7张图,20分钟完全搞定async/await原理!(收藏)
Posted SHERlocked93
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了7张图,20分钟完全搞定async/await原理!(收藏)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
async/await用法
其实你要实现一个东西之前,最好是先搞清楚这两样东西
这个东西有什么用?
这个东西是怎么用的?
有什么用?
async/await的用处就是:用同步方式,执行异步操作,怎么说呢?举个例子
比如我现在有一个需求:先请求完接口1,再去请求接口2,我们通常会这么做
function request(num) { // 模拟接口请求
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
request(1).then(res1 => {
console.log(res1) // 1秒后 输出 2
request(2).then(res2 => {
console.log(res2) // 2秒后 输出 4
})
})
或者我现在又有一个需求:先请求完接口1,再拿接口1返回的数据,去当做接口2的请求参数,那我们也可以这么做
request(5).then(res1 => {
console.log(res1) // 1秒后 输出 10
request(res1).then(res2 => {
console.log(res2) // 2秒后 输出 20
})
})
其实这么做是没问题的,但是如果嵌套的多了,不免有点不雅观,这个时候就可以用async/await来解决了
async function fn () {
const res1 = await request(5)
const res2 = await request(res1)
console.log(res2) // 2秒后输出 20
}
fn()
是怎么用?
还是用刚刚的例子
需求一:
async function fn () {
await request(1)
await request(2)
// 2秒后执行完
}
fn()
需求二:
async function fn () {
const res1 = await request(5)
const res2 = await request(res1)
console.log(res2) // 2秒后输出 20
}
fn()

其实就类似于生活中的排队,咱们生活中排队买东西,肯定是要上一个人买完,才轮到下一个人。而上面也一样,在async函数中,await规定了异步操作只能一个一个排队执行,从而达到用同步方式,执行异步操作的效果,这里注意了:await只能在async函数中使用,不然会报错哦
刚刚上面的例子await后面都是跟着异步操作Promise,那如果不接Promise会怎么样呢?
function request(num) { // 去掉Promise
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(num * 2)
}, 1000)
}
async function fn() {
await request(1) // 2
await request(2) // 4
// 1秒后执行完 同时输出
}
fn()
可以看出,如果await后面接的不是Promise的话,其实是达不到排队的效果的
说完await,咱们聊聊async吧,async是一个位于function之前的前缀,只有async函数中,才能使用await。那async执行完是返回一个什么东西呢?
async function fn () {}
console.log(fn) // [AsyncFunction: fn]
console.log(fn()) // Promise {<fulfilled>: undefined}
可以看出,async函数执行完会自动返回一个状态为fulfilled的Promise,也就是成功状态,但是值却是undefined,那要怎么才能使值不是undefined呢?很简单,函数有return返回值就行了
async function fn (num) {
return num
}
console.log(fn) // [AsyncFunction: fn]
console.log(fn(10)) // Promise {<fulfilled>: 10}
fn(10).then(res => console.log(res)) // 10
可以看出,此时就有值了,并且还能使用then方法进行输出
总结
总结一下async/await的知识点
await只能在async函数中使用,不然会报错
async函数返回的是一个状态为fuifilled的Promise对象,有无值看有无return值
await后面只有接了Promise才能实现排队效果
async/await作用是用同步方式,执行异步操作
什么是语法糖?
前面说了,async/await是一种语法糖,诶!好多同学就会问,啥是语法糖呢?我个人理解就是,语法糖就是一个东西,这个东西你就算不用他,你用其他手段也能达到这个东西同样的效果,但是可能就没有这个东西这么方便了。
举个生活中的例子吧:你走路也能走到北京,但是你坐飞机会更快到北京。
举个代码中的例子吧:ES6的
class也是语法糖,因为其实用普通function也能实现同样效果
回归正题,async/await是一种语法糖,那就说明用其他方式其实也可以实现他的效果,我们今天就是讲一讲怎么去实现async/await,用到的是ES6里的迭代函数——generator函数
generator函数
基本用法
generator函数跟普通函数在写法上的区别就是,多了一个星号*,并且只有在generator函数中才能使用yield,什么是yield呢,他相当于generator函数执行的中途暂停点,比如下方有3个暂停点。而怎么才能暂停后继续走呢?那就得使用到next方法,next方法执行后会返回一个对象,对象中有value 和 done两个属性
value:暂停点后面接的值,也就是yield后面接的值
done:是否generator函数已走完,没走完为false,走完为true
function* gen() {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 3, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: undefined, done: true }
可以看到最后一个是undefined,这取决于你generator函数有无返回值
function* gen() {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
return 4
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 3, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 4, done: true }
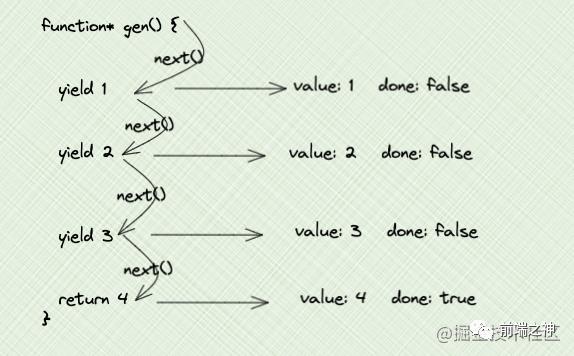
yield后面接函数
yield后面接函数的话,到了对应暂停点yield,会马上执行此函数,并且该函数的执行返回值,会被当做此暂停点对象的value
function fn(num) {
console.log(num)
return num
}
function* gen() {
yield fn(1)
yield fn(2)
return 3
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next())
// 1
// { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(g.next())
// 2
// { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(g.next())
// { value: 3, done: true }
yield后面接Promise
前面说了,函数执行返回值会当做暂停点对象的value值,那么下面例子就可以理解了,前两个的value都是pending状态的Promise对象
function fn(num) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(num)
}, 1000)
})
}
function* gen() {
yield fn(1)
yield fn(2)
return 3
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next()) // { value: Promise { <pending> }, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: Promise { <pending> }, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 3, done: true }
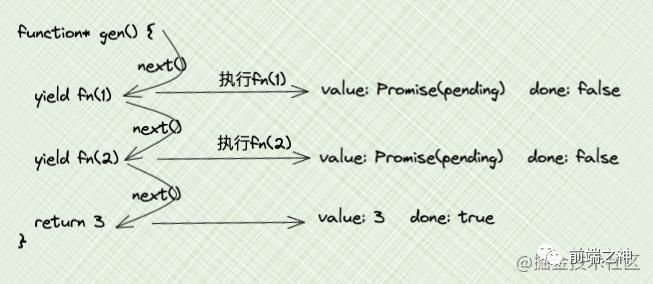
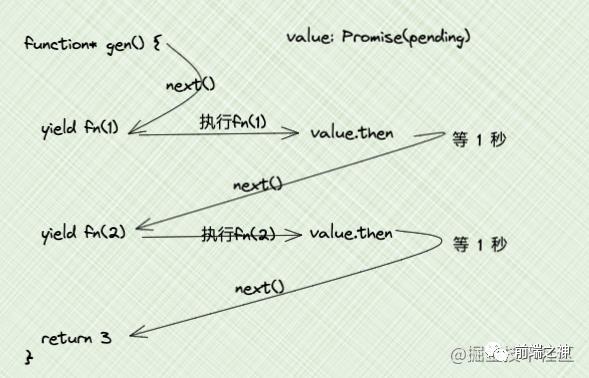
其实我们想要的结果是,两个Promise的结果1 和 2,那怎么做呢?很简单,使用Promise的then方法就行了
const g = gen()
const next1 = g.next()
next1.value.then(res1 => {
console.log(next1) // 1秒后输出 { value: Promise { 1 }, done: false }
console.log(res1) // 1秒后输出 1
const next2 = g.next()
next2.value.then(res2 => {
console.log(next2) // 2秒后输出 { value: Promise { 2 }, done: false }
console.log(res2) // 2秒后输出 2
console.log(g.next()) // 2秒后输出 { value: 3, done: true }
})
})
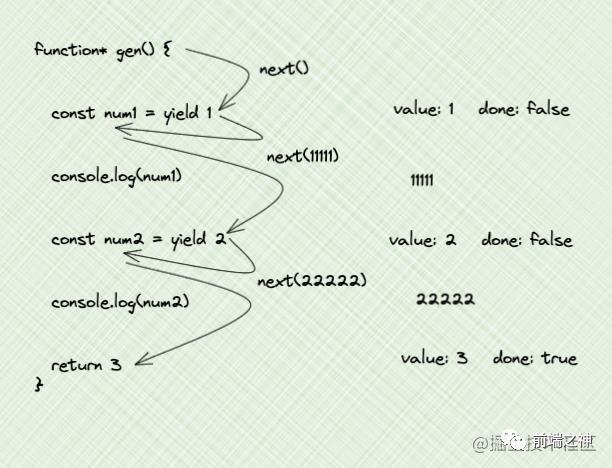
next函数传参
generator函数可以用next方法来传参,并且可以通过yield来接收这个参数,注意两点
第一次next传参是没用的,只有从第二次开始next传参才有用
next传值时,要记住顺序是,先右边yield,后左边接收参数
function* gen() {
const num1 = yield 1
console.log(num1)
const num2 = yield 2
console.log(num2)
return 3
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(g.next(11111))
// 11111
// { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(g.next(22222))
// 22222
// { value: 3, done: true }
Promise+next传参
前面讲了
yield后面接Promise
next函数传参
那这两个组合起来会是什么样呢?
function fn(nums) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(nums * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
function* gen() {
const num1 = yield fn(1)
const num2 = yield fn(num1)
const num3 = yield fn(num2)
return num3
}
const g = gen()
const next1 = g.next()
next1.value.then(res1 => {
console.log(next1) // 1秒后同时输出 { value: Promise { 2 }, done: false }
console.log(res1) // 1秒后同时输出 2
const next2 = g.next(res1) // 传入上次的res1
next2.value.then(res2 => {
console.log(next2) // 2秒后同时输出 { value: Promise { 4 }, done: false }
console.log(res2) // 2秒后同时输出 4
const next3 = g.next(res2) // 传入上次的res2
next3.value.then(res3 => {
console.log(next3) // 3秒后同时输出 { value: Promise { 8 }, done: false }
console.log(res3) // 3秒后同时输出 8
// 传入上次的res3
console.log(g.next(res3)) // 3秒后同时输出 { value: 8, done: true }
})
})
})
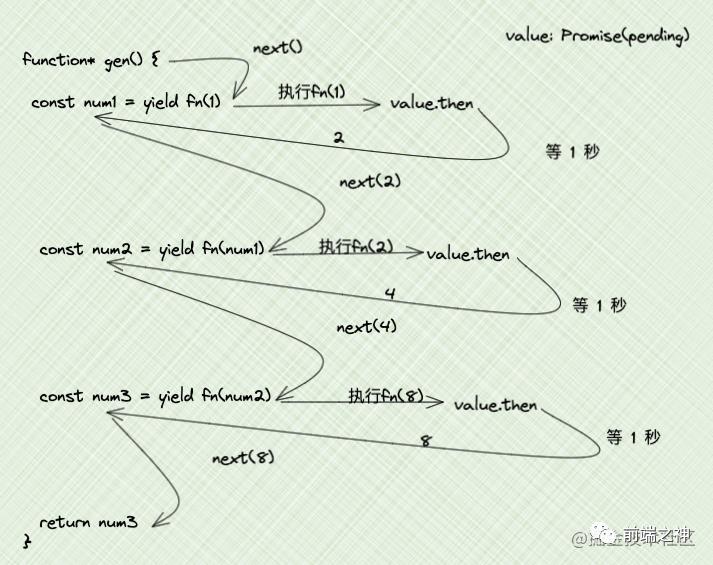
实现async/await
其实上方的generator函数的Promise+next传参,就很像async/await了,区别在于
gen函数执行返回值不是Promise,asyncFn执行返回值是Promise
gen函数需要执行相应的操作,才能等同于asyncFn的排队效果
gen函数执行的操作是不完善的,因为并不确定有几个yield,不确定会嵌套几次

那我们怎么办呢?我们可以封装一个高阶函数。什么是高阶函数呢?高阶函数的特点是:参数是函数,返回值也是函数。下方的highorderFn就是一个高阶函数
function highorderFn(函数) {
// 一系列处理
return 函数
}
我们可以封装一个高阶函数,接收一个generator函数,并经过一系列处理,返回一个具有async函数功能的函数
function generatorToAsync(generatorFn) {
// 经过一系列处理
return 具有async函数功能的函数
}
返回值Promise
之前我们说到,async函数的执行返回值是一个Promise,那我们要怎么实现相同的结果呢
function* gen() {
}
const asyncFn = generatorToAsync(gen)
console.log(asyncFn()) // 期望这里输出 Promise
其实很简单,generatorToAsync函数里做一下处理就行了
function* gen() {
}
function generatorToAsync (generatorFn) {
return function () {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
})
}
}
const asyncFn = generatorToAsync(gen)
console.log(asyncFn()) // Promise
加入一系列操作
咱们把之前的处理代码,加入generatorToAsync函数中
function fn(nums) {
return new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(nums * 2)
}, 1000)
})
}
function* gen() {
const num1 = yield fn(1)
const num2 = yield fn(num1)
const num3 = yield fn(num2)
return num3
}
function generatorToAsync(generatorFn) {
return function () {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const g = generatorFn()
const next1 = g.next()
next1.value.then(res1 => {
const next2 = g.next(res1) // 传入上次的res1
next2.value.then(res2 => {
const next3 = g.next(res2) // 传入上次的res2
next3.value.then(res3 => {
// 传入上次的res3
resolve(g.next(res3).value)
})
})
})
})
}
}
const asyncFn = generatorToAsync(gen)
asyncFn().then(res => console.log(res)) // 3秒后输出 8
可以发现,咱们其实已经实现了以下的async/await的结果了
async function asyncFn() {
const num1 = await fn(1)
const num2 = await fn(num1)
const num3 = await fn(num2)
return num3
}
asyncFn().then(res => console.log(res)) // 3秒后输出 8
完善代码
上面的代码其实都是死代码,因为一个async函数中可能有2个await,3个await,5个await ,其实await的个数是不确定的。同样类比,generator函数中,也可能有2个yield,3个yield,5个yield,所以咱们得把代码写成活的才行
function generatorToAsync(generatorFn) {
return function() {
const gen = generatorFn.apply(this, arguments) // gen有可能传参
// 返回一个Promise
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
function go(key, arg) {
let res
try {
res = gen[key](arg) // 这里有可能会执行返回reject状态的Promise
} catch (error) {
return reject(error) // 报错的话会走catch,直接reject
}
// 解构获得value和done
const { value, done } = res
if (done) {
// 如果done为true,说明走完了,进行resolve(value)
return resolve(value)
} else {
// 如果done为false,说明没走完,还得继续走
// value有可能是:常量,Promise,Promise有可能是成功或者失败
return Promise.resolve(value).then(val => go('next', val), err => go('throw', err))
}
}
go("next") // 第一次执行
})
}
}
const asyncFn = generatorToAsync(gen)
asyncFn().then(res => console.log(res))
这样的话,无论是多少个yield都会排队执行了,咱们把代码写成活的了
示例
async/await版本
async function asyncFn() {
const num1 = await fn(1)
console.log(num1) // 2
const num2 = await fn(num1)
console.log(num2) // 4
const num3 = await fn(num2)
console.log(num3) // 8
return num3
}
const asyncRes = asyncFn()
console.log(asyncRes) // Promise
asyncRes.then(res => console.log(res)) // 8
使用generatorToAsync函数的版本
function* gen() {
const num1 = yield fn(1)
console.log(num1) // 2
const num2 = yield fn(num1)
console.log(num2) // 4
const num3 = yield fn(num2)
console.log(num3) // 8
return num3
}
const genToAsync = generatorToAsync(gen)
const asyncRes = genToAsync()
console.log(asyncRes) // Promise
asyncRes.then(res => console.log(res)) // 8
最后
如果你觉得这篇内容对你挺有启发,我想邀请你帮我三个小忙:
点个「在看」,让更多的人也能看到这篇内容(喜欢不点在看,都是耍流氓 -_-)
欢迎加我微信「 sherlocked_93 」拉你进技术群,长期交流学习...
关注公众号「前端下午茶」,持续为你推送精选好文,也可以加我为好友,随时聊骚。

点个在看支持我吧,转发就更好了
以上是关于7张图,20分钟完全搞定async/await原理!(收藏)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章