《嵌入操作系统 - RT-Thread开发笔记》手把手教你使用RT-Thread制作GD32系列BSP
Posted Bruceoxl
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了《嵌入操作系统 - RT-Thread开发笔记》手把手教你使用RT-Thread制作GD32系列BSP相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
熟悉RT-Thread的朋友都知道,RT-Thread提供了许多BSP,但不是所有的板子都能找到相应的BSP,这时就需要移植新的BSP。RT-Thread的所有BSP中,最完善的BSP就是STM32系列,但从2020年下半年开始,国内出现史无前例的芯片缺货潮,芯片的交期和价格不断拉升,STM32的价格也是水涨船高,很多朋友也在考虑使用国产替代,笔者使用的兆易创新的GD32系列,我看了下RT-Thread中GD系列BSP,都是玩家各自为政,每个人都是提交自己使用的板子的BSP,充斥着大量冗余的代码,对于有强迫症的我就非常不爽,就根据手头的板子,参看STM32的BSP架构,构建了GD32的BSP架构。
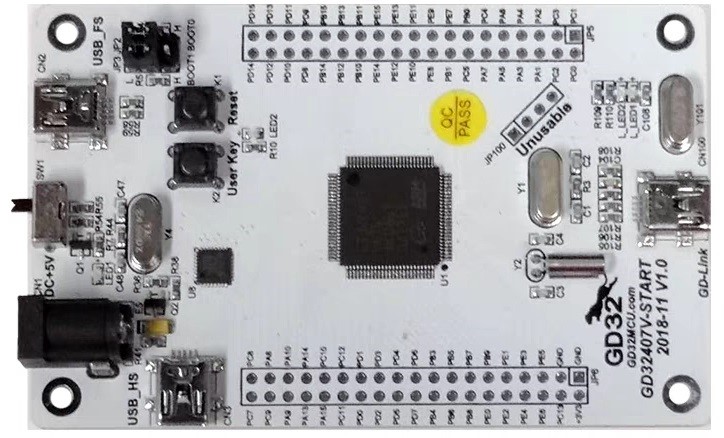
笔者使用的开发板是兆易创新设计的GD32407V-START开发板。其主控芯片为GD32F407VKT6,主频168MHz,内部3072K Flash,192KB SRAM,资源相当丰富。
1 BSP 框架制作
在具体移植GD32407V-START的BSP之前,先做好GD32的BSP架构。BSP 框架结构如下图所示:
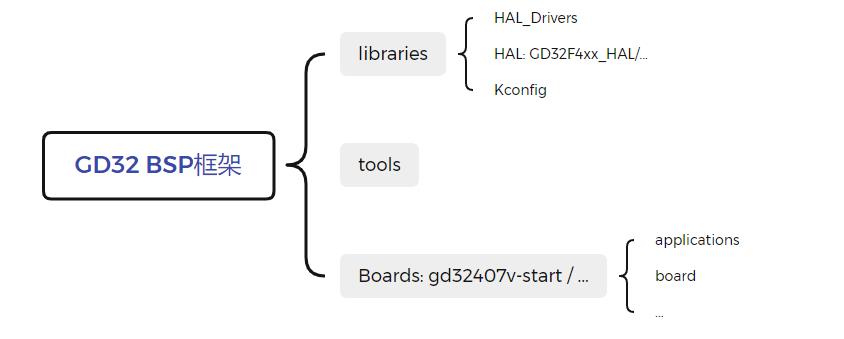
GD32的BSP架构主要分为三个部分:libraries、tools和具体的Boards,其中libraries包含了GD32的通用库,包括每个系列的HAL以及适配RT-Thread的drivers;tools是生成工程的Python脚本工具;另外就是Boards文件,当然这里的Boards有很多,我这里值列举了GD32407V-START。
这里先谈谈libraries和tools的构建,然后在后文单独讨论具体板级BSP的制作。
1.1 Libraries构建
Libraries文件夹包含兆易创新提供的HAL库,这个直接在兆易创新的官网就可以下载。
然后将HAL库复制到libraries目录下,重命名为GD32F4xx_HAL,其他的系列类似。

GD32F4xx_HAL就是官方的文件,基本是不用动的,只是在文件夹中需要添加构建工程的脚本文件SConscript,其实也就是Python脚本。
SConscript文件的内容如下:
import rtconfig #导包
from building import *
# get current directory
cwd = GetCurrentDir() #获取当然路径
# The set of source files associated with this SConscript file.
src = Split('''
CMSIS/GD/GD32F4xx/Source/system_gd32f4xx.c
GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_gpio.c
GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_rcu.c
GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_exti.c
GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_misc.c
GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_syscfg.c
''')#将括号中的字符串分割后成列表(list),以便包含到工程中
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_SERIAL']):#如果打开了RT_USING_SERIAL的宏,则会包含以下源文件
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_usart.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_I2C']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_i2c.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_SPI']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_spi.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_CAN']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_can.c']
if GetDepend(['BSP_USING_ETH']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_enet.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_ADC']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_adc.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_DAC']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_dac.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_RTC']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_rtc.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_WDT']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_wwdgt.c']
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_fwdgt.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_SDIO']):
src += ['GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Source/gd32f4xx_sdio.c']
#头文件路径
path = [
cwd + '/CMSIS/GD/GD32F4xx/Include',
cwd + '/CMSIS',
cwd + '/GD32F4xx_standard_peripheral/Include',]
CPPDEFINES = ['USE_STDPERIPH_DRIVER']
#定义一个组,组名为'Libraries', depend为空表示依赖任何一个其他宏,另外当前的头文件路径添加到工程中
group = DefineGroup('Libraries', src, depend = [''], CPPPATH = path, CPPDEFINES = CPPDEFINES)
Return('group')
该文件主要的作用就是添加库文件和头文件路径,一部分文件是属于基础文件,因此直接调用Python库的Split包含,另外一部分文件是根据实际的应用需求添加的。
这里是以GDF4来举例的,其他系列的都是类似的。
接下来说说Kconfig文件,这里是对内核和组件的功能进行配置,对RT-Thread的组件进行自由裁剪。
如果使用RT-Thread studio,则通过RT-Thread Setting可以体现Kconfig文件的作用。
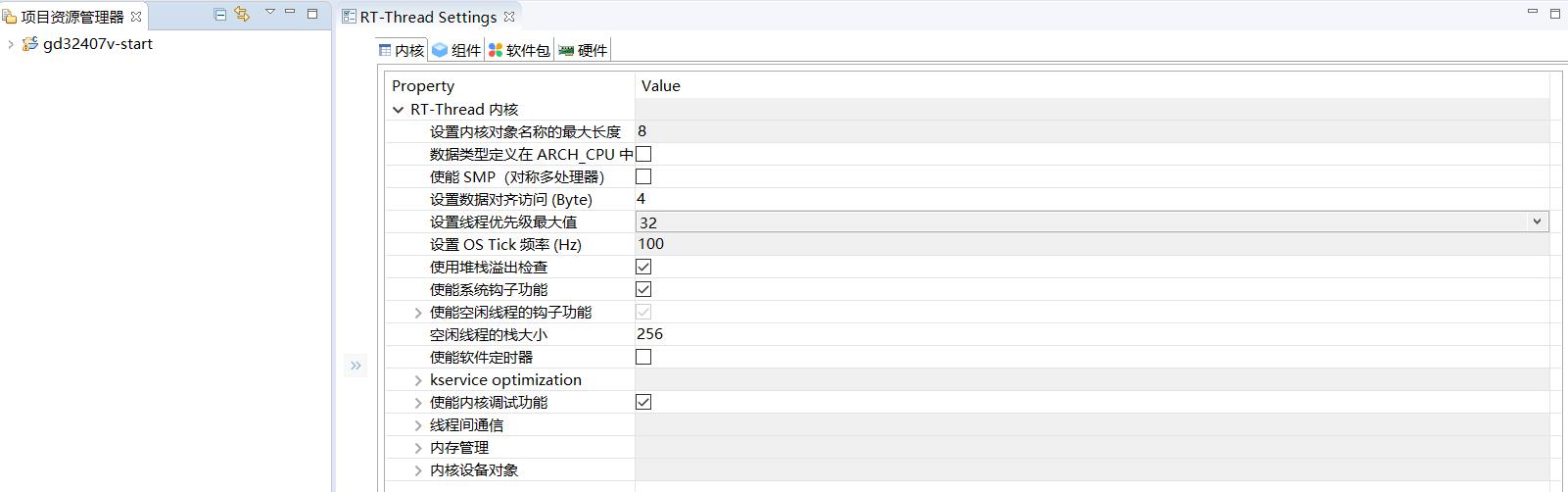
如果使用ENV环境,则在使用 menuconfig配置和裁剪 RT-Thread时体现。
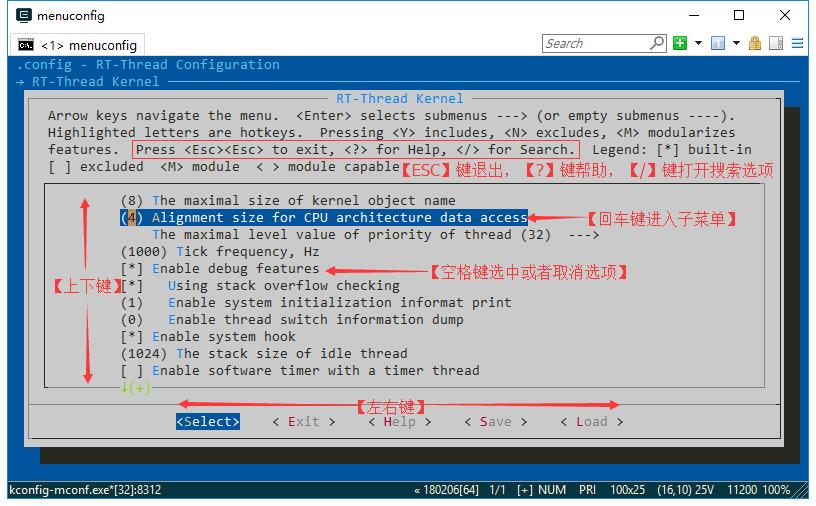
后面所有的Kconfig文件都是一样的逻辑。下表列举一些常用的Kconfig句法规则。
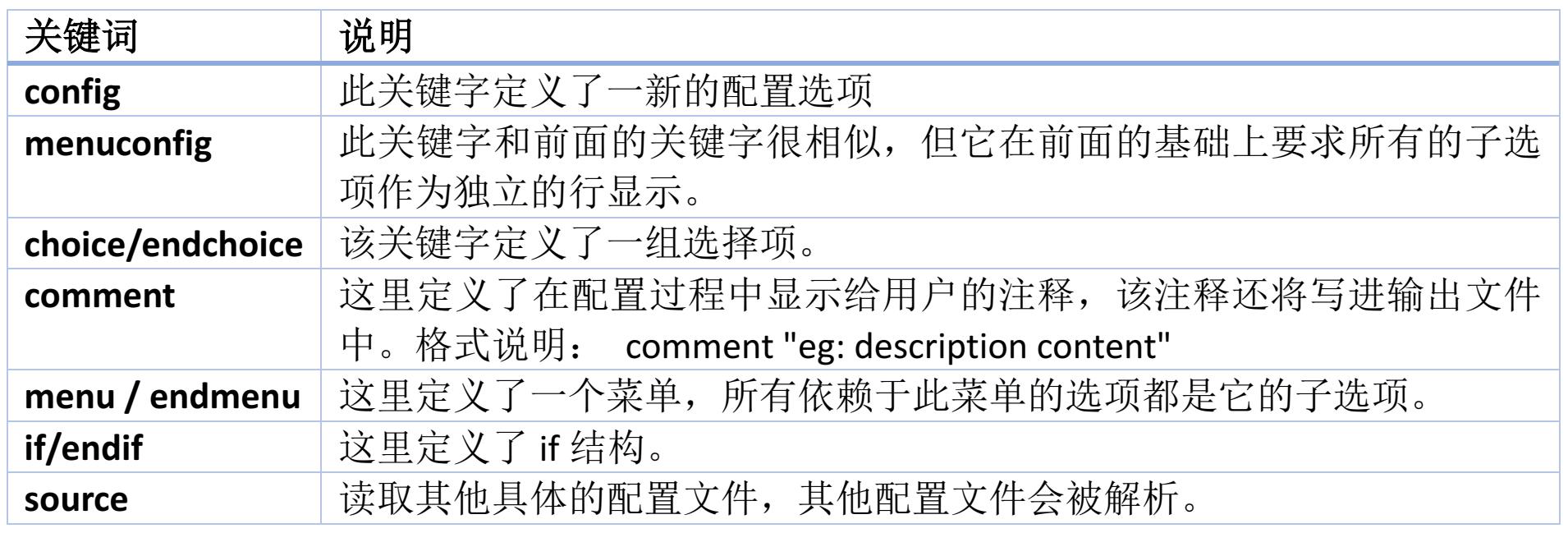
Kconfig的语法规则网上资料很多,自行去学习吧。
bsp/gd32/Kconfig内容如下:
config SOC_FAMILY_GD32
bool
config SOC_SERIES_GD32F4
bool
select ARCH_ARM_CORTEX_M4
select SOC_FAMILY_GD32
因为该架构目前笔者只移植了GDF4的,因此这里的内容比较少,如果有些的系列,直接参考F4的配置例子在这里加就可以了。
最后谈谈HAL_Drivers,这个文件夹就是GD32的外设驱动文件夹,为上层应用提供调用接口。

目前只有串口和GPIO的驱动,该文件夹是整个GD32共用的,因此在编写和修改都要慎重。关于drv_xxx文件在后句具体移植BSP的时候讲解,这里主要将整体架构,SConscript和Kconfig的作用和前面的一样,只是具体的内容不同罢了。
好了,先看bsp/gd32/HAL_Drivers/SConscript文件。
Import('RTT_ROOT')
Import('rtconfig')
from building import *
cwd = GetCurrentDir()#获取当前路径
# add the general drivers.
src = Split("""
""")#添加共同的驱动文件,暂无
# add pin drivers.
if GetDepend('RT_USING_PIN'):
src += ['drv_gpio.c']
if GetDepend(['RT_USING_SERIAL']):
src += ['drv_usart.c']
path = [cwd]
group = DefineGroup('Drivers', src, depend = [''], CPPPATH = path)
Return('group')
和GD32F4xx_HAL文件夹中的SConscript是类似的。
bsp/gd32/HAL_Drivers/Kconfig文件结构如下:
if BSP_USING_USBD
config BSP_USBD_TYPE_FS
bool
# "USB Full Speed (FS) Core"
config BSP_USBD_TYPE_HS
bool
# "USB High Speed (HS) Core"
config BSP_USBD_SPEED_HS
bool
# "USB High Speed (HS) Mode"
config BSP_USBD_SPEED_HSINFS
bool
# "USB High Speed (HS) Core in FS mode"
config BSP_USBD_PHY_EMBEDDED
bool
# "Using Embedded phy interface"
config BSP_USBD_PHY_UTMI
bool
# "UTMI: USB 2.0 Transceiver Macrocell Interace"
config BSP_USBD_PHY_ULPI
bool
# "ULPI: UTMI+ Low Pin Interface"
endif
1.2 Tools构建
该文件夹就是工程构建的脚本,
import os
import sys
import shutil
cwd_path = os.getcwd()
sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(cwd_path), 'rt-thread', 'tools'))
# BSP dist function
def dist_do_building(BSP_ROOT, dist_dir):
from mkdist import bsp_copy_files
import rtconfig
print("=> copy gd32 bsp library")
library_dir = os.path.join(dist_dir, 'libraries')
library_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(BSP_ROOT), 'libraries')
bsp_copy_files(os.path.join(library_path, rtconfig.BSP_LIBRARY_TYPE),
os.path.join(library_dir, rtconfig.BSP_LIBRARY_TYPE))
print("=> copy bsp drivers")
bsp_copy_files(os.path.join(library_path, 'HAL_Drivers'), os.path.join(library_dir, 'HAL_Drivers'))
shutil.copyfile(os.path.join(library_path, 'Kconfig'), os.path.join(library_dir, 'Kconfig'))
以上代码很简单,主要使用了Python的OS模块的join函数,该函数的作用就是连接两个或更多的路径名。最后将BSP依赖的文件复制到指定目录下。
在使用scons --dist 命令打包的时候,就是依赖的该脚本,生成的dist 文件夹的工程到任何目录下使用,也就是将BSP相关的库以及内核文件提取出来,可以将该工程任意拷贝。
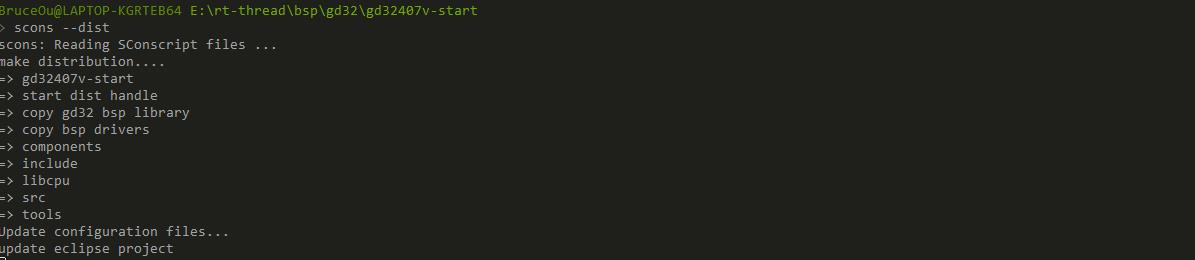
1.3 gd32407v-start构建
该文件夹就gd32407v-start的具体BSP文件,文件结构如下:
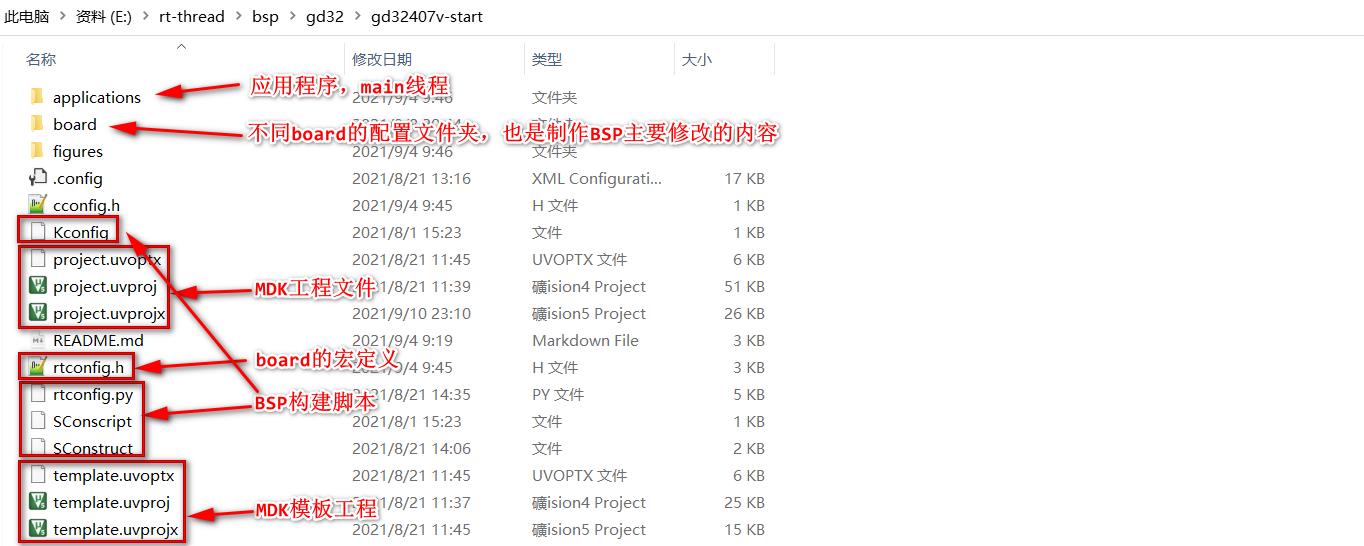
在后面将具体讲解如何构建该部分内容。
2 BSP移植
2.1 Keil环境准备
目前市面通用的MDK for ARM版本有Keil 4和Keil 5:使用Keil 4建议安装4.74及以上;使用Keil 5建议安装5.20以上版本。笔者的MDK是5.30。
从MDK的官网可以下载得到MDK的安装包,然后安装即可,关于的MDK安装请看笔者的教程。
MDK安装教程:https://blog.csdn.net/bruceoxl/article/details/108548573
MDK下载地址:https://www.keil.com/download/product/

安装完成后会自动打开,我们将其关闭。
接下来我们下载GD32F30x的软件支持包。
下载地址:http://www.gd32mcu.com/cn/download

下载好后双击GigaDevice.GD32F4xx_DFP.2.1.0.pack运行即可:
点击[Next]即可安装完成。
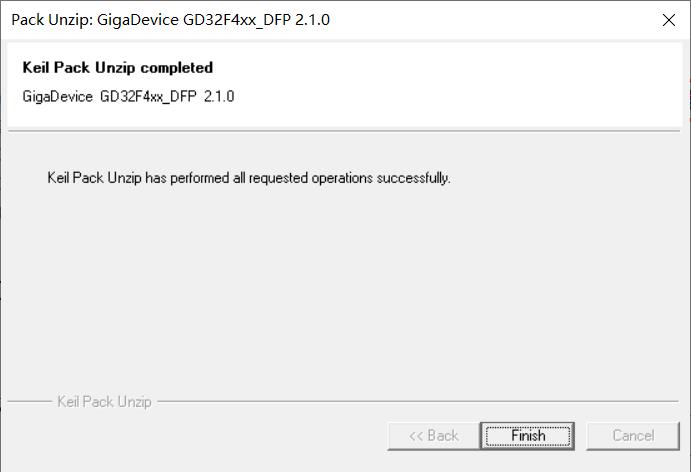
安装成功后,重新打开Keil,则可以在File->Device Database中出现Gigadevice的下拉选项,点击可以查看到相应的型号。

2.2 BSP工程制作
1.构建基础工程
首先看看RT-Thread代码仓库中已有很多BSP,而我要移植的是Cortex-M4内核。这里我找了一个相似的内核,把它复制一份,并修改文件名为:gd32407v-start。这样就有一个基础的工程。然后就开始增删改查,完成最终的BSP,几乎所有的BSP的制作都是如此。
2.修改BSP构建脚本
bsp/gd32/gd32407v-start/Kconfig修改后的内容如下:
mainmenu "RT-Thread Configuration"
config BSP_DIR
string
option env="BSP_ROOT"
default "."
config RTT_DIR
string
option env="RTT_ROOT"
default "../../.."
config PKGS_DIR
string
option env="PKGS_ROOT"
default "packages"
source "$RTT_DIR/Kconfig"
source "$PKGS_DIR/Kconfig"
source "../libraries/Kconfig"
source "board/Kconfig"
该文件是获取所有路径下的Kconfig。
bsp/gd32/gd32407v-start/SConscript修改后的内容如下:
# for module compiling
import os
Import('RTT_ROOT')
from building import *
cwd = GetCurrentDir()
objs = []
list = os.listdir(cwd)
for d in list:
path = os.path.join(cwd, d)
if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(path, 'SConscript')):
objs = objs + SConscript(os.path.join(d, 'SConscript'))
Return('objs')
该文件是用于遍历当前目录的所有文件夹。
bsp/gd32/gd32407v-start/SConstruct修改后的内容如下:
import os
import sys
import rtconfig
if os.getenv('RTT_ROOT'):
RTT_ROOT = os.getenv('RTT_ROOT')
else:
RTT_ROOT = os.path.normpath(os.getcwd() + '/../../..')
sys.path = sys.path + [os.path.join(RTT_ROOT, 'tools')]
try:
from building import *
except:
print('Cannot found RT-Thread root directory, please check RTT_ROOT')
print(RTT_ROOT)
exit(-1)
TARGET = 'rtthread.' + rtconfig.TARGET_EXT
DefaultEnvironment(tools=[])
env = Environment(tools = ['mingw'],
AS = rtconfig.AS, ASFLAGS = rtconfig.AFLAGS,
CC = rtconfig.CC, CCFLAGS = rtconfig.CFLAGS,
AR = rtconfig.AR, ARFLAGS = '-rc',
CXX = rtconfig.CXX, CXXFLAGS = rtconfig.CXXFLAGS,
LINK = rtconfig.LINK, LINKFLAGS = rtconfig.LFLAGS)
env.PrependENVPath('PATH', rtconfig.EXEC_PATH)
if rtconfig.PLATFORM == 'iar':
env.Replace(CCCOM = ['$CC $CCFLAGS $CPPFLAGS $_CPPDEFFLAGS $_CPPINCFLAGS -o $TARGET $SOURCES'])
env.Replace(ARFLAGS = [''])
env.Replace(LINKCOM = env["LINKCOM"] + ' --map rtthread.map')
Export('RTT_ROOT')
Export('rtconfig')
SDK_ROOT = os.path.abspath('./')
if os.path.exists(SDK_ROOT + '/libraries'):
libraries_path_prefix = SDK_ROOT + '/libraries'
else:
libraries_path_prefix = os.path.dirname(SDK_ROOT) + '/libraries'
SDK_LIB = libraries_path_prefix
Export('SDK_LIB')
# prepare building environment
objs = PrepareBuilding(env, RTT_ROOT, has_libcpu=False)
gd32_library = 'GD32F4xx_HAL'
rtconfig.BSP_LIBRARY_TYPE = gd32_library
# include libraries
objs.extend(SConscript(os.path.join(libraries_path_prefix, gd32_library, 'SConscript')))
# include drivers
objs.extend(SConscript(os.path.join(libraries_path_prefix, 'HAL_Drivers', 'SConscript')))
# make a building
DoBuilding(TARGET, objs)
该文件用于链接所有的依赖文件,并调用make进行编译。
3.修改开发环境信息
bsp/gd32/gd32407v-start/cconfig.h修改后的内容如下:
#ifndef CCONFIG_H__
#define CCONFIG_H__
/* Automatically generated file; DO NOT EDIT. */
/* compiler configure file for RT-Thread in GCC*/
#define HAVE_NEWLIB_H 1
#define LIBC_VERSION "newlib 2.4.0"
#define HAVE_SYS_SIGNAL_H 1
#define HAVE_SYS_SELECT_H 1
#define HAVE_PTHREAD_H 1
#define HAVE_FDSET 1
#define HAVE_SIGACTION 1
#define GCC_VERSION_STR "5.4.1 20160919 (release) [ARM/embedded-5-branch revision 240496]"
#define STDC "2011"
#endif
该文件是是编译BSP的环境信息,需根据实时修改。
4.修改KEIL的模板工程
双击:template.uvprojx即可修改模板工程。
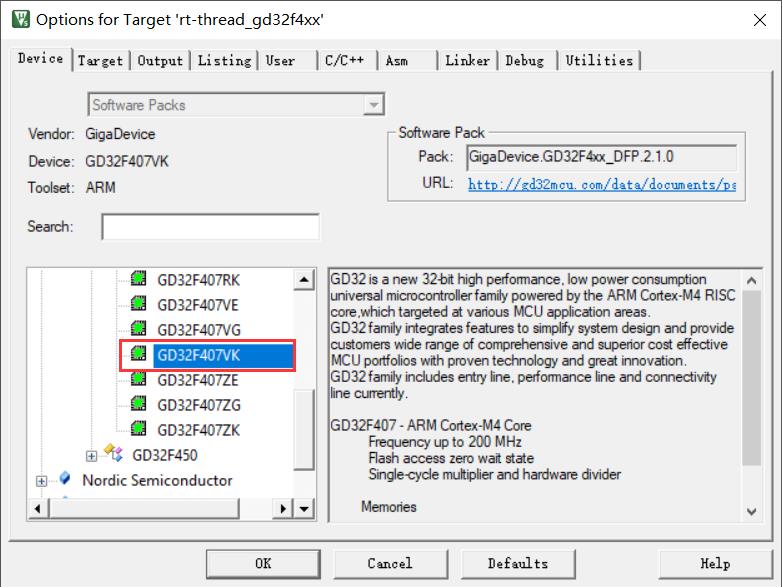
修改为对应芯片设备:
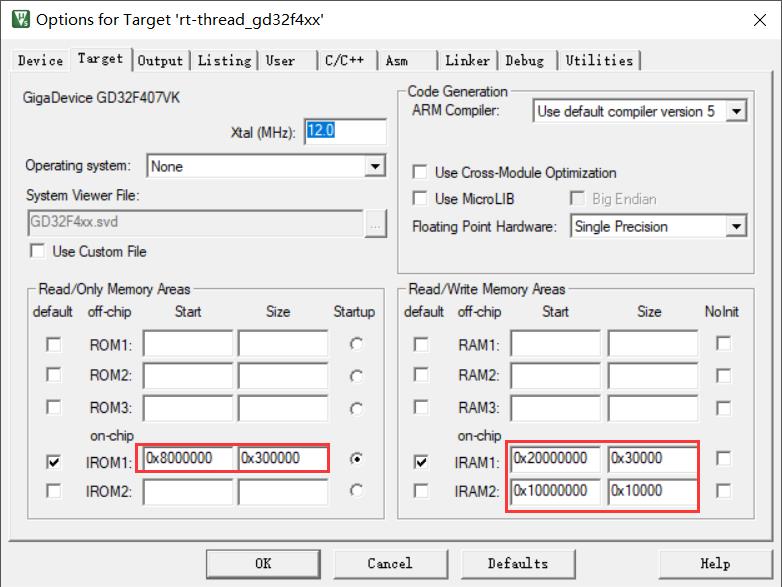
修改FLASH和RAM的配置:
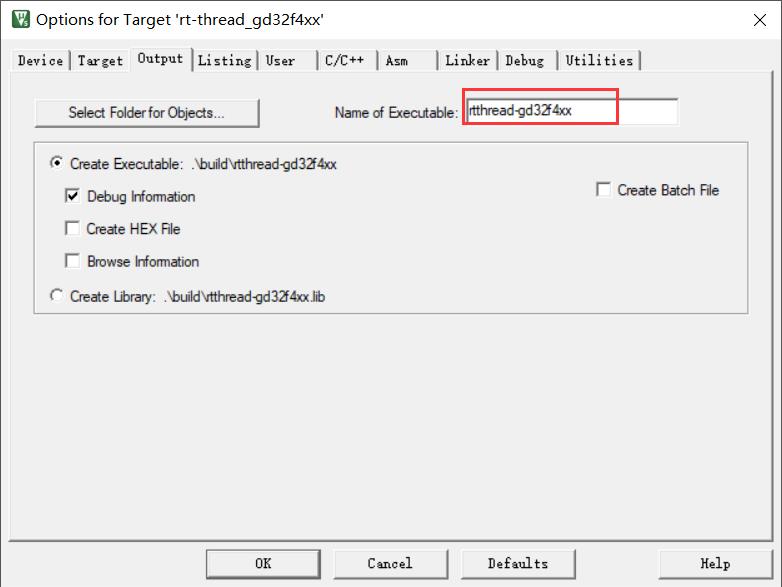
修改可执行文件名字:
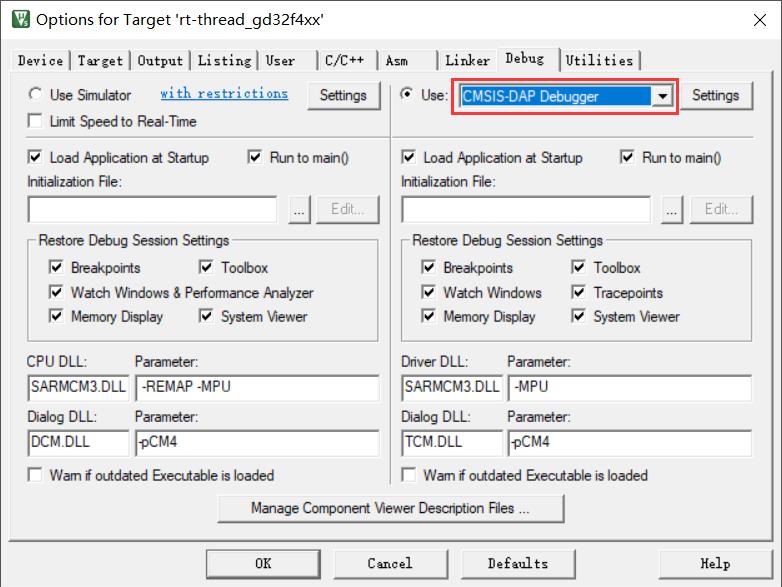
修改默认调试工具:CMSIS-DAP Debugger。
修改编程算法:GD32F4xx FMC。

5.修改board文件夹
(1) 修改bsp/gd32/gd32407v-start/board/linker_scripts/link.icf
修改后的内容如下:
/*###ICF### Section handled by ICF editor, don't touch! ****/
/*-Editor annotation file-*/
/* IcfEditorFile="$TOOLKIT_DIR$\\config\\ide\\IcfEditor\\cortex_v1_0.xml" */
/*-Specials-*/
define symbol __ICFEDIT_intvec_start__ = 0x08000000;
/*-Memory Regions-*/
define symbol __ICFEDIT_region_ROM_start__ = 0x08000000;
define symbol __ICFEDIT_region_ROM_end__ = 0x082FFFFF;
define symbol __ICFEDIT_region_RAM_start__ = 0x20000000;
define symbol __ICFEDIT_region_RAM_end__ = 0x2002FFFF;
/*-Sizes-*/
define symbol __ICFEDIT_size_cstack__ = 0x2000;
define symbol __ICFEDIT_size_heap__ = 0x2000;
/**** End of ICF editor section. ###ICF###*/
export symbol __ICFEDIT_region_RAM_end__;
define symbol __region_RAM1_start__ = 0x10000000;
define symbol __region_RAM1_end__ = 0x1000FFFF;
define memory mem with size = 4G;
define region ROM_region = mem:[from __ICFEDIT_region_ROM_start__ to __ICFEDIT_region_ROM_end__];
define region RAM_region = mem:[from __ICFEDIT_region_RAM_start__ to __ICFEDIT_region_RAM_end__];
define region RAM1_region = mem:[from __region_RAM1_start__ to __region_RAM1_end__];
define block CSTACK with alignment = 8, size = __ICFEDIT_size_cstack__ { };
define block HEAP with alignment = 8, size = __ICFEDIT_size_heap__ { };
initialize by copy { readwrite };
do not initialize { section .noinit };
keep { section FSymTab };
keep { section VSymTab };
keep { section .rti_fn* };
place at address mem:__ICFEDIT_intvec_start__ { readonly section .intvec };
place in ROM_region { readonly };
place in RAM_region { readwrite,
block CSTACK, block HEAP };
place in RAM1_region { section .sram };
该文件是IAR编译的链接脚本,根据《GD32F407xx_Datasheet_Rev2.1》可知,GD32F407VKT6的flash大小为3072KB,SRAM大小为192KB,因此需要设置ROM和RAM的起始地址和堆栈大小等。
(2) 修改bsp/gd32/gd32407v-start/board/linker_scripts/link.ld
修改后的内容如下:
/* Program Entry, set to mark it as "used" and avoid gc */
MEMORY
{
CODE (rx) : ORIGIN = 0x08000000, LENGTH = 3072k /* 3072KB flash */
DATA (rw) : ORIGIN = 0x20000000, LENGTH = 192k /* 192KB sram */
}
ENTRY(Reset_Handler)
_system_stack_size = 0x200;
SECTIONS
{
.text :
{
. = ALIGN(4);
_stext = .;
KEEP(*(.isr_vector)) /* Startup code */
. = ALIGN(4);
*(.text) /* remaining code */
*(.text.*) /* remaining code */
*(.rodata) /* read-only data (constants) */
*(.rodata*)
*(.glue_7)
*(.glue_7t)
*(.gnu.linkonce.t*)
/* section information for finsh shell */
. = ALIGN(4);
__fsymtab_start = .;
KEEP(*(FSymTab))
__fsymtab_end = .;
. = ALIGN(4);
__vsymtab_start = .;
KEEP(*(VSymTab))
__vsymtab_end = .;
. = ALIGN(4);
/* section information for initial. */
. = ALIGN(4);
__rt_init_start = .;
KEEP(*(SORT(.rti_fn*)))
__rt_init_end = .;
. = ALIGN(4);
. = ALIGN(4);
_etext = .;
} > CODE = 0
/* .ARM.exidx is sorted, so has to go in its own output section. */
__exidx_start = .;
.ARM.exidx :
{
*(.ARM.exidx* .gnu.linkonce.armexidx.*)
/* This is used by the startup in order to initialize the .data secion */
_sidata = .;
} > CODE
__exidx_end = .;
/* .data section which is used for initialized data */
.data : AT (_sidata)
{
. = ALIGN(4);
/* This is used by the startup in order to initialize the .data secion */
_sdata = . ;
*(.data)
*(.data.*)
*(.gnu.linkonce.d*)
. = ALIGN(4);
/* This is used by the startup in order to initialize the .data secion */
_edata = . ;
} >DATA
.stack :
{
. = . + _system_stack_size;
. = ALIGN(4);
_estack = .;
} >DATA
__bss_start = .;
.bss :
{
. = ALIGN(4);
/* This is used by the startup in order to initialize the .bss secion */
_sbss = .;
*(.bss)
*(.bss.*)
*(COMMON)
. = ALIGN(4);
/* This is used by the startup in order to initialize the .bss secion */
_ebss = . ;
*(.bss.init)
} > DATA
__bss_end = .;
_end = .;
/* Stabs debugging sections. */
.stab 以上是关于《嵌入操作系统 - RT-Thread开发笔记》手把手教你使用RT-Thread制作GD32系列BSP的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章