Android ActivityResultContracts 请求权限(封装;含android 11权限变更)
Posted 匆忙拥挤repeat
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android ActivityResultContracts 请求权限(封装;含android 11权限变更)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
android 11 权限变更
- Beginning with Android 11, ACTION_MANAGE_OVERLAY_PERMISSION intents always bring the user to the top-level Settings screen, where the user can grant or revoke the SYSTEM_ALERT_WINDOW permissions for apps. Any package: data in the intent is ignored.
- If your app targets Android 11 or higher and needs to access the phone number APIs shown in the following list, you must request the READ_PHONE_NUMBERS permission, instead of the READ_PHONE_STATE permission.
The getLine1Number() method in both the TelephonyManager class and the TelecomManager class.
The unsupported getMsisdn() method in the TelephonyManager class.
<manifest>
<!-- Grants the READ_PHONE_STATE permission only on devices that run
Android 10 (API level 29) and lower. -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE"
android:maxSdkVersion="29" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.READ_PHONE_NUMBERS" />
</manifest>
权限申请
官方文档
文档中的 流程图:
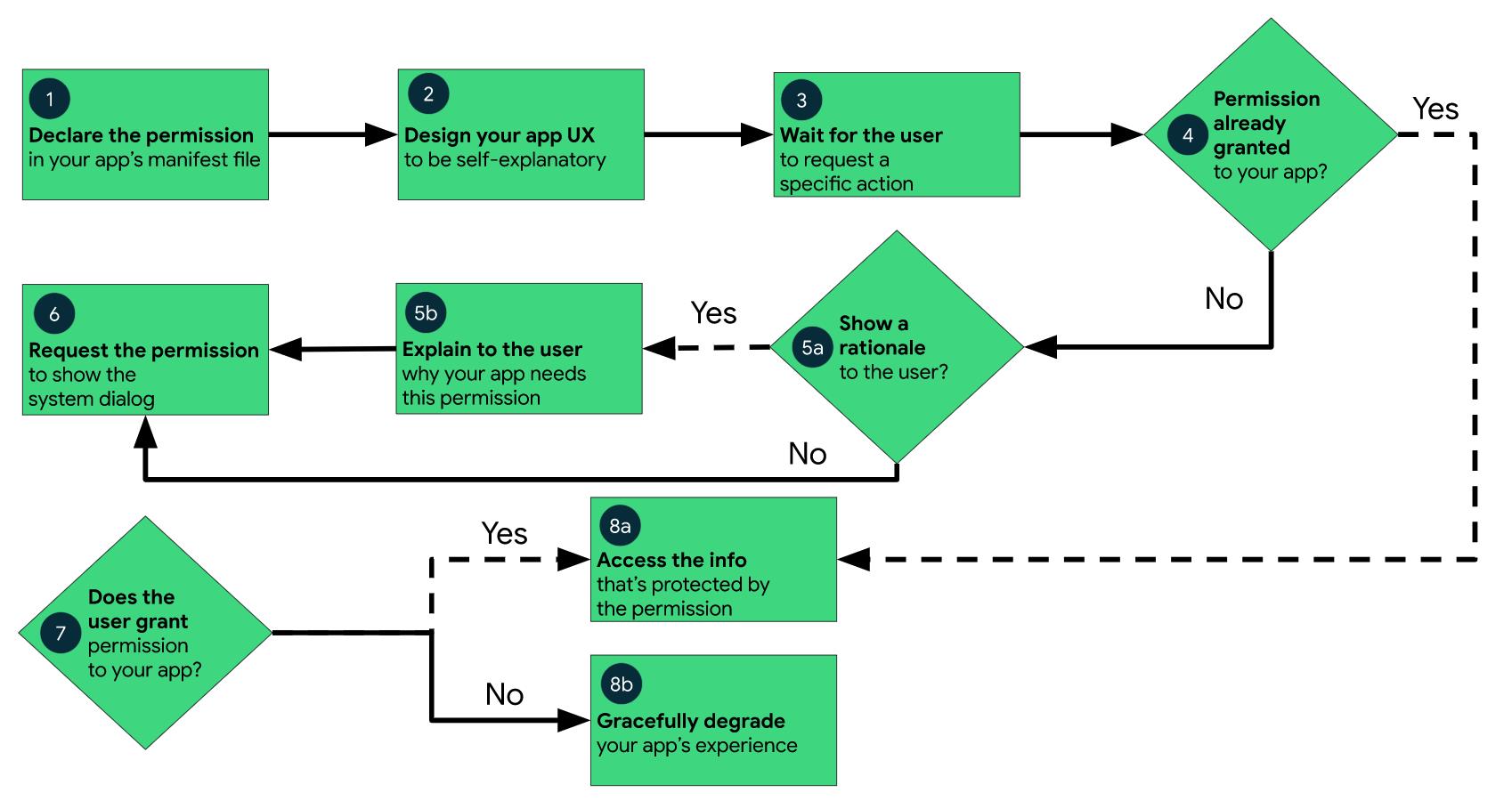
通过文档与流程图,再结合
Android ActivityResultContracts 替代 startActivityForResult
inline fun SupportFragment.requestPermission(crossinline block: (Boolean) -> Unit): ActivityResultLauncher<String> {
return registerForActivityResult(ActivityResultContracts.RequestPermission()) { result ->
block(result)
}
}
对单个权限的请求流程做了封装。
通常一个功能,要请求的权限也很少超过两个。如果超过了,那可能这是一个组合功能,可以拆解成较细粒度的功能。
BasePermissionExtendFragment.kt
import android.content.Context
import android.content.Intent
import android.net.Uri
import android.provider.Settings
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.activity.result.contract.ActivityResultContracts
import androidx.appcompat.app.AlertDialog
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat
import androidx.core.content.ContextCompat
import androidx.core.content.PermissionChecker
/**
* desc:
* author: stone
* email: aa86799@163.com
* time: 2021/6/9 14:40
*/
abstract class BasePermissionExtendFragment : BaseExtendFragment() {
private var mGrantedCallback: (() -> Unit)? = null
private var mDeniedCallback: (() -> Unit)? = null
val mRequestPermissionLauncher =
requestPermission { isGranted: Boolean ->
if (isGranted) {
if (mGrantedCallback != null) {
mGrantedCallback?.invoke()
return@requestPermission
}
Toast.makeText(requireContext(), "granted", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
} else {
if (mDeniedCallback != null) {
mDeniedCallback?.invoke()
return@requestPermission
}
Toast.makeText(requireContext(), "denied", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
AlertDialog.Builder(requireContext())
.setTitle("why need it , please go to setting and open it")
.setPositiveButton("confirm") { dialog, _ ->
}
.create().show()
}
}
fun checkPermission(
permission: String,
grantedCallback: (() -> Unit)? = null,
rationaleCallback: (() -> Unit)? = null,
deniedCallback: (() -> Unit)? = null
) {
mGrantedCallback = grantedCallback
mDeniedCallback = deniedCallback
val selfPermission = ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(requireContext(), permission)
when {
// 已授权
selfPermission == PermissionChecker.PERMISSION_GRANTED -> {
if (mGrantedCallback != null) {
mGrantedCallback?.invoke()
return
}
Toast.makeText(requireContext(), "granted", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
// 拒绝,但未选中 "不再提醒"; 可能弹窗提示用户,需要此权限的原因
ActivityCompat.shouldShowRequestPermissionRationale(requireActivity(), permission) -> {
if (rationaleCallback != null) {
rationaleCallback.invoke()
return
}
// show tips, needs permission why it is
AlertDialog.Builder(requireContext())
.setTitle("why need it ")
.setNegativeButton("cancel") { dialog, _ ->
}
.setPositiveButton("confirm") { dialog, _ ->
mRequestPermissionLauncher.launch(permission)
}
.create().show()
}
// 拒绝,且不再提醒
selfPermission == PermissionChecker.PERMISSION_DENIED -> {
mRequestPermissionLauncher.launch(permission)
}
}
}
// 打开当前应用的 系统设置界面
fun toSelfSetting(context: Context) {
Intent().apply {
addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK)
action = Settings.ACTION_APPLICATION_DETAILS_SETTINGS
data = Uri.fromParts("package", context.packageName, null)
context.startActivity(this)
}
}
}
grantedCallback: 授权后的正常操作;
rationaleCallback: 拒绝(可以提醒)的操作;
deniedCallback: 拒绝(不再提醒的)的操作。
PermissionExtend.kt
对 BasePermissionExtendFragment 进行扩展。增加特定权限的统一处理。
/**
* desc:
* author: stone
* email: aa86799@163.com
* time: 2021/6/9 14:42
*/
/**
* 图片等文件读写操作,可能要用到 WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 外部存储权限。
* android 11 及以上 不再提供 WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE 权限,被标记为 已过时。
* 为了兼容性,>=6 && <=10 需要 权限检查。
*/
fun BasePermissionExtendFragment.storagePermissionHandle(granted: (() -> Unit)? = null) {
val permission = Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE
checkPermission(permission, grantedCallback = {
granted?.invoke()
}, rationaleCallback = {
alert(getString(R.string.reject_tip), resources.getString(R.string.warning)) {
positiveButton(getString(R.string.confirm)) { dialog ->
mRequestPermissionLauncher.launch(permission)
}
}.show()
}, deniedCallback = {
alert(getString(R.string.reject_tip), resources.getString(R.string.warning)) {
positiveButton(getString(R.string.confirm)) { dialog ->
toSelfSetting(requireContext())
}
}.show()
})
}
/**
* 请求相机权限. 通常也需要请求 外部存储权限 (WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE)
*/
fun BasePermissionExtendFragment.cameraPermissionHandle(albumPermission: Boolean = true, granted: (() -> Unit)? = null) {
val permission = Manifest.permission.CAMERA
checkPermission(permission, grantedCallback = {
if (albumPermission)
storagePermissionHandle(granted)
else
granted?.invoke()
}, rationaleCallback = {
alert(getString(R.string.needCameraPermission), resources.getString(R.string.warning)) {
positiveButton(getString(R.string.confirm)) { dialog ->
mRequestPermissionLauncher.launch(permission)
}
}.show()
}, deniedCallback = {
alert(getString(R.string.startCameraPermissionHint), resources.getString(R.string.warning)) {
positiveButton(getString(R.string.confirm)) { dialog ->
toSelfSetting(requireContext())
}
}.show()
})
}
/**
* 请求定位权限. 要先检查是否开启了定位服务
*/
fun BasePermissionExtendFragment.locationPermissionHandle(granted: (() -> Unit)? = null) {
if (!checkLocationService()) return
val permission = Manifest.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION
checkPermission(permission, grantedCallback = {
granted?.invoke()
}, rationaleCallback = {
alert(getString(R.string.needLocationPermission), resources.getString(R.string.warning)) {
positiveButton(getString(R.string.confirm)) { dialog ->
mRequestPermissionLauncher.launch(permission)
}
}.show()
}, deniedCallback = {
alert(getString(R.string.location_is_required), resources.getString(R.string.warning)) {
positiveButton(getString(R.string.confirm)) {
toSelfSetting(requireContext())
}
}.show()
})
}
// 如果打开了定位服务,true; 否则 让用户去设置页面打开定位服务
private fun BasePermissionExtendFragment.checkLocationService(): Boolean {
return if (CheckLocationService.isLocServiceEnable(ExpressApplication.instance())) {
true
} else {
alert(getString(R.string.if_not_be_able_connect_bluetooth_printer)) {
positiveButton(R.string.confirm) {
val locationSet = Intent(Settings.ACTION_LOCATION_SOURCE_SETTINGS)
startActivity(locationSet)
}
negativeButton(R.string.cancel) {
}
}.show()
false
}
}
想对一个具体权限进行怎样的提示与处理,就定义在这里。
类似 定位权限 的申请麻烦点,它首先要依赖定位服务。
定位服务检测:
import android.content.Context
import android.location.LocationManager
object CheckLocationService {
/**
* 手机是否开启位置服务,如果没有开启那么所有app将不能使用定位功能
*/
fun isLocServiceEnable(context: Context): Boolean {
val locationManager = context.getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE) as LocationManager
val gps = locationManager.isProviderEnabled(LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER)
val netWork = locationManager.isProviderEnabled(LocationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER)
return gps || netWork
}
}
最终调用者就舒服了:
storagePermissionHandle { }
cameraPermissionHandle { }
locationPermissionHandle { }
以上是关于Android ActivityResultContracts 请求权限(封装;含android 11权限变更)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章