我的物联网之路—Linux中的C编程—多线程编程
Posted Zhbk's Iot
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了我的物联网之路—Linux中的C编程—多线程编程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
| 日期 | 变更记录 |
|---|---|
| 2021-9-29 | 创建 |
什么是线程
线程是在共享内存空间种并发的多道执行路径,它们共享一个进程的资源。进程是系统中程序执行和资源分配的基本单位。线程是进程内的基本调度单位,也可以称为轻量级进程
线程分类
1. 用户级线程
2. 核心级线程
线程基本操作
由于线程共享进程的资源和地址空间,因此在对这些资源进行操作时,必须考虑到线程间资源访问的唯一性问题,这里介绍的是POSIX中线程同步的方法,主要有互斥锁和信号量的方式
互斥锁
互斥锁只有两种状态,就是上锁和解锁。互斥锁使得共享资源按序在各个线程中操作。可分为:快速锁、递归互斥锁、检错互斥锁
信号量
信号量也是操作系统中所用到的PV原语,它广泛用于进程或线程间的同步与互斥,本质上是非负的整数计数器,当信号量sem的值大于或等于0时,该线程具有公共资源的访问权限。互斥与同步的区别在于,互斥用的是同一个信号量,同步反之。
Example
线程创建
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *pthread_2(void *param)
{
int i;
// pthread_cancel(*(pthread_t *)param);
// 取消th1线程,那么就不会去执行pthread_1函数了
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程2:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
if(i == 5)
{
pthread_exit("exit");
}
}
}
void *pthread_1(void *param)
{
pthread_cancel(*(pthread_t *)param);
// 根据创建线程的函数,会先执行pthread_2一次然后回到pthread_1函数
// 但是又把th2传过来,把th2线程取消掉
while (1)
{
printf("我是线程1\\n");
sleep(1);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t th1,th2;
printf("主进程,下面开始创建线程\\n");
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, pthread_1, (void *)&th2);
// 创建线程标识符为th1,pthread_1是线程起始地址
pthread_create(&th2, NULL, pthread_2, (void *)&th1);
// 创建线程标识符为th2,pthread_2是线程起始地址,把th1传到pthread_2中
printf("线程创建结束\\n");
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
// 将线程挂起,等待结束
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
}
互斥锁
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
// 互斥锁
// 创建快速互斥锁
int flag = 0;
void *pthread_2(void *param)
{
int i;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
// 锁住线程资源
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程2:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
// 解锁
}
void *pthread_1(void *param)
{
int i;
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程1:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t th1,th2;
//pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER);
printf("主进程,下面开始创建线程\\n");
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, pthread_1, NULL);
pthread_create(&th2, NULL, pthread_2, (void *)&th1);
// 会先去执行th1的线程
printf("线程创建结束\\n");
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
// 将线程吊起
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
}
信号量
信号量互斥
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
sem_t sem;
//sem信号量实现三个线程互斥
void *pthread_3(void *param)
{
int i;
sem_wait(&sem); //sem = sem -1;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程3:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
sem_post(&sem); //sem = sem + 1;
}
void *pthread_2(void *param)
{
int i;
sem_wait(&sem); //sem = sem -1;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程2:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
sem_post(&sem); //sem = sem + 1;
}
void *pthread_1(void *param)
{
int i;
sem_wait(&sem); //sem = sem -1;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程1:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
sem_post(&sem); //sem = sem + 1;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t th1,th2, th3;
sem_init(&sem, 0, 1);
// 信号量初始化1
printf("主进程,下面开始创建线程\\n");
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, pthread_1, NULL);
pthread_create(&th2, NULL, pthread_2, NULL);
// 首先去执行th1线程
pthread_create(&th3, NULL, pthread_3, NULL);
printf("线程创建结束\\n");
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
// 将线程掉起
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
pthread_join(th3, NULL);
}
信号量同步
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
sem_t sem1, sem2, sem3;
//3个线程1,2,3
//执行顺序 3 1 2
void *pthread_3(void *param)
{
int i;
sem_wait(&sem1); //sem = sem -1;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程3:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
sem_post(&sem3); //sem = sem + 1;
}
void *pthread_2(void *param)
{
int i;
sem_wait(&sem2); //sem = sem -1;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程2:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
sem_post(&sem1); //sem = sem + 1;
}
void *pthread_1(void *param)
{
int i;
sem_wait(&sem3); //sem = sem -1;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("我是线程1:%d\\n", i);
sleep(1);
}
sem_post(&sem2); //sem = sem + 1;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t th1, th2, th3;
sem_init(&sem1, 0, 1);
sem_init(&sem2, 0, 0);
sem_init(&sem3, 0, 0);
printf("主进程,下面开始创建线程\\n");
pthread_create(&th1, NULL, pthread_1, NULL);
pthread_create(&th2, NULL, pthread_2, NULL);
pthread_create(&th3, NULL, pthread_3, NULL);
// 初始化后,sem1 = 0 ,sem2 ,sem3 =-1
printf("线程创建结束\\n");
pthread_join(th1, NULL);
pthread_join(th2, NULL);
pthread_join(th3, NULL);
}
函数说明
pthread_create

pthread_exit
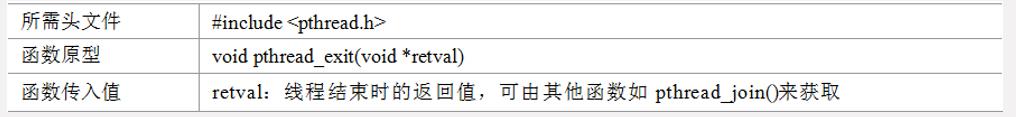
pthread_join

pthread_mutex_init
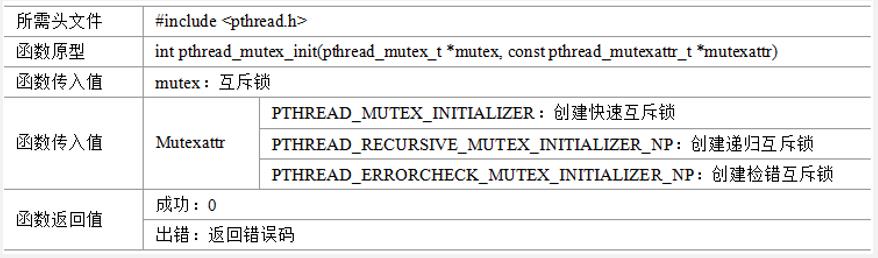
pthread_mutex_lock
pthread_mutex_trylock
pthread_mutex_unlock
pthread_mutex_destroy

sem_init

sem_wait
sem_trywait
sem_post
sem_getvalue
sem_destroy

以上是关于我的物联网之路—Linux中的C编程—多线程编程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章