Android 低功耗蓝牙开发(数据交互)
Posted 初学者-Study
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android 低功耗蓝牙开发(数据交互)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
在上一篇低功耗蓝牙开发文章中,我讲述了扫描和连接,本篇文章讲述数据的交互。当了解了数据交互后就可以开始进行低功耗蓝牙硬件和手机App软件相结合的项目,例如蓝牙音箱、蓝牙灯、蓝牙锁等等。
正文
因为本篇文章会接着上一篇文章进行一个续写,上一篇文章 Android 低功耗蓝牙开发(扫描、连接),没看过的可以先看看,这样可以平稳过度,当然如果对扫描和连接都没有问题的可以直接从本篇文章开始看。
一、BluetoothGattCallback
在进行编码之前首先要了解一个很重要的东西,那就是BluetoothGattCallback,这个类非常重要,可以说你能不能进行低功耗蓝牙的数据交互全看它了。
之前在进行低功耗蓝牙连接的时候使用的是Gatt连接,不知道你是否还记得。回顾一下:
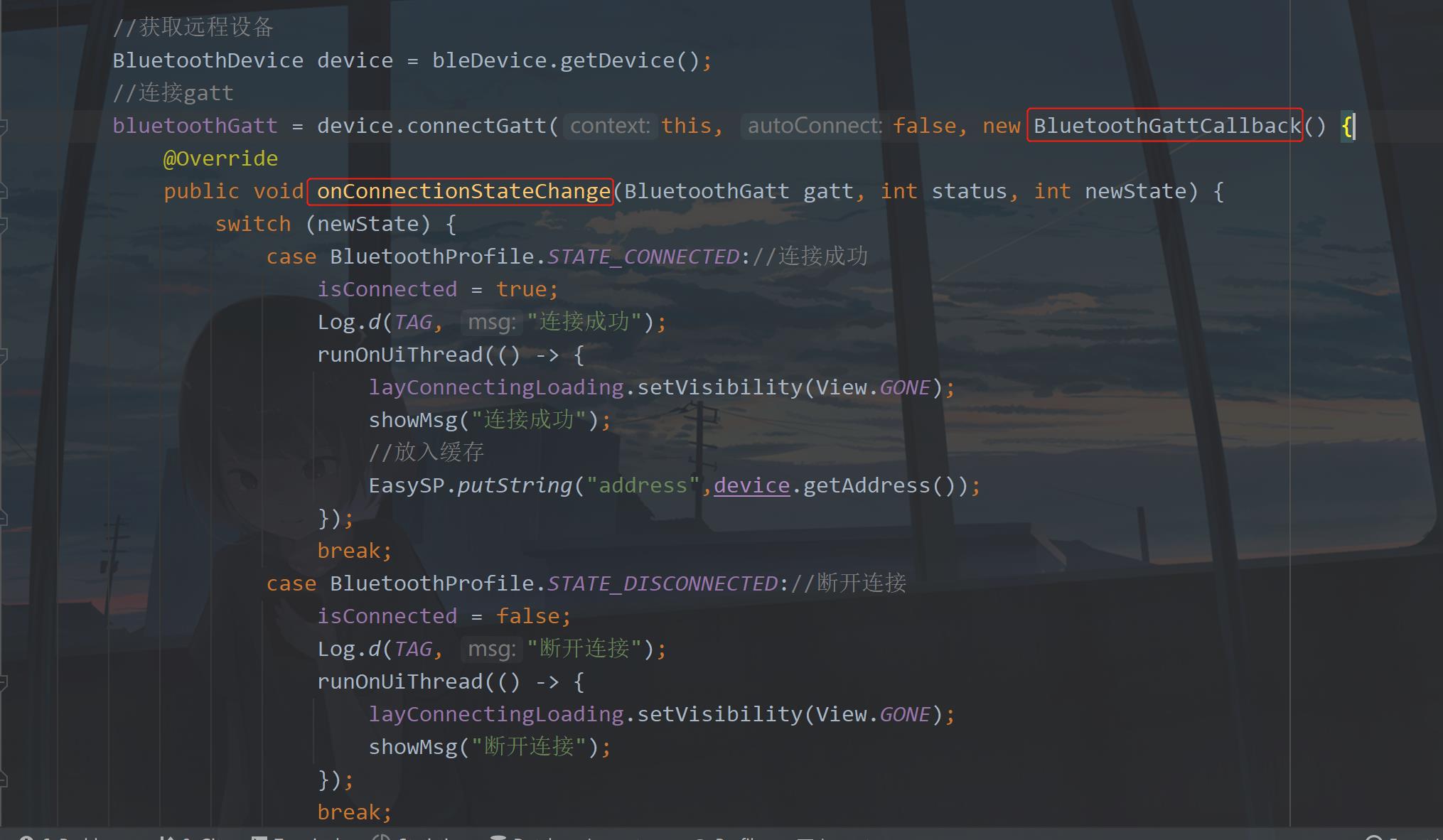
可以看到通过连接gatt,使用了抽象类BluetoothGattCallback,重写了里面的一个onConnectionStateChange方法,进行设备连接状态的回调。这个类里面还有一些方法,可以用于针对开发中的使用进行调用。下面来介绍一下:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| onPhyUpdate | 物理层改变回调 |
| onPhyRead | 设备物理层读取回调 |
| onConnectionStateChange | Gatt连接状态回调 |
| onServicesDiscovered | 发现服务回调 |
| onCharacteristicRead | 特性读取回调 |
| onCharacteristicWrite | 特性写入回调 |
| onCharacteristicChanged | 特性改变回调 |
| onDescriptorRead | 描述读取回调 |
| onDescriptorWrite | 描述写入回调 |
| onReliableWriteCompleted | 可靠写入完成回调 |
| onReadRemoteRssi | 读取远程设备信号值回调 |
| onMtuChanged | MtuSize改变回调 |
| onConnectionUpdated | 连接更新回调 |
这里光有一个表好像是没有啥用,在介绍详细的API方法及里面的属性值之前先做好准备工作。
BluetoothGattCallback是一个抽象类,那么自然需要一个实现类,在之前的文章中我是通过匿名实现里面的onConnectionStateChange方法对低功耗蓝牙设备进行连接和断开的监听的。
不过在实际开发中这样的做法并不可取,因为一个蓝牙项目里面不可能只有一个地方需要使用这个监听,那么此时就需要封装一个类去单独实现BluetoothGattCallback中的方法,然后再根据需要取使用。
下面在com.llw.bledemo下新建一个callback包,包里面新建一个BleCallback类,然后继承BluetoothGattCallback,重写里面的onConnectionStateChange方法,代码如下:
public class BleCallback extends BluetoothGattCallback {
private static final String TAG = BleCallback.class.getSimpleName();
/**
* 连接状态改变回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param status gatt连接状态
* @param newState 新状态
*/
@Override
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status, int newState) {
if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {
switch (newState) {
case BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED://连接成功
Log.d(TAG, "连接成功");
break;
case BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED://断开连接
Log.e(TAG, "断开连接");
break;
default:
break;
}
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "onConnectionStateChange: " + status);
}
}
}
为了区别于上一篇文章,我这里会新建一个DataExchangeActivity来做数据的交互,不会影响到上一篇文章的内容。然后在MainActivity,点击列表item时调用的connectDevice方法中跳转到DataExchangeActivity中,通过传递蓝牙对象过去。
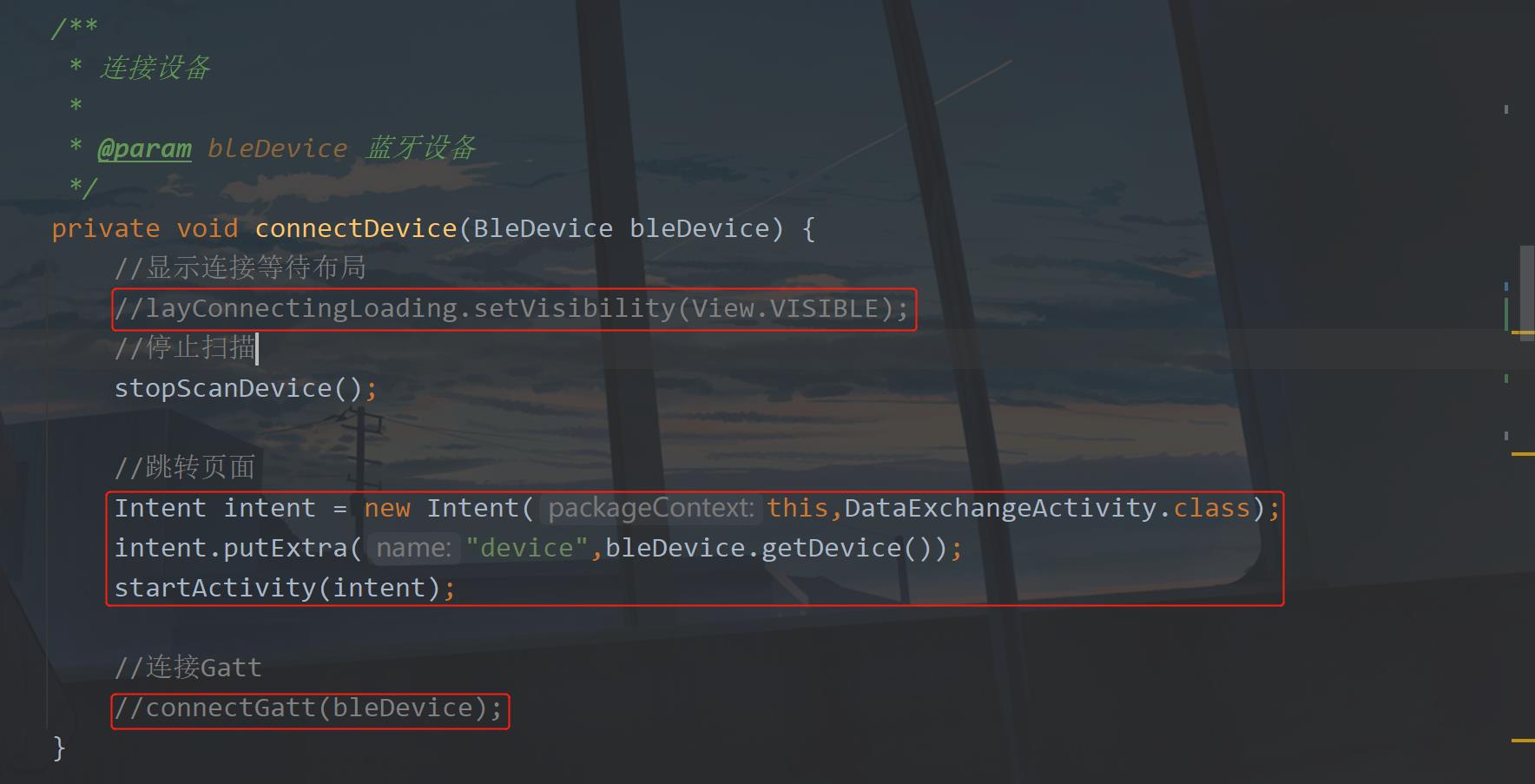
接下来看看DataExchangeActivity中做了什么?
public class DataExchangeActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = DataExchangeActivity.class.getSimpleName();
/**
* Gatt
*/
private BluetoothGatt bluetoothGatt;
/**
* 设备是否连接
*/
private boolean isConnected = false;
/**
* Gatt回调
*/
private BleCallback bleCallback;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_data_exchange);
//初始化
bleCallback = new BleCallback();
//获取上个页面传递过来的设备
BluetoothDevice device = getIntent().getParcelableExtra("device");
//连接gatt 设置Gatt回调
bluetoothGatt = device.connectGatt(this, false, bleCallback);
}
/**
* 断开设备连接
*/
private void disconnectDevice() {
if (isConnected && bluetoothGatt != null) {
bluetoothGatt.disconnect();
}
}
/**
* Toast提示
*
* @param msg 内容
*/
private void showMsg(String msg) {
Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
很简单这个代码,就是接收上个页面传递过来的蓝牙对象,然后进行gatt连接。直接传入实例化之后的bleCallback即可,请注意关于gatt的处理都是在子线程中进行的,可以验证一下:
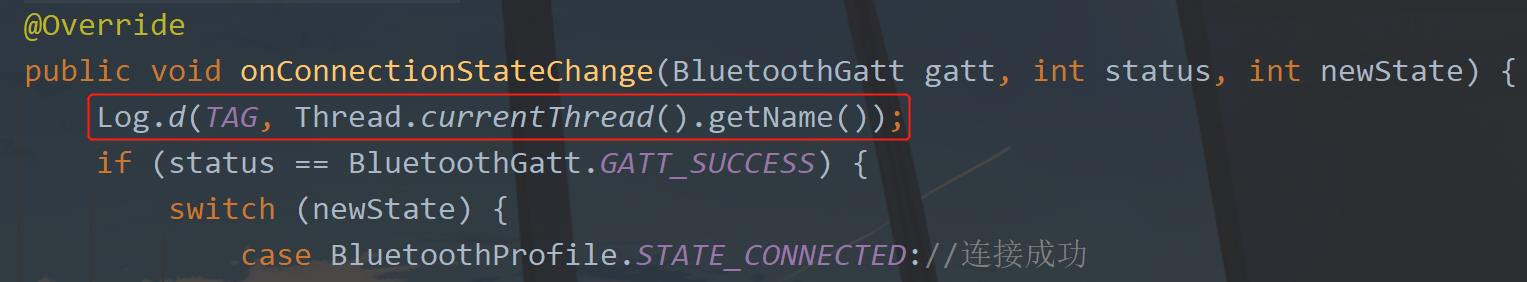
运行一下,进入交互页面。
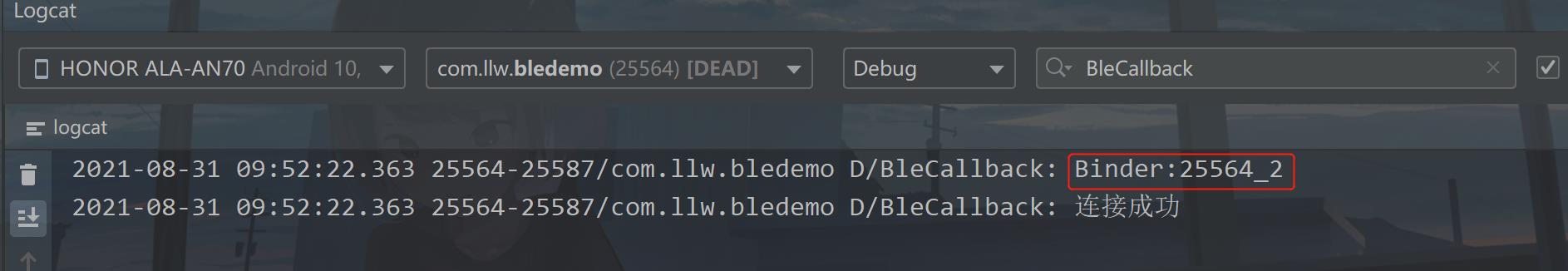
下面进行GattCallback中的API介绍。
1. onPhyUpdate
/**
* 物理层改变回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param txPhy 发送速率 1M 2M
* @param rxPhy 接收速率 1M 2M
* @param status 更新操作的状态
*/
@Override
public void onPhyUpdate(BluetoothGatt gatt, int txPhy, int rxPhy, int status) {
super.onPhyUpdate(gatt, txPhy, rxPhy, status);
}
通过gatt.setPreferredPhy()方法触发,例如:
//设置 2M
gatt.setPreferredPhy(BluetoothDevice.PHY_LE_2M, BluetoothDevice.PHY_LE_2M, BluetoothDevice.PHY_OPTION_NO_PREFERRED);
2. onPhyRead
/**
* 读取物理层回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param txPhy 发送速率 1M 2M
* @param rxPhy 接收速率 1M 2M
* @param status 更新操作的状态
*/
@Override
public void onPhyRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, int txPhy, int rxPhy, int status) {
super.onPhyRead(gatt, txPhy, rxPhy, status);
}
通过gatt.readPhy();进行触发,该方法不需要传入参数。
3. onServicesDiscovered
/**
* 发现服务回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param status gatt状态
*/
@Override
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
super.onServicesDiscovered(gatt, status);
}
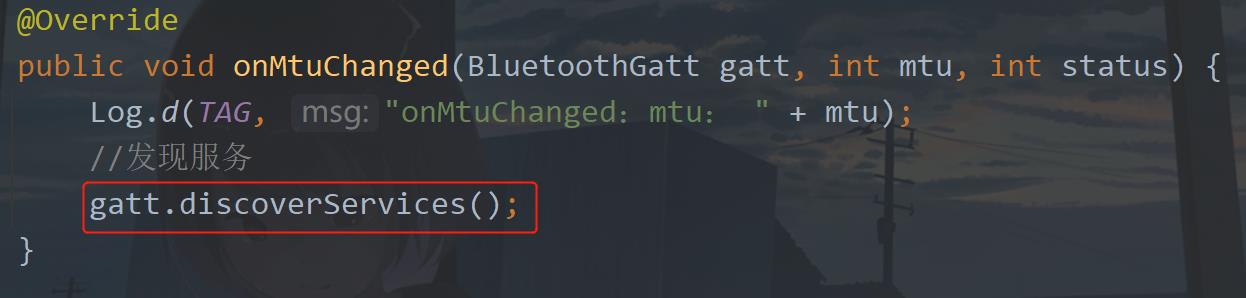
通过gatt.discoverServices(); 触发,没有输入参数。
4. onCharacteristicRead
/**
* 特性读取回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param characteristic 特性
* @param status gatt状态
*/
@Override
public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {
super.onCharacteristicRead(gatt, characteristic, status);
}
通过gatt.readCharacteristic(characteristic);触发,需要构建一个BluetoothGattCharacteristic 对象,在后面的实例中会演示。
5. onCharacteristicWrite
/**
* 特性写入回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param characteristic 特性
* @param status gatt状态
*/
@Override
public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {
super.onCharacteristicWrite(gatt, characteristic, status);
}
通过gatt.writeCharacteristic(characteristic);触发,需要BluetoothGattCharacteristic 对象,在后面的实例中会演示。
6. onCharacteristicChanged
/**
* 特性改变回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param characteristic 特性
*/
@Override
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
super.onCharacteristicChanged(gatt, characteristic);
}
此回调的触发需要远程设备特性改变,通俗的说就是,你需要给设备发送消息之后,才会触发这个回调。在后面的实例中会演示。
7. onDescriptorRead
/**
* 描述符获取回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param descriptor 描述符
* @param status gatt状态
*/
@Override
public void onDescriptorRead(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, int status) {
super.onDescriptorRead(gatt, descriptor, status);
}
通过gatt.readDescriptor(descriptor);触发,需要传入BluetoothGattDescriptor对象,在后面的实例中会演示。
8. onDescriptorWrite
/**
* 描述符写入回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param descriptor 描述符
* @param status gatt状态
*/
@Override
public void onDescriptorWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, int status) {
super.onDescriptorWrite(gatt, descriptor, status);
}
通过gatt.writeDescriptor(descriptor);触发,需要传入BluetoothGattDescriptor 对象,在后面的实例中会演示。
9. onReliableWriteCompleted
/**
* 可靠写入完成回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param status gatt状态
*/
@Override
public void onReliableWriteCompleted(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
super.onReliableWriteCompleted(gatt, status);
}
通过gatt.executeReliableWrite();触发,不需要参数,在实际中用的不是很多。
10. onReadRemoteRssi
/**
* 读取远程设备的信号强度回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param rssi 信号强度
* @param status gatt状态
*/
@Override
public void onReadRemoteRssi(BluetoothGatt gatt, int rssi, int status) {
super.onReadRemoteRssi(gatt, rssi, status);
}
通过gatt.readRemoteRssi();触发,无需参数,实际中使用不多。
11. onMtuChanged
/**
* Mtu改变回调
*
* @param gatt gatt
* @param mtu new MTU size
* @param status gatt状态
*/
@Override
public void onMtuChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, int mtu, int status) {
super.onMtuChanged(gatt, mtu, status);
}
通过gatt.requestMtu(512);触发,需要传入请求的Mtu大小,最大是512,这里单位是字节,512是理论最大值,如果不设置就是默认23字节,而且传输本身用掉3字节,实际上携带数据只有20字节。在后面的实例中会演示。
最后的一个onConnectionUpdated回调无法进行覆写,就不介绍了,下面进入使用API环节。
二、使用
1. 连接设备
第一步是连接,代码在上面已经写好,连接上设备之后,
2. 获取MTU Size
下一步就是获取MtuSize。
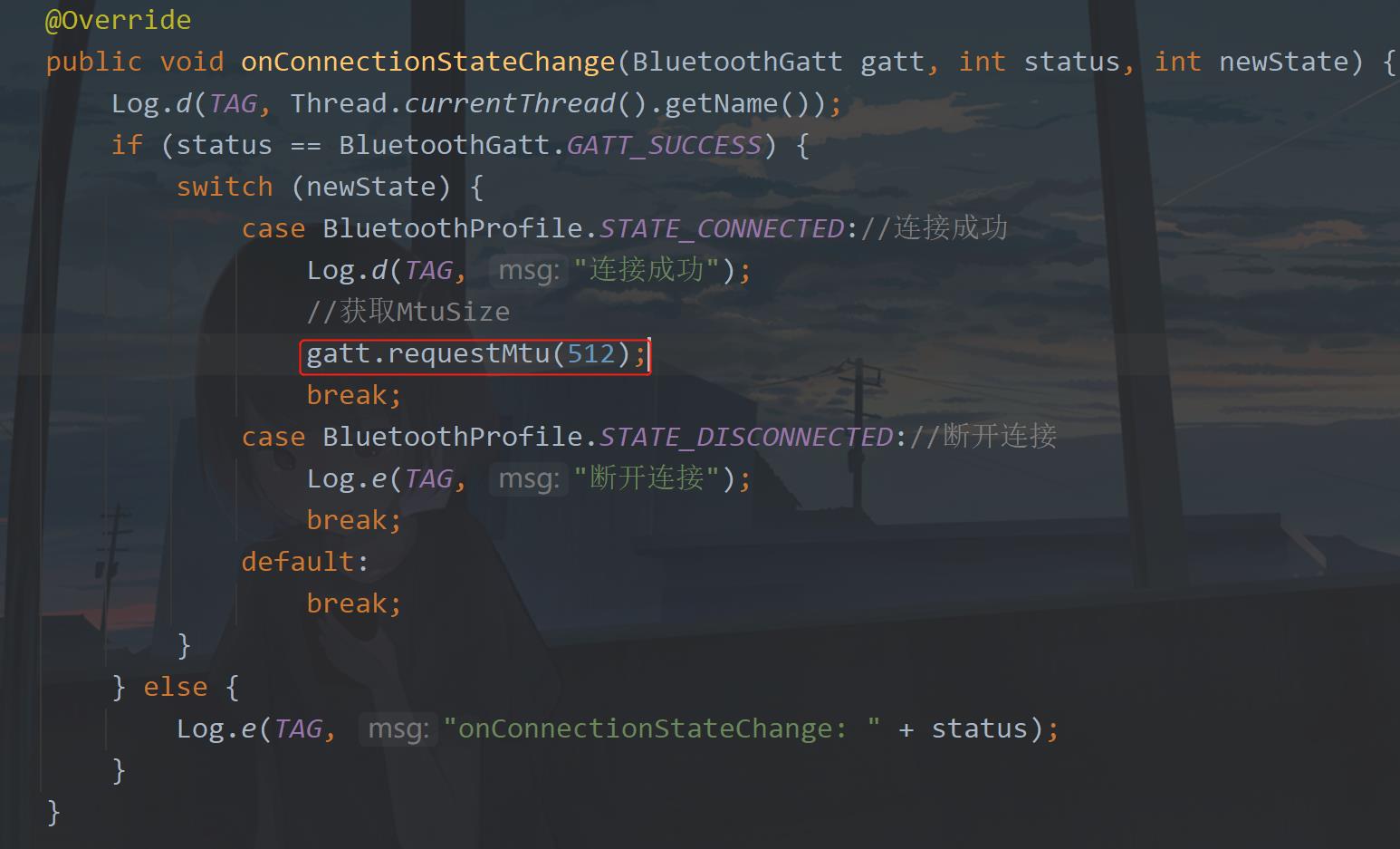
然后会触发onMtuChanged回调,
3. 发现服务
在onMtuChanged回调中去发现服务。
然后就会触发onServicesDiscovered回调,在这个回调中要做的就是打开通知开关。这个在之前没有提到,因为它不在基础的回调API中,但是打开通知开关属于描述符的内容,因此当你设置了之后会触发onDescriptorWriteh回调,还是先来看这个通知怎么打开吧。
4. 打开通知
为了规范一些,将使用到的方法封装起来,这样便于管理,增加一个BleHelper类和BleConstant类。
新建一个utils包,包下建两个类,下面先看这个BleConstant类
public class BleConstant {
/**
* 服务 UUID
*/
public static final String SERVICE_UUID = "0000ff01-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb";
/**
* 特性写入 UUID
*/
public static final String CHARACTERISTIC_WRITE_UUID = "0000ff02-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb";
/**
* 特性读取 UUID
*/
public static final String CHARACTERISTIC_READ_UUID = "0000ff10-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb";
/**
* 描述 UUID
*/
public static final String DESCRIPTOR_UUID = "00002902-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb";
/**
* 电池服务 UUID
*/
public static final String BATTERY_SERVICE_UUID = "0000180f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb";
/**
* 电池特征(特性)读取 UUID
*/
public static final String BATTERY_CHARACTERISTIC_READ_UUID = "00002a19-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb";
/**
* OTA服务 UUID
*/
public static final String OTA_SERVICE_UUID = "5833ff01-9b8b-5191-6142-22a4536ef123";
/**
* OTA特征(特性)写入 UUID
*/
public static final String OTA_CHARACTERISTIC_WRITE_UUID = "5833ff02-9b8b-5191-6142-22a4536ef123";
/**
* OTA特征(特性)表示 UUID
*/
public static final String OTA_CHARACTERISTIC_INDICATE_UUID = "5833ff03-9b8b-5191-6142-22a4536ef123";
/**
* OTA数据特征(特性)写入 UUID
*/
public static final String OTA_DATA_CHARACTERISTIC_WRITE_UUID = "5833ff04-9b8b-5191-6142-22a4536ef123";
}
这里面都是常规的UUID常量值,就是一些服务和特性的标识符,这个UUID常量值由SIG联盟所规定的,当然也可以根据自己的硬件去做设置,值不是固定的,请根据实际的硬件为主。
下面是BleHelper类,代码如下:
public class BleHelper {
/**
* 启用指令通知
*/
public static boolean enableIndicateNotification(BluetoothGatt gatt) {
//获取Gatt 服务
BluetoothGattService service = gatt.getService(UUID.fromString(BleConstant.OTA_SERVICE_UUID));
if (service == null) {
return false;
}
//获取Gatt 特征(特性)
BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattCharacteristic = service.getCharacteristic(UUID.fromString(BleConstant.OTA_CHARACTERISTIC_INDICATE_UUID));
return setCharacteristicNotification(gatt, gattCharacteristic);
}
/**
* 设置特征通知
* return true, if the write operation was initiated successfully
*/
private static boolean setCharacteristicNotification(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattCharacteristic) {
//如果特性具备Notification功能,返回true就代表设备设置成功
boolean isEnableNotification = gatt.setCharacteristicNotification(gattCharacteristic, true);
if (isEnableNotification) {
//构建BluetoothGattDescriptor对象
BluetoothGattDescriptor gattDescriptor = gattCharacteristic.getDescriptor(UUID.fromString(BleConstant.DESCRIPTOR_UUID));
gattDescriptor.setValue(BluetoothGattDescriptor.ENABLE_NOTIFICATION_VALUE);
//写入描述符
return gatt.writeDescriptor(gattDescriptor);
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
代码没有什么难度,下面就是在发现服务的回调中调用BleHelper中的方法。
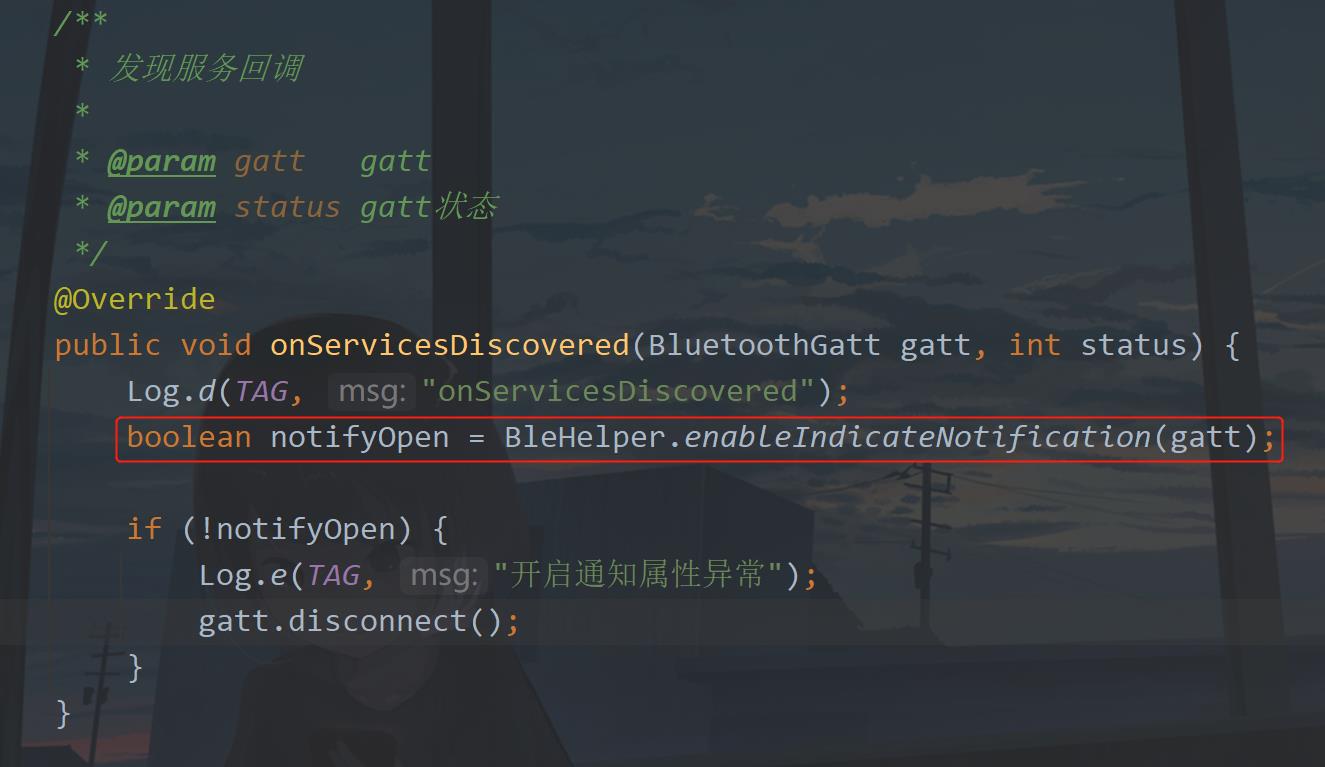
当开启通知失败时断开gatt连接。
下面会进入onDescriptorWrite回调
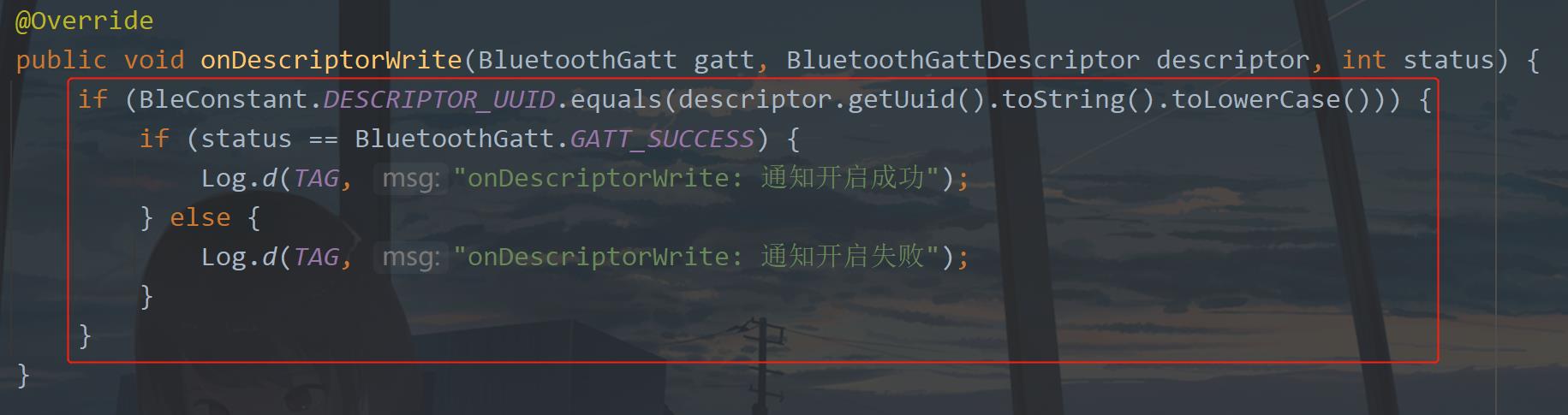
当通知开启成功可以就可以进行数据的交互了,不过在此之前先运行一下,看程序是否按照我们所想的运行,看一下日志:
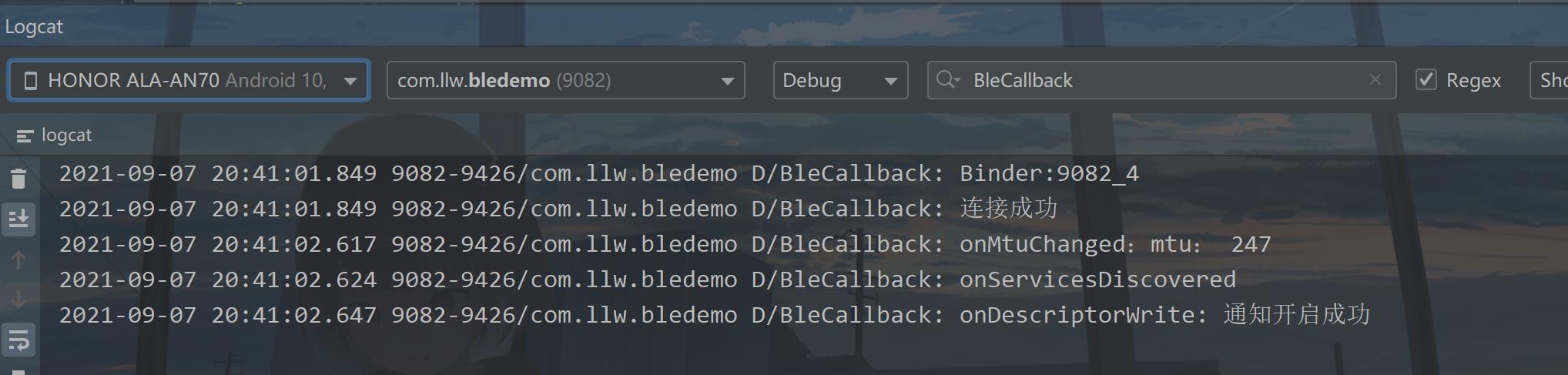
Very Good!
现在基本的前置工作都准备好了,下一步就是数据的读写了,首先来看看写数据到设备。
5. 写入数据
常规来说写入数据的话肯定是要对设备做点什么,列如一个蓝牙灯,控制这个灯开关,那么这就是一条指令,指令的内容是App与设备端协商好的,这个要以实际的需求为主。假设我对一个蓝牙手环要进行数据的写入,那么肯定会有很多的指令,所以可以封装一个方法集中处理,依然写在BleHelper中。方法如下:
/**
* 发送指令
* @param gatt gatt
* @param command 指令
* @param isResponse 是否响应
* @return
*/
public static boolean sendCommand(BluetoothGatt gatt, String command, boolean isResponse) {
//获取服务
BluetoothGattService service = gatt.getService(UUID.fromString(BleConstant.OTA_SERVICE_UUID));
if (service == null) {
Log.e("TAG", "sendCommand: 服务未找到");
return false;
}
//获取特性
BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic = service.getCharacteristic(UUID.fromString(BleConstant.OTA_CHARACTERISTIC_WRITE_UUID));
if (characteristic == null) {
Log.e("TAG", "sendCommand: 特性未找到");
return false;
}
//写入类型 WRITE_TYPE_DEFAULT 默认有响应, WRITE_TYPE_NO_RESPONSE 无响应。
characteristic.setWriteType(isResponse ?
BluetoothGattCharacteristic.WRITE_TYPE_DEFAULT : BluetoothGattCharacteristic.WRITE_TYPE_NO_RESPONSE);
//将字符串command转Byte后进行写入
characteristic.setValue(ByteUtils.hexStringToBytes(command));
boolean result = gatt.writeCharacteristic(characteristic);
Log.d("TAG", result ? "写入初始化成功:" + command : "写入初始化失败:" + command);
return result;
}
下面解释一下这个方法的内容,首先通过服务UUID获取到Gatt服务,然后通过写数据特性UUID从服务中获取写数据特性,这里的UUID的值请根据自己的实际情况填写,不知道就问硬件工程师。然后根据传入的isResponse去设置是否需要响应,这里要弄清楚有响应和无响应的区别,有响应的速度比无响应慢,但是有响应更安全,因为你可以对每一次发出的数据进行一个确认,是否发送到,有无丢失。不过这样的话效率会比较低,一般来说实际开发中大部分指令型消息都会选择无响应,数据型消息会选择有响应。
这里增加一个工具类,代码如下:
public class ByteUtils {
/**
* Convert hex string to byte[]
*
* @param hexString the hex string
* @return byte[]
*/
public static byte[] hexStringToBytes(String hexString) {
if (hexString == null || hexString.equals("")) {
return null;
}
hexString = hexString.toUpperCase();
int length = hexString.length() / 2;
char[] hexChars = hexString.toCharArray();
byte[] d = new byte[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
int pos = i * 2;
d[i] = (byte) (charToByte(hexChars[pos]) << 4 | charToByte(hexChars[pos + 1]));
}
return d;
}
public static String bytesToHexString(byte[] src) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("");
if (src == null || src.length <= 0) {
return null;
}
for (int i = 0; i < src.length; i++) {
int v = src[i] & 0xFF;
String hv = Integer.toHexString(v);
if (hv.length() < 2) {
stringBuilder.append(0);
}
stringBuilder.append(hv);
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
/**
* Convert char to byte
*
* @param c char
* @return byte
*/
private static byte charToByte(char c) {
return (以上是关于Android 低功耗蓝牙开发(数据交互)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Android 低功耗蓝牙开发(扫描连接数据交互)Kotlin版
Android 低功耗蓝牙开发(扫描连接数据交互)Kotlin版
Android 低功耗蓝牙开发 (扫描过滤自定义服务与特性)Kotlin版