JavaLearn #(14)网络及分类TCPUDP协议IPSocketTCP编程UDP编程
Posted LRcoding
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JavaLearn #(14)网络及分类TCPUDP协议IPSocketTCP编程UDP编程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1. 网络基本概念
1.1 计算机网络
定义:是指将地理位置不同的具有独立功能(没有网络可以独立存在的)的多台计算机及其外部设备,通过通信线路连接起来,在网络操作系统,网络管理软件及网络通信协议的管理和协调下,实现资源共享和信息传递的计算机系统
- 主干:计算机网络是计算机系统
- 网络功能:资源共享、信息传递
- 网络组成
- 网络硬件:计算机、外部设备、通信连接
- 网络软件:网络操作系统、网络管理软件、网络通信协议
分类–按照规模:
- 局域网 LAN
- 城域网 MAN
- 广域网 WAN
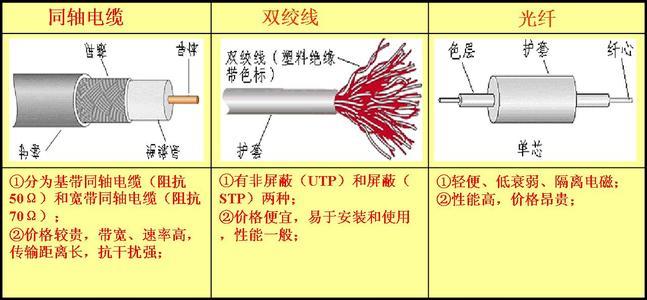
分类–按照传输介质:
-
同轴电缆网络(类似于有线电视网的电缆)
-
双绞线网络
-
光纤网络(传输的为光信号)
-
卫星网络
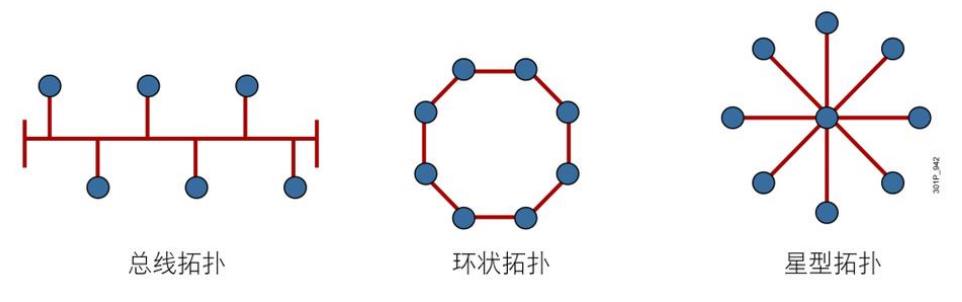
分类–拓扑结构:
-
星形网络(最常使用)
-
总线网络:信号在传递过程中都能收到,辨别是自己的则接收
-
环状网络:同样的传递方式
1.2 网络通信协议
在网络中实现通信,必须要有一些约定(通信协议),对速率、传输代码、传输控制步骤等指定标准(好比交通规则)
问题:网络通信涉及内容很多:源地址、目标地址、加密解密、流量控制、路由控制等,如何实现如此复杂的网络协议?
===》分层:将复杂的成份分解成一些简单的成份,再将它们复合起来(同层间可以通信、上一层可以调用下一层,而不与再下一层发生关系)
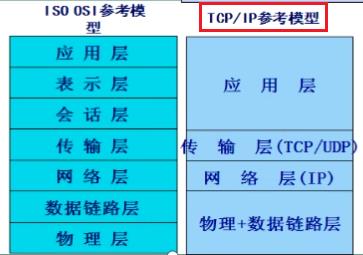
网络通信协议分层:
- 名义上的标准:ISO --> OSI 参考模型
- 事实上的标准:TCP/IP协议栈
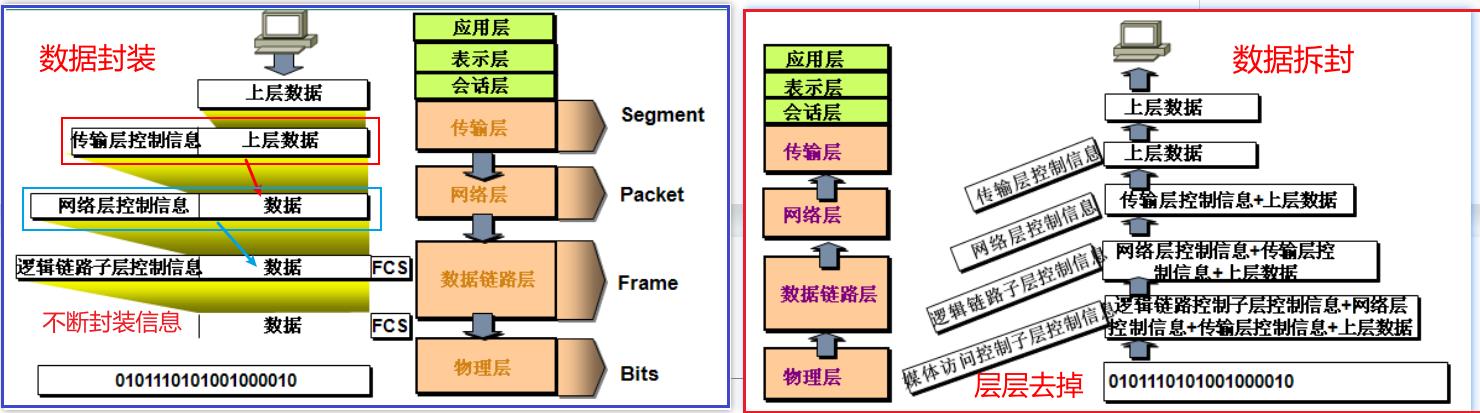
数据的封装与拆封:在传输过程中,经过每一层,都需要添加各种数据,最终发送到另一端,另一端再拆解这些数据
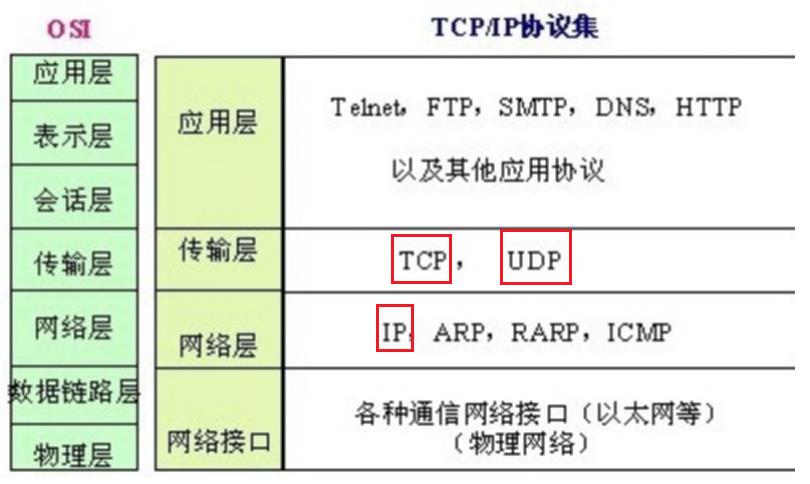
1.3 TCP/IP协议栈
网络通信最常采用的协议
- 网络层主要协议:IP协议
- 传输层主要协议:TCP 和 UDP 协议
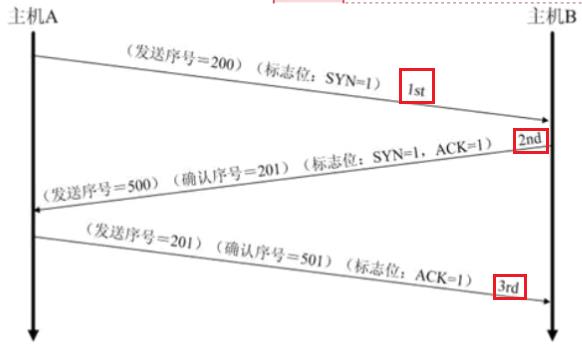
1.4 TCP协议
面向连接的、可靠的、基于字节流的传输层通信协议(打电话的案例)
- 面向连接(一段信息分段后发送,发送顺序和接收顺序一致)
- 点到点的通信
- 高可靠性:三次握手
- 占用系统资源多、效率低
应用案列:HTTP、FTP、Telnet、SMTP
1.5 UDP协议
无连接的传输层协议,提供面向事务的简单不可靠信息传送服务(发电报、发送群发短信)
- 非面向连接,传输不可靠,可能丢失(一段信息分段后发送,不一定哪一段先到达)
- 发送不管对方是否准备好,接收方收到后也不回复
- 可以广播发送
- 非常简单的协议,开销少
应用案例:DNS、SNMP
1.6 IP地址和端口
IP地址,用来标志网络中的一个通信实体(计算机、路由器)的地址
分类:
- IPV4:32位地址,点分十进制表示,如192.168.0.1
- IPV6:128位写个8个16位的无符号整数,每个整数用4个十六进制位标识,数之间用 : 分割
特殊的 IP 地址:
- 127.0.0.1:本机地址
- 192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255 私有地址,专门为组织机构内部使用
端口(port):
- IP地址用来标志一台计算机,但一个计算机可以提供多种应用程序,使用端口来区分应用程序
- 范围:0 – 65535(16位整数)
端口分类:
- 0 – 1023 :公认端口(比如 80给了 WWW,21给了 FTP等)
- 1024 – 49151:注册端口(分配给用户或应用程序)
- 49152 – 65535:动态/私有端口
IP和端口API:
- InetAddress 类:封装计算机的 ip地址,没有端口
- InetSocketAddress:包含端口,用于 socket 通信
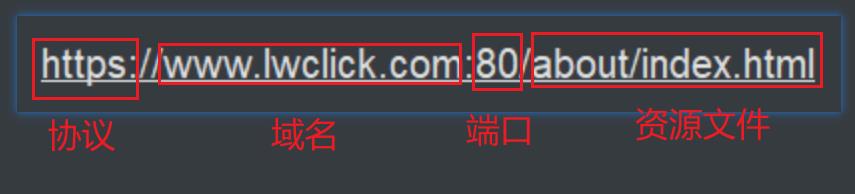
1.7 URL 统一资源定位符
Uniform Resource Locator:由 4部分组成:协议、存放资源的主机域名、端口号、资源文件名
1.8 Socket 套接字
Socket实际是传输层供给应用层的编程接口
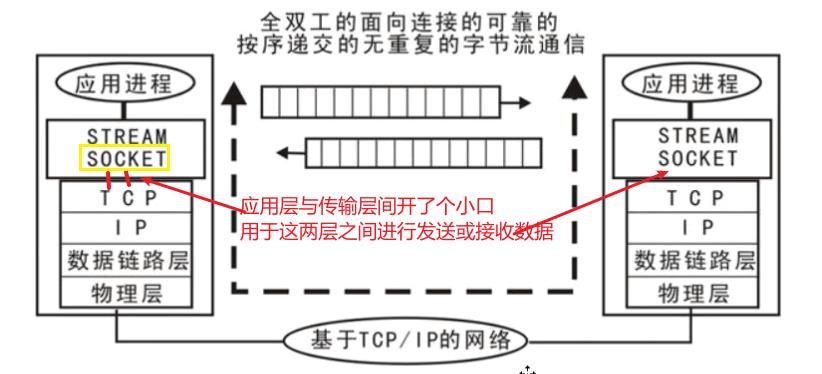
类似于寄信:用户(应用层)将信(数据)投入邮筒即可(邮筒的口,就是socket),进入Socket之后,怎么送信就是邮局、公路交管(传输层、网络层)等的事。
2. 网络编程常用类
2.1 封装IP地址 – InetAddress
// 1.获取 IP地址
InetAddress ia = InetAddress.getLocalHost(); // 本机的 ip
// 2.操作 IP地址
System.out.println(ia); // DESKTOP-F31QQ1H/192.168.0.102
System.out.println(ia.getHostAddress()); // 192.168.0.102
System.out.println(ia.getHostName()); // DESKTOP-F31QQ1H
InetAddress ia2 = InetAddress.getByName("www.lwclick.com"); // 通过域名获取ip
System.out.println(ia2);
2.2 封装 IP 和 Port – InetSocketAddress
// 创建一个 InetSocketAddress 对象
InetSocketAddress isa = new InetSocketAddress("www.lwclick.com", 8888);
// 获取对象内容
System.out.println(isa); // www.lwclick.com/104.21.41.202:8888
System.out.println(isa.getAddress()); // www.lwclick.com/104.21.41.202
System.out.println(isa.getPort()); // 8888
2.3 URL类
// 创建一个 URL 协议:https 域名/IP地址:lwclick.com 端口:80 路径:/categories/mysql/
URL url = new URL("https://lwclick.com:80/categories/MySQL/");
// 获取 URL 各个组成部分
System.out.println(url.getProtocol()); // https
System.out.println(url.getHost()); // lwclick.com
System.out.println(url.getPort()); // 80
System.out.println(url.getDefaultPort()); // 443 默认的 https 端口
System.out.println(url.getPath()); // /categories/MySQL/
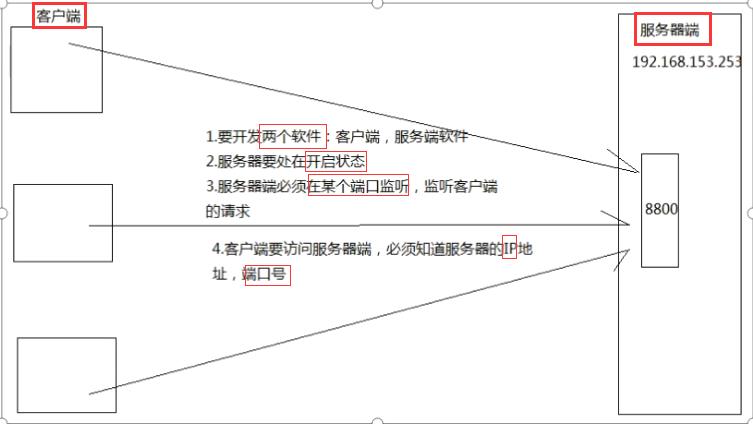
3. TCP编程
3.1 一次单向通信
-
服务器端:
-
创建 ServerSocket,在指定端口监听(
accept()方法)并处理请求(如果客户端请求到来,返回对应的Socket,否则的话一直等待,线程也被阻塞)
-
-
客户端:
- 创建 Socket,需要指定服务器的 ip 和端口号,向服务器发送和接收响应
-
发送数据:
- 需要使用输出流(OutputStream),可以通过 DataOutputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream 进行包装,提高效率
-
接收数据:
- 使用输入流(InputStream),使用 DataInputStream 和 ObjectInputStream 进行包装
服务器端:
public class LoginServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.创建一个 ServerSocket,配置监听端口
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
// 2.使用 ServerSocket 在指定端口监听
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept(); // 请求不到,在此阻塞; 请求到了,返回一个socket,继续执行
// 3.接收客户端的请求数据,输出结果
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream(); // 获取流
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is); // 同样使用数据流进行包装
String info = dis.readUTF(); // 读取对应类型的写入的数据
System.out.println("客户端的请求:" + info);
// 4.关闭资源
dis.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
}
客户端:
public class LoginClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.创建一个 Socket,指明服务器端ip和端口
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8080); // InetAddress.getByName()获取ip
// 2.发送数据给服务器端
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream(); // 信息通过流发送,输出流
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os); // 数据流进行包装
dos.writeUTF("userName=lwclick&pwd=123");
// 3.关闭资源
dos.close(); // 关闭高层流,低层自动关闭
}
}
注意:测试时,服务器端需要先启动,然后再启动客户端
3.2 一次双向通信
服务器端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
String info = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("客户端的请求:" + info);
// ============================== 向客户端发送数据 =====================================
// 4. 给客户端一个响应
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream(); // 此处的socket为接收的客户端的响应
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF("登录成功,欢迎!");
// 5.关闭资源
dos.close();
dis.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
客户端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getL ocalHost(), 8080);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
dos.writeUTF("userName=lwclick&pwd=123");
// ============================== 接收服务器端反馈 =====================================
// 3.接收服务器端响应,并输出
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
String info = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("服务器端的响应:" + info);
// 4.关闭资源
dis.close();
dos.close();
}
3.3 传输对象
User 类:在网络上传输,类一定要实现序列化接口
public class User implements Serializable {
private String userId;
private String password;
// getter / setter / toString / constructor
}
服务器端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
// =============== 此处使用【对象流】接收数据 ===================
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
User user = (User)ois.readObject();
System.out.println("客户端的请求:" + user);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
if (user.getUserId().indexOf("lwclick") >= 0 && user.getPassword().length() > 6) {
dos.writeUTF("登录成功,欢迎!");
} else {
dos.writeUTF("登录失败,请重试!");
}
dos.close();
ois.close();
serverSocket.close();
}
客户端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8080);
// 获取用户输入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("userId: ");
String userId = sc.next();
System.out.print("password: ");
String password = sc.next();
User user = new User(userId, password);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
// 【对象流】进行包装
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(user);
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
String info = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println("服务器端的响应:" + info);
dis.close();
oos.close();
}
3.4 引入多线程
将服务器端接到请求后的处理步骤,放到线程的 run()方法 中,每过来一个请求,就创建一个线程去执行
线程类:
public class LoginThread extends Thread {
private Socket socket;
public LoginThread() {
}
public LoginThread(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
DataOutputStream dos = null;
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
User user = (User)ois.readObject();
System.out.println("客户端的请求:" + user);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
dos = new DataOutputStream(os);
if (user.getUserId().indexOf("lwclick") >= 0 && user.getPassword().length() > 6) {
dos.writeUTF("登录成功,欢迎!");
} else {
dos.writeUTF("登录失败,请重试!");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (dos != null) {
dos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (ois != null) {
ois.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
服务器端: 为每一个登录请求,创建一个线程来处理
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
int i = 1;
while (true) {
Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 为每一个登录请求,创建一个线程来处理
new LoginThread(socket).start();
// 统计客户端的IP地址和总的请求次数
InetAddress ia = socket.getInetAddress();
System.out.println("这是第" + (i++) + "个请求,对方的IP地址是:" + ia.getHostAddress());
}
}
客户端:(无需改变)
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket(InetAddress.getLocalHost(), 8080);
// 获取用户输入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("userId: ");
String userId = sc.next();
System.out.print("password: ");
String password = sc.next();
User user = new User(userId, password);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
// 【对象流】进行包装
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
oos.writeObject(user);
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(is);
String info = dis.r以上是关于JavaLearn #(14)网络及分类TCPUDP协议IPSocketTCP编程UDP编程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章