ML-ZF算法的matlab仿真
Posted fpga&matlab
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了ML-ZF算法的matlab仿真相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
clear all;clc
N = 2; % Number of Transmit antennas
M = 2; % Number of Receive antennas
EbNoVec = 5:3:11; % Eb/No in dB
modOrd = 2; % constellation size = 2^modOrd
numSym = N; % number of symbols
% Seed states for repeatability
rand('twister', 12345); randn('state', 98765);
% Get all bit combinations for ML receiver
bits = de2bi(0:2^(modOrd*N)-1, 'left-msb')';
% Split them per Transmit antenna
b = zeros(N, modOrd, length(bits));
for i = 1:length(bits)
b(:, :, i) = reshape(bits(:,i), modOrd, N)';
end
% Preallocate variables for speed
dist = zeros(length(bits), 1);
[BER_ZF, BER_MMSE, BER_ML] = deal(zeros(1, length(EbNoVec)));
% Create QPSK mod-demod objects
hMod = modem.pskmod('M', 2^modOrd, 'SymbolOrder', 'gray', 'InputType', 'bit');
hDemod = modem.pskdemod(hMod);
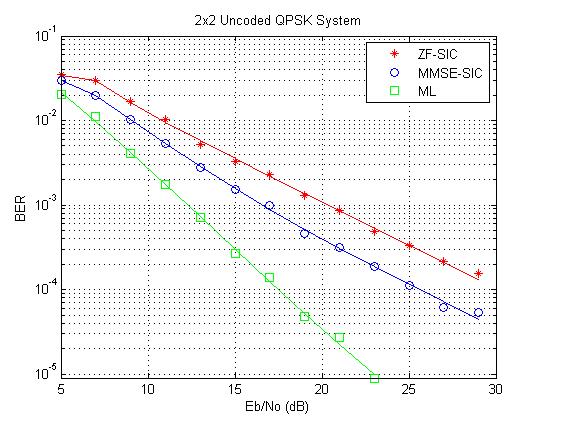
% Set up a figure for visualizing BER results
h = gcf; grid on; hold on;
set(gca,'yscale','log','xlim',[EbNoVec(1)-0.01, EbNoVec(end)],'ylim',[1e-4 1]);
xlabel('Eb/No (dB)'); ylabel('BER'); set(h,'NumberTitle','off');
set(h, 'renderer', 'zbuffer'); set(h,'Name','Spatial Multiplexing');
title('2x2 Uncoded QPSK System');
% Loop over selected EbNo points
for idx = 1:length(EbNoVec)
nErrs_zf = 0; nErrs_mmse = 0; nErrs_ml = 0;
nBits = 0;
while ( ((nErrs_zf < 100) || (nErrs_mmse < 100) || (nErrs_ml < 100)) ...
&& (nBits < 1e4))
% Create array of bits to modulate
msg = randint(modOrd, numSym, 2);
% Modulate data
source = modulate(hMod, msg);
% Split source among N transmitters (symbol-wise)
Tx = reshape(source, N, numel(source)/N); clear source;
% Flat Rayleigh Fading - independent links
RayleighMat = (randn(M, N) + sqrt(-1)*randn(M, N))/sqrt(2);
% Calculate SNR from EbNo
snr = EbNoVec(idx) + 10*log10(modOrd);
% Add channel noise power to faded data
r = awgn(RayleighMat*Tx, snr); clear Tx;
r_store = r;
% Assume perfect channel estimation
H = RayleighMat;
% Zero-Forcing SIC receiver
E_zf = zeros(modOrd, numSym); k = zeros(N, 1);
% Initialization
G = pinv(H);
[val, k0] = min(sum(abs(G).^2,2));
% Start Zero-Forcing Nulling Loop
for n = 1:N
% Find best transmitter signal using minimum norm
k(n) = k0;
% Select Weight vector for best transmitter signal
w = G(k(n),:);
% Calculate output for transmitter n and demodulate bitstream
y = w * r;
E_zf(:, k(n):N:end) = reshape(demodulate(hDemod, y), modOrd, numSym/N);
% Subtract effect of the transmitter n from received signal
z = modulate(hMod, demodulate(hDemod, y));
r = r - H(:, k(n))*z;
% Adjust channel estimate matrix for next minimum norm search
H(:, k(n)) = zeros(M, 1);
G = pinv(H);
for aa = 1:n
G(k(aa), :) = inf;
end
[val, k0] = min(sum(abs(G).^2,2));
end
% Restore variables for next receiver
H = RayleighMat; r = r_store;
% MMSE SIC receiver
E_mmse = zeros(modOrd, numSym); k = zeros(N, 1);
% Initialization
G = inv(H'*H + N/(10^(0.1*snr))*eye(N)) * H';
[val, k0] = min(sum(abs(G).^2,2));
% Start MMSE Nulling Loop
for n = 1:N
% Find best transmitter signal using Min Norm
k(n) = k0;
% Select Weight vector for best transmitter signal
w = G(k(n),:);
% Calculate output for transmitter n and demodulate bitstream
y = w * r;
E_mmse(:, k(n):N:end) = reshape(demodulate(hDemod, y), modOrd, numSym/N);
% Subtract effect of the transmitter n from received signal
z = modulate(hMod, demodulate(hDemod, y));
r = r - H(:, k(n))*z;
% Adjust channel estimate matrix for next min Norm search
H(:, k(n)) = zeros(M, 1);
G = inv(H'*H + N/(10^(0.1*snr))*eye(N)) * H';
for aa = 1:n
G(k(aa), :) = inf;
end
[val, k0] = min(sum(abs(G).^2,2));
end
% Restore variables for next receiver
H = RayleighMat; r = r_store;
% ML receiver
for i = 1:2^(modOrd*N)
% Signal constellation for each bit combination
sig = modulate(hMod, b(:, :, i)').';
% Distance metric for each constellation
dist(i) = sum(abs(r - H*sig).^2);
end
% Get the minimum
[notUsed, val] = min(dist);
E_ml = b(:,:,val)'; % detected bits
% Collect errors
nErrs_zf = nErrs_zf + biterr(msg, E_zf);
nErrs_mmse = nErrs_mmse + biterr(msg, E_mmse);
nErrs_ml = nErrs_ml + biterr(msg, E_ml);
nBits = nBits + length(msg(:));
end
% Calculate BER for current point
BER_ZF(idx) = nErrs_zf./nBits;
BER_MMSE(idx) = nErrs_mmse./nBits;
BER_ML(idx) = nErrs_ml./nBits;
% Plot results
semilogy(EbNoVec(1:idx), BER_ZF(1:idx), 'r*', ...
EbNoVec(1:idx), BER_MMSE(1:idx), 'bo', ...
EbNoVec(1:idx), BER_ML(1:idx), 'gs');
legend('ZF-SIC', 'MMSE-SIC', 'ML');
drawnow;
end
% Draw the lines
semilogy(EbNoVec, BER_ZF, 'r-', EbNoVec, BER_MMSE, 'b-', ...
EbNoVec, BER_ML, 'g-');
hold off;
openfig('spatMuxResults.fig');
以上是关于ML-ZF算法的matlab仿真的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章