JavaScipt 面试题+知识点
Posted ~,555555
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JavaScipt 面试题+知识点相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
变量类型
前置知识
-
值类型 vs 引用类型
// 值类型 let a = 100; let b = a; a = 200; console.log(b); //100// 引用类型 let a = { age: 20 }; let b = a; b.age = 21; console.log(a.age); //21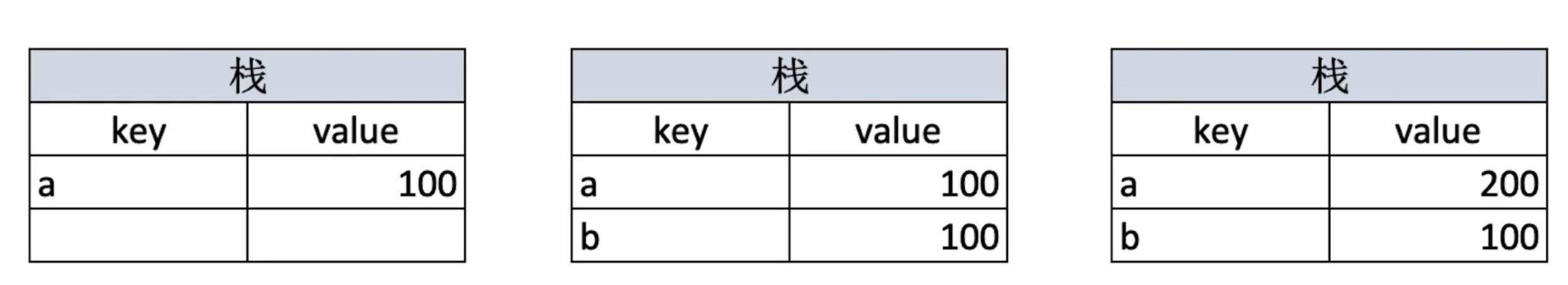
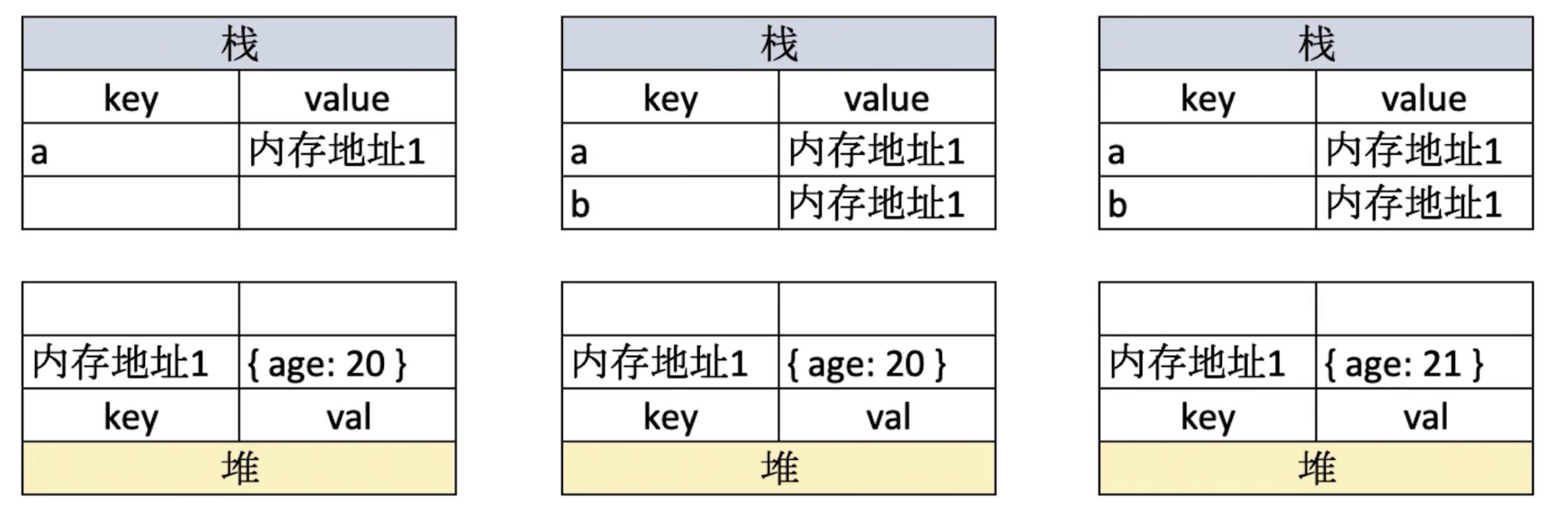
// 常见值类型 let a // undefined const s = 'abc' const n = 100 const b = true const m = Symbol('m');// 常见引用类型 const obj = { x: 100 }; const arr = ['a', 'b', 'c']; const n = null // 特殊引用类型 指针指向空地址 // 特殊引用类型 因为不用于存储数据,所以没有“拷贝、复制函数”一说 function fn(){} -
逻辑运算
-
truthy变量:!!a === true 的变量
let a = 100; !a; //false !!a; //true -
falsy变量:!!a === false 的变量
在 javascript 中只有 8 个 falsy 值。
// 以下是falsely变量 除此之外都是truely变量 !!0 === false !!-0 ===false !!NaN === false !!0n ===false (bigInt) !!'' === false !!null === false !!undefined === false !!false === false
-
if 语句 判断的是否为truthy或者falsy。
-
与或非同样判断的是 truthy或者falsy
console.log(10&&0); //0 console.log(''||'abc') //'abc' console.log(!window.abc) //true
-
题目
-
typeof 能判断哪些类型
// typeof 可以判断所有值类型 let a; typeof a; //undefined let str = 'abc'; typeof str; // string const n = 100; typeof n; // number const b = true; typeof b; // boolean const s = Symbol('s'); typeof s; // symbol let big = BigInt(10e15); typeof big; // bigint// 能判断引用类型 typeof console.log // function typeof function(){} // function // 能识别引用类型 typeof null; // object typeof [1, 2, 3]; // object typeof {x:100}; // object -
何时使用 === 何时使用 ==
// 除了 == null以外,其他一律用 ===, 例如 const obj = {x:100} if(obj.a == null) {} // 相当于 if(obj.a === null || obj===undefined){} -
值类型和引用类型的区别
值类型的值直接存储在栈中,而引用类型在栈中存储的是地址,地址指向其在堆中对应的值。
-
手写深拷贝
const obj = { age: 20, name: '张三', address: { city: 'beijing' }, arr: [1, 2, 3, [4, 5, 6]] } /** * 深拷贝 * @param {Object} obj 要拷贝的对象 */ function deepClone(obj) { if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj === undefined) { // 如果obj不是object类型或者为undefined return obj; } // 初始化返回结果 let result; if (obj instanceof Array) { result = []; } else { result = {}; } for(let key in obj){ // 保证key 不为原型的属性 if(obj.hasOwnProperty(key)){ // 递归 如果是数组,此时的key为索引 result[key] = deepClone(obj[key]); } } return result; } const obj2 = deepClone(obj);
类
前置知识
-
class
- constructor
- 属性
- 方法
class Student{ constructor(name,number){ this.name = name; this.number = number; } sayHi(){ console.log(`姓名${this.name} 学号:${this.number}`); } } // 实例化对象 const Alex = new Student('Alex','001'); console.log(Alex.name); console.log(Alex.number); Alex.sayHi(); -
继承
- extends
- super
- 执行
super.method(...)来调用一个父类方法。 - 执行
super(...)来调用一个父类 constructor(只能在我们的 constructor 中)。
- 执行
// 父类 class People{ constructor(name){ this.name = name; } eat(){ console.log(`${this.name} can eat`); } } // 子类 class Student extends People{ constructor(name,number){ super(name); this.number = number; } sayHi(){ super.eat(); console.log(`姓名${this.name} 学号:${this.number}`); } } const Alex = new Student('Alex','001'); console.log(Alex.name); console.log(Alex.number); Alex.sayHi();
题目
-
如何准确判断一个变量是否为数组?
Array.isArray(xx)或者xx instanceof Array -
手写一个简易的jQuery,考虑插件和拓展性?
class jQuery{ constructor(selector){ this.selector = selector; const result = document.querySelectorAll(selector); for(let i =0; i<result.length;i++){ this[i] = result[i]; } this.length = result.length; } get(index){ return this[index]; } each(fn){ for(let i=0;i<this.length;i++){ fn(this[i]) } } on(type,fn){ return this.each(elem=>{ elem.addEventListener(type,fn,false); }) } } // 插件 jQuery.prototype.dialog =function(info){ alert(info); } // 复写 class myJQuery extends jQuery{ constructor(selector){ super(selector); } getLenth(){ console.log(this.length); } } new myJQuery('p').getLenth(); -
如何理解class的原型本质
人们常说
class是一个语法糖,因为我们实际上可以在没有class的情况下声明相同的内容。尽管,它们之间存在着重大差异:
-
首先,通过
class创建的函数具有特殊的内部属性标记[[IsClassConstructor]]: true。因此,它与手动创建并不完全相同。编程语言会在许多地方检查该属性。例如,与普通函数不同,必须使用
new来调用它: -
类方法不可枚举。 类定义将
"prototype"中的所有方法的enumerable标志设置为false。这很好,因为如果我们对一个对象调用
for..in方法,我们通常不希望 class 方法出现。 -
类总是使用
use strict。 在类构造中的所有代码都将自动进入严格模式。
-
作用域和闭包
前置知识
-
自由变量
- 一个变量在当前作用域没有定义,但是被使用了
- 向上一级作用域,一层一层依次寻找,直至找到为止
- 如果到全局作用域都没有找到,则报错
xx is not defined
-
作用域
- 全局作用域
- 函数作用域
- 块级作用域
-
闭包
-
作用域应用的特殊情况,有两种表现:①函数作为参数传递 ②函数作为返回值被返回
-
最关键的地方:在函数定义的位置找!
-
所有的自由变量的查找,是在函数定义的地方,向上级作用域查找,不是在执行的地方。
// 函数作为返回值 function create() { let a = 100; return function () { console.log(a); } } let fn = create(); let a = 200; fn(); //100// 函数作为参数 function print(fn){ let a = 200; fn(); } let a =100; function fn(){ console.log(a); } print(fn); //100
-
-
this
this的值是在函数调用时确定的,不是在函数定义时确定的。
-
作为普通函数
function fn1(){ console.log(this); } fn1(); // window -
使用call apply bind
fn1.call({x:100}); // this指向 {x:100} const fn2 = fn1.bind({x:200}); fn2(); //{x:200} -
作为对象方法被调用
const zhangsan = { name: '张三', sayHi(){ // this 即当前对象 console.log(this); }, wait(){ setTimeout(function(){ // this指向window console.log(this); },10); }, waitAbitLonger(){ setTimeout(() => { console.log(this); }, 100); } } zhangsan.sayHi(); zhangsan.wait(); //window zhangsan.waitAbitLonger(); //指向对象张三 const wait = zhangsan.waitAbitLonger; wait(); // window -
在class方法中被调用
class People{ constructor(name){ this.name = name; this.age = 20; } sayHi(){ console.log(this); } } const zhangsan = new People('张三'); zhangsan.sayHi(); // zhangsan 对象 -
箭头函数
-
题目
-
this的不同应用场景,如何取值? -
手写
bind函数function fn1(...args){ console.log('this',this); console.log(...args); return 'this is fn1' } // const fn2 = fn1.bind({x:200},10,20,30); 原生bind // const res = fn2(); // console.log(res); // 手写bind Function.prototype.bind1= function(){ // 将参数变为数组 const args = [...arguments]; // 获取this const t = args.shift(); // 此时的this指向调用bind1的函数 比如fn1.bind1() 则bind1()中的this指向fn1 const self = this; //返回一个函数 return function(){ return self.apply(t,args); } } let test = fn1.bind1({x:200},10,20,30); console.log(test());// 手写apply function fn(...args) { console.log(this); //(**) console.log('I got called with ' + [...args].join(' ')); return [...args].reduce((total, curr) => total + curr, 0); } Function.prototype.applyTest = function (t, args) { // 此时的this 指向调用applyTest的函数 // t为需要被指定的上下文 t.__proto__.fn = this; // 为什么要在原型链上添加,因为如果不在原型链添加 在(**)中打印this时就多了这个函数 let result = t.fn(...args); delete t.__proto__.fn; return result } let result = fn.apply({ zs: 100 }, [2, 3, 4]); console.log(result); // 瞎写补充一点 Function.prototype.applyTest = function (t, args) { if (t == undefined) { if (args == undefined) { // 此时没有上下文 也没有参数 直接调用函数即可 return this(args); } else { // 展开参数 return this(...args); } } t.__proto__.fn = this; let result; if (args == undefined) { result = t.fn(args); } else { result = t.fn(...args); } delete t.__proto__.fn; return result; } -
闭包在实际开发中的应用场景,举例说明
// 隐藏闭包中的数据 缓存数据 // 例子1 function createCache(){ const data = {}; // 闭包中的数据被隐藏 不被外界访问 return { set: function(key,val){ data[key] = val; }, get:function(key){ return data[key]; } } } const c = createCache(); c.set('a',100); console.log(c.get('a')); // 例子2 function slow(x) { // 这里可能会有重负载的 CPU 密集型工作 alert(`Call以上是关于JavaScipt 面试题+知识点的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章