Entity Framework Core中更改跟踪工作原理
Posted JimCarter
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Entity Framework Core中更改跟踪工作原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/ef/core/change-tracking/
文章目录
1. 什么时候跟踪、什么时候不跟踪?
每个dbcontext实例都会跟踪对实体的更改,当调用SaveChanges方法时把这些更改应用到数据库。这些跟踪操作由更改跟踪器完成。
什么时候跟踪?
- 查数据库时返回的查询结果
- 通过
Add、Attach、Update等类似方法附加到context上的数据 - 一个新实体关联到了已被跟踪实体上
什么时候不再跟踪?
- 数据库上下文已被释放
- 更改跟踪器(change tracker)被清除了(调用了
ChangeTracker.Clear) - 手动分离(detach)实体
2. 实体的状态
每个实体都有5个状态:
Detached:实体未被DbContext跟踪Added:是个新实体,并且没有插入到数据库中。执行SaveChanges时会被插入。Unchanged:实体从数据库查出来之后一直都没被更改过(实体从数据库查询出来之后默认的就是这个状态)。Modified:实体从数据库查出来之后有被更改过。执行SaveChanges时会更新。Deleted:实体存在于数据库中。执行SaveChanges时会从数据库删除此数据。
下图展示了不同的状态:
| 实体状态 | 数据库上下文(DbContext)会跟踪 | 存在于数据库中 | 属性已修改 | SaveChanges 上的操作 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Detached | 否 | - | - | - |
Added | 是 | 否 | - | 插入 |
Unchanged | 是 | 是 | 否 | - |
Modified | 是 | 是 | 是 | 更新 |
Deleted | 是 | 是 | - | 删除 |
这几个状态的关系如下:
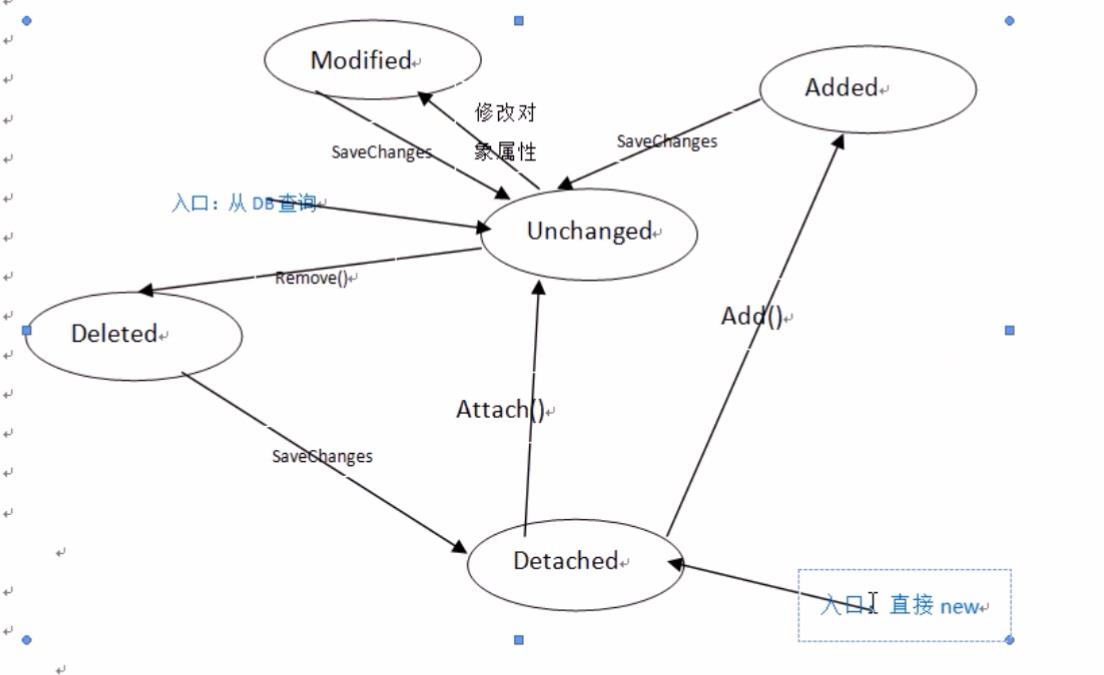
3. 手动跟踪实体
实体可以手动附加(attached)到数据库上下文上。应用场景主要有:
- 创建了新实体需要插入到数据库中:主要是通过
DbContext.Add方法(等效于DbSet<T>.Add)实现。 - 重新附加之前处于已分离(detached)状态的实体:当应用程序将实体发送给客户端,客户端更之后返回,此时应重新附加实体已响应更改。通过
DbContext.Attach和DbContext.Update实现。
3.1 附加现有实体
使用context.Attach方法
//此时Blog实体和Post子实体都处于Unchanged状态,无主键的实体被认为是Added
context.Attach(
new Blog
{
Id = 1,
Name = ".NET Blog",
Posts =
{
new Post
{
Id = 1,
Title = "Announcing the Release of EF Core 5.0",
Content = "Announcing the release of EF Core 5.0, a full featured cross-platform..."
},
new Post
{
Id = 2,
Title = "Announcing F# 5",
Content = "F# 5 is the latest version of F#, the functional programming language..."
},
new Post
{
//Added状态
Title = "Announcing .NET 5.0",
Content = ".NET 5.0 includes many enhancements, including single file applications, more..."
},
}
});
如果附加的实体主键有值则被认为是Unchanged状态,如果主键没有赋值则认为是Added状态。当调用SaveChanges方法时,Added状态的实体会提交的数据库,Unchanged状态的实体会过滤掉。
3.2 更新现有实体
使用context.Update方法
//此时Blog实体和Post子实体处于Modfied状态,无主键的实体认为是Added状态
context.Update(
new Blog
{
Id = 1,
Name = ".NET Blog",
Posts =
{
new Post
{
Id = 1,
Title = "Announcing the Release of EF Core 5.0",
Content = "Announcing the release of EF Core 5.0, a full featured cross-platform..."
},
new Post
{
//Added状态
Title = "Announcing F# 5",
Content = "F# 5 is the latest version of F#, the functional programming language..."
}
}
});
3.3 删除实体
3.3.1 删除子实体
一般都不会对新new出来的实体调用DbContext.Delete. 也不同于DbContext.Add,DbContext.Attach,DbContext.Update方法,DbContext.Delete常见于删除处于Unchanged或Modified状态的实体。
当delete一个实体时,如果这个实体处于detached状态,则自动会先attach它然后再删除,即:
context.Attach(post);
context.Remove(post);
//等同于
context.Remove(post);
3.3.2 删除父实体
删除父实体比删除子实体会麻烦一点.因为当删除父实体之后子实体的外键就会找不引用成为无效的状态,大多数数据库都会报错。解决方式有两种:
- 将子实体的外键属性设置可为null,表明断开子父关系。当ef检测到外键可空时,删除父实体就会默认将外键置空。
- 将子实体也一并删除。当ef检测到外键不可空时,删父实体时会一并把子实体删除。
3.4 自定义跟踪
使用DbContext.ChangeTracker.TrackGraph方法可以自定义实体的状态,它在开始跟踪前会调用一个委托,可以在这个委托里定义自己的逻辑。
考虑以下功能代码,如果key为0则新增,如果为负则删除,如果为正则更新:
public static void UpdateBlog(Blog blog)
{
using var context = new BlogsContext();
context.ChangeTracker.TrackGraph(
blog, node =>
{
var propertyEntry = node.Entry.Property("Id");
var keyValue = (int)propertyEntry.CurrentValue;
if (keyValue == 0)
{
node.Entry.State = EntityState.Added;
}
else if (keyValue < 0)
{
propertyEntry.CurrentValue = -keyValue;
node.Entry.State = EntityState.Deleted;
}
else
{
node.Entry.State = EntityState.Modified;
}
Console.WriteLine($"Tracking {node.Entry.Metadata.DisplayName()} with key value {keyValue} as {node.Entry.State}");
});
context.SaveChanges();
}
4. 访问跟踪实体
对于每个跟踪实体,efcore会跟踪以下几个内容:
- 实体的状态,如
Unchanged、Added、、、、等。 - 实体间的关系
- 实体属性当前的值
- 实体属性的原始值,一般是从数据库查询出来的值
- 哪些属性的值改变过了
- 属性的临时值(如新增是会给主键分配一个临时值)
4.1 访问实体(EntityEntry<T>)
可以通过dbContxt.Entry(blog)方法获取跟踪实体的信息, 返回的是一个EntityEntry<T>类型的对象。
下面是使用EntityEntry来处理整个实体的几个常用方法:
| EntityEntry 成员 | 描述 |
|---|---|
EntityEntry.State | 获取和设置 EntityState 实体的。(与EF6不同的是,设置单个实体的状态并不会影响到其关联的实体的状态,与Add、Attach之类的方法不一样) |
EntityEntry.Entity | 获取实体实例。 |
EntityEntry.Context | 此实体对应的DbContext |
EntityEntry.Metadata | IEntityType 实体类型的元数据。 |
EntityEntry.IsKeySet | 实体是否已设置其键值。 |
EntityEntry.Reload() | 用从数据库中读取的值覆盖属性值。 |
EntityEntry.DetectChanges() | 强制检测此实体是否更改 |
4.2 访问实体的某个属性(PropertyEntry<TEntity,TProperty>)
可以通过context.Entry(blog).Property(e => e.Name)方法获取跟踪实体的某个属性的值,返回类型是PropertyEntry<TEntity,TProperty>。该类型常用的方法有以下几种:
| PropertyEntry 成员 | 描述 |
|---|---|
PropertyEntry<TEntity,TProperty>.CurrentValue | 获取和设置属性的当前值。 |
PropertyEntry<TEntity,TProperty>.OriginalValue | 获取并设置属性的原始值(如果可用)。 原始值是从数据库中查出来的值,如果当前实体被断开连接,然后又附加到了其它数据库上下文上,则此值与 CurrentValue一样。 |
PropertyEntry<TEntity,TProperty>.EntityEntry | 属性对应的 EntityEntry<TEntity>。 |
PropertyEntry.Metadata | IProperty 属性的元数据。 |
PropertyEntry.IsModified | 指示此属性是否被标记为已修改,并允许更改此状态。 可设置为false,让ef强制更新数据库, SaveChanges只会更新标记为已修改的属性 |
PropertyEntry.IsTemporary | 指示此属性是否标记为临时,并允许更改此状态。 临时值通常由efcore生成,如主键值。当手动给当前属性赋值只会,则 IsTemporary为false。 |
4.2.1 访问实体的全部属性
context.Entry(blog).Properties:获取所有属性context.Entry(blog).CurrentValues:获取所有属性的当前值context.Entry(blog).OriginalValues;:所有属性的原始值context.Entry(blog).GetDatabaseValues();:所有属性的数据库值
这几个方法组合起来,可以完成以下常见操作:
- 使用DTO的值,更新当前实体的值:
context.Entry(blog).CurrentValues.SetValues(blogDto);,入参是object,所以DTO的类型不一定要与实体的类型保持一致,但是DTO属性名需要与实体属性名匹配。 - 根据
Dictionary里的值设置跟踪实体的值:
var blogDictionary = new Dictionary<string, object> { ["Id"] = 1, ["Name"] = "1unicorn2" };
context.Entry(blog).CurrentValues.SetValues(blogDictionary);
- 从数据库值设置跟踪实体的值:
var databaseValues = context.Entry(blog).GetDatabaseValues();
context.Entry(blog).CurrentValues.SetValues(databaseValues);
context.Entry(blog).OriginalValues.SetValues(databaseValues);
- 创建一个包含当前值/原始值/数据库值数据的克隆对象
context.Entry(blog).CurrentValues.ToObject();
context.Entry(blog).GetDatabaseValues().ToObject();
这个克隆对象不会被dbcontext跟踪。
4.3 访问实体的导航属性
可使用以下三种方法获取实体的导航属性:
EntityEntry<TEntity>.Reference:适用于导航属性是单个对象的情景。EntityEntry<TEntity>.Collection:导航属性是集合时的情景EntityEntry.Navigation:导航属性是单个对象或者集合都适用。
//适用于单个对象
ReferenceEntry<Post, Blog> referenceEntry1 = context.Entry(post).Reference(e => e.Blog);
ReferenceEntry<Post, Blog> referenceEntry2 = context.Entry(post).Reference<Blog>("Blog");
ReferenceEntry referenceEntry3 = context.Entry(post).Reference("Blog");
//适用于集合
CollectionEntry<Blog, Post> collectionEntry1 = context.Entry(blog).Collection(e => e.Posts);
CollectionEntry<Blog, Post> collectionEntry2 = context.Entry(blog).Collection<Post>("Posts");
CollectionEntry collectionEntry3 = context.Entry(blog).Collection("Posts");
//都适用
NavigationEntry navigationEntry = context.Entry(blog).Navigation("Posts");
NavigationEntry常见成员有以下几种:
| NavigationEntry 成员 | 描述 |
|---|---|
MemberEntry.CurrentValue | 获取和设置导航的当前值。 这是集合导航的整个集合。 |
NavigationEntry.Metadata | INavigationBase 导航的元数据。 |
NavigationEntry.IsLoaded | 获取或设置一个值,该值指示是否已从数据库完全加载相关实体或集合。 |
NavigationEntry.Load() | 从数据库加载相关实体或集合;请参阅 显式加载相关数据。 |
NavigationEntry.Query() | 查询 EF Core 将使用将此导航作为IQueryable 可以进一步组合的来加载 |
4.3.1 访问实体的全部导航属性
以下代码表示强制加载全部导航属性的数据:
foreach (var navigationEntry in context.Entry(blog).Navigations)
{
navigationEntry.Load();
}
4.4 访问跟踪实体的所有成员
常规属性和导航属性有不同的状态和行为,所以上面的章节介绍了二者的单独处理。但是有时候我们需要对成员做统一的处理,并不关心它是普通属性和导航属性。可以使用EntityEntry.Member和EntityEntry.Members:
foreach (var memberEntry in context.Entry(blog).Members)
{
Console.WriteLine(
$"Member {memberEntry.Metadata.Name} is of type {memberEntry.Metadata.ClrType.ShortDisplayName()} and has value {memberEntry.CurrentValue}");
}
4.5 访问所有的跟踪实体
可以使用ChangeTracker.Entries()方法获取数据库上下文中所有被跟踪的的实体:
context.ChangeTracker.Entries();//获取所有跟踪实体
context.ChangeTracker.Entries<Post>();//获取类型为Post的跟踪实体
context.ChangeTracker.Entries<ITest>();//获取实现了ITest接口的所有跟踪实体
4.6 Find和FindAsync方法
DbContext.Find、 DbContext.FindAsync 、 DbSet<TEntity>.Find和 DbSet<TEntity>.FindAsync方法用来根据主键值查找单个实体。查找时首先会查找已跟踪实体里存不存在,如果不存在则再访问数据库。
var orderline = context.OrderLines.Find(orderId);//单一主键
var orderline = context.OrderLines.Find(orderId, productId);//联合主键
4.7 使用DbSet访问本地视图中的跟踪实体
efcore的查询始终在数据库上执行,并且仅返回已保存到数据库的实体。但是可以通过DbSet<T>.Local方法,查询在DbContext的本地视图(LocalView)中的 跟踪数据。通过这个方法你可以查询到处于Added状态的实体,可以过滤掉处于Deleted状态的实体(一般的linq查询是获取不到这两种状态的实体,因为都没有保存到数据库)。
查看以下代码:
using var context = new BlogsContext();
var posts = context.Posts.Include(e => e.Blog).ToList();
Console.WriteLine("Local view after loading posts:");
foreach (var post in context.Posts.Local)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Post: {post.Title}");
}
context.Remove(posts[1]);
context.Add(
new Post
{
Title = "What’s next for System.Text.Json?",
Content = ".NET 5.0 was released recently and has come with many...",
Blog = posts[0].Blog
});
Console.WriteLine("Local view after adding and deleting posts:");
foreach (var post in context.Posts.Local)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Post: {post.Title}");
}
输出结果是:
Local view after loading posts:
Post: Announcing the Release of EF Core 5.0
Post: Announcing F# 5
Post: Announcing .NET 5.0
Local view after adding and deleting posts:
Post: What’s next for System.Text.Json?
Post: Announcing the Release of EF Core 5.0
Post: Announcing .NET 5.0
如果把Local方法去掉,会发现两次输出并没有什么区别:
Local view after loading posts:
Post: Announcing the Release of EF Core 5.0
Post: Announcing F# 5
Post: Announcing .NET 5.0
Local view after adding and deleting posts:
Post: Announcing the Release of EF Core 5.0
Post: Announcing F# 5
Post: Announcing .NET 5.0
DbSet<T>.Local方法返回的是LocalView<T>类,这个类实现了ICollection<T>接口,与ObservableCollection<T>类似,当增加或删除集合中的实体时会发出通知。
LocalView的通知会挂靠到DbContext上,使本地视图与DbContext保持同步,具体体现在:
- 给
DbSet.Local添加新实体时,数据库上下文也会跟踪这个实体,并将其置为Added状态。 - 删除
DbSet.Local中的实体时,会被标记为Deleted状态。 - 如果数据库上下文跟踪了一个实体,那么这个实体会自动出现在
DbSet.Local里。 - 如果change tracker将一个实体标记为
Deleted,那么这个实体不再出现在DbSet.Local。
所以更改实体状态的话我们又多了LocalView这种方式。以下代码的输出结果与上面的例子一样:
using var context = new BlogsContext();
var posts = context.Posts.Include(e => e.Blog).ToList();
Console.WriteLine("Local view after loading posts:");
foreach (var post in context.Posts.Local)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Post: {post.Title}");
}
context.Posts.Local.Remove(posts[1]);
context.Posts.Local.Add(
new Post
{
Title = "What’s next for System.Text.Json?",
Content = ".NET 5.0 was released recently and has come with many...",
Blog = posts[0].Blog
});
Console.WriteLine("Local view after adding and deleting posts:");
foreach (var post in context.Posts.Local)
{
Console.WriteLine($" Post: {post.Title}");
}
将本地视图与WPF/WinForm中的绑定结合
LocalView可以返回ObservableCollection和BindingList供绑定使用:
LocalView<TEntity>.ToObservableCollection()返回适用于WPF的ObservableCollection<T>数据绑定。LocalView<TEntity>.ToBindingList()返回适用于WinForm的BindingList<T>数据绑定。
5. 关系修正
efcore通过外键和导航属性来维护实体间的关系。如果更改了外键的值efcore则会自动更新导航属性以反映此更改。同理如果更改了导航也会同步更新外键的值,这种机制称为==“关系修正”==。修正经常发生在查询时:当从数据库查询实体,会首先进行修正。因为数据库里只存外键值,没有导航属性的值。
以下例子:Blog与BlogAssets是一对一,Blog与Post是一对多,Post与Tag是多对多
using var context = new BlogsContext();
var blogs = context.Blogs
.Include(e => e.Posts)
.Include(e => e.Assets)
.ToList();
Console.WriteLine(context.ChangeTracker.DebugView.LongView);
“关系修正”还会发生在已跟踪的实体与查询返回的新实体之间。考虑以下代码:
using var context = new BlogsContext();
var blogs = context.Blogs.ToList();
Console.WriteLine(context.ChangeTracker.DebugView.LongView);//此时Blog的Assets和Posts导航都为空
/*输出如下
Blog {Id: 1} Unchanged
Id: 1 PK
Name: '.NET Blog'
Assets: <null>
Posts: []
Blog {Id: 2} Unchanged
Id: 2 PK
Name: 'Visual Studio Blog'
Assets: <null>
Posts: []
*/
var assets = context.Assets.ToList();
Console.WriteLine(context.ChangeTracker.DebugView.LongView);//此时Blog的Assets导航已经有值了
/*
Blog {Id: 1} Unchanged
Id: 1 PK
Name: '.NET Blog'
Assets: {Id: 1}
Posts: []
Blog {Id: 2} Unchanged
Id: 2 PK
Name: 'Visual Studio Blog'
Assets: {Id: 2}
Posts: []
BlogAssets {Id: 1} Unchanged
Id: 1 PK
Banner: <null>
BlogId: 1 FK
Blog: {Id: 1}
BlogAssets {Id: 2} Unchanged
Id: 2 PK
Banner: <null>
BlogId: 2 FK
Blog: {Id: 2}
*/
var posts = context.Posts.ToList();
Console.WriteLine(context.ChangeTracker.DebugView.LongView);//都有值了
/*
Blog {Id: 1} Unchanged
Id: 1 PK
Name: '.NET Blog'
Assets: {Id: 1}
Posts: [{Id: 1}, {Id: 2}]
Blog {Id: 2} Unchanged
Id: 2 PK
Name: 'Visual Studio Blog'
Assets: {Id: 2}
Posts: [{Id: 3}, {Id: 4}]
BlogAssets {Id: 1} Unchanged
Id: 1 PK
Banner: <null>
BlogId: 1 FK
Blog: {Id: 1}
BlogAssets {Id: 2} Unchanged
Id: 2 PK
Banner: <null>
BlogId: 2 FK
Blog: {Id: 2}
Post {Id: 1} Unchanged
Id: 1 PK
BlogId: 1 FK
Content: 'Announcing the release of EF Core 5.0, a full featured cross...'
Title: 'Announcing the Release of EF Core 5.0'
Blog: {Id: 1}
Tags: []
Post {Id: 2} Unchanged
Id: 2 PK
BlogId: 1 FK
Content: 'F# 5 is the latest version of F#, the functional programming...'
Title: 'Announcing F# 5'
Blog: {Id: 1}
Tags: []
Post {Id: 3} Unchanged
Id: 3 PK
BlogId: 2 FK
Content: 'If you are focused on squeezing out the last bits of perform...'
Title: 'Disassembly improvements for optimized managed debugging'
Blog: {Id: 2}
Tags: []
Post {Id: 4} Unchanged
Id: 4 PK
BlogId: 2 FK
Content: 'Examine when database queries were executed and measure how ...'
Title: 'Database Profiling with Visual Studio'
Blog: {Id: 2}
Tags: []
*/
关系修正不会从数据库查询相关数据。它仅仅是“连接”由DbContext跟踪的那些实体。
5.1 使用导航属性来更改关系
更改两个实体间关系最简单的方式就是操作导航,这也是建议的方式。efcore会适当的修正反向导航和对应的外键值。通过以下方式完成:
- 添加或者删除导航属性中的实体
- 将导航属性指向不同的实体或者置为null
5.1.1 添加或者删除集合导航中的实体
以下代码是将一个Blog中的某个Post移动到另外一个Blog中:
using var context = new BlogsContext();
var dotNetBlog = context.Blogs.Include(e => e.Posts).Single(e => e.Name == ".NET Blog");
var vsBlog = context.Blogs.Include(e => e.Posts).Single(e => e.Name == "Visual Studio Blog");
Console.WriteLine(context.ChangeTracker.DebugView.LongView);
var post = vsBlog.Posts.Single(e => e.Title.StartsWith("D以上是关于Entity Framework Core中更改跟踪工作原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
如何使用 Entity Framework Core 在一种方法中保存两次更改
有没有办法以编程方式检查 Entity Framework Core 中的待定模型更改?
Entity Framework Core 中的动态变化模式
Entity Framework Core 5 重新加载问题
Entity Framework Core: `SqlNullValueException: Data is Null.` 如何排查?