Halo2 学习笔记——设计之Proving system之Inner product argument
Posted mutourend
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Halo2 学习笔记——设计之Proving system之Inner product argument相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 引言
Halo2中使用的polynomial commitment scheme为Inner product argument。
其中Halo2中的 PC DL . Open \\text{PC}_\\text{DL}.\\text{Open} PCDL.Open使用了BCMS20( B¨unz 等人2020年论文《proof-carrying data from accumulation schemes》)中附录A.2中类似的算法。
2. BCMS20(proof-carry data)中的inner product argument
B¨unz 等人2020年论文《proof-carrying data from accumulation schemes》,详细可参看博客 proof-carrying data from accumulation schemes学习笔记 中的1.5节内容。
以下所有算法中的oracle access都是基于相同的random oracle
ρ
0
\\rho_0
ρ0。
为了方便描述,假设
d
+
1
d+1
d+1和
D
+
1
D+1
D+1均为2的幂乘,即满足
d
+
1
=
2
k
,
D
+
1
=
2
m
d+1=2^k,D+1=2^m
d+1=2k,D+1=2m。
对于向量
a
⃗
∈
S
n
\\vec{a}\\in S^n
a∈Sn,二分法时,
l
(
a
⃗
)
=
(
a
1
,
⋯
,
a
n
/
2
)
l(\\vec{a})=(a_1,\\cdots,a_{n/2})
l(a)=(a1,⋯,an/2)和
r
(
a
⃗
)
=
(
a
n
/
2
+
1
,
⋯
,
a
n
)
r(\\vec{a})=(a_{n/2+1},\\cdots,a_n)
r(a)=(an/2+1,⋯,an)分别表示
a
⃗
\\vec{a}
a的左半部分和右半部分。
基于discrete logarithm,对单变量多项式 p ( X ) = c 0 + c 1 X + ⋯ + c d X d p(X)=c_0+c_1X+\\cdots+c_dX^d p(X)=c0+c1X+⋯+cdXd的polynomial commitment算法实现细节为:
-
P C D L . S e t u p PC_{DL}.Setup PCDL.Setup:

-
P C D L . T r i m PC_{DL}.Trim PCDL.Trim:(暂时只考虑所有polynomial degree均为 d d d的情况)

-
P C D L . C o m m i t PC_{DL}.Commit PCDL.Commit:引入随机数 w w w,对多项式系数进行commit C = w S + ∑ i = 0 d c i G i C=wS+\\sum_{i=0}^{d}c_iG_i C=wS+∑i=0dciGi。
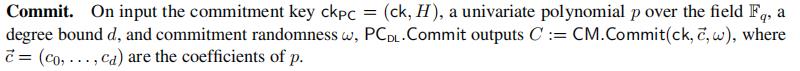
-
P C D L . O p e n PC_{DL}.Open PCDL.Open:借助[BCCGP16; BBBPWM18]中inner product argument的变种,计算evaluation proof π \\pi π:(evaluation point为 z z z)
– 1. 计算evaluation v = p ( z ) ∈ F q v=p(z)\\in\\mathbb{F}_q v=p(z)∈Fq。
– 2. sample 随机多项式 p ˉ ∈ F q ≤ d [ X ] \\bar{p}\\in\\mathbb{F}_q^{\\leq d}[X] pˉ∈Fq≤d[X],使得 p ˉ ( z ) = 0 \\bar{p}(z)=0 pˉ(z)=0。
– 3. sample 相应的commitment randomness w ˉ ∈ F q \\bar{w}\\in\\mathbb{F}_q wˉ∈Fq。
– 4. 计算随机多项式 p ˉ \\bar{p} pˉ的hiding commitment: C ˉ = C M . C o m m i t ρ 0 ( c k ⃗ , p ˉ ; w ˉ ) \\bar{C}=CM.Commit^{\\rho_0}(\\vec{ck},\\bar{p};\\bar{w}) Cˉ=CM.Commitρ0(ck,pˉ;wˉ)。
– 5. 计算challenge α = ρ ( C , z , v , C ˉ ) ∈ F q ∗ \\alpha=\\rho(C,z,v,\\bar{C})\\in\\mathbb{F}_q^* α=ρ(C,z,v,Cˉ)∈Fq∗。
– 6. 计算多项式: p ′ = p + α p ˉ = ∑ i = 0 d c i X i ∈ F q [ X ] p'=p+\\alpha \\bar{p}=\\sum_{i=0}^{d}c_iX^i\\in\\mathbb{F}_q[X] p′=p+αpˉ=∑i=0dciXi∈Fq[X]。
– 7. 计算commitment randomness: w ′ = w + α w ˉ ∈ F q w'=w+\\alpha\\bar{w}\\in\\mathbb{F}_q w′=w+αwˉ以上是关于Halo2 学习笔记——设计之Proving system之Inner product argument的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章