了解map和set的底层实现
Posted 两片空白
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了了解map和set的底层实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
前言
本文主要写的是map和set的简单实现,通过实现来揭开map和set的面纱。是其对于我们来讲不再神秘。
本文实现map和set,最主要的模块有,如何使得map和set共用一颗红黑树。实现map和set的迭代器(主要是迭代器++和--)的基本功能。
一.map和set如何共用一颗红黑树
通过STL源码,我们知道,map和set底层使用的都是红黑树。那怎么实现的map和set共用一颗红黑树的呢?
通过模板来实现的。模板可以使得不同类型代码,可以复用同一个模板来生成对应的代码。
set结点保存的是一个个的值,而map保存的是一个个的键值对。我们只需要在传红黑树的模板参数时,set传需要保存值的类型,map传键值对的类型pair<T1,T2>,键值对里模板参数类型为树比较值的类型和需要保存值的类型。
现在还有一个问题,建树需要比较保存的值,set比较的就是保存的值,map比较的是保存的键值对pair<key,value>key的值。可以看出来set的值可以直接比较,但是,map需要通过对键值对进行解引用才能得到key的值,两者方式不同。
我们可以通过仿函数进行解决。仿函数是使用起来想是调用了一个函数,实际是()操作符的重载。一般比较都可以通过仿函数来实现。
解决方法是:在map里定义一个类,写一个仿函数来得到键值对key的值。在set里定义一个类,写一个仿函数来得到set保存的值。将类名作为模板参数传给红黑树,要使用比较时,只需要用该模板参数实例化一个对象,作用域要取出值的结点,就能取出set或者map对应的值了。

红黑树的代码:
//结点
template<class T>
struct BRTreeNode
{
BRTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _col(RED)//新增结点的颜色为红色
{}
BRTreeNode *_left;
BRTreeNode *_right;
BRTreeNode *_parent;
T _data;//保存不同的值
Color _col;//结点颜色
};
//如果是set,T为保存值的类型,K
//如果是map,T为保存键值对的类型,pair<K,V>
//KofT为仿函数类型
template<class K,class T,class KofT>
class BRTree
{
public:
typedef BRTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef BRTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
public:
//不能用引用,return 的是匿名函数,生命周期只在那一行
Iterator begin(){
Node *cur = _root;
while (cur&&cur->_left){
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Iterator(cur);
}
Iterator end(){
return Iterator(nullptr);
}
pair<Iterator, bool> insert(const T& data){
//定义仿函数对象,作用于要取出值的结点,取出对应值
KofT koft;
//空结点,直接生成后,更新头节点。
if (_root == nullptr){
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return pair<Iterator, bool>(_root, true);
}
Node *cur = _root;
Node *parent = nullptr;
while (cur){
if (koft(data) > koft(cur->_data)){
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (koft(data) < koft(cur->_data)){
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else{
return pair<Iterator, bool>(cur, false);
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_parent = parent;
if (koft(parent->_data)>koft(cur->_data)){
parent->_left = cur;
}
else{
parent->_right = cur;
}
Node *newnode = cur;
while (parent&&parent->_col == RED){
//此时肯定有grandfather,并且一定是黑色
Node *grandfather = parent->_parent;
//调整主要看uncle,下面判断uncle在哪边
if (grandfather->_left == parent){//如果父亲在左边,
Node *uncle = grandfather->_right;//叔叔就在右边
//情况1:叔叔存在且为红色,变色就好了
if (uncle&&uncle->_col == RED){
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续往上更新
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//情况2:uncle不存在或者uncle为黑色,旋转+变色
//两种情况,cur在parent的右边,左右双旋,cur在parent的右边,右单旋。
else{
//parent在grandfather的左边,如果cur在parent的右边,左右双旋,这里是先左单旋再右单旋
if (cur == parent->_right){
SigelLeft(parent);//parent成为cur的儿子了
swap(cur, parent);//换回来,方便后面变色
}
//后面就都是cur在parent的右边,只有右单旋就好了
SigelRight(grandfather);
//变色处理,画图就理解怎么变色了
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
}
else//uncle在左边
{
Node *uncle = grandfather->_left;
//和上面一样,只是方向不一样
if (uncle&&uncle->_col == RED){
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else{
if (cur == parent->_left){
SigelRight(parent);
swap(cur, parent);
}
SigelLeft(grandfather);
//变色
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;//防止变色将根节点变成红色
return pair<Iterator, bool>(newnode, false);
}
private:
void SigelLeft(Node *parent){
KofT koft;
Node *subr = parent->_right;
Node *subrl = subr->_left;
Node *pparent = parent->_parent;
parent->_right = subrl;
if (subrl){//subrl可能为空
subrl->_parent = parent;
}
subr->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subr;
if (pparent == nullptr){//根节点
subr->_parent = nullptr;
_root = subr;
}
else{//子树
subr->_parent = pparent;
if (koft(pparent->_data) < koft(subr->_data)){
pparent->_right = subr;
}
else{
pparent->_left = subr;
}
}
}
void SigelRight(Node *parent){
KofT koft;
Node *subl = parent->_left;
Node *sublr = subl->_right;
Node *pparent = parent->_parent;
parent->_left = sublr;
if (sublr){
sublr->_parent = parent;
}
subl->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subl;
if (pparent == nullptr){
subl->_parent = nullptr;
_root = subl;
}
else{
subl->_parent = pparent;
if (koft(pparent->_data) < koft(subl->_data)){
pparent->_right = subl;
}
else{
pparent->_left = subl;
}
}
}
private:
Node *_root = nullptr;
};二.迭代器的实现
set和map迭代器实际就是红黑树的结点。将迭代器封装成一个类,成员变量为树的结点,成员函数(是一些操作符重载函数)来实现迭代器的功能。
//成员变量,就是结点
typedef BRTreeNode<T> Node;
Node* _node = nullptr;set和map迭代器实现相同,只是结点保存的值的类型不同,这里主要拿map举例。
- 迭代器具有解引用的功能
//返回结点保存值
typedef BRTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Sef;
Ref operator*()const{
return _node->_data;
}
//返回结点保存值的地址
Ptr operator->()const{
return &(_node->_data);
}- 迭代器具有比较功能
//比较结点地址是否相等
bool operator!=(const Sef& s){
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Sef& s){
return _node == s._node;
}- 迭代器具有++和--功能
由于map和set是一颗红黑树,迭代器的++和--并不是简单的一直往父结点走。通过迭代器遍历,我们知道,迭代器的走向是按照中序遍历走的。
实现迭代器的++,有两种情况:
1.如果右子树存在,需要找右子树的最左结点。
2.如果右子树不存在,说明这个结点的父节点所在的这棵树已经访问完了,需要往上访问。我们需要找到右结点不是当前结点的结点。
//实现迭代器++
Sef& operator++(){//不需要包含参数,直接用_node
//右边右节点,找最左边的结点
if (_node&&_node->_right){
_node = _node->_right;
while (_node->_left){
_node = _node->_left;
}
}
//右边没有结点,找右孩子不是cur的父亲。
else{
Node *parent = _node->_parent;
//找右结点不是当前结点的结点
while (parent&&parent->_right == _node){
_node = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}实现迭代器的--,则是相反的情况,代码如下:
Sef operator--(){
//左边存在,找左边最右边的结点
if (_node->_left){
_node = _node->_left;
while (_node->_right){
_node = _node->_right;
}
}
//不存在,找左孩子不是_node的父亲
else{
Node *parent = _node->_parent;
while (parent&&parent->_left == _node){
_node = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}set和map的begin指向的最左边的结点,end为空结点。(注意:在STL库中,set和map底层红黑树是由头节点的,end为头节点)
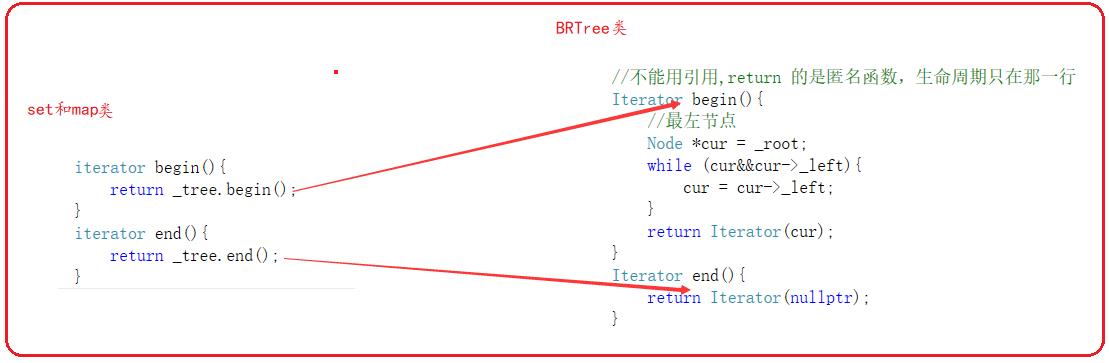
三.map的operator[]操作符重载
map的operator[]使用的是insert()函数实现的。
注意insert返回值是一个键值对,pair<iterator,bool>,
当插入成功时,iterator为插入成功结点的迭代器,bool为true
当插入失败时,即结点存在,iterator返回的是已存在结点的迭代器,bool为false
operator[],返回值是insert返回键值对里的迭代器里保存值pair<key,value>的value。
T& operator[](const K& k){
pair<iterator, bool> ret = Insert(pair<K, T>(k, T()));
return ret.first->second;
}四.总代码
4.1 map代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include"BRTree.h"
namespace wy{
template<class K,class T>
class map{
public:
//仿函数来获取值
struct MapKofT{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, T>& k){
return k.first;
}
};
//BRTree<K, pair<K, T>, MapKofT>没有实例化对象,找不到Iterator,编译错误,typename使得能编译通过
typedef typename BRTree<K, pair<K, T>, MapKofT>::Iterator iterator;
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const pair<K, T>& data){
return _tree.insert(data);
}
iterator begin(){
return _tree.begin();
}
iterator end(){
return _tree.end();
}
T& operator[](const K& k){
pair<iterator, bool> ret = Insert(pair<K, T>(k, T()));
return ret.first->second;
}
private:
BRTree<K, pair<K, T>, MapKofT> _tree;//不是指针,用指针的话,刚开始树为空,访问不了树的结点。
};
}4.2 set代码
#include"BRTree.h"
namespace wy{
template<class K>
class set{
public:
//仿函数来获取值
struct SetKofK{
const K& operator()(const K& k){
return k;
}
};
typedef typename BRTree<K, K, SetKofK>::Iterator iterator;
pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const K& k){
return _tree.insert(k);
}
iterator begin(){
return _tree.begin();
}
iterator end(){
return _tree.end();
}
private:
BRTree<K, K, SetKofK> _tree;
};
}4.3 红黑树代码
再写代码时,有几个值得注意的地方:
返回迭代器,时只够构造一个迭代器,此时生成的是匿名对象,不能引用。第一,斌来就是一个临时变量,第二,生命周期在当前行,出当前行空间iu被释放了。
类中使用到的类名,使用的类要在当前类前定义或者声明。
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
//结点颜色
enum Color{
BLACK,
RED,
};
//结点
template<class T>
struct BRTreeNode
{
BRTreeNode(const T& data)
:_left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _parent(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _col(RED)//新增结点的颜色为红色
{}
BRTreeNode *_left;
BRTreeNode *_right;
BRTreeNode *_parent;
T _data;//保存不同的值
Color _col;//结点颜色
};
//迭代器实际是一个结点
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct BRTreeIterator
{
typedef BRTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef BRTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Sef;
//会默认生成拷贝构造,构造,可以是值拷贝,析构不需要释放空间
BRTreeIterator(Node *node)
:_node(node)
{}
//实现迭代器++
Sef& operator++(){//不需要包含参数,直接用_node
//右边右节点,找最左边的结点
if (_node&&_node->_right){
_node = _node->_right;
while (_node->_left){
_node = _node->_left;
}
}
//右边没有结点,找右孩子不是cur的父亲。
else{
Node *parent = _node->_parent;
while (parent&&parent->_right == _node){
_node = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Sef operator--(){
//右边存在,找左边最右边的结点
if (_node->_left){
_node = _node->_left;
while (_node->_right){
_node = _node->_right;
}
}
//不存在,找左孩子不是_node的父亲
else{
Node *parent = _node->_parent;
while (parent&&parent->_left == _node){
_node = parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Sef& s){
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Sef& s){
return _node == s._node;
}
Ref operator*()const{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()const{
return &(_node->_data);
}
Node* _node = nullptr;
};
template<class K,class T,class KofT>
class BRTree
{
public:
typedef BRTreeNode<T> Node;
//迭代器
typedef BRTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> Iterator;
public:
//不能用引用,return 的是匿名函数,生命周期只在那一行
Iterator begin(){
//最左节点
Node *cur = _root;
while (cur&&cur->_left){
cur = cur->_left;
}
return Iterator(cur);
}
Iterator end(){
return Iterator(nullptr);
}
pair<Iterator, bool> insert(const T& data){
//定义仿函数对象,作用于要取出值的结点,取出对应值
KofT koft;
//空结点,直接生成后,更新头节点。
if (_root == nullptr){
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return pair<Iterator, bool>(_root, true);
}
Node *cur = _root;
Node *parent = nullptr;
while (cur){
if (koft(data) > koft(cur->_data)){
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (koft(data) < koft(cur->_data)){
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else{
return pair<Iterator, bool>(cur, false);
}
}
cur = new Node(data);
cur->_parent = parent;
if (koft(parent->_data)>koft(cur->_data)){
parent->_left = cur;
}
else{
parent->_right = cur;
}
Node *newnode = cur;
while (parent&&parent->_col == RED){
//此时肯定有grandfather,并且一定是黑色
Node *grandfather = parent->_parent;
//调整主要看uncle,下面判断uncle在哪边
if (grandfather->_left == parent){//如果父亲在左边,
Node *uncle = grandfather->_right;//叔叔就在右边
//情况1:叔叔存在且为红色,变色就好了
if (uncle&&uncle->_col == RED){
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
//继续往上更新
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
//情况2:uncle不存在或者uncle为黑色,旋转+变色
//两种情况,cur在parent的右边,左右双旋,cur在parent的右边,右单旋。
else{
//parent在grandfather的左边,如果cur在parent的右边,左右双旋,这里是先左单旋再右单旋
if (cur == parent->_right){
SigelLeft(parent);//parent成为cur的儿子了
swap(cur, parent);//换回来,方便后面变色
}
//后面就都是cur在parent的右边,只有右单旋就好了
SigelRight(grandfather);
//变色处理,画图就理解怎么变色了
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
}
}
else//uncle在左边
{
Node *uncle = grandfather->_left;
//和上面一样,只是方向不一样
if (uncle&&uncle->_col == RED){
grandfather->_col = RED;
parent->_col = BLACK;
uncle->_col = BLACK;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else{
if (cur == parent->_left){
SigelRight(parent);
swap(cur, parent);
}
SigelLeft(grandfather);
//变色
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;//防止变色将根节点变成红色
return pair<Iterator, bool>(newnode, false);
}
private:
void SigelLeft(Node *parent){
KofT koft;
Node *subr = parent->_right;
Node *subrl = subr->_left;
Node *pparent = parent->_parent;
parent->_right = subrl;
if (subrl){//subrl可能为空
subrl->_parent = parent;
}
subr->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = subr;
if (pparent == nullptr){//根节点
subr->_parent = nullptr;
_root = subr;
}
else{//子树
subr->_parent = pparent;
if (koft(pparent->_data) < koft(subr->_data)){
pparent->_right = subr;
}
else{
pparent->_left = subr;
}
}
}
void SigelRight(Node *parent){
KofT koft;
Node *subl = parent->_left;
Node *sublr = subl->_right;
Node *pparent = parent->_parent;
parent->_left = sublr;
if (sublr){
sublr->_parent = parent;
}
subl->_right = parent;
parent->_parent = subl;
if (pparent == nullptr){
subl->_parent = nullptr;
_root = subl;
}
else{
subl->_parent = pparent;
if (koft(pparent->_data) < koft(subl->_data)){
pparent->_right = subl;
}
else{
pparent->_left = subl;
}
}
}
private:
Node *_root = nullptr;
};
以上是关于了解map和set的底层实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章