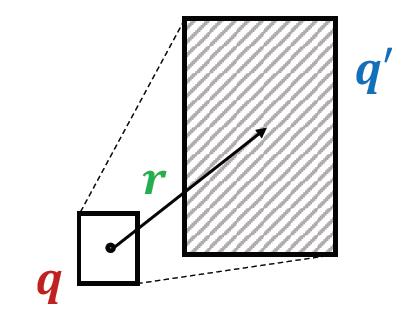
然后还有求相交操作Geometric Intersection Operator
J
\\mathcal{J}
J
Take multiple boxes as input and produce the intersection box.
求相交后的结果小于等于原来Box的面积,相交结果的中心应尽量接近求交的矩形中心。
这个求相交操作也是分别求相交后的结果的面积和中心两个部分。
对于中心:以输入矩形的中心做加权求和后作为新矩形中心。看下图的红色部分。
对于面积:是三个投影相交的公共部分。看下图的阴影部分。
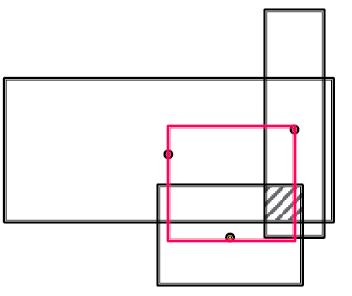
求中心的数学表达: 以上是关于CS224W摘要11.Reasoning over Knowledge Graphs的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
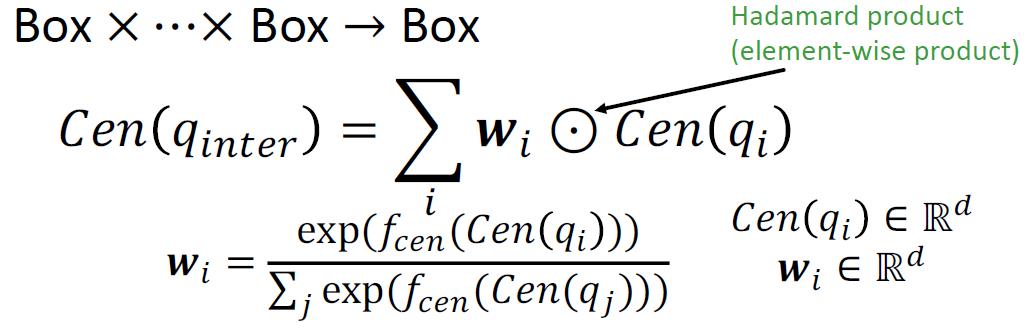
w
i
∈
R
d
w_i\\in\\R^d
wi∈Rd is calculated by a neural network
f
c
e
n
f_{cen}
fcen (with trainable weights)
这里老师还给出了
w
i
w_i
wi的另一种解释,相当于自注意力机制权重,从上面的图可以看到,面积大的那么新中心离其越近。实际上上面的
w
i
w_i
wi就是走的softmax公式,就是算权重。
求Offset(相交阴影)的表达如下:
O
f
f
(
q
i
n
t
e
r
)
=
min
(
o
f
f
(
q
1
)
,
⋯
,
o
f
f
(
q
n
)
)
⊙
σ
(
f
o
f
f
(
o
f
f
(
q
1
)
,
⋯
,
o
f
f
(
q
n
)
)
)
Off(q_{inter})=\\min\\left(off(q_1),\\cdots,off(q_n)\\right)\\odot\\sigma(f_{off}(off(q_1),\\cdots,off(q_n)))
Off(qinter)=min(off(q1),⋯,off(qn))⊙σ(foff(off(q1),⋯,off(qn)))
前面一项是找出所有输入矩形框中最小的那个。
f