Halo2学习笔记——设计之Protocol Description
Posted mutourend
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Halo2学习笔记——设计之Protocol Description相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 引言
security parameter以
λ
\\lambda
λ表示,除非明确说明,所有算法和adversaries都是probabilistic (interactive) Turing machines that run in polynomial time in this security parameter。
n
e
g
l
(
λ
)
negl(\\lambda)
negl(λ) 表示a function that is negligible in
λ
\\lambda
λ。
1.1 Cryptographic Groups
-
G \\mathbb{G} G:表示a cyclic group of prime order p p p。
-
O \\mathcal{O} O:表示the identity of a group。
-
G \\mathbb{G} G中的scalars of elements 为 scalar field F \\mathbb{F} F of size p p p 中 的元素。
-
以大写字母来表示group element,以小写或希腊字母来表示scalar。
-
以粗体字来表示向量,即 a ∈ F n \\mathbf{a} \\in \\mathbb{F}^n a∈Fn and G ∈ G n \\mathbf{G} \\in \\mathbb{G}^n G∈Gn。
-
group operation为加法运算。
-
scalar a a a与group element G G G的乘积表示为 [ a ] G [a]G [a]G。
-
⟨ a , b ⟩ \\langle \\mathbf{a},\\mathbf{b}\\rangle ⟨a,b⟩表示2个相同长度scalar向量 a , b ∈ F n \\mathbf{a},\\mathbf{b}\\in\\mathbb{F}^n a,b∈Fn的inner product。
-
⟨ a , G ⟩ \\langle \\mathbf{a},\\mathbf{G}\\rangle ⟨a,G⟩ with a ∈ F n , G ∈ G n \\mathbf{a}\\in\\mathbb{F}^n,\\mathbf{G}\\in\\mathbb{G}^n a∈Fn,G∈Gn表示multiscalar multiplication。
-
0 n \\mathbf{0}^n 0n表示a vector of length n n n that only contains zeroes in F \\mathbb{F} F。
-
Discrete Log Relation Problem:
The advantage metric
Adv G , n dl-rel ( A , λ ) = Pr [ G G , n dl-rel ( A , λ ) ] \\text{Adv}_{\\mathbb{G},n}^{\\text{dl-rel}}(\\mathcal{A}, \\lambda) = \\textnormal{Pr} \\left[ \\mathsf{G}_{\\mathbb{G},n}^{\\text{dl-rel}}(\\mathcal{A}, \\lambda) \\right] AdvG,ndl-rel(A,λ)=Pr[GG,ndl-rel(A,λ)]
is defined with respect the following game.
G a m e G G , n dl-rel ( A , λ ) : ‾ G ← G λ n a ← A ( G ) Return ( ⟨ a , G ⟩ = O ∧ a ≠ 0 n ) \\begin{array}{ll} &\\underline{\\bold{Game} \\, \\mathsf{G}^{\\text{dl-rel}}_{\\mathbb{G},n}(\\mathcal{A}, \\lambda):} \\\\ &\\mathbf{G} \\gets \\mathbb{G}^n_\\lambda \\\\ &\\mathbf{a} \\gets \\mathcal{A}(\\mathbf{G}) \\\\ &\\textnormal{Return} \\, \\left( \\langle \\mathbf{a}, \\mathbf{G} \\rangle = \\mathcal{O} \\land \\mathbf{a} \\neq \\mathbf{0}^n \\right) \\end{array} GameGG,ndl-rel(A,λ):G←Gλna←A(G)Return(⟨a,G⟩=O∧a=0n)
即已知
n
n
n-length vector
G
∈
G
n
\\mathbf{G}\\in\\mathbb{G}^n
G∈Gn group elements,discrete log relation problem 会ask for
g
∈
F
n
\\mathbf{g}\\in\\mathbb{F}^n
g∈Fn,使得
g
≠
0
n
\\mathbf{g}\\neq \\mathbf{0}^n
g=0n 且
⟨
a
,
G
⟩
=
O
\\langle \\mathbf{a},\\mathbf{G}\\rangle=\\mathcal{O}
⟨a,G⟩=O,可将其称为 non-trivial discrete log relation。
该problem的hardness与 JT20 Lemma3中的 hardness of the discrete log problem in the group 紧密相连。可使用game
G
G
,
n
dl-rel
\\mathsf{G}_{\\mathbb{G},n}^{\\text{dl-rel}}
GG,ndl-rel 来定义该problem。
1.2 Interactive Proofs
interactive proof由3个算法组成 IP = ( Setup , P , V ) \\text{IP}=(\\text{Setup},\\mathcal{P},\\mathcal{V}) IP=(Setup,P,V):
- Setup ( 1 λ ) \\text{Setup}(1^{\\lambda}) Setup(1λ):输出为 p p \\mathbf{pp} pp,为public parameters。
Prover P \\mathcal{P} P 和 Verifier V \\mathcal{V} V 为interactive machines (with access to p p \\mathbf{pp} pp),以 ⟨ P ( x ) , V ( y ) ⟩ \\langle\\mathcal{P}(x),\\mathcal{V}(y)\\rangle ⟨P(x),V(y)⟩来表示execute a two-party protocol between Prover P \\mathcal{P} P 和 Verifier V \\mathcal{V} V on inputs x , y x,y x,y 的算法。在协议的最后,Verifier输出a decision bit。
1.3 Zero knowledge Arguments of Knowledge
Proofs of knowledge为:interactive proofs,Prover致力于令Verifier相信,针对某statement x x x,其知道某witness ω \\omega ω,使得 ( x , ω ) ∈ R (x,\\omega)\\in\\mathcal{R} (x,ω)∈R,其中 R \\mathcal{R} R为polynomial-time decidable relation R \\mathcal{R} R。
Halo2中主要关注具有computationally-bounded prover的argument of knowledge。
argument of knowledge主要有以下4个安全视角:
- Completeness:若Prover基于valid witness运算,则其总是可使Verifier信服。
- Soundness:cheating Prover无法在不知道valid witness的情况下,使Verifier信服错误的proof。cheating Prover成功的概率为soundness error。
- Knowledge soundness:若Verifier信服该statement是正确的,Prover是否实际处理的(”知道“)就是相应的valid witness。cheating Prover成功的概率为knowledge error。
- Zero knowledge:即Verifier是否可从proof中知道相应的valid witness。
1.3.1 Completeness

1.3.2 Soundness
-
Public coin是指:all of the messages sent by the verifier are each sampled with fresh randomness。
-
Fiat-Shamir transformation是指:In this transformation an interactive, public coin argument can be made non-interactive in the random oracle model by replacing the verifier algorithm with a cryptographically strong hash function that produces sufficiently random looking output。
-
State-Restoration Soundness:
详细参见论文 GT20- Tight State-Restoration Soundness in the Algebraic Group Model:
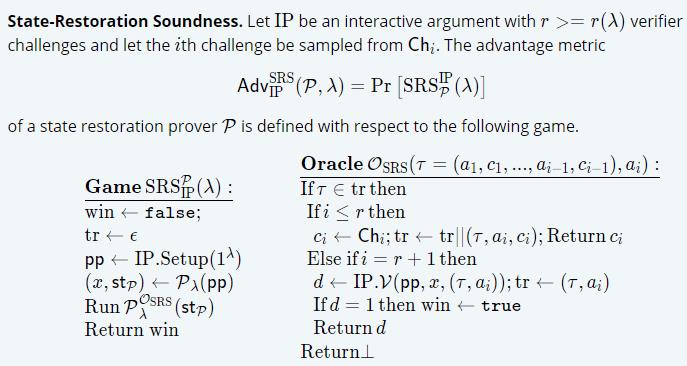
-
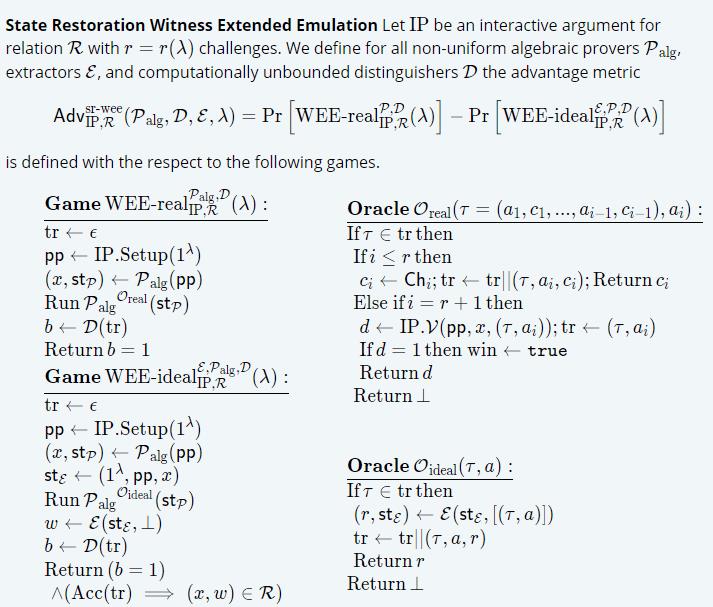
Knowledge Soundness:又名 witness extended emulation,是指:any successful prover algorithm there exists an efficient emulator that can extract a witness from it by rewinding it and supplying it with fresh randomness。
Halo2中对 witness extended emulation 的定义做了小调整,即Halo2中的provers为state restoration provers,定义为可rewind the verifier。此外,为了避免在witness extraction过程中对state restoration prover的rewind,Halo2中将协议定义在了algebraic group model:

algebraic group支持所谓的“online” extraction:即the extractor can obtain the witness from the representations themselves for a single (accepting) transcript。 -
State Restoration Witness Extended Emulation:
1.3.3 Zero Knowledge
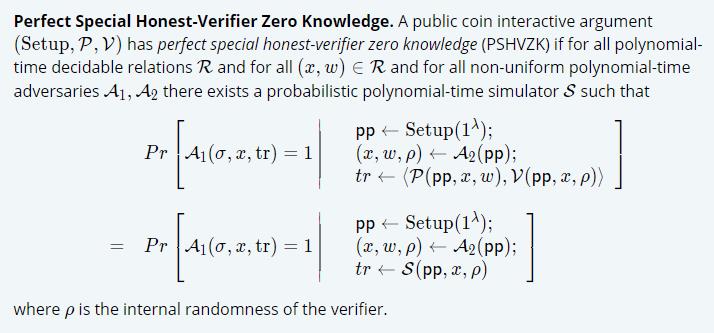
通常zero-knowledge定义中,要求Verifier act “honestly”,并send challenges that correspond only with their internal randomness,Verifier不可adaptively respond to the prover based on the prover’s messages。Halo2中使用了增强版定义:即强制要求the simulator to output a transcript with the same (adversarially provided) challenges that the verifier algorithm sends to the prover
2. Protocol
参考资料
以上是关于Halo2学习笔记——设计之Protocol Description的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章