ROS2 中的 launch 文件入门的 6 个疑问
Posted frank909
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ROS2 中的 launch 文件入门的 6 个疑问相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文记录了 ROS2 中 launch 文件学习过程中我个人觉得重要的 6 个基本问题,和大家分享,希望可以帮到初学者。
疑问1:launch 文件有什么用?
通过 launch 文件,ROS2 可以同时启动许多节点,这样简化了用命令行去多次启动不同的 Node。
疑问2:launch 文件怎么用?
完整的命令:
ros2 launch <package_name> <launch_file_name>
也可以直接启动 launch 文件,像这样:
ros2 launch turtlesim_mimic_launch.py
turtlesim_mimic_launch.py 是一个 python 文件,在里面定义了一个 launch 文件的内容。
但 ROS1 launch 是不支持 py 文件的,而事实上 launch 文件在 ROS2 中有 3 种格式可以实现:
- python 脚本
- xml 文件
- yaml 文件
疑问3:launch 文件里面应该有什么?
node 相关
launch file 文件当中最重要的是 node 信息,它指定了包的信息、node 的名字还有可执行文件的路径。
<node pkg="turtlesim" exec="turtlesim_node" name="sim" namespace="turtlesim2">
<param name="background_r" value="$(var background_r)"/>
<param name="background_g" value="$(var background_g)"/>
<param name="background_b" value="$(var background_b)"/>
</node>
include
include 可以在一个 launch file 中包含另外的 launch file
group
group 可以把多个 node 组合在一起
疑问4:如何编写一个 launch file?
无论是 python、xml 还是 yaml,编写 launch file 的步骤差不多一样。
- 设置命令行参数的默认值,
- 设置 launch file 的包含关系,通过 标签
- 设置 Node 信息,包括 name、namespace、parameter
- 如果需要设置 remmaping 则设置 remapping 关系
官方文档有出示个一个例子
# example.launch.py
import os
from ament_index_python import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.actions import GroupAction
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch.substitutions import LaunchConfiguration
from launch.substitutions import TextSubstitution
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch_ros.actions import PushRosNamespace
def generate_launch_description():
# args that can be set from the command line or a default will be used
background_r_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
"background_r", default_value=TextSubstitution(text="0")
)
background_g_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
"background_g", default_value=TextSubstitution(text="255")
)
background_b_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
"background_b", default_value=TextSubstitution(text="0")
)
chatter_ns_launch_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(
"chatter_ns", default_value=TextSubstitution(text="my/chatter/ns")
)
# include another launch file
launch_include = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('demo_nodes_cpp'),
'launch/topics/talker_listener.launch.py'))
)
# include another launch file in the chatter_ns namespace
launch_include_with_namespace = GroupAction(
actions=[
# push-ros-namespace to set namespace of included nodes
PushRosNamespace(LaunchConfiguration('chatter_ns')),
IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(
get_package_share_directory('demo_nodes_cpp'),
'launch/topics/talker_listener.launch.py'))
),
]
)
# start a turtlesim_node in the turtlesim1 namespace
turtlesim_node = Node(
package='turtlesim',
namespace='turtlesim1',
executable='turtlesim_node',
name='sim'
)
# start another turtlesim_node in the turtlesim2 namespace
# and use args to set parameters
turtlesim_node_with_parameters = Node(
package='turtlesim',
namespace='turtlesim2',
executable='turtlesim_node',
name='sim',
parameters=[{
"background_r": LaunchConfiguration('background_r'),
"background_g": LaunchConfiguration('background_g'),
"background_b": LaunchConfiguration('background_b'),
}]
)
# perform remap so both turtles listen to the same command topic
forward_turtlesim_commands_to_second_turtlesim_node = Node(
package='turtlesim',
executable='mimic',
name='mimic',
remappings=[
('/input/pose', '/turtlesim1/turtle1/pose'),
('/output/cmd_vel', '/turtlesim2/turtle1/cmd_vel'),
]
)
return LaunchDescription([
background_r_launch_arg,
background_g_launch_arg,
background_b_launch_arg,
chatter_ns_launch_arg,
launch_include,
launch_include_with_namespace,
turtlesim_node,
turtlesim_node_with_parameters,
forward_turtlesim_commands_to_second_turtlesim_node,
])
这是用 python 写的,最后返回的是 LaunchDescription 信息,这个等同于 xml 中 标签中的内容
<!-- example.launch.xml -->
<launch>
<!-- args that can be set from the command line or a default will be used -->
<arg name="background_r" default="0"/>
<arg name="background_g" default="255"/>
<arg name="background_b" default="0"/>
<arg name="chatter_ns" default="my/chatter/ns"/>
<!-- include another launch file -->
<include file="$(find-pkg-share demo_nodes_cpp)/launch/topics/talker_listener.launch.py"/>
<!-- include another launch file in the chatter_ns namespace-->
<group>
<!-- push-ros-namespace to set namespace of included nodes -->
<push-ros-namespace namespace="$(var chatter_ns)"/>
<include file="$(find-pkg-share demo_nodes_cpp)/launch/topics/talker_listener.launch.py"/>
</group>
<!-- start a turtlesim_node in the turtlesim1 namespace -->
<node pkg="turtlesim" exec="turtlesim_node" name="sim" namespace="turtlesim1"/>
<!-- start another turtlesim_node in the turtlesim2 namespace
and use args to set parameters -->
<node pkg="turtlesim" exec="turtlesim_node" name="sim" namespace="turtlesim2">
<param name="background_r" value="$(var background_r)"/>
<param name="background_g" value="$(var background_g)"/>
<param name="background_b" value="$(var background_b)"/>
</node>
<!-- perform remap so both turtles listen to the same command topic -->
<node pkg="turtlesim" exec="mimic" name="mimic">
<remap from="/input/pose" to="/turtlesim1/turtle1/pose"/>
<remap from="/output/cmd_vel" to="/turtlesim2/turtle1/cmd_vel"/>
</node>
</launch>
yaml 要写也很容易。
# example.launch.yaml
launch:
# args that can be set from the command line or a default will be used
- arg:
name: "background_r"
default: "0"
- arg:
name: "background_g"
default: "255"
- arg:
name: "background_b"
default: "0"
- arg:
name: "chatter_ns"
default: "my/chatter/ns"
# include another launch file
- include:
file: "$(find-pkg-share demo_nodes_cpp)/launch/topics/talker_listener.launch.py"
# include another launch file in the chatter_ns namespace
- group:
- push-ros-namespace:
namespace: "$(var chatter_ns)"
- include:
file: "$(find-pkg-share demo_nodes_cpp)/launch/topics/talker_listener.launch.py"
# start a turtlesim_node in the turtlesim1 namespace
- node:
pkg: "turtlesim"
exec: "turtlesim_node"
name: "sim"
namespace: "turtlesim1"
# start another turtlesim_node in the turtlesim2 namespace and use args to set parameters
- node:
pkg: "turtlesim"
exec: "turtlesim_node"
name: "sim"
namespace: "turtlesim2"
param:
-
name: "background_r"
value: "$(var background_r)"
-
name: "background_g"
value: "$(var background_g)"
-
name: "background_b"
value: "$(var background_b)"
# perform remap so both turtles listen to the same command topic
- node:
pkg: "turtlesim"
exec: "mimic"
name: "mimic"
remap:
-
from: "/input/pose"
to: "/turtlesim1/turtle1/pose"
-
from: "/output/cmd_vel"
to: "/turtlesim2/turtle1/cmd_vel"
疑问5:如何在 ros2 launch 时传递参数?
我们注意到上面的 launch file 中有 args,比如 background_r,命令行启动时可以将数据透传过去,通过 key:=value 形式。
如:
ros2 launch <package_name> <launch_file_name> background_r:=255
疑问6:remap 起什么作用?
remap 是一个非常有用的技巧,一般用来做 Topic 的映射的。
其实就是移花接木,或者说是瞒天过海。
<remap from="/different_topic" to="/needed_topic"/>
把 from 中的 topic,转换成 to 指定的 topic
有 2 种用途:
- 把一个 node 原本来发布的 topic,映射为另外一个名字
- 把其他的 node 发布的原始 topic,映射为所需要的 topic
ROS2 官方教程的示例中有如下代码
Node(
package='turtlesim',
executable='mimic',
name='mimic',
remappings=[
('/input/pose', '/turtlesim1/turtle1/pose'),
('/output/cmd_vel', '/turtlesim2/turtle1/cmd_vel'),
]
)
实践
官方教程有很详细的指引,这里简单概述一下。
1.创建 launch 文件
turtlesim_mimic_launch.py
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
return LaunchDescription([
Node(
package='turtlesim',
namespace='turtlesim1',
executable='turtlesim_node',
name='sim'
),
Node(
package='turtlesim',
namespace='turtlesim2',
executable='turtlesim_node',
name='sim'
),
Node(
package='turtlesim',
executable='mimic',
name='mimic',
remappings=[
('/input/pose', '/turtlesim1/turtle1/pose'),
('/output/cmd_vel', '/turtlesim2/turtle1/cmd_vel'),
]
)
])
2.启动
ros2 launch turtlesim_mimic_launch.py
你会看到两个乌龟界面。
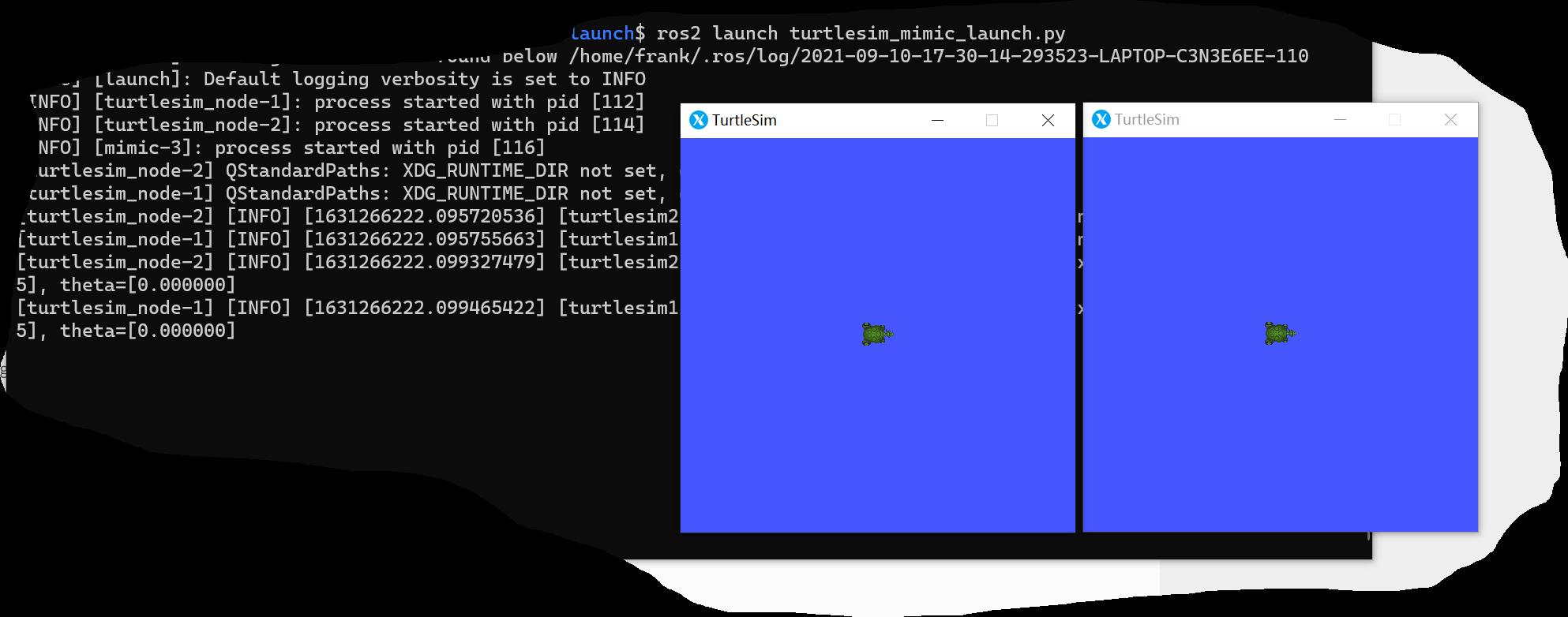
3. 调试
发送命令让乌龟动起来.
新开一个终端,敲下面的命令。
ros2 topic pub -r 1 /turtlesim1/turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/msg/Twist "{linear: {x: 2.0, y: 0.0, z: 0.0}, angular: {x: 0.0, y: 0.0, z: -1.8}}"
我们仔细观察看到,发送的是 /turtlesim1/turtle1/cmd_vel 这个 Topic,但 2 只乌龟都运动起来,这是因为我们在 mimic 这个节点中做了remap 动作,相当于进行了消息的透传。
我们可以通过 rqt_graph 查看更详细的信息。
新开一个终端然后输入 rqt_graph。
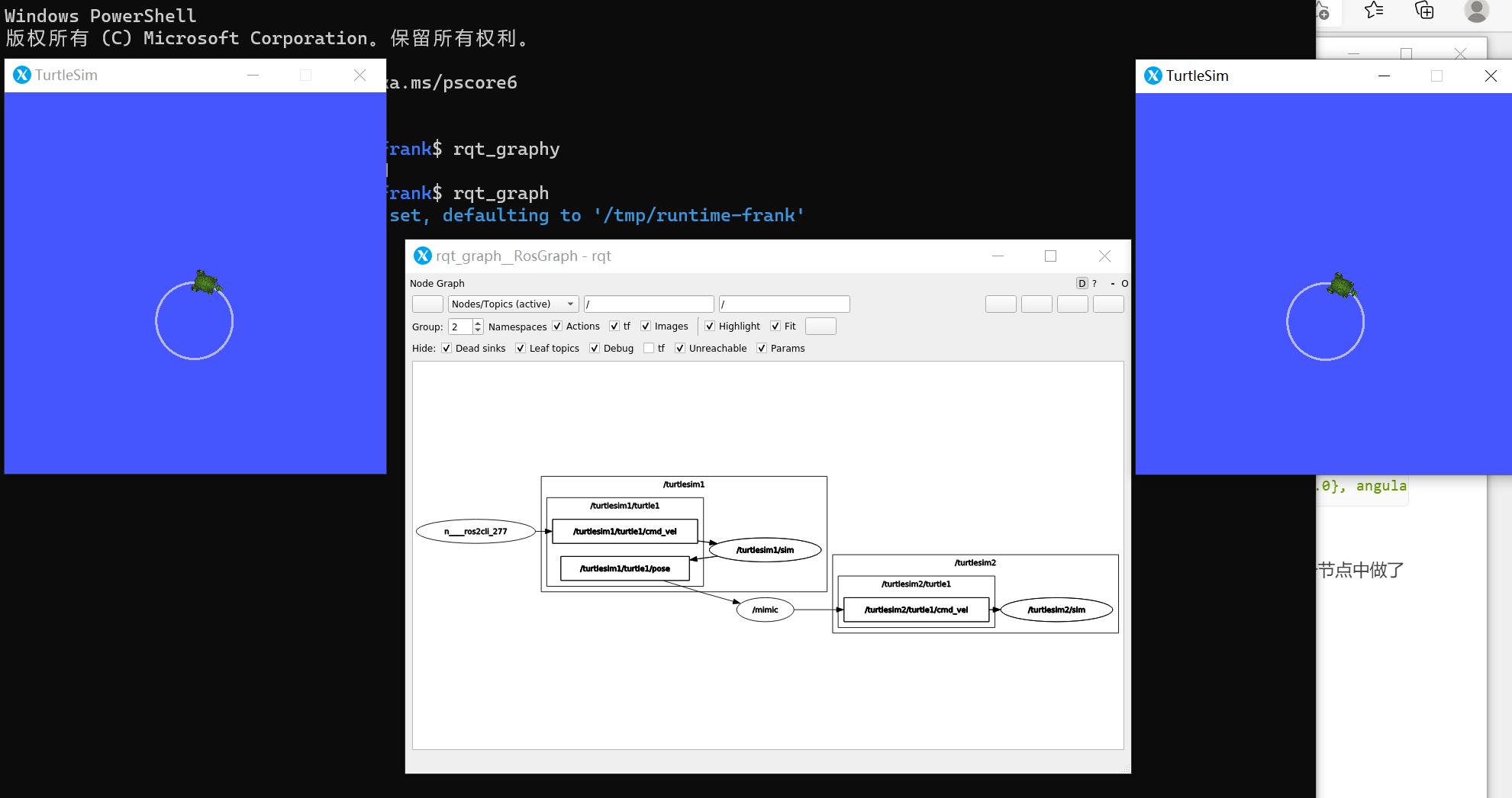
它们之间的关系还是一目了然的。
参考
以上是关于ROS2 中的 launch 文件入门的 6 个疑问的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章