cgb2107-day18
Posted cgblpx
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了cgb2107-day18相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一,Spring AOP
–1,概述
是面向切面编程,扩展了面向对象的不足.
切面Aspect: 其实就是一个类, 要用@Aspect注解
通知Advice: 就是类里的方法, 分为:前置通知 后置通知 环绕通知 返回后通知 异常通知
切点Pointcut: 就是定义了方法的触发时间,切入点表达式
–2,使用步骤
加入jar包
<dependencies>
<!--添加aop依赖包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
–3,创建切面
package cn.tedu.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect //切面:通知 + 切点
public class Timer {
//2,切点表达式,通过execution属性声明
//* cn.tedu.service.*.*(..) 方法返回值 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表)
@Pointcut("execution(* cn.tedu.controller.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){}
//1,通知:分类: 前置通知 后置通知 环绕通知 返回后通知 异常通知
//前置通知:在调用你的目标方法前,就要执行
@Before("pointcut()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("我是前置通知~~~~~");
//常见的使用场景:权限 缓存 开启事务 日志
}
//后置通知:在调用你的目标方法后,就要执行
@After("pointcut()")
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){
System.out.println("我是后置通知~~~~~");
//常见的使用场景:结束事务 日志 释放资源
}
//环绕通知:在调用你的目标方法之前和之后,都要执行
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//计时开始
Object o = joinPoint.proceed();//继续执行你的目标方法
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//计时结束
System.out.println("aop统计的总耗时是:"+(end-start));
return o;//放回给调用者,继续执行方法
}
}
–4,测试
创建启动类
package cn.tedu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class RunApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RunApp.class);
}
}
创建HelloController 类
package cn.tedu.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController//Controller + ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("hello")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("hello")
public String hello(){
for (int i = 0; i <100 ; i++) {
System.out.println("=");
}
return "恭喜您,访问成功~";
}
//统计hello()方法的性能
//缺点:目前只能统计hello()方法的性能,想要统计其他方法的性能--AOP
//AOP思想好处:让程序员更加关注业务本身,把通用的代码形成切面
@RequestMapping("hello2")
public String hello2(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
hello();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
return "访问时间:"+(end-start) ;
}
}
测试
访问HelloController 里的每个方法,都会执行对应的通知
二,两个框架的整合
–1,需求
获取汽车数据
–2,开发步骤
0,项目结构
1,RunApp启动类
package cn.tedu;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class RunApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(RunApp.class);
}
}
2,application.yml改端口
server:
port: 8090
3,Car类,封装数据
package cn.tedu.pojo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//模型层,用来封装数据
@Component//交给spring框架进行ioc
public class Car {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String color;
private Double price;
//get set tostring
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\\'' +
", color='" + color + '\\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
4,CarService接口,定义抽象方法
package cn.tedu.service;
import cn.tedu.pojo.Car;
import java.util.List;
//接口里都是抽象方法
//jdk1.8也可以有static或者default的普通方法
public interface CarService {
//简写形式,public abstract
List<Car> get();//获取Car数据
}
5,CarServiceImpl实现类,重写抽象方法
package cn.tedu.service;
import cn.tedu.pojo.Car;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//实现类实现了接口要重写抽象方法,否则就是一个抽象类
@Service//和Component一样,都可以完成ioc,只是更好的表示了是service层的代码
public class CarServiceImpl implements CarService{
//重写的要求:方法声明和父类一样,有权限
public List<Car> get(){
Car c1 = new Car();//空对象,属性都是默认值null
c1.setId(10);c1.setName("bmw");c1.setColor("red");c1.setPrice(9.9);
Car c2 = new Car();//空对象,属性都是默认值null
c2.setId(20);c2.setName("audi");c2.setColor("black");c2.setPrice(6.6);
List<Car> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(c1);
list.add(c2);
return list;//给调用者返回list数据
}
}
6,CarController,接受请求
package cn.tedu.controller;
import cn.tedu.pojo.Car;
import cn.tedu.service.CarService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("car")
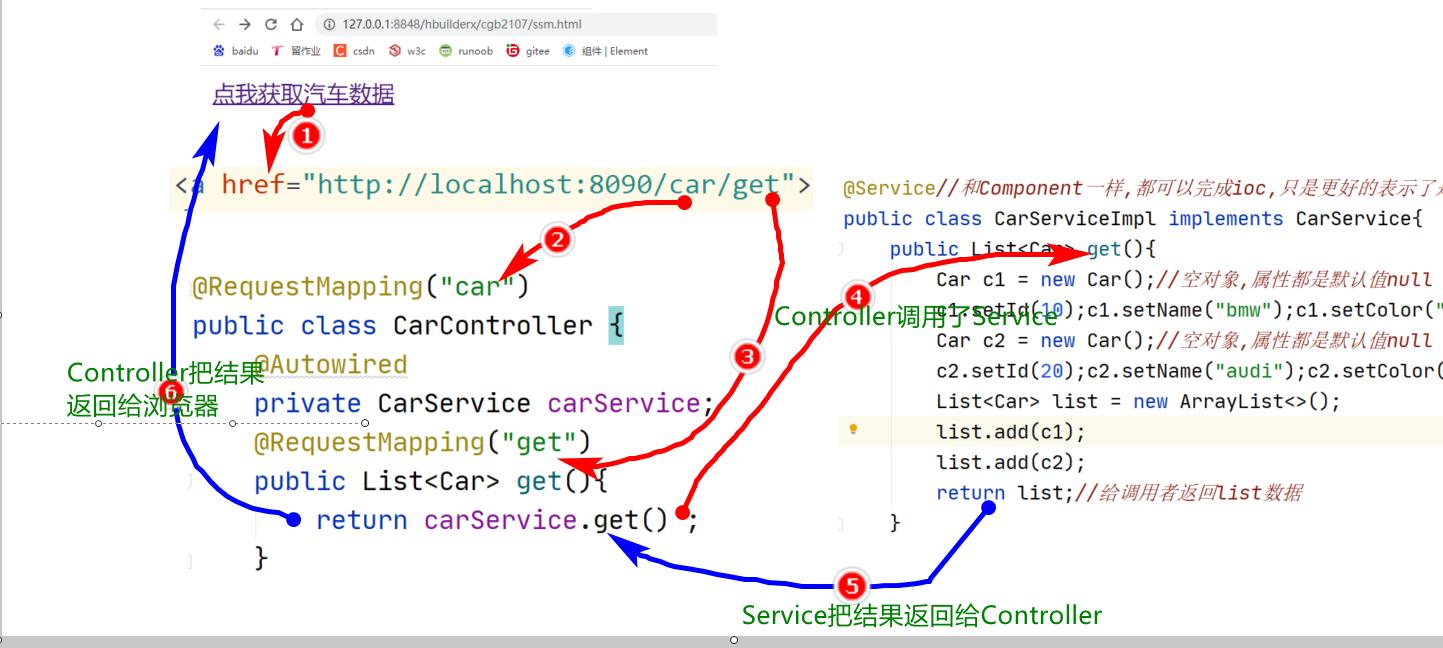
public class CarController {
//1,调用CarServiceImpl里准备好的汽车数据--DI
@Autowired
private CarService carService;
//2,提供方法,给浏览器返回汽车数据
@RequestMapping("get")
public List<Car> get(){
//调用service的功能,service会把结果返回来
return carService.get() ;
}
}
–3,测试

–4,总结

三,标题
以上是关于cgb2107-day18的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章