技巧:自定义内存管理
Posted 学习只为旅行
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了技巧:自定义内存管理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

const成员函数内部不能修改成员变量!!!

这个关键字在工程中用的比较少

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int m_value;
int * const m_pCount;//指针为常量,不能被改变,但是指向的值可以!
/* mutable int m_count; */
public:
Test(int value = 0) : m_pCount(new int(0))
{
m_value = value;
/* m_count = 0; */
}
int getValue() const//const成员函数不能改变成员变量的值
{
/* m_count++; */
*m_pCount = *m_pCount + 1;//这里成员变量是个指针,没有改变指针值,但是可以改变指针指向的内容的值,合法
return m_value;
}
void setValue(int value)
{
/* m_count++; */
*m_pCount = *m_pCount + 1;
m_value = value;
}
int getCount() const
{
/* return m_count; */
return *m_pCount;
}
~Test()
{
delete m_pCount;
}
};
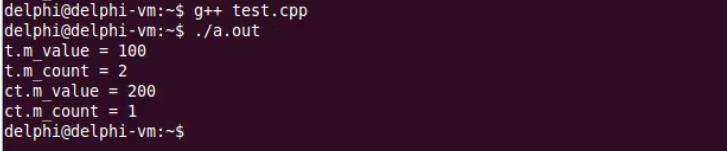
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Test t;
t.setValue(100);
cout << "t.m_value = " << t.getValue() << endl;
cout << "t.m_count = " << t.getCount() << endl;
const Test ct(200);
cout << "ct.m_value = " << ct.getValue() << endl;
cout << "ct.m_count = " << ct.getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}

堆,也可以在静态存储区或者栈!



重载的new 和 delete 是类的成员函数,默认为静态成员函数,写不写static都是静态的!!!
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
static const unsigned int COUNT = 4;
static char c_buffer[];
static char c_map[];
int m_value;
public:
void* operator new (unsigned int size)
{
void* ret = NULL;
for(int i=0; i<COUNT; i++)
{
if( !c_map[i] )
{
c_map[i] = 1;
ret = c_buffer + i * sizeof(Test);
cout << "succeed to allocate memory: " << ret << endl;
break;
}
}
return ret;
}
void operator delete (void* p)
{
if( p != NULL )
{
char* mem = reinterpret_cast<char*>(p);
int index = (mem - c_buffer) / sizeof(Test);
int flag = (mem - c_buffer) % sizeof(Test);
if( (flag == 0) && (0 <= index) && (index < COUNT) )
{
c_map[index] = 0;
cout << "succeed to free memory: " << p << endl;
}
}
}
};
char Test::c_buffer[sizeof(Test) * Test::COUNT] = {0};
char Test::c_map[Test::COUNT] = {0};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
cout << "===== Test Single Object =====" << endl;
Test* pt = new Test;
delete pt;
cout << "===== Test Object Array =====" << endl;
Test* pa[5] = {0};
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
pa[i] = new Test;
cout << "pa[" << i << "] = " << pa[i] << endl;
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << "delete " << pa[i] << endl;
delete pa[i];
}
return 0;
}
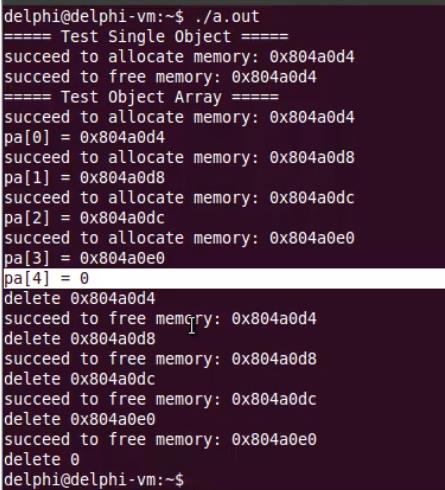
pa[4]越界,new不出来,返回NULL


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
static unsigned int c_count;
static char* c_buffer;
static char* c_map;
int m_value;
public:
static bool SetMemorySource(char* memory, unsigned int size)
{
bool ret = false;
c_count = size / sizeof(Test);
ret = (c_count && (c_map = reinterpret_cast<char*>(calloc(c_count, sizeof(char)))));
if( ret )
{
c_buffer = memory;
}
else
{
free(c_map);
c_map = NULL;
c_buffer = NULL;
c_count = 0;
}
return ret;
}
void* operator new (unsigned int size)
{
void* ret = NULL;
if( c_count > 0 )
{
for(int i=0; i<c_count; i++)
{
if( !c_map[i] )
{
c_map[i] = 1;
ret = c_buffer + i * sizeof(Test);
cout << "succeed to allocate memory: " << ret << endl;
break;
}
}
}
else
{
ret = malloc(size);
}
return ret;
}
void operator delete (void* p)
{
if( p != NULL )
{
if( c_count > 0 )
{
char* mem = reinterpret_cast<char*>(p);
int index = (mem - c_buffer) / sizeof(Test);
int flag = (mem - c_buffer) % sizeof(Test);
if( (flag == 0) && (0 <= index) && (index < c_count) )
{
c_map[index] = 0;
cout << "succeed to free memory: " << p << endl;
}
}
else
{
free(p);
}
}
}
};
unsigned int Test::c_count = 0;
char* Test::c_buffer = NULL;
char* Test::c_map = NULL;
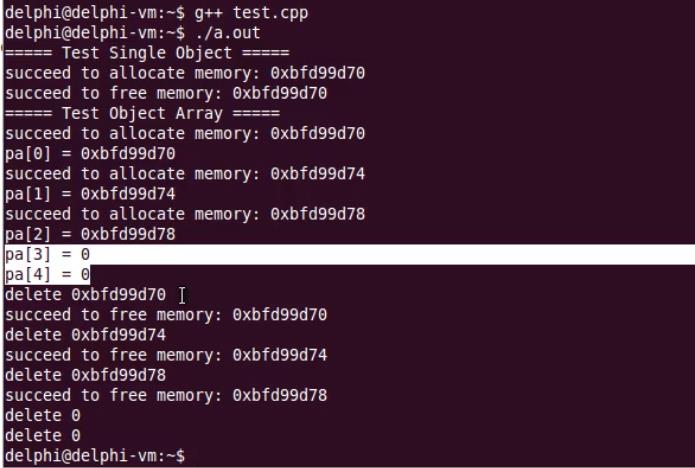
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char buffer[12] = {0};//栈上创建
Test::SetMemorySource(buffer, sizeof(buffer));
cout << "===== Test Single Object =====" << endl;
Test* pt = new Test;
delete pt;
cout << "===== Test Object Array =====" << endl;
Test* pa[5] = {0};
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
pa[i] = new Test;
cout << "pa[" << i << "] = " << pa[i] << endl;
}
for(int i=0; i<5; i++)
{
cout << "delete " << pa[i] << endl;
delete pa[i];
}
return 0;
}


#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
int m_value;
public:
Test()
{
m_value = 0;
}
~Test()
{
}
void* operator new (unsigned int size)
{
cout << "operator new: " << size << endl;
return malloc(size);
}
void operator delete (void* p)
{
cout << "operator delete: " << p << endl;
free(p);
}
void* operator new[] (unsigned int size)
{
cout << "operator new[]: " << size << endl;
return malloc(size);
}
void operator delete[] (void* p)
{
cout << "operator delete[]: " << p << endl;
free(p);
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Test* pt = NULL;
pt = new Test;
delete pt;
pt = new Test[5];
delete[] pt;
return 0;
}
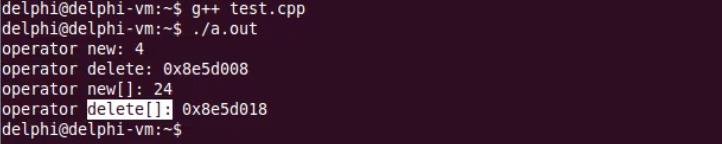
为什么是24,多余的4字节保存数组信息,方便delete[ ],delete[ ]和delete完全不同,不要混用!!!
小结

以上是关于技巧:自定义内存管理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章