Android Codec2初始化流程
Posted 小和尚念经敲木鱼
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android Codec2初始化流程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、MediaCodec调用流程
首先,我们先看下MediaCodec::CreateByType函数里面做了什么:
sp<MediaCodec> MediaCodec::CreateByType(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, const AString &mime, bool encoder, status_t *err, pid_t pid,
uid_t uid) {
sp<AMessage> format;
return CreateByType(looper, mime, encoder, err, pid, uid, format);
}
sp<MediaCodec> MediaCodec::CreateByType(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, const AString &mime, bool encoder, status_t *err, pid_t pid,
uid_t uid, sp<AMessage> format) {
Vector<AString> matchingCodecs;
MediaCodecList::findMatchingCodecs(
mime.c_str(),
encoder,
0,
format,
&matchingCodecs);
if (err != NULL) {
*err = NAME_NOT_FOUND;
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < matchingCodecs.size(); ++i) {
sp<MediaCodec> codec = new MediaCodec(looper, pid, uid);
AString componentName = matchingCodecs[i];
status_t ret = codec->init(componentName);
if (err != NULL) {
*err = ret;
}
if (ret == OK) {
return codec;
}
ALOGD("Allocating component '%s' failed (%d), try next one.",
componentName.c_str(), ret);
}
return NULL;
}
CreateByType调用CreateByType的重载函数。
CreateByType(
const sp<ALooper> &looper, const AString &mime, bool encoder, status_t *err, pid_t pid,
uid_t uid, sp<AMessage> format)
里面主要是做了下面两件事:
1、查找支持的Codec。
2、根据matchingCodecs创建MediaCodec 对应的解码器调用init。
MediaCodec::init再根据创建来的名字调用mGetCodecBase这个 function
status_t MediaCodec::init(const AString &name) {
mResourceManagerProxy->init();
mInitName = name;
mCodecInfo.clear();
bool secureCodec = false;
const char *owner = "";
mCodec = mGetCodecBase(name, owner);
if (mIsVideo) {
if (mCodecLooper == NULL) {
mCodecLooper = new ALooper;
mCodecLooper->setName("CodecLooper");
mCodecLooper->start(false, false, android_PRIORITY_AUDIO);
}
mCodecLooper->registerHandler(mCodec);
} else {
mLooper->registerHandler(mCodec);
}
mLooper->registerHandler(this);
mCodec->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::CodecCallback>(
new CodecCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
mBufferChannel = mCodec->getBufferChannel();
mBufferChannel->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback>(
new BufferCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
sp<AMessage> msg = new AMessage(kWhatInit, this);
if (mCodecInfo) {
msg->setObject("codecInfo", mCodecInfo);
// name may be different from mCodecInfo->getCodecName() if we stripped
// ".secure"
}
msg->setString("name", name);
}
mGetCodecBase指向的是下列函数:
创建一个父类的对象,具体这父类对象是走Codec2还是ACodec的决定在下列函数中:
sp<CodecBase> MediaCodec::GetCodecBase(const AString &name, const char *owner) {
if (owner) {
if (strcmp(owner, "default") == 0) {
return new ACodec;
} else if (strncmp(owner, "codec2", 6) == 0) {
return CreateCCodec();
}
}
if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("c2.")) {
return CreateCCodec();
} else if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("omx.")) {
// at this time only ACodec specifies a mime type.
return new ACodec;
} else if (name.startsWithIgnoreCase("android.filter.")) {
return new MediaFilter;
} else {
return NULL;
}
}
如果走CCodec里面调用MediaCodec.cpp文件中:
static CodecBase *CreateCCodec() {
return new CCodec;
}
这时候就走到的CCodec这个类中,它的构造函数:
// CCodec
CCodec::CCodec()
: mChannel(new CCodecBufferChannel(std::make_shared<CCodecCallbackImpl>(this))),
mConfig(new CCodecConfig) {
}
这里的 mChannel 和 mConfig 都是new出来的。
class CCodecBufferChannel : public BufferChannelBase;
上面的 mBufferChannel = mCodec->getBufferChannel(); 就是把CCodec的mChannel返回到MediaCodec中。
std::shared_ptr<BufferChannelBase> CCodec::getBufferChannel() {
return mChannel;
}
也就是说MediaCodec调用BufferChannelBase类型的mBufferChannel 实际上是调用CCodec里面的 mChannel
mBufferChannel设置一个new 的BufferCallback()对象的。
mCodec->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::CodecCallback>(
new CodecCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
实际上设置的是CodecBase里面的CodecCallback mCallback
struct CodecBase : public AHandler{
void setCallback(std::unique_ptr<CodecCallback> &&callback) {
mCallback = std::move(callback);
}
protected:
std::unique_ptr<CodecCallback> mCallback;
}
之后设置了BufferCallBack。
mBufferChannel->setCallback(
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback>(
new BufferCallback(new AMessage(kWhatCodecNotify, this))));
实际上设置的是BufferChannelBase::BufferCallback mCallback的指针。
class BufferChannelBase {
public:
void setCallback(std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback> &&callback) {
mCallback = std::move(callback);
}
protected:
std::unique_ptr<CodecBase::BufferCallback> mCallback;
};
之后Init发送kWhatInit消息,处理之后就调用了CCodec->initiateAllocateComponent()。接下来我们需要看CCodec里面的调用逻辑了。
2、CCodec调用流程
CCodec的源码路径如下:
frameworks/av/media/codec2
首先看下mConfig和mChannel的定义和初始化,具体如下:
//CCodec.h
class CCodec : public CodecBase {
Mutexed<std::unique_ptr<CCodecConfig>> mConfig;
std::shared_ptr<CCodecBufferChannel> mChannel;
}
//CCodec.cpp
CCodec::CCodec()
: mChannel(new CCodecBufferChannel(std::make_shared<CCodecCallbackImpl>(this))),
mConfig(new CCodecConfig){}
构造函数初始化的时候,就创建new CCodecCallbackImpl对象出来,CCodecCallbackImpl是继承CCodecCallBack的 就做一个适配封装处理。CCodecCallbackImpl 是CCodec的友元类。
上面调用了CCodec->initiateAllocateComponent(),其实CCodec::initiateAllocateComponent 也就是发送kWhatAllocate消息。一切都交给CCodec::onMessageReceived 进行处理。在接受 onMessageReceived 中的case语句中,kWhatAllocate 调用CCodec::allocate
接着使用client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService(“default”);创建一个服务,根据传入的setAsPreferredCodec2ComponentStore 设置SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore 默认是false.但是默认是false,这里没有传入。
这里的client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService(“default”);创建成功后调用SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore,将vendor下支持的Codec2的server设置进来。之后将重置的mClientListener、获得的componentName名字、Codec2Client::Component的组件comp及Codec2Client::CreateFromService(“default”)返回的client,一起作为参数,再重新调用CreateComponentByName创建组件。
之后给CCodecBufferChannel mChannel设置组件,用于绑定组件的回调。
class CCodecBufferChannel : public BufferChannelBase;
接着CCodec::allocate中调用CCodecConfig::initialize、CCodecConfig::queryConfiguration、CodecCallback::onComponentAllocated函数。
具体的代码调用逻辑,如下所示:
//Codec2Client::Component : public Codec2Client::Configurable
status_t CCodecConfig::initialize(
const std::shared_ptr<C2ParamReflector> &client,
const std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Configurable> &configurable);
//具体CCodec::allocate的调用逻辑如下(删除不必要语句):
void CCodec::allocate(const sp<MediaCodecInfo> &codecInfo) {
if (codecInfo == nullptr) {
mCallback->onError(UNKNOWN_ERROR, ACTION_CODE_FATAL);
return;
}
ALOGD("allocate(%s)", codecInfo->getCodecName());
mClientListener.reset(new ClientListener(this));
AString componentName = codecInfo->getCodecName();
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client> client;
// set up preferred component store to access vendor store parameters
client = Codec2Client::CreateFromService("default");
if (client) {
ALOGI("setting up '%s' as default (vendor) store", client->getServiceName().c_str());
SetPreferredCodec2ComponentStore(std::make_shared<Codec2ClientInterfaceWrapper>(client));
}
std::shared_ptr<Codec2Client::Component> comp;
c2_status_t status = Codec2Client::CreateComponentByName(
componentName.c_str(),
mClientListener,
&comp,
&client);
ALOGI("Created component [%s]", componentName.c_str());
mChannel->setComponent(comp);
Mutexed<std::unique_ptr<Config>>::Locked configLocked(mConfig);
const std::unique_ptr<Config> &config = *configLocked;
status_t err = config->initialize(mClient->getParamReflector(), comp);
config->queryConfiguration(comp);
mCallback->onComponentAllocated(componentName.c_str());
}
小结:
1、MediaCodec创建CCodec的对象,并用赋值给mCodec。
2、设置mCodec的CodecCallback 和 mBufferChannel的BufferCallback。
3、调用mCodec的initiateAllocateComponent,并且根据传入的codecInfo创建Service服务,并获得平台硬件编解码支持的服务。
2、根据componentName创建解码组件,并且调用数据回调类CCodecBufferChannel::setComponent设置组件。
3、调用initialize、queryConfiguration、onComponentAllocated等函数初始化。
3、整体时序图
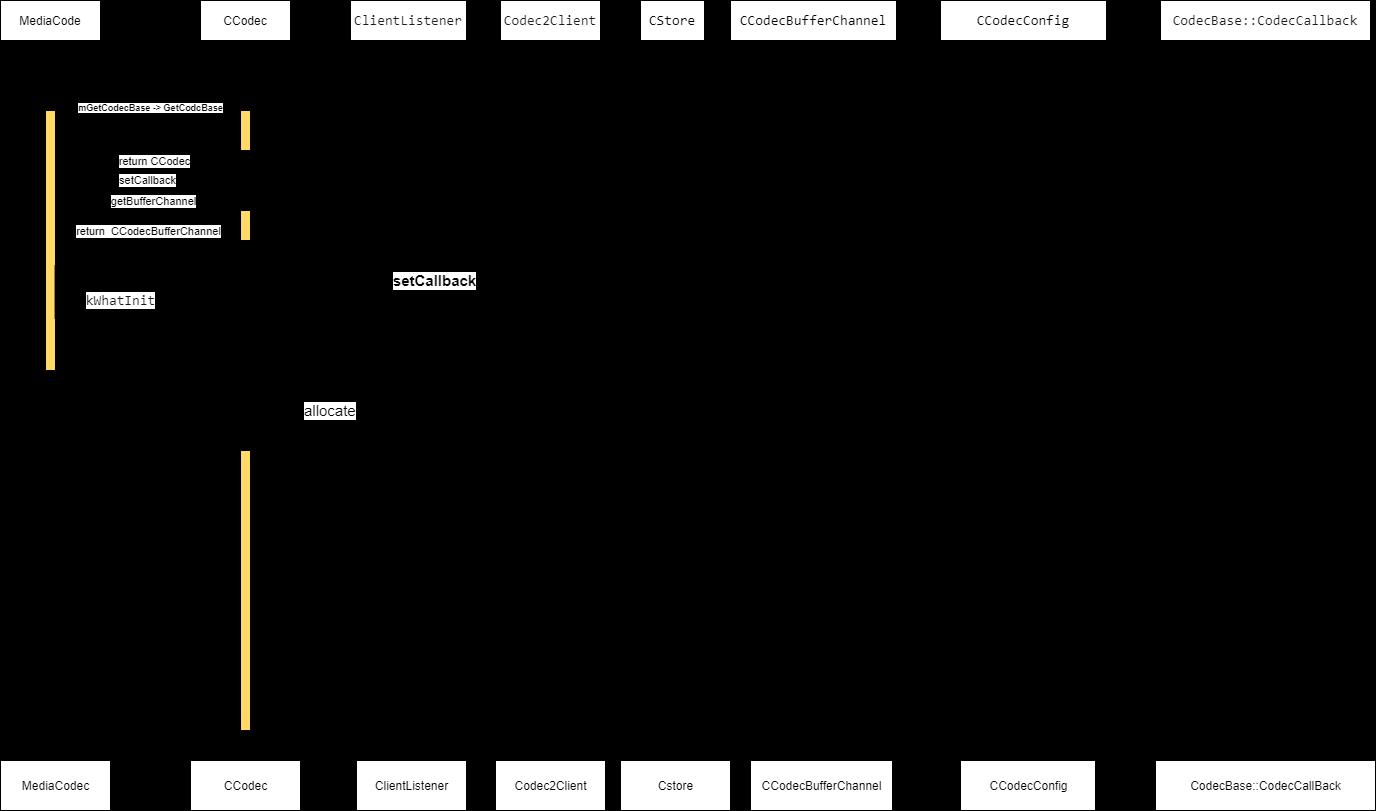
站在巨人的肩膀上!
参考连接:
最后,如果错误,希望读者不吝赐教,共同进步!
以上是关于Android Codec2初始化流程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
Android 逆向ART 脱壳 ( DexClassLoader 脱壳 | DexClassLoader 构造函数 | 参考 Dalvik 的 DexClassLoader 类加载流程 )(代码片段
Android 逆向ART 脱壳 ( DexClassLoader 脱壳 | DexClassLoader 构造函数 | 参考 Dalvik 的 DexClassLoader 类加载流程 )(代码片段
Android 逆向整体加固脱壳 ( DEX 优化流程分析 | DexPrepare.cpp 中 dvmOptimizeDexFile() 方法分析 | /bin/dexopt 源码分析 )(代码片段