Codeforces Global Round 16 A-E
Posted hesorchen
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Codeforces Global Round 16 A-E相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
A. Median Maximization
n个非负数的和是s,问中位数最大可以是多少。
前一半都取0最优。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
void solve()
{
long long n, s;
cin >> n >> s;
long long m = (n + 1) / 2;
n -= (m - 1);
cout << (s / n) << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
B. MIN-MEX Cut
给一个01字符串,一个01字符串的mex运算返回0/1/2。可以将所给的01字符串分割成若干个子字符串,问所有子字符串的mex总和最小是多少。
先将连续的相同字符都处理成一个字符。然后是一个01交替出现的字符串,考虑不分割时答案为2,所有1可以拆成单独的子字符串,贡献为0,连续的一段0可以拆成一个子字符串,贡献为1,也就是看连续的0出现了几段,和2取min即可。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
void solve()
{
string a;
cin >> a;
string b = a;
a.clear();
for (auto it : b)
{
if (a.size() && it == a.back())
continue;
a += it;
}
int s0 = 0;
for (auto it : a)
s0 += it == '0';
cout << min(2, s0) << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
C. MAX-MEX Cut
在B题的基础变为两个01字符串,分割的时候两个字符串同步。求所有子字符串最大mex和。
例如:
01100
11100
0 11 00
1 11 00
2 0 1
容易发现,除下列两种情况,其他都分割成长度为1的子字符串就是最优的。
01
01
10
10
分类讨论太麻烦了,选择了DP,DP[i]只会从DP[i-1]、DP[i-2]转移
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int dp[N];
int get(char a, char b)
{
set<int> st;
st.insert(a);
st.insert(b);
if (st.size() == 2)
return 2;
if (st.count('0'))
return 1;
return 0;
}
int get(char a, char b, char c, char d)
{
set<int> st;
st.insert(a);
st.insert(b);
st.insert(c);
st.insert(d);
if (st.size() == 2)
return 2;
if (st.count('0'))
return 1;
return 0;
}
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
string a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
dp[i] = 0;
a = ' ' + a;
b = ' ' + b;
dp[1] = get(a[1], b[1]);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[i - 1] + get(a[i], b[i]));
if (i >= 2)
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[i - 2] + get(a[i], b[i], a[i - 1], b[i - 1]));
}
cout << dp[n] << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
D1. Seating Arrangements (easy version)
读完题就会了。求顺序对即可(甚至不用数据结构优化)。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int a[N];
void solve()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++)
ans += a[i] > a[j];
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
D2. Seating Arrangements (hard version)
最后的结果是确定的,对于ai相同的,贪心从上到下,从右到左放置。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 300 + 5;
int a[N * N];
int b[N * N];
int mp[N][N];
int fk[N][N];
void solve()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int all = n * m;
for (int i = 1; i <= all; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
b[i] = a[i];
}
sort(b + 1, b + 1 + all);
int ct = 0;
map<int, deque<int>> res;
for (int i = 1; i <= all; i++)
res[a[i]].push_back(i);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
mp[i][j] = b[++ct];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = m; j >= 1; j--)
{
fk[i][j] = res[mp[i][j]].front();
res[mp[i][j]].pop_front();
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
for (int k = 1; k < j; k++)
ans += fk[i][k] < fk[i][j];
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
E. Buds Re-hanging
能切的先全部切出来。最后肯定形成了若干个深度为2、叶子数量大于0的子树。
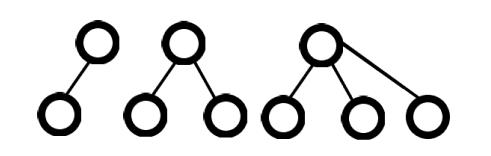
然后将所有子树连接起来即可。显然将当前子树的根连接到上一个子树的一个叶子上是最优的。因此答案就是拆完之后的叶子总数-(子树的数量-1)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
vector<int> mp[N];
int typ[N]; //1为叶子结点 0为切断后子树的根结点
int num[N]; //typ[2]的根结点含有的儿子数量
int dfs(int u, int fa)
{
vector<int> vec;
for (auto v : mp[u])
{
if (v == fa)
continue;
vec.emplace_back(dfs(v, u));
}
int num_leaves = 0;
for (auto it : vec)
num_leaves += it;
if (num_leaves) //儿子节点有叶子 就可以切断
{
typ[u] = 0;
num[u] = num_leaves;
}
else
typ[u] = 1; //叶子返回1
return typ[u];
}
void solve()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
mp[i].clear();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
mp[u].emplace_back(v);
mp[v].emplace_back(u);
}
dfs(1, -1);
int res = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (typ[i] == 0) //i是一颗子树的根
{
ans += num[i]; //叶子总数
res++; //子树的数量
}
cout << ans - (res - 1) << endl;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
以上是关于Codeforces Global Round 16 A-E的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章