高并发有序的容器ConcurrentSkipListMap原理分析
Posted 踩踩踩从踩
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了高并发有序的容器ConcurrentSkipListMap原理分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
跳表
Skip list(跳表)是一种可以代替平衡树的数据结构,默认是按照Key值升序的。Skip list让已排序的数据分布在多层链表中,以0-1随机数决定一个数据的向上攀升与否,通过“空间来换取时间”的一个算法,在每个节点中增加了向前的指针,在插入、删除、查找时可以忽略一些不可能涉及到的结点,从而提高了效率。
ConcurrentSkipListMap
概述
ConcurrentSkipListMap基于跳表实现的实现高并发容器,用了一个大的概念,空间来换取时间的一个算法,也就是通过在每个节点中增加了向前的指针,记录插入的顺序,然后进行增删改查。
它的优点
- ConcurrentSkipListMap 的key是有序的。按照注释上说,可以按照自然值进行排序或通过map提供的{@link Comparator}进行排序
- ConcurrentSkipListMap 支持更高的并发,对比ConcurrentHashMap里面它是无锁编程的,源码中完全使用用unsafe来保证数据数据的安全。
无论是jdk1.7还是还是jdk1.8 中concurrentHashMap都不能达到无锁编程,不能全部使用unsafe来保证数据安全,因此并发量还是低了
它是Doug Lea 在jdk1.6时提出的一个类,相对ConcurrenthashMap来说晚一个版本,更适合高并发有序场景下使用。
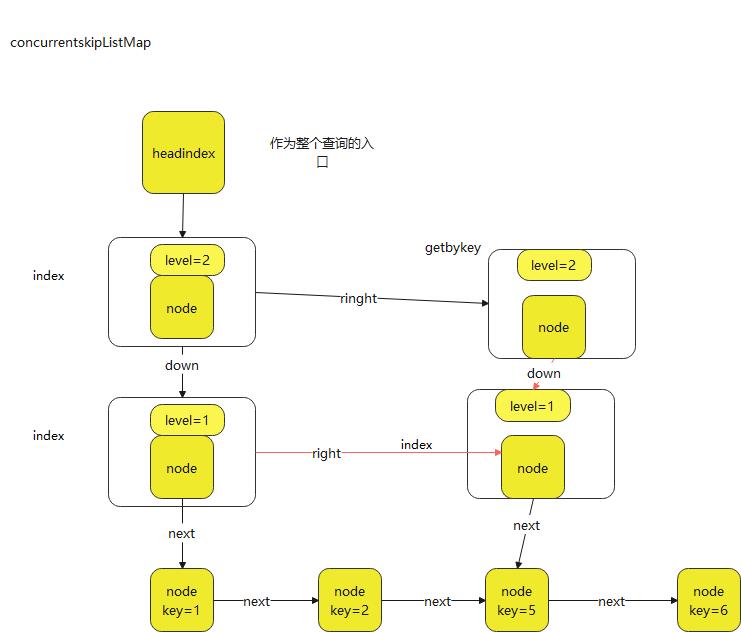
通过添加索引,来快速查找和删除数据,初始化时,创建headindex一个节点,任何插入和删除都从这里开始,而跳表的跳来自于产生的index,然后跳过一部分不必要的数据,每个node节点都要存储三个指针,效率确实降低了很多。
源码分析
从下面属性分析
/**
* 用于标识基准面index的特殊值
*/
private static final Object BASE_HEADER = new Object();
/**
* 跳表头部的index索引值
*/
private transient volatile HeadIndex<K,V> head;
/**
* 比较器
* @serial
*/
final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
- head 属性是在构造方法时,会创建的一个属性,是所有的查询删除的起点
private void initialize() {
keySet = null;
entrySet = null;
values = null;
descendingMap = null;
head = new HeadIndex<K,V>(new Node<K,V>(null, BASE_HEADER, null),
null, null, 1);
}- 跳表的核心设计思想,通过级别 和多个指针来达到跳跃的效果
/**
* 指向每个级别的节点跟踪其级别。
*/
static final class HeadIndex<K,V> extends Index<K,V> {
final int level;
HeadIndex(Node<K,V> node, Index<K,V> down, Index<K,V> right, int level) {
super(node, down, right);
this.level = level;
}
}- 在node节点中提供的各种cas操作数据安全的方法
/**
* cas比较值
*/
boolean casValue(Object cmp, Object val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, valueOffset, cmp, val);
}
/**
* cas设置next的值
*/
boolean casNext(Node<K,V> cmp, Node<K,V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
- 最重要的put方法中
/**
* 主插入法。如果不存在,则添加元素,或
* 如果存在且OnlyFabSent为false,则替换值
* @param key the key
* @param value必须与键关联的值
* @param 仅当已存在时才发送不应插入
* @return 旧的值存在则返回, 为空插入
*/
private V doPut(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
Node<K,V> z; // added node
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;
outer: for (;;) {
for (Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;) {
if (n != null) {
Object v; int c;
Node<K,V> f = n.next;
if (n != b.next) // 不一致读取
break;
if ((v = n.value) == null) { // n为空被删除
n.helpDelete(b, f);
break;
}
if (b.value == null || v == n) // b值被删除
break;
if ((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) > 0) {
b = n;
n = f;
continue;
}
if (c == 0) {
if (onlyIfAbsent || n.casValue(v, value)) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") V vv = (V)v;
return vv;
}
break; // restart if lost race to replace value
}
// else c < 0; 失败
}
z = new Node<K,V>(key, value, n);
if (!b.casNext(n, z))
break; // 如果失去附加到b的竞争,请重新启动
break outer;
}
}
int rnd = ThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed();
if ((rnd & 0x80000001) == 0) { // 测试最高和最低位
int level = 1, max;
while (((rnd >>>= 1) & 1) != 0)
++level;
Index<K,V> idx = null;
HeadIndex<K,V> h = head;
if (level <= (max = h.level)) {
for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i)
idx = new Index<K,V>(z, idx, null);
}
else { // 试着提高一个层次
level = max + 1; // 在数组中保留,然后选择要使用的
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Index<K,V>[] idxs =
(Index<K,V>[])new Index<?,?>[level+1];
for (int i = 1; i <= level; ++i)
idxs[i] = idx = new Index<K,V>(z, idx, null);
for (;;) {
h = head;
int oldLevel = h.level;
if (level <= oldLevel) // 小于老的优先级跳出
break;
HeadIndex<K,V> newh = h;
Node<K,V> oldbase = h.node;
for (int j = oldLevel+1; j <= level; ++j)
newh = new HeadIndex<K,V>(oldbase, newh, idxs[j], j);
if (casHead(h, newh)) {
h = newh;
idx = idxs[level = oldLevel];
break;
}
}
}
// 查找插入点 和接头
splice: for (int insertionLevel = level;;) {
int j = h.level;
for (Index<K,V> q = h, r = q.right, t = idx;;) {
if (q == null || t == null)
break splice;
if (r != null) {
Node<K,V> n = r.node;
// 删除前比较检查避免了需要重新检查
int c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key);
if (n.value == null) {
if (!q.unlink(r))
break;
r = q.right;
continue;
}
if (c > 0) {
q = r;
r = r.right;
continue;
}
}
if (j == insertionLevel) {
if (!q.link(r, t))
break; // restart
if (t.node.value == null) {
findNode(key);
break splice;
}
if (--insertionLevel == 0)
break splice;
}
if (--j >= insertionLevel && j < level)
t = t.down;
q = q.down;
r = q.right;
}
}
}
return null;
}这里对并发容器新增方法,所有的新增数据都使用了cas来保证数据的安全
/**
* compareAndSet next field
*/
boolean casNext(Node<K,V> cmp, Node<K,V> val) {
return UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);
}
以上是关于高并发有序的容器ConcurrentSkipListMap原理分析的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章