尚硅谷设计模式学习(10)---[组合模式(Composite Pattern)]
Posted 小智RE0
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了尚硅谷设计模式学习(10)---[组合模式(Composite Pattern)]相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
🚀🚀🚀尚硅谷传送门==>B站尚硅谷Java设计模式
❤❤❤感谢尚硅谷❤❤❤
🕐🕑🕒最近开始计划学习一下设计模式了,加油!!!
📢情景引入
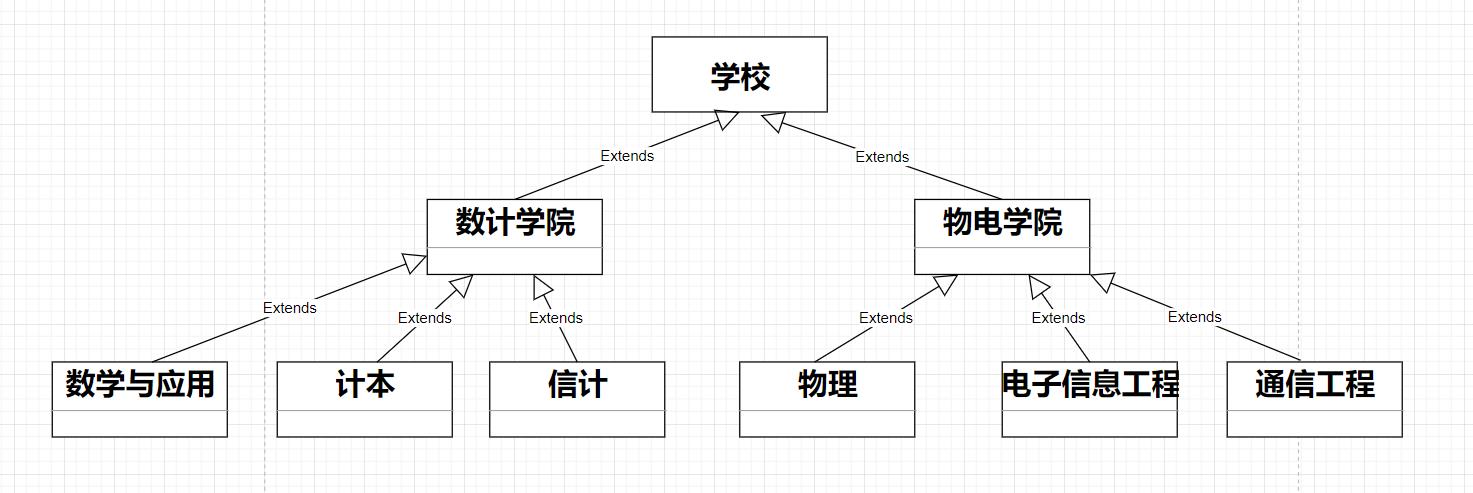
编写程序展示一个学校院系结构:
要在一个页面中展示出学校的院系组成,
一个学校有多个学院,一个学院有多个系。
传统思路分析
不能很好实现的管理的操作
🌈组合模式
把学校、院、系都看做是组织结构,他们之间没有继承的关系,而是一个树形结构,可以更好的实现管理操作。
关于组合模式::又称为部分与整体模式,将对象组合成树状结构以表示“整体-部分”的层次关系.
组合模式使得客户端对单个对象和组合对象的访问具有一致性,(组合能让客户端以一致的方式处理个别对象以及组合对象)
Component :组合中对象声明(接口/抽象类),可实现所有类的公用接口默认方法,用于访问和管理Component 子部件
Leaf : 表示叶子节点,作为被管理者
Composite : 非叶子节点,存储子部件
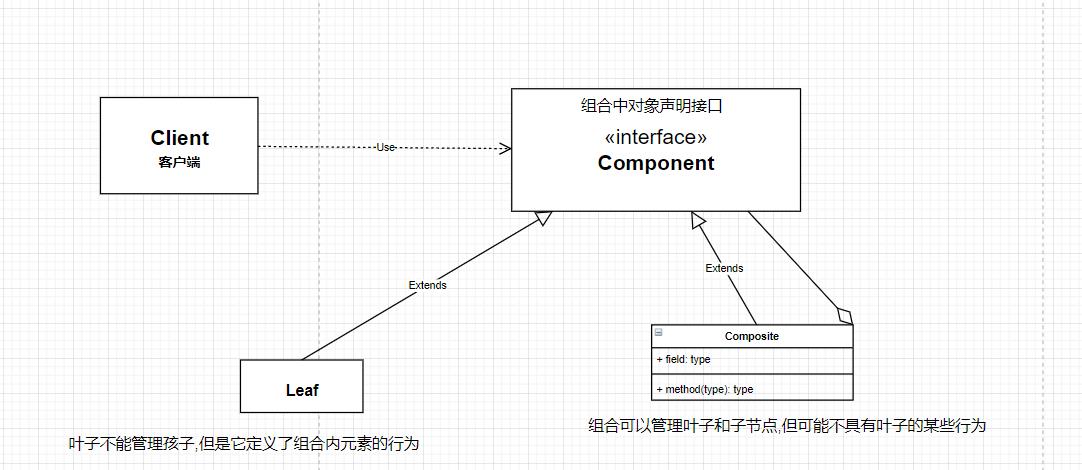
注意使用组合模式需要确保有相似的方法及属性的几个对象;比如这里的学校,学院它就有相似的添加,删除方法; 学校,学院,系 有相似的输出方法.
具有较强的扩展性。如果更改组合对象时,只需要调整内部的层次关系,客户端不用做出任何改动.
客户端只需要面对一致的对象而不用考虑整体部分或者节点叶子的问题
接着回到案例

作为组织管理 的抽象类OrganizationComponent
//组织管理
public abstract class OrganizationComponent {
private String name;
//描述;
private String describe;
//初始化;
public OrganizationComponent(String name, String describe) {
this.name = name;
this.describe = describe;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getDescribe() {
return describe;
}
public void setDescribe(String describe) {
this.describe = describe;
}
//由于叶子节点可能不需要某些方法,所以就没用抽象方法;
//添加方法;
protected void addMethod(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent){
//抛出不支持操作的异常;
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//删除方法;
protected void removeMethod(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent){
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//输出打印方法; 大学,学院,院系都需要的;作为抽象方法;
protected abstract void print();
}
大学University
//大学 ; 作为 Composite 管理College(学院)
public class University extends OrganizationComponent{
//这里存放的是学院;
List<OrganizationComponent> ogc=new ArrayList<OrganizationComponent>();
public University(String name, String describe) {
super(name, describe);
}
//添加方法;
@Override
protected void addMethod(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
ogc.add(organizationComponent);
}
//删除方法;
@Override
protected void removeMethod(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
ogc.remove(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return super.getName();
}
@Override
public String getDescribe() {
return super.getDescribe();
}
//输出方法;
@Override
protected void print() {
System.out.println("<<===大学====>>"+getName());
for (OrganizationComponent organizationComponent : ogc) {
organizationComponent.print();
}
}
}
学院College
//学院 管理 ==>系
public class College extends OrganizationComponent{
//这里存放的是Department (院系)
List<OrganizationComponent> ogc=new ArrayList<OrganizationComponent>();
public College(String name, String describe) {
super(name, describe);
}
//添加方法;
@Override
protected void addMethod(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
ogc.add(organizationComponent);
}
//删除方法;
@Override
protected void removeMethod(OrganizationComponent organizationComponent) {
ogc.remove(organizationComponent);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return super.getName();
}
@Override
public String getDescribe() {
return super.getDescribe();
}
//输出方法;
@Override
protected void print() {
System.out.println("!!!!!!!!!学院====>"+getName());
for (OrganizationComponent organizationComponent : ogc) {
organizationComponent.print();
}
}
}
系Department
//院系
public class Department extends OrganizationComponent{
public Department(String name, String describe) {
super(name, describe);
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return super.getName();
}
@Override
public String getDescribe() {
return super.getDescribe();
}
@Override
protected void print() {
System.out.println("院系====>"+getName());
}
}
模拟客户端Client
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//大学
OrganizationComponent university = new University("霍格沃兹","著名魔法学院");
//学院;
OrganizationComponent college1 = new College("格兰芬多","英勇无畏");
OrganizationComponent college2 = new College("拉文克劳","智慧聪敏");
//添加院系;
college1.addMethod(new Department("计算机专业","计科"));
college1.addMethod(new Department("网络工程","网络"));
college2.addMethod(new Department("物理专业","物理"));
college2.addMethod(new Department("通信专业","通信"));
//添加学院;
university.addMethod(college1);
university.addMethod(college2);
university.print();
}
}
执行输出
<<===大学====>>霍格沃兹
!!!!!!!!!学院====>格兰芬多
院系====>计算机专业
院系====>网络工程
!!!!!!!!!学院====>拉文克劳
院系====>物理专业
院系====>通信专业
组合模式在HashMap中的应用
比如说这样一个案例
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Integer,String> hashMap1 =new HashMap<Integer, String>();
//这里直接存放叶子节点;
hashMap1.put(0,"阿猫");
Map<Integer,String> hashMap2 =new HashMap<Integer, String>();
hashMap2.put(1,"阿喵");
hashMap2.put(2,"阿华");
//将第二个加到第一个map中去;
hashMap1.putAll(hashMap2);
System.out.println(hashMap1);
//{0=阿猫, 1=阿喵, 2=阿华}
}
}
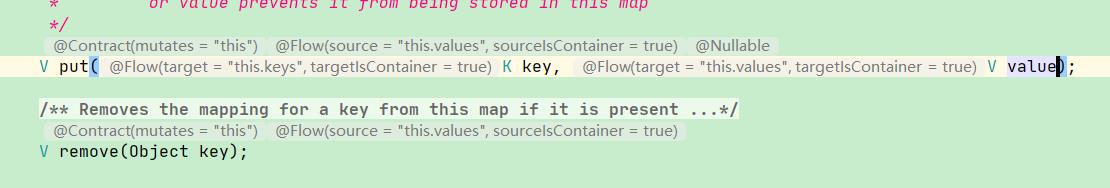
进入Map接口看看;
其中的put添加方法仅为抽象方法.
注意到Map接口的实现类AbstractMap是个抽象类; 类似于组合模式的Component(抽象构建)
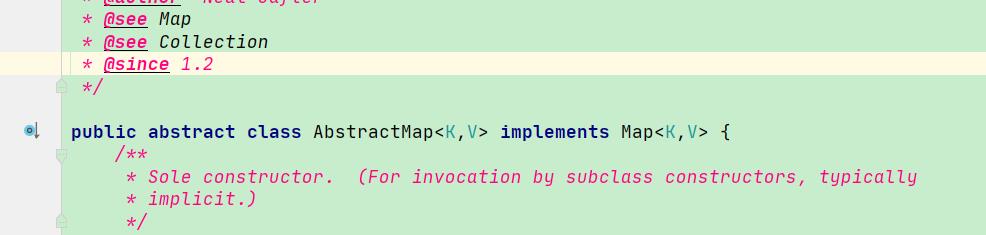
其中重写 put 方法时,默认实现,抛出不支持操作的异常对象.

AbstractMap的子类HashMap ; 类似于组合模式的Composite(中间构建)

实现了 put方法

继续;
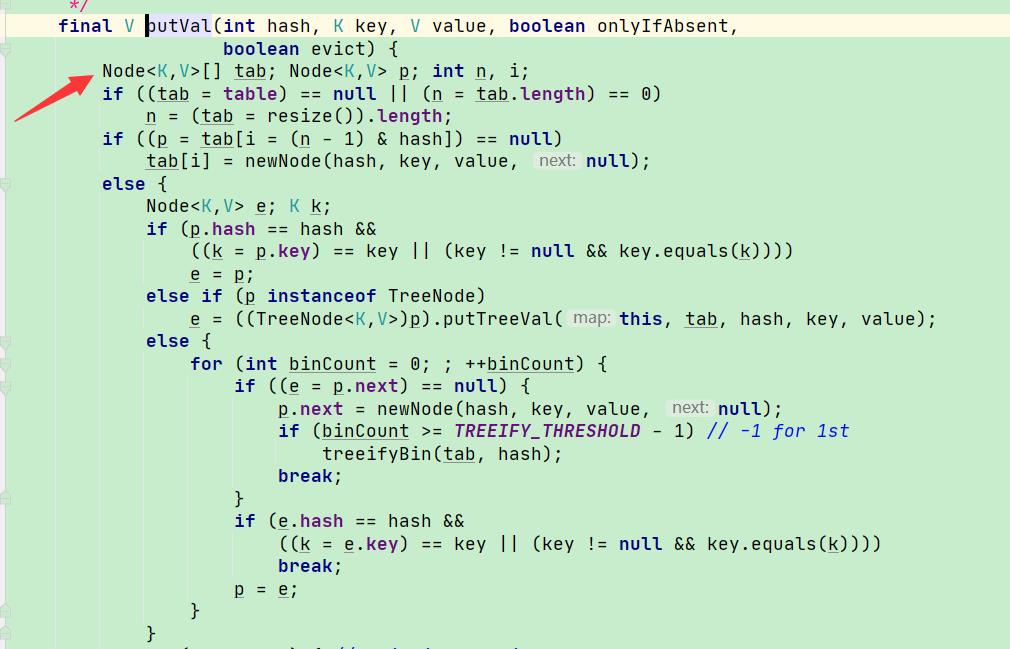
存入Node节点中 ; 类似于组合模式的叶子节点 Leaf

以上是关于尚硅谷设计模式学习(10)---[组合模式(Composite Pattern)]的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章