「深度学习一遍过」必修22:基于GoogLeNet的MNIST手写数字识别
Posted 小泽yyds
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了「深度学习一遍过」必修22:基于GoogLeNet的MNIST手写数字识别相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本专栏用于记录关于深度学习的笔记,不光方便自己复习与查阅,同时也希望能给您解决一些关于深度学习的相关问题,并提供一些微不足道的人工神经网络模型设计思路。
专栏地址:「深度学习一遍过」必修篇
目录
项目 GitHub 地址
项目心得
- 2014 年——GoogLeNet:这是 google 推出的基于 Inception 模块的深度神经网络模型,在 2014 年的 ImageNet 竞赛中夺得了冠军,在随后的两年中一直在改进,形成了 Inception V2、Inception V3、Inception V4 等版本。;该项目自己搭建了 GoogLeNet 网络并在 MNIST 手写数字识别项目中得到了应用。(注:net.py 代码着实很长,原因是冗余的太多了,正像我的朋友吃午饭时讲的那样:“这个代码重复部分很多,完全可以写到一个函数里调用啊,这样写太没有灵魂了。”怎么说呢,主要当时快写完了,后来想想也是;也不能说这样写清晰地展现了 GoogLeNet 的架构,反而会让人觉得这是一个憨批程序员,一根筋,不懂得变通,所以这个自我复现的 GoogLeNet 版本的 net.py 文件代码就这样留着吧,也算是一个提醒,以后写代码在实现功能的基础上争取精简一些...)
项目代码
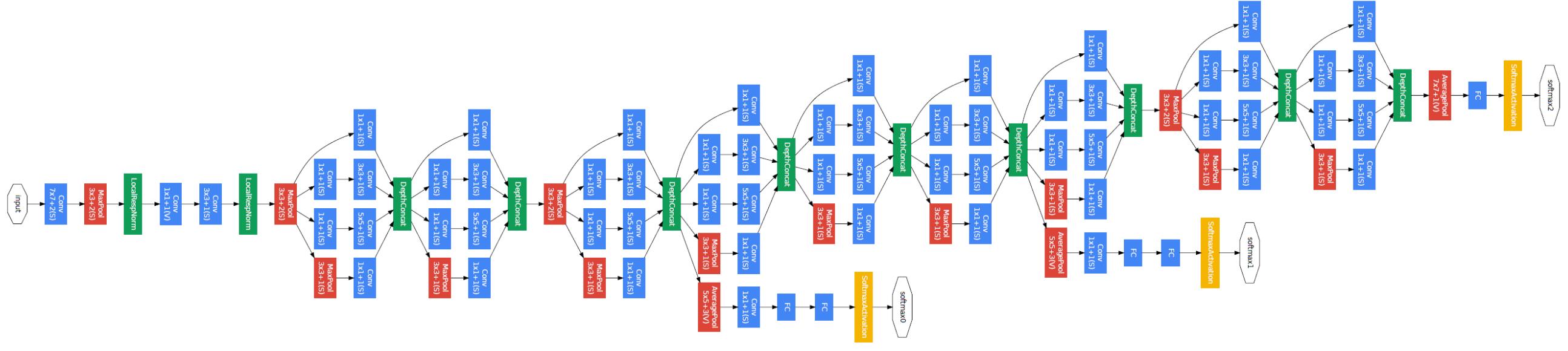
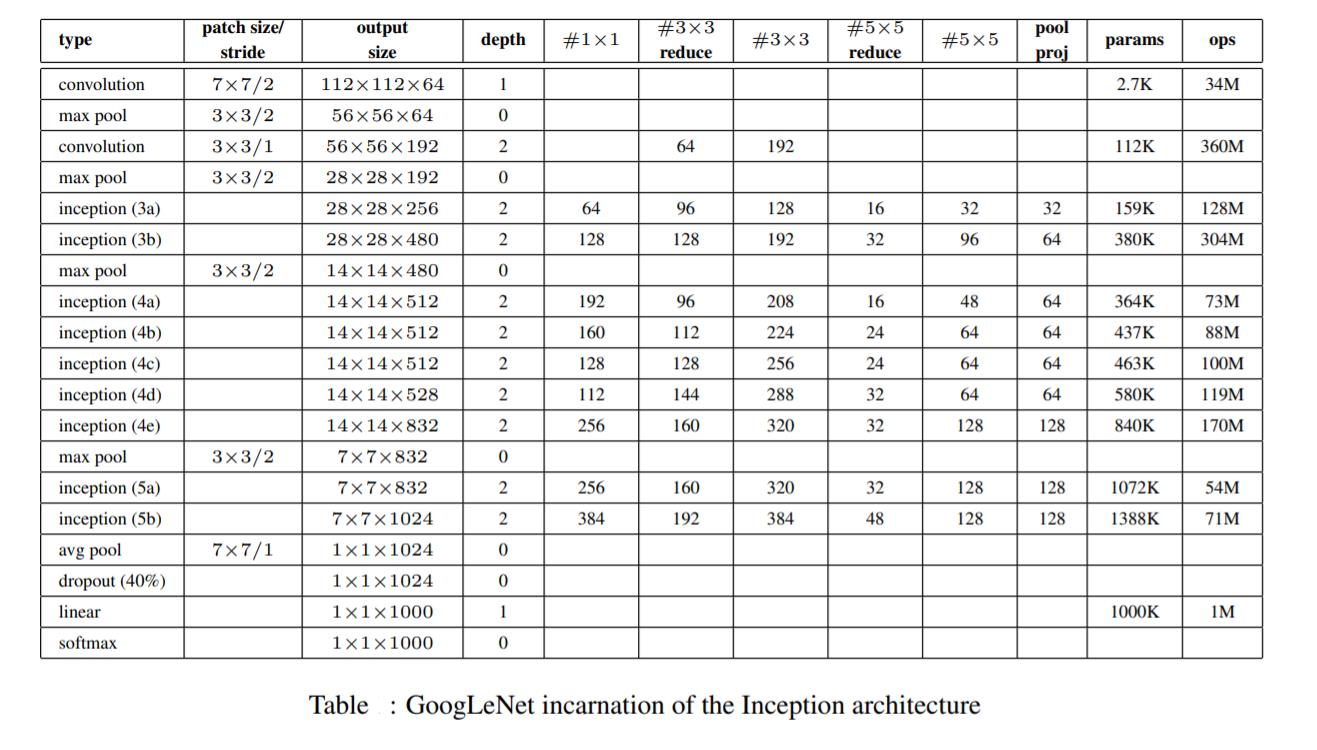
net.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# 作者:赵泽荣
# 时间:2021年9月10日(农历八月初四)
# 个人站点:1.https://zhao302014.github.io/
# 2.https://blog.csdn.net/IT_charge/
# 个人GitHub地址:https://github.com/zhao302014
# ------------------------------------------------- #
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
# 自己搭建一个 GoogLeNet 模型结构
# · 提出时间:2014 年
# · GoogLeNet,一个 22 层的深度网络,2014 年 ILSVRC 挑战赛冠军,将 Top5 的错误率降低到 6.67%
# · 起名为 “GoogLeNet” 而非 “GoogleNet”,是为了向早期的 LeNet 致敬
# · 创新点之深度方面:层数更深,论文中采用了 22 层,为了避免上述提到的梯度消失问题,GoogLeNet 巧妙的在不同深度处增加了两个 loss 来保证梯度回传消失的现象
# · 创新点之宽度方面:采用了 Inception 结构,这是一种网中网(Network In Network)的结构,即原来的结点也是一个网络
# · 基准 GoogLeNet 截止到下述代码的 f22 层;由于本实例是手写数字识别(10分类问题),故再后续了一层全连接层 f_output
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- #
class MyGoogLeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MyGoogLeNet, self).__init__()
self.ReLU = nn.ReLU() # 无论是 3x3 卷积还是 1x1 卷积,后面都紧跟着激活函数(比如relu)。
self.lrn = nn.LocalResponseNorm(4) # 局部响应归一化层(加快收敛,具体而言:在训练大量数据过程中,一旦每批训练数据的分布各不相同(batch 梯度下降),那么网络就要在每次迭代都去学习适应不同的分布,这样将会大大降低网络的训练速度,这也正是为什么我们需要对数据都要做一个归一化预处理的原因)
# 第一层:convolution 层
self.c1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3) # (224 - 7 + 2*3) / 2 + 1 = 112
# max pooling 层
self.s1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) # (112 - 3 + 2*1) / 2 + 1 = 56
# 第二、三层:convolution 层
self.c2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=192, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (56 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 56
self.c3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=192, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (56 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 56
# max pooling 层
self.s2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) # (56 - 3 + 2*1) / 2 + 1 = 28
# 第四、五层:inception 层(每个通道内将两个卷积串联,可组合出更多的非线性特征)
self.c5_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (28 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c5_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=96, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (28 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c5_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=96, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c5_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=32, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (28 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c5_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.s5_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c5_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=32, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (28 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 28
# 第六、七层:inception 层
self.c7_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (28 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c7_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (28 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c7_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=192, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c7_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=32, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (28 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c7_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=96, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.s7_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 28
self.c7_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=256, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (28 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 28
# max pooling 层
self.s3 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 2 + 1 = 14
# 第八、九层:inception 层
self.c9_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=480, out_channels=192, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c9_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=480, out_channels=96, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c9_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=96, out_channels=208, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c9_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=480, out_channels=16, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c9_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=16, out_channels=48, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.s9_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c9_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=480, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
# 第十、十一层:inception 层
self.c11_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=160, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c11_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=112, kernel_size=1,stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c11_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=112, out_channels=224, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c11_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=24, kernel_size=1,stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c11_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=24, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1,padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.s11_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c11_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1,stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
# 第十二、十三层:inception 层
self.c13_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c13_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c13_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=256, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c13_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=24, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c13_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=24, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.s13_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c13_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
# 第十四、十五层:inception 层
self.c15_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=112, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c15_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=144, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c15_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=144, out_channels=288, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c15_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=32, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c15_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.s15_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c15_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=512, out_channels=64, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
# 第十六、十七层:inception 层
self.c17_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=528, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c17_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=528, out_channels=160, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c17_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=160, out_channels=320, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c17_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=528, out_channels=32, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c17_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.s17_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (14 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 14
self.c17_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=528, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (14 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 14
# max pooling 层
self.s4 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) # (28 - 3 + 2*1) / 2 + 1 = 14
# 第十八、十九层:inception 层
self.c19_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=832, out_channels=256, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (7 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c19_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=832, out_channels=160, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (7 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c19_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=160, out_channels=320, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (7 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c19_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=832, out_channels=32, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (7 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c19_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (7 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.s19_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (7 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c19_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=832, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (7 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 7
# 第二十、二十一层:inception 层
self.c21_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=832, out_channels=384, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (7 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c21_2_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=832, out_channels=192, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (7 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c21_2_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=384, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (7 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c21_3_1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=832, out_channels=48, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (7 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c21_3_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=48, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (7 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.s21_4_1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1) # (7 - 3 + 2*1) / 1 + 1 = 7
self.c21_4_2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=832, out_channels=128, kernel_size=1, stride=1) # (7 - 1 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 7
# avg pooling 层
self.s5 = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=7, stride=1) # (7 - 7 + 2*0) / 1 + 1 = 1
# 第二十二层:全连接层
self.Flatten = nn.Flatten()
self.f21 = nn.Linear(1024, 1000)
# 为满足该实例另加 ↓
self.f_output = nn.Linear(1000, 10)
def forward(self, x): # 输入shape: torch.Size([1, 3, 224, 224])
x = self.ReLU(self.c1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 112, 112])
x = self.s1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])
x = self.ReLU(self.lrn(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 56, 56])
x = self.ReLU(self.c2(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 56, 56])
x = self.ReLU(self.c3(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 56, 56])
x = self.s2(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 28, 28])
x5_1 = self.ReLU(self.c5_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 28, 28])
x5_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c5_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 28, 28])
x5_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c5_2_2(x5_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28])
x5_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c5_3_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 28, 28])
x5_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c5_3_2(x5_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 28, 28])
x5_4_1 = self.s5_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 28, 28])
x5_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c5_4_2(x5_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 28, 28])
x = torch.cat((x5_1, x5_2_2, x5_3_2, x5_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 28, 28])
x7_1 = self.ReLU(self.c7_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28])
x7_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c7_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 28, 28])
x7_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c7_2_2(x7_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 28, 28])
x7_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c7_3_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 28, 28])
x7_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c7_3_2(x7_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 28, 28])
x7_4_1 = self.s7_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 28, 28])
x7_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c7_4_2(x7_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 28, 28])
x = torch.cat((x7_1, x7_2_2, x7_3_2, x7_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 480, 28, 28])
x = self.s3(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 480, 14, 14])
x9_1 = self.ReLU(self.c9_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 14, 14])
x9_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c9_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 14, 14])
x9_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c9_2_2(x9_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 208, 14, 14])
x9_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c9_3_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 16, 14, 14])
x9_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c9_3_2(x9_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 48, 14, 14])
x9_4_1 = self.s9_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 480, 14, 14])
x9_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c9_4_2(x9_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 14, 14])
x = torch.cat((x9_1, x9_2_2, x9_3_2, x9_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x11_1 = self.ReLU(self.c11_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 160, 14, 14])
x11_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c11_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 112, 14, 14])
x11_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c11_2_2(x11_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 224, 14, 14])
x11_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c11_3_1(x) ) # shape: torch.Size([1, 24, 14, 14])
x11_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c11_3_2(x11_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 14, 14])
x11_4_1 = self.s11_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x11_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c11_4_2(x11_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 14, 14])
x = torch.cat((x11_1, x11_2_2, x11_3_2, x11_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x13_1 = self.ReLU(self.c13_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 14, 14])
x13_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c13_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 14, 14])
x13_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c13_2_2(x13_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14])
x13_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c13_3_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 24, 14, 14])
x13_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c13_3_2(x13_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 14, 14])
x13_4_1 = self.s13_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x13_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c13_4_2(x13_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 14, 14])
x = torch.cat((x13_1, x13_2_2, x13_3_2, x13_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x15_1 = self.ReLU(self.c15_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 112, 14, 14])
x15_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c15_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 144, 14, 14])
x15_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c15_2_2(x15_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 288, 14, 14])
x15_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c15_3_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 14, 14])
x15_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c15_3_2(x15_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 14, 14])
x15_4_1 = self.s15_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 512, 14, 14])
x15_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c15_4_2(x15_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 64, 14, 14])
x = torch.cat((x15_1, x15_2_2, x15_3_2, x15_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 528, 14, 14])
x17_1 = self.ReLU(self.c17_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 14, 14])
x17_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c17_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 160, 14, 14])
x17_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c17_2_2(x17_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 320, 14, 14])
x17_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c17_3_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 14, 14])
x17_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c17_3_2(x17_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 14, 14])
x17_4_1 = self.s17_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 528, 14, 14])
x17_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c17_4_2(x17_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 14, 14])
x = torch.cat((x17_1, x17_2_2, x17_3_2, x17_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 832, 14, 14])
x = self.s4(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 832, 7, 7])
x19_1 = self.ReLU(self.c19_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 7, 7])
x19_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c19_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 160, 7, 7])
x19_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c19_2_2(x19_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 320, 7, 7])
x19_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c19_3_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 7, 7])
x19_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c19_3_2(x19_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 7, 7])
x19_4_1 = self.s19_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 832, 7, 7])
x19_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c19_4_2(x19_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 7, 7])
x = torch.cat((x19_1, x19_2_2, x19_3_2, x19_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 832, 7, 7])
x21_1 = self.ReLU(self.c21_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 7, 7])
x21_2_1 = self.ReLU(self.c21_2_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 192, 7, 7])
x21_2_2 = self.ReLU(self.c21_2_2(x21_2_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 7, 7])
x21_3_1 = self.ReLU(self.c21_3_1(x)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 48, 7, 7])
x21_3_2 = self.ReLU(self.c21_3_2(x21_3_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 7, 7])
x21_4_1 = self.s21_4_1(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 832, 7, 7])
x21_4_2 = self.ReLU(self.c21_4_2(x21_4_1)) # shape: torch.Size([1, 128, 7, 7])
x = torch.cat((x21_1, x21_2_2, x21_3_2, x21_4_2), dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 1024, 7, 7])
x = self.s5(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 1024, 1, 1])
x = F.dropout(x, p=0.5) # shape: torch.Size([1, 1024, 1, 1])
x = self.Flatten(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 1024])
x = self.f21(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 1000])
# 为满足该实例另加 ↓
x = self.f_output(x) # shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
x = F.softmax(x, dim=1) # shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
print(x.shape)
return x
if __name__ == '__main__':
x = torch.rand([1, 3, 224, 224])
model = MyGoogLeNet()
y = model(x)train.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# 作者:赵泽荣
# 时间:2021年9月10日(农历八月初四)
# 个人站点:1.https://zhao302014.github.io/
# 2.https://blog.csdn.net/IT_charge/
# 个人GitHub地址:https://github.com/zhao302014
# ------------------------------------------------- #
import torch
from torch import nn
from net import MyGoogLeNet
import numpy as np
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Scale(224), # 缩放图像大小为 224*224
transforms.ToTensor() # 仅对数据做转换为 tensor 格式操作
])
# 加载训练数据集
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, transform=data_transform, download=True)
# 给训练集创建一个数据集加载器
train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 加载测试数据集
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, transform=data_transform, download=True)
# 给测试集创建一个数据集加载器
test_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 如果显卡可用,则用显卡进行训练
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# 调用 net 里定义的模型,如果 GPU 可用则将模型转到 GPU
model = MyGoogLeNet().to(device)
# 定义损失函数(交叉熵损失)
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义优化器(SGD:随机梯度下降)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9)
# 学习率每隔 10 个 epoch 变为原来的 0.1
lr_scheduler = lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.1)
# 定义训练函数
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
loss, current, n = 0.0, 0.0, 0
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
# 单通道转为三通道
X = np.array(X)
X = X.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置
image = np.concatenate((X, X, X), axis=0)
image = image.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置回来
image = torch.tensor(image) # 将 numpy 数据格式转为 tensor
# 前向传播
image, y = image.to(device), y.to(device)
output = model(image)
cur_loss = loss_fn(output, y)
_, pred = torch.max(output, axis=1)
cur_acc = torch.sum(y == pred) / output.shape[0]
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad()
cur_loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
loss += cur_loss.item()
current += cur_acc.item()
n = n + 1
print('train_loss:' + str(loss / n))
print('train_acc:' + str(current / n))
# 定义测试函数
def test(dataloader, model, loss_fn):
# 将模型转换为验证模式
model.eval()
loss, current, n = 0.0, 0.0, 0
# 非训练,推理期用到(测试时模型参数不用更新,所以 no_grad)
with torch.no_grad():
for batch, (X, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
# 单通道转为三通道
X = np.array(X)
X = X.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置
image = np.concatenate((X, X, X), axis=0)
image = image.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置回来
image = torch.tensor(image) # 将 numpy 数据格式转为 tensor
image, y = image.to(device), y.to(device)
output = model(image)
cur_loss = loss_fn(output, y)
_, pred = torch.max(output, axis=1)
cur_acc = torch.sum(y == pred) / output.shape[0]
loss += cur_loss.item()
current += cur_acc.item()
n = n + 1
print('test_loss:' + str(loss / n))
print('test_acc:' + str(current / n))
# 开始训练
epoch = 100
for t in range(epoch):
lr_scheduler.step()
print(f"Epoch {t + 1}\\n----------------------")
train(train_dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
test(test_dataloader, model, loss_fn)
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "save_model/{}model.pth".format(t)) # 模型保存
print("Done!")test.py
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# ------------------------------------------------- #
# 作者:赵泽荣
# 时间:2021年9月10日(农历八月初四)
# 个人站点:1.https://zhao302014.github.io/
# 2.https://blog.csdn.net/IT_charge/
# 个人GitHub地址:https://github.com/zhao302014
# ------------------------------------------------- #
import torch
from net import MyGoogLeNet
import numpy as np
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torchvision.transforms import ToPILImage
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Scale(224), # 缩放图像大小为 224*224
transforms.ToTensor() # 仅对数据做转换为 tensor 格式操作
])
# 加载训练数据集
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=True, transform=data_transform, download=True)
# 给训练集创建一个数据集加载器
train_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 加载测试数据集
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root='./data', train=False, transform=data_transform, download=True)
# 给测试集创建一个数据集加载器
test_dataloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=8, shuffle=True)
# 如果显卡可用,则用显卡进行训练
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# 调用 net 里定义的模型,如果 GPU 可用则将模型转到 GPU
model = MyGoogLeNet().to(device)
# 加载 train.py 里训练好的模型
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("./save_model/99model.pth"))
# 获取预测结果
classes = [
"0",
"1",
"2",
"3",
"4",
"5",
"6",
"7",
"8",
"9",
]
# 把 tensor 转成 Image,方便可视化
show = ToPILImage()
# 进入验证阶段
model.eval()
# 对 test_dataset 里 10000 张手写数字图片进行推理
for i in range(len(test_dataset)):
x, y = test_dataset[i][0], test_dataset[i][1]
# tensor格式数据可视化
show(x).show()
# 扩展张量维度为 4 维
x = Variable(torch.unsqueeze(x, dim=0).float(), requires_grad=False).to(device)
# 单通道转为三通道
x = x.cpu()
x = np.array(x)
x = x.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置
x = np.concatenate((x, x, x), axis=0)
x = x.transpose((1, 0, 2, 3)) # array 转置回来
x = torch.tensor(x).to(device) # 将 numpy 数据格式转为 tensor,并转回 cuda 格式
with torch.no_grad():
pred = model(x)
# 得到预测类别中最高的那一类,再把最高的这一类对应classes中的哪一个标签
predicted, actual = classes[torch.argmax(pred[0])], classes[y]
# 最终输出预测值与真实值
print(f'Predicted: "{predicted}", Actual: "{actual}"')欢迎大家交流评论,一起学习
希望本文能帮助您解决您在这方面遇到的问题
感谢阅读
END
以上是关于「深度学习一遍过」必修22:基于GoogLeNet的MNIST手写数字识别的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
 https://github.com/zhao302014/Classic_model_examples/tree/main/2014_GoogLeNet_MNIST
https://github.com/zhao302014/Classic_model_examples/tree/main/2014_GoogLeNet_MNIST