Embeded linux之probe
Posted 扑克face
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Embeded linux之probe相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、基于linux-3.18.20、mac驱动
二、启动时机:
所谓的"probe”,是指在Linux内核中,如果存在相同名称的device和device_driver,内核就会执行device_driver中的probe回调函数,而该函数就是所有driver的入口,可以执行诸如硬件设备初始化、字符设备注册、设备文件操作ops注册等动作("remove”是它的反操作,发生在device或者device_driver任何一方从内核注销时。
- 将struct device类型的变量注册到内核中时自动触发(device_register,device_add,device_create_vargs,device_create)
- 将struct device_driver类型的变量注册到内核中时自动触发(driver_register)
- 手动查找同一bus下的所有device_driver,如果有和指定device同名的driver,执行probe操作(device_attach)
- 手动查找同一bus下的所有device,如果有和指定driver同名的device,执行probe操作(driver_attach)
- 自行调用driver的probe接口,并在该接口中将该driver绑定到某个device结构中----即设置dev->driver(device_bind_driver)
三、流程
3.1 注册平台驱动
ret = platform_driver_register(&usrmac_dev_driver);
#define platform_driver_register(drv) platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE)
__platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE)
{
...
return driver_register(&drv->driver);
}
int driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv)
{
...
ret = bus_add_driver(drv);
...
}
int bus_add_driver(struct device_driver *drv)
{
...
return bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);
...
}
本函数没有给__driver_attach传递参数。
int bus_for_each_dev(struct bus_type *bus, struct device *start, void *data, int (*fn)(struct device *, void *))
{
....
klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,(start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL));
while ((dev = next_device(&i)) && !error)
error = fn(dev, data);
....
}
分支一:赋值i->i_klist、i->i_cur
因为start为NULL,故传递的第三个参数n为NULL
void klist_iter_init_node(struct klist *k, struct klist_iter *i,
struct klist_node *n)
{
i->i_klist = k;
i->i_cur = n;
if (n)
kref_get(&n->n_ref);
}
其中
i->i_klist = k = &bus->p->klist_devices
i->i_cur = n = (start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL) = NULL;
分之二:
static struct device *next_device(struct klist_iter *i)
{
struct klist_node *n = klist_next(i);
struct device *dev = NULL;
struct device_private *dev_prv;
if (n)
{
dev_prv = to_device_private_bus(n);
dev = dev_prv->device;
}
return dev;
}
#define to_device_private_bus(obj) container_of(obj, struct device_private, knode_bus)
参数:
i为
struct klist_iter {
struct klist *i_klist;
struct klist_node *i_cur;
};
被赋值为
i->i_klist = k;
i->i_cur = n;
next_device(&i),因为第一个节点为头节点,需要从下一个开始
struct klist_node *n = klist_next(i);
n为
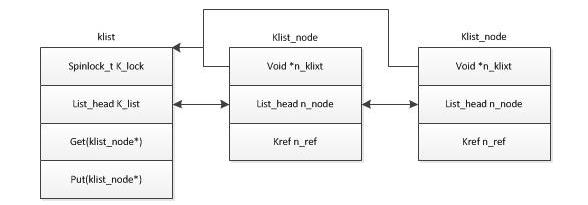
struct klist_node {
void *n_klist; /* never access directly */
struct list_head n_node;
struct kref n_ref;
};
struct kref {
atomic_t refcount;
};
klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_devices, &i,(start ?&start->p->knode_bus : NULL))作用是定义个klist_iter指向此klist,以便以后直接使用
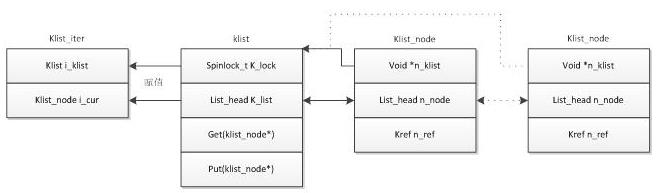
struct klist_node *klist_next(struct klist_iter *i)
{
...
struct klist_node *last = i->i_cur;
if (last)
{
//此处不执行
}
else
next = to_klist_node(i->i_klist->k_list.next);
i->i_cur = NULL;
while (next != to_klist_node(&i->i_klist->k_list))
{
if (likely(!knode_dead(next)))
{
kref_get(&next->n_ref);
i->i_cur = next;
break;
}
next = to_klist_node(next->n_node.next);
}
...
}
static struct klist_node *to_klist_node(struct list_head *n)
{
return container_of(n, struct klist_node, n_node);
}
取出了包含i->i_klist->k_list.next的n_node指针,不过next所指的和n_node地址偏差一个head指针(list_head包括head和next俩指针)。
while循环是从第一个目标to_klist_node(i->i_klist->k_list.next)循环,当再次循环到头节点to_klist_node(&i->i_klist->k_list)时截止(这是个循环链表,总会再次循环回来的)。
还一个结束的条件,当循环到knode_dead(next)为真时break,不过,likely说明了next通常不会是dead的。
Klist_iter找到合适的即停止搜索,找到此处的device_private的device。
此结构即为传入probe函数的参数。
找到参数后,继续执行return bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);中error = fn(dev, data);即__driver_attach函数。
第一个参数dev为刚刚while ((dev = next_device(&i)) && !error)索引产生。
static int __driver_attach(struct device *dev, void *data)
{
...
if (!dev->driver)
driver_probe_device(drv, dev);
...
}
int driver_probe_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
{
...
ret = really_probe(dev, drv);
...
}
static int really_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
...
if (dev->bus->probe)
{
ret = dev->bus->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
}
else if (drv->probe)
{
ret = drv->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
}
...
}
static struct platform_driver usrmac_dev_driver = {
.probe = usrmac_dev_probe,
.remove = usrmac_dev_remove,
.suspend = usrmac_dev_suspend,
.resume = usrmac_dev_resume,
.driver =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = USRMAC_DRIVER_NAME,
.of_match_table = usrmac_of_match,
},
};
static int usrmac_dev_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
//struct platform_device *pdev即Klist_iter找到的
}
以上是关于Embeded linux之probe的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章